EGN 3365 Exam 2
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/76
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:29 PM on 3/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
1
New cards
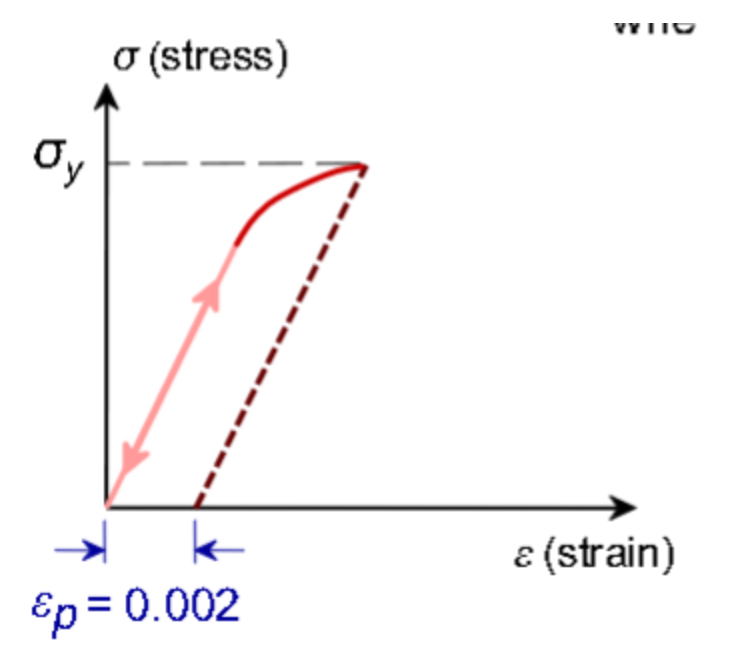
The given stress-strain graph represents?
Elastic then plastic deformation
2
New cards
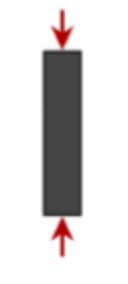
What does the figure represent?
Simple compression
3
New cards
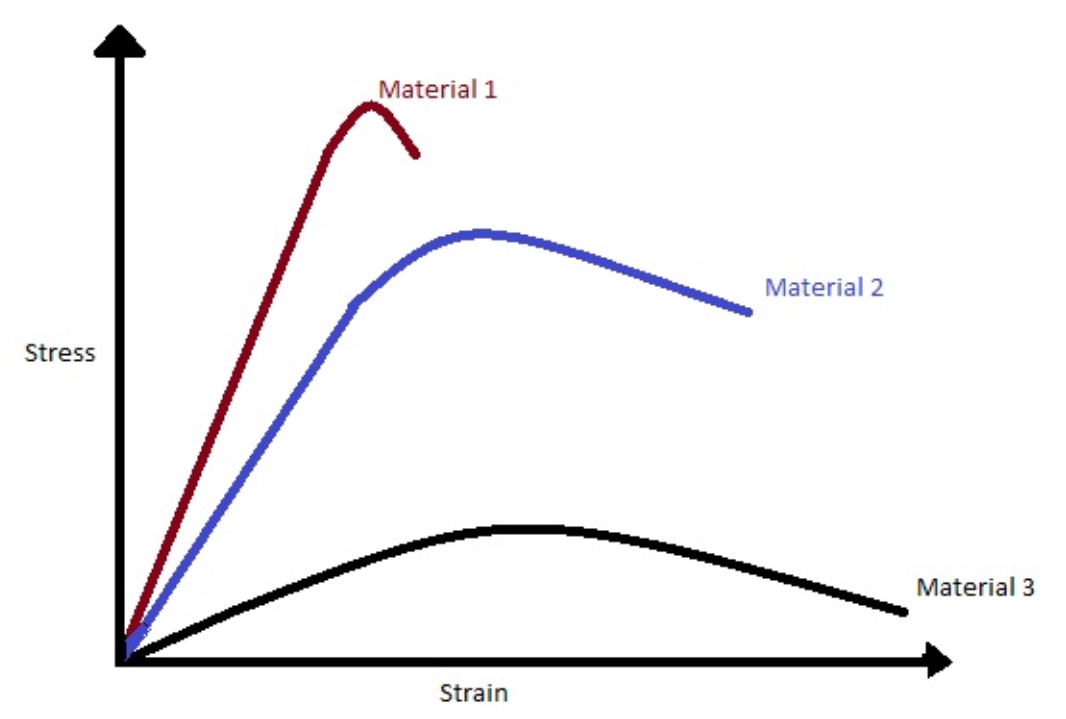
Which material has the highest toughness?
Material 2
4
New cards
For an engineering strain of 1, calculate percentage elongation (ductility) of the specimen?
100
5
New cards
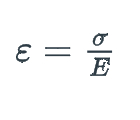
A specimen of copper having a rectangular cross-section 15.2 mm X 19.1 mm is pulled in tension with 44,500 N force, producing only elastic deformation. Calculate the resulting strain. ( Elastic modulus of copper = 110 GPa)
1\.39 x 10^-3
6
New cards
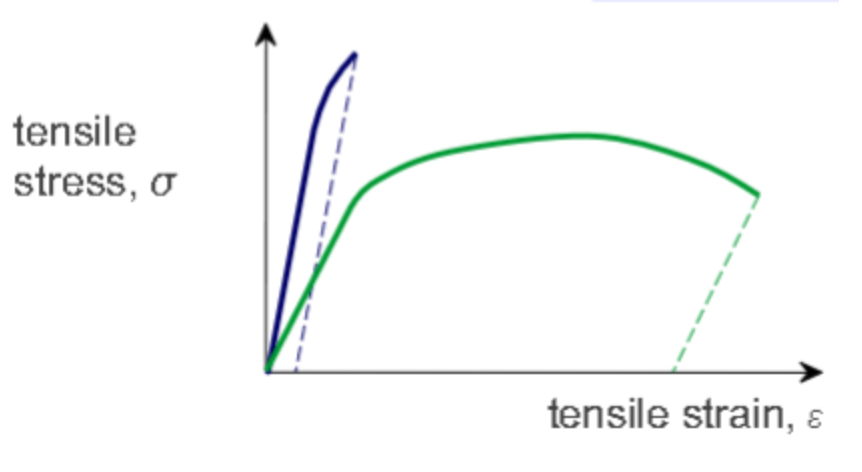
Ductility is the amount of plastic deformation at failure.
From the given graph below, determine which line represent a material with high ductility and which line represent a material with low ductility.
From the given graph below, determine which line represent a material with high ductility and which line represent a material with low ductility.
Blue line: Low ductility.
Green line: High ductility.
Green line: High ductility.
7
New cards
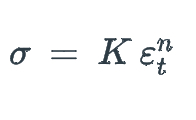
For some metal alloy, the true stress of 345 MPa produces a plastic true strain of 0.02. How much does a specimen of this material elongate when true stress of 415 MPa is applied if the original length is 500 mm? Assume a value of 0.22 for the strain-hardening exponent, n.
23\.7mm
8
New cards
Poisson's ratio for metals, ceramics and polymers is in the range:
0\.15 < v
9
New cards
Deformation of a sample to an engineering strain of 2 means that the sample is ___________ its original length.
A. Half
B. Twice
C. Three times
D. 2% longer than
A. Half
B. Twice
C. Three times
D. 2% longer than
Three times
10
New cards
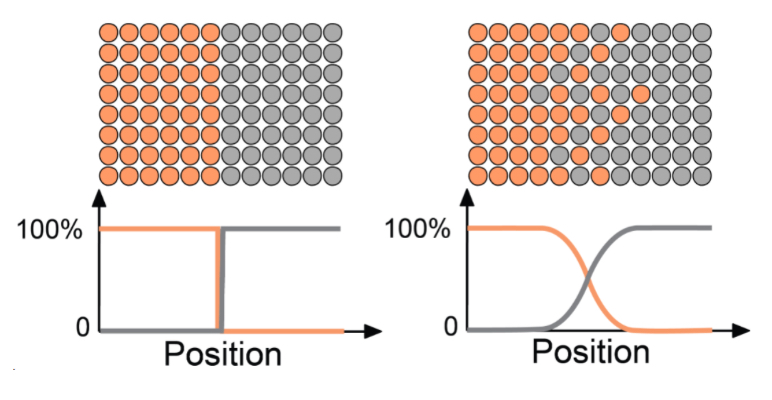
What best describes the figure?
A. Not an example of diffusion
B. Left: before diffusion, right: after diffusion
C. Left: after diffusion, right: before diffusion
D. None of the above
A. Not an example of diffusion
B. Left: before diffusion, right: after diffusion
C. Left: after diffusion, right: before diffusion
D. None of the above
Left: before diffusion; right: after diffusion
11
New cards
What is diffusion
Mass transport by atomic motion
12
New cards
Atoms tend to _____________ from regions of _____________ concentration to regions of _____________ concentration.
Migrate, high, low
13
New cards
What is self-diffusion?
Migration of host atoms in pure metals
14
New cards
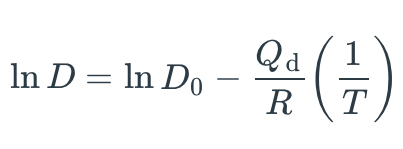
What is the derivation of the equation relating the diffusion coefficients at two temperatures T1 and T2, given that:
D₂ = D₁exp \[-Qd/R(1/T2-1/T2)\]
15
New cards
At 300°C the diffusion coefficient and activation energy for Cu in Si are
D₁ (300°C) = 7.8 × 10⁻⁻¹¹ m²/s
Qd = 41.5 kJ/mol
Compute the diffusion coefficient D₂ at 400°C.
D₁ (300°C) = 7.8 × 10⁻⁻¹¹ m²/s
Qd = 41.5 kJ/mol
Compute the diffusion coefficient D₂ at 400°C.
28\.46 × 10⁻⁻¹¹ m²/s
16
New cards
Non-steady state diffusion is a function of:
Time and position
17
New cards
Fick’s first law of diffusion is applicable to
Steady state diffusion
18
New cards
What’s Fick’s second law of diffusion?
dC/dt = D d²C/dx²
19
New cards
What's Fick’s first law of diffusion?
J = −D dC/dx
20
New cards
What’s the relationship between the diffusion coefficient and temperature?
Increases with increasing temp
21
New cards
What is interdiffusion?
Diffusion of atoms of one material into another material
22
New cards
Diffusion rate of vacancy diffusion depends on
Number of vacancies, activation energy
23
New cards
interstitial diffusion
smaller atoms diffuse between adjacent atoms, faster than vacancy diffusion
24
New cards
Case hardening is an example of _________ diffusion
Interstitial
25
New cards
case hardening
outer surface is hardened by diffusing carbon atoms into surface
26
New cards
Doping
adding impurities to a semiconductor to increase conductivity
27
New cards
Process of doping
1. P rich layers on surface
2. Heat it
3. Doped semiconductor regions
28
New cards
Diffusion is faster for
open crystal structures, materials with secondary bonding, smaller diffusing atoms, lower density materials
29
New cards
Tensile load (pulling)
If a specimen is being elongated or extended
30
New cards
Compressive load (pushing)
Specimen is compressed or contracted
31
New cards
Deformation
Change in dimension
32
New cards
shear forces
Parallel to cross sectional area
33
New cards
Plastic deformation
permanent change in shape by bending and folding
34
New cards
Elastic deformation
material returns to original state when stress is removed
35
New cards
Common states of stress
Simple tension, torsion, simple compression, bi-axial tension, hydrostatic compression
36
New cards
Yield strength
point where the material begins to plastically deform
37
New cards
Toughness
the ability of a material to resist fracture
38
New cards
Hardness
resistance to localized surface deformation and compressive stresses
39
New cards
Resilience
Ability of a material to store energy
40
New cards
Ductility
amount of plastic deformation at failure
41
New cards
Engineering stress
tensile, shear
42
New cards
Engineering strain
tensile, lateral, shear
43
New cards
Percent elongation
the total percent increase in length of a specimen during the tensile test
44
New cards
Dislocation
A defect where atoms are misaligned around it
45
New cards
Edge dislocation
extra half plane of atoms inserted into a crystal structure
46
New cards
Dislocation line
The line where dislocations happen
47
New cards
Screw dislocation
lattice plane shifts similar to a spiral staircase
48
New cards
Burgers vector
measure of lattice distortion
49
New cards
Twin boundary
a reflection of atom positions across the twin plane
50
New cards
Solidification
Result of casting molten material
51
New cards
Grain boundaries
Regions between grains (crystals)
52
New cards
Point defects
vacancy, interstitial atoms, substitutional atoms
53
New cards
Vacancies are
vacant atomic sites
54
New cards
Dislocations move when
Stresses are applied
55
New cards
A catalyst \____________ the rate is a chemical reaction without being consumed
Increases
56
New cards
Dislocation types include
Edge, screw, and mixed
57
New cards
two diffusion mechanisms
vacancy and interstitial
58
New cards
The applied mechanical force is normalized to
Stress
59
New cards
The degree of deformation is normalized to
strain
60
New cards
Elastic deformation is
nonpermanent and reversible
61
New cards
Plastic deformation is
permanent and nonrecoverable
62
New cards
Stiffness
a material's resistance to elastic deformation
63
New cards
Strength
A materials resistance to plastic deformation
64
New cards
In an optical microscope, grain boundaries appear as white lines after the surface is prepared by etching. T/F
false
65
New cards
According for Fick’s first law, the concentration of diffusing species is a function of both time and position. T/F
false
66
New cards
D_interstitial << D_substitutional
T/F
T/F
false
67
New cards
In edge dislocation, burger’s vector is perpendicular to dislocation line. T/F
true
68
New cards
Diffusion coefficient _________ with increasing temperature
increases
69
New cards
What are the interfacial defects?
twin boundaries, grain boundaries, stacking faults
70
New cards
I can observe individual atoms using an optical microscope. T/F
false
71
New cards
What’s an example to processing using diffusion
case hardening
72
New cards
Interstitial diffusion is more rapid than vacancy diffusion. T/F
true
73
New cards
Equiaxed grains are
Roughly the same dimension in all directions
74
New cards
Columnar grains are
grains elongated in one direction
75
New cards
Rate of diffusion is __________ of time
independent
76
New cards
Diffusion is ____________ of time
dependent
77
New cards
What are the 5 interfacial defects?
external surfaces, phase boundaries, optical boundaries, twin boundaries, stacking faults