Chapter 12
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
D
1. Which of the following statements about oxidation and reduction is not true?
A. The conversion of an alkyne to an alkene is reduction.
B. The conversion of an alkene to an alkane is reduction.
C. Oxidation results in a decrease in the number of C-H bonds.
D. Reduction results in an increase in the number of C-Z bonds.
A
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction

A
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction
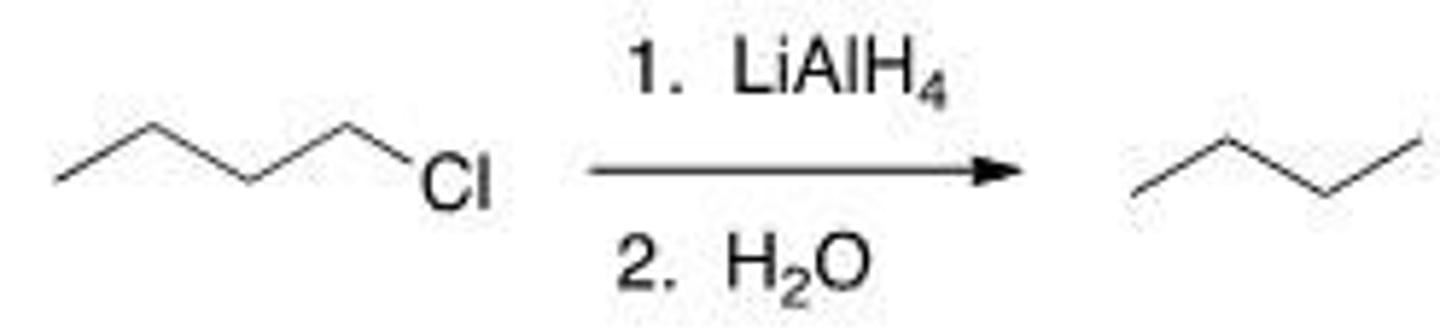
B
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction
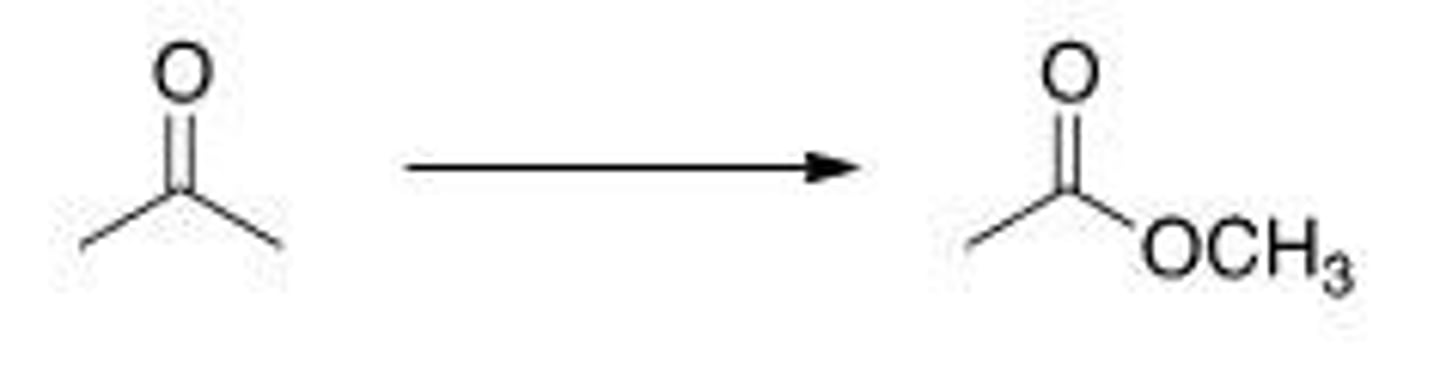
A
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction

B
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction

A
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction
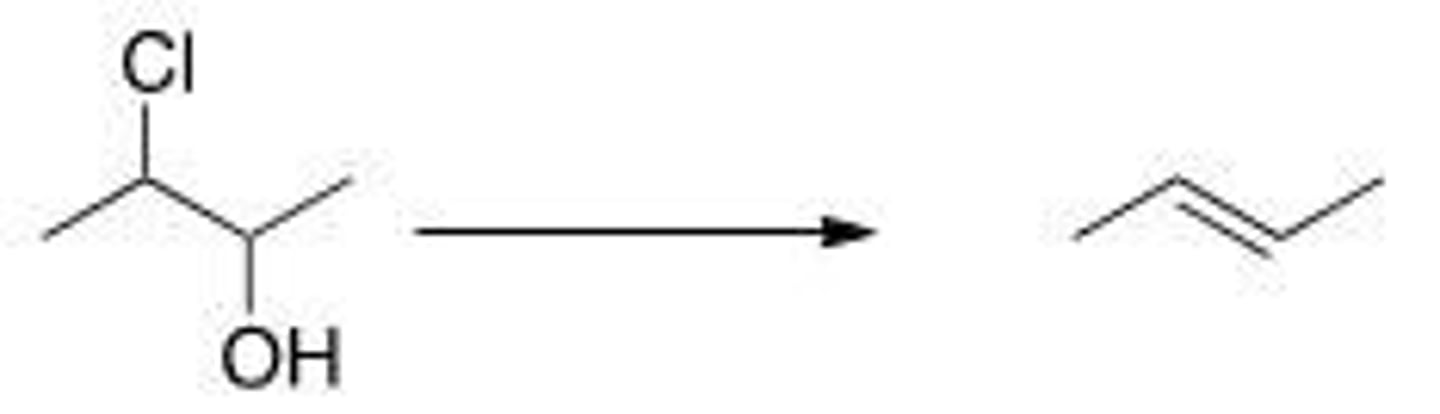
B
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction

A
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction

A
What is the correct classification of the following reaction?
A. Reduction reaction
B. Oxidation reaction
C. Elimination reaction
D. Substitution reaction

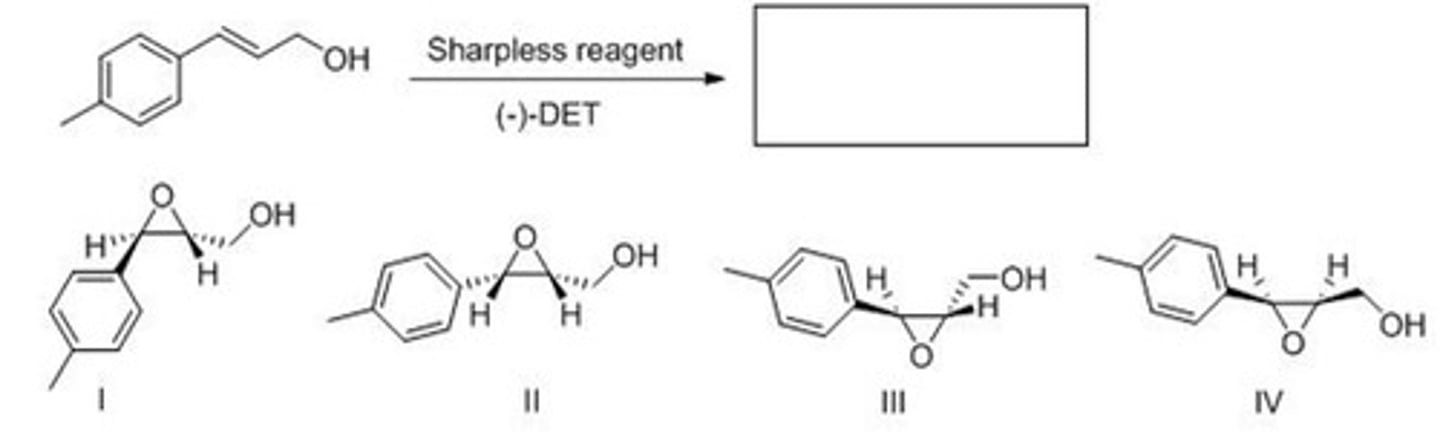
D
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing oxidation level (from lowest to highest).
A. I < III < II < IV
B. II < III < I < IV
C. IV < I < III < II
D. II < IV < III < I
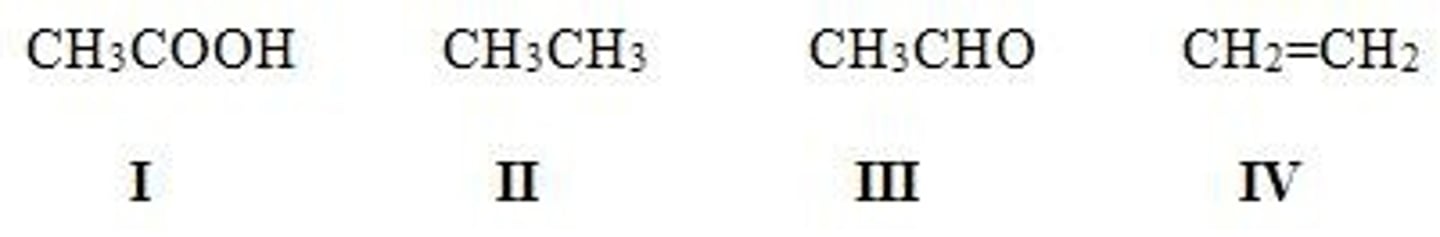
B
12. What happens to the carbon atom in the transformation of chloromethane to methyllithium?
CH3Cl + 2Li -> CH3Li + LiCl
A. Oxidized
B. Reduced
C. Oxidized and reduced
D. Neither oxidized nor reduced
C
13. Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing oxidation level, putting the compound with the highest oxidation level first.
A. II > IV > I > III
B. I > III > IV > II
C. III > I > II > IV
D. III > I > IV > II
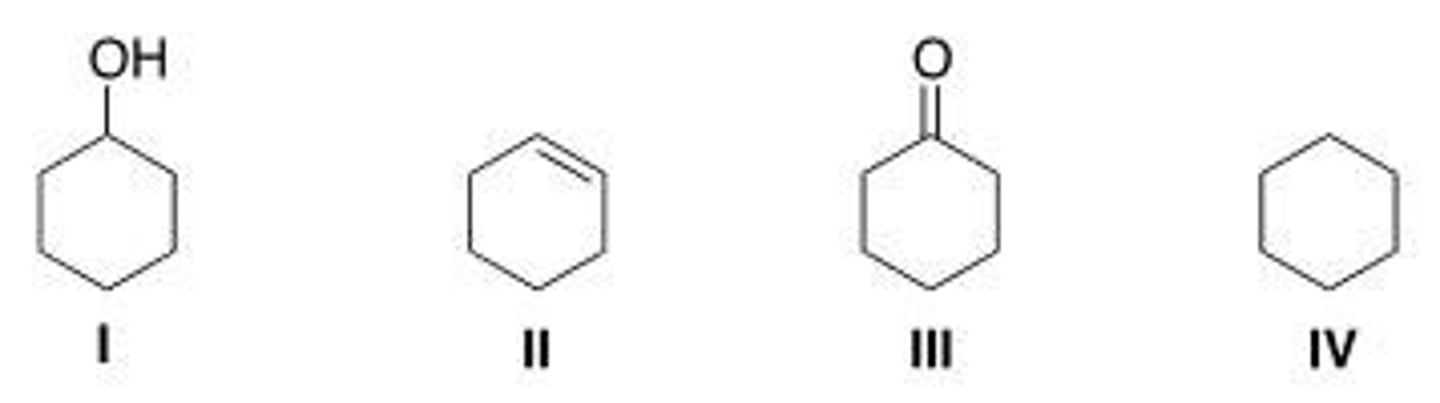
A
Which of the following classes of organic compounds cannot undergo reduction easily?
A. Alkanes
B. Alkenes
C. Alkynes
Carboxylic acids
D
Determine the product(s) of the following reaction.
A. I and III
B. II and III
C. I, II, and III
D. I or II
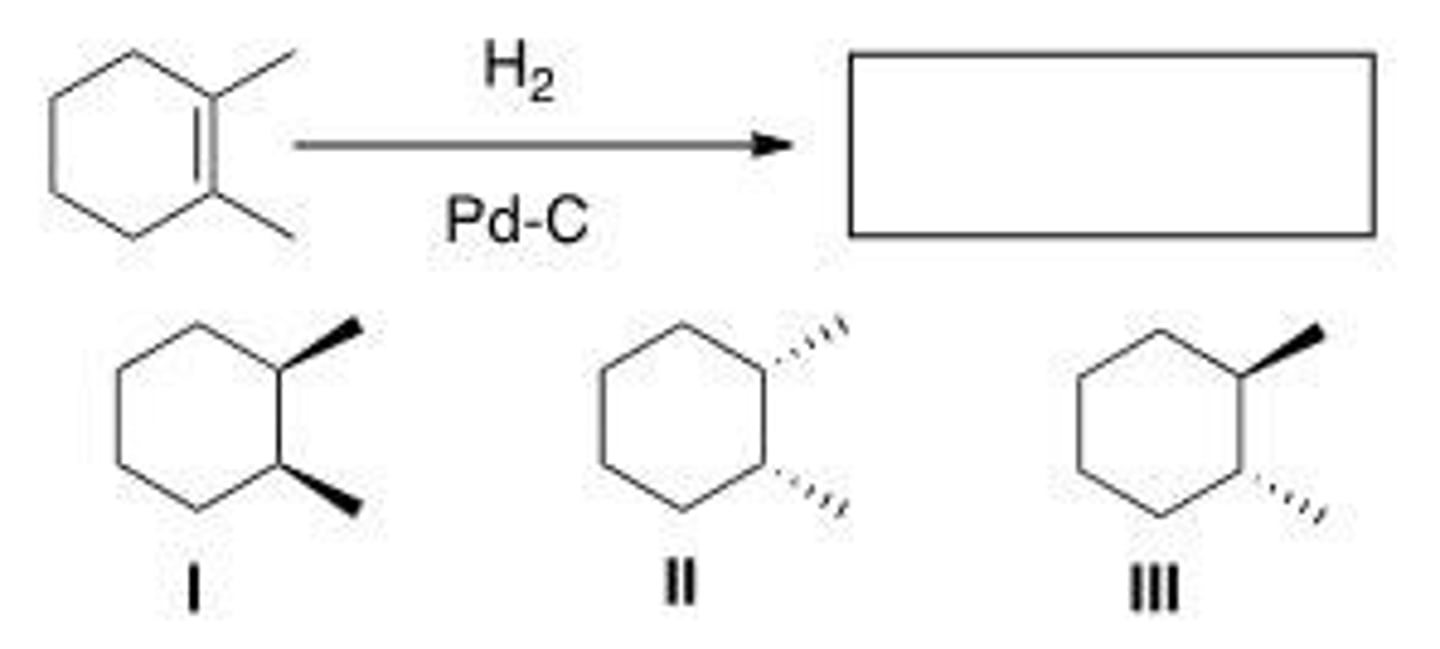
B
Rank the following alkenes in order of decreasing heat of hydrogenation.
A. I > II > III
B. III > I > II
C. II > I > III
D. III > II > I
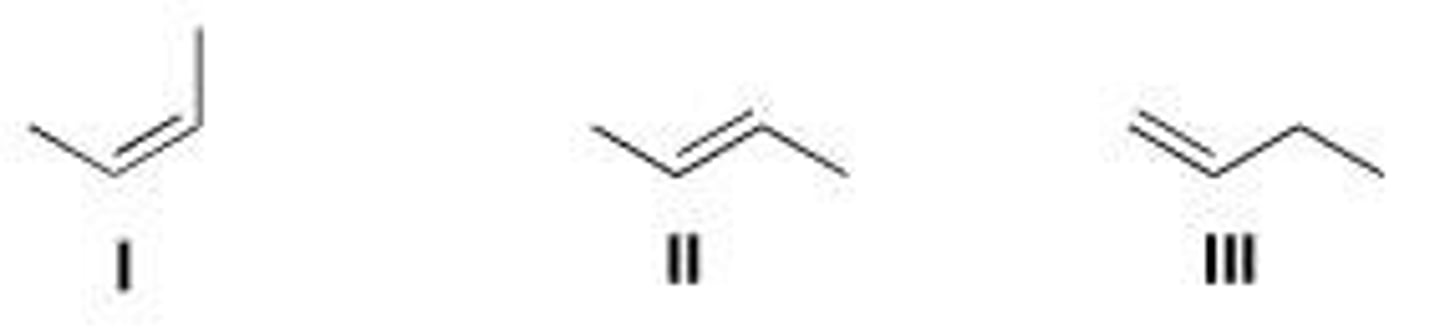
D
17. Which of the following explains why heats of hydrogenation cannot be used to determine the relative stability of compounds A and B below?
A. Compound A is trisubstituted while compound B is monosubstituted.
B. Compound A has E configuration while compound B has no E/Z configuration.
C. Both compounds A and B have no E/Z configurations.
D. Hydrogenation of A and B give different alkanes.

B
Rank the following alkenes in order of increasing rate of hydrogenation.
A. I < III < IV < II
B. IV < III < II < I
C. I < II < III < IV
D. IV < II < III < I
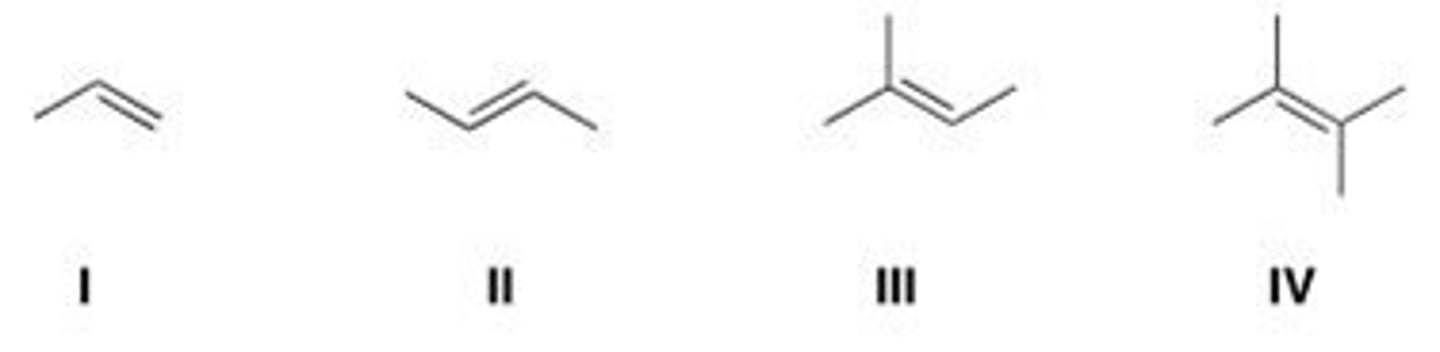
D
A compound X of molecular formula C8H12 with no triple bonds reacts with one equivalent of H2 to give a new compound having molecular formula C8H14. What can be inferred about the structure of compound X?
A. Compound X has 3 rings.
B. Compound X has 3 p bonds.
C. Compound X has 1 ring and 2 p bonds.
D. Compound X has 2 rings and 1 p bond.
C
Determine the product of the following reaction.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
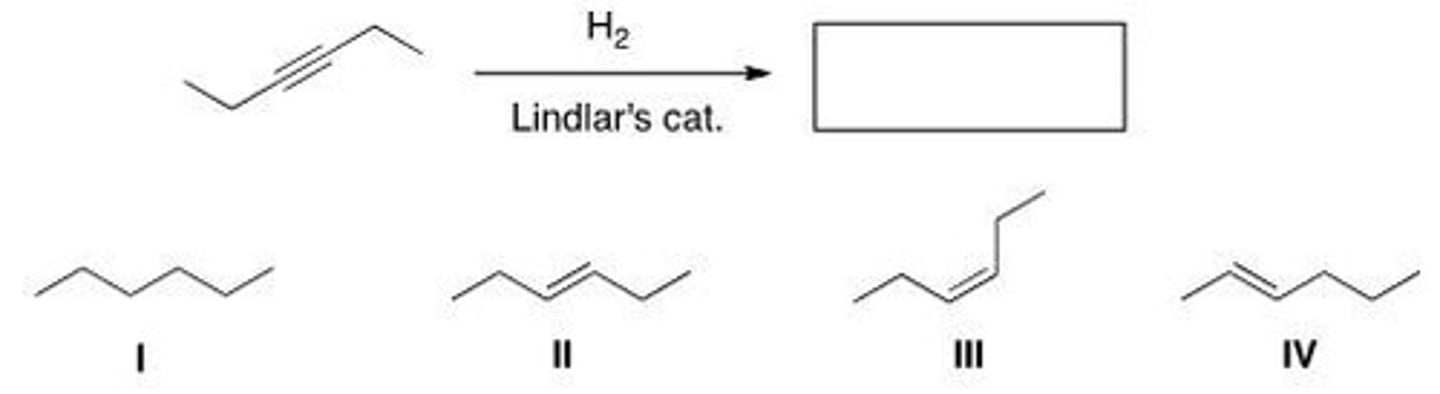
D
What reagent is required to accomplish the following transformation?
A. Na, NH3
B. H2, Pd-C
C. H2, Ni
D. H2, Lindlar catalyst

A
What reagent is required to accomplish the following transformation?
A. Na, NH3
B. H2, Pd-C
C. H2, Ni
D. H2, Lindlar catalyst

D
What is the starting material in the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
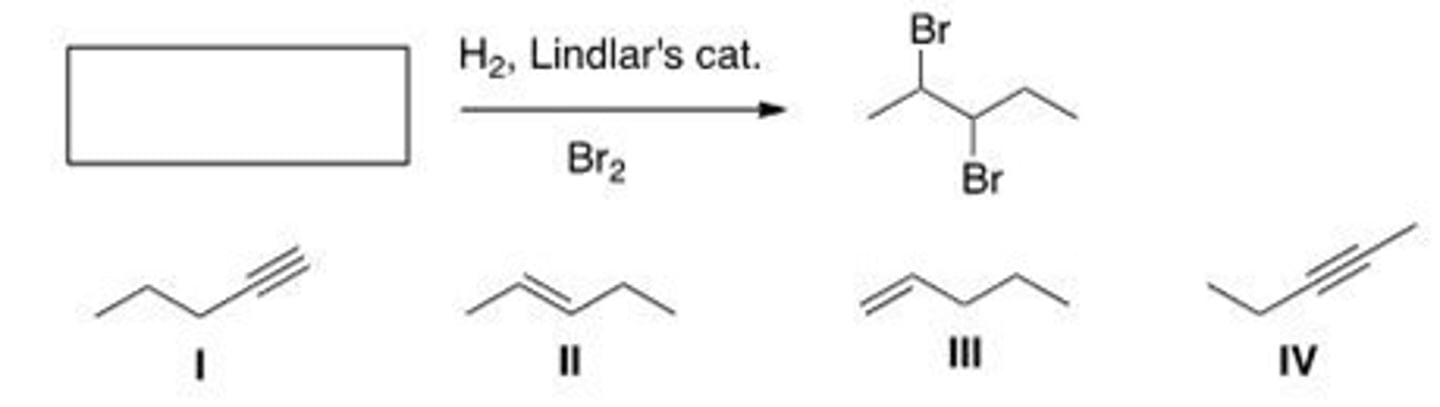
B
Determine the product of the following reaction.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
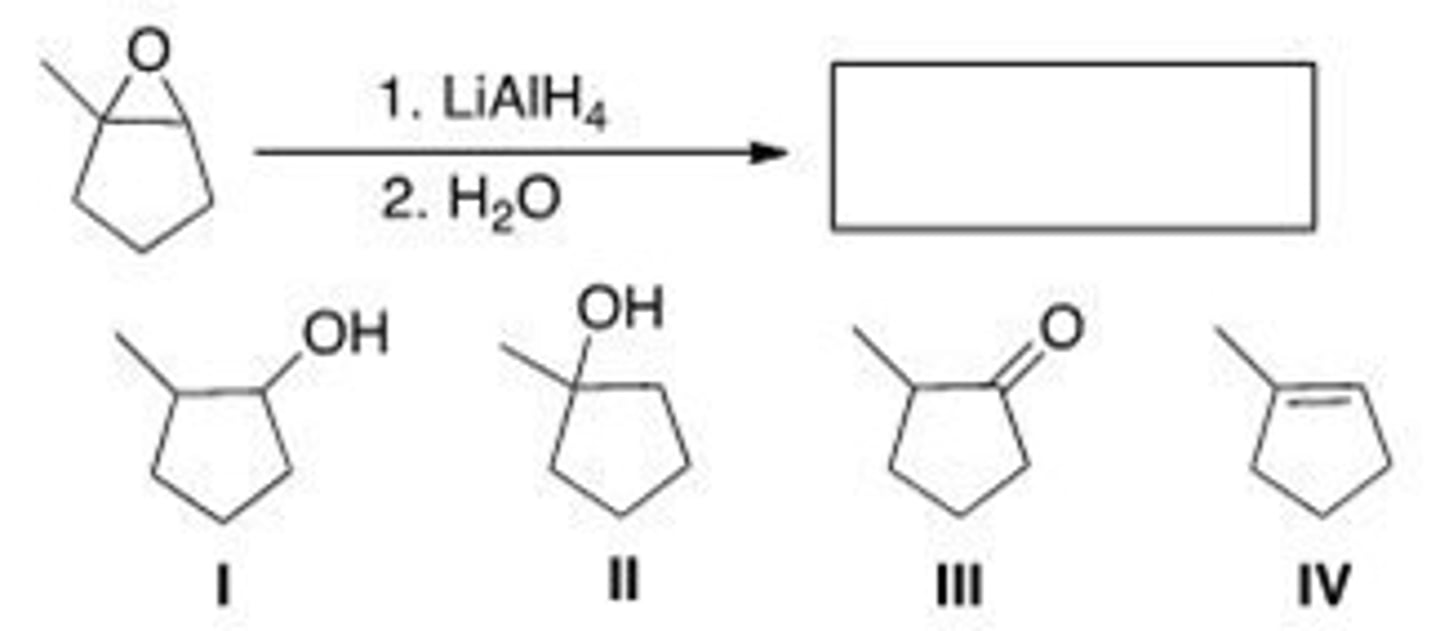
A
Which of the following statements about the reduction of epoxides with LiA1H4 is true?
A. The nucleophile is a hydride (H-).
B. In unsymmetrical epoxides, nucleophilic attack of H- occurs at the more substituted carbon atom.
C. The reaction follows SN1 mechanism.
D. The nucleophile, H-, is a weak nucleophile.
A
Which is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
A. Only I and II
B. Only I and III
C. Only II and III
D. I, II, and III
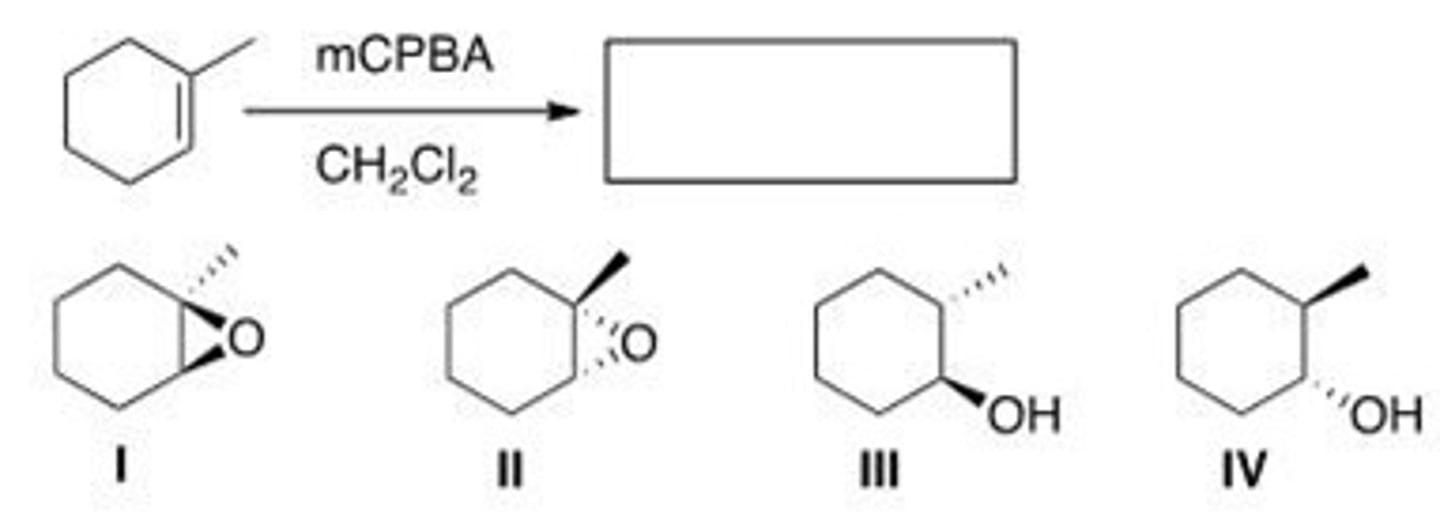
C
Which of the following products do not form in the following reaction?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only III and IV
D. Only I and II
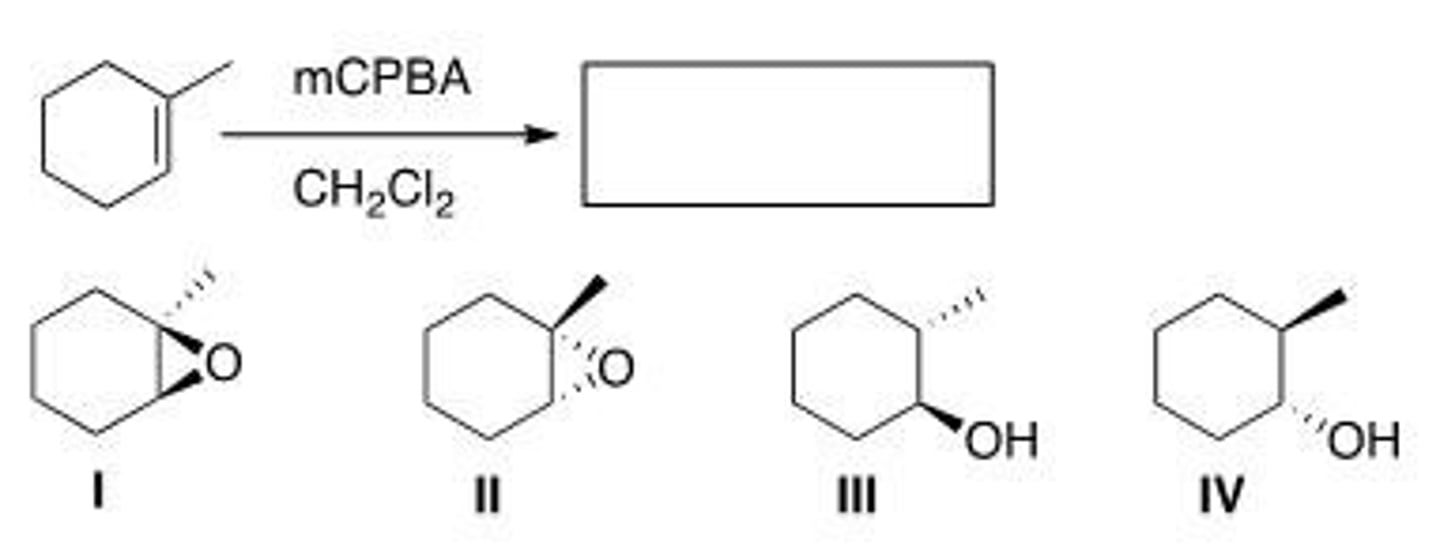
D
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only III
D. Only I and II
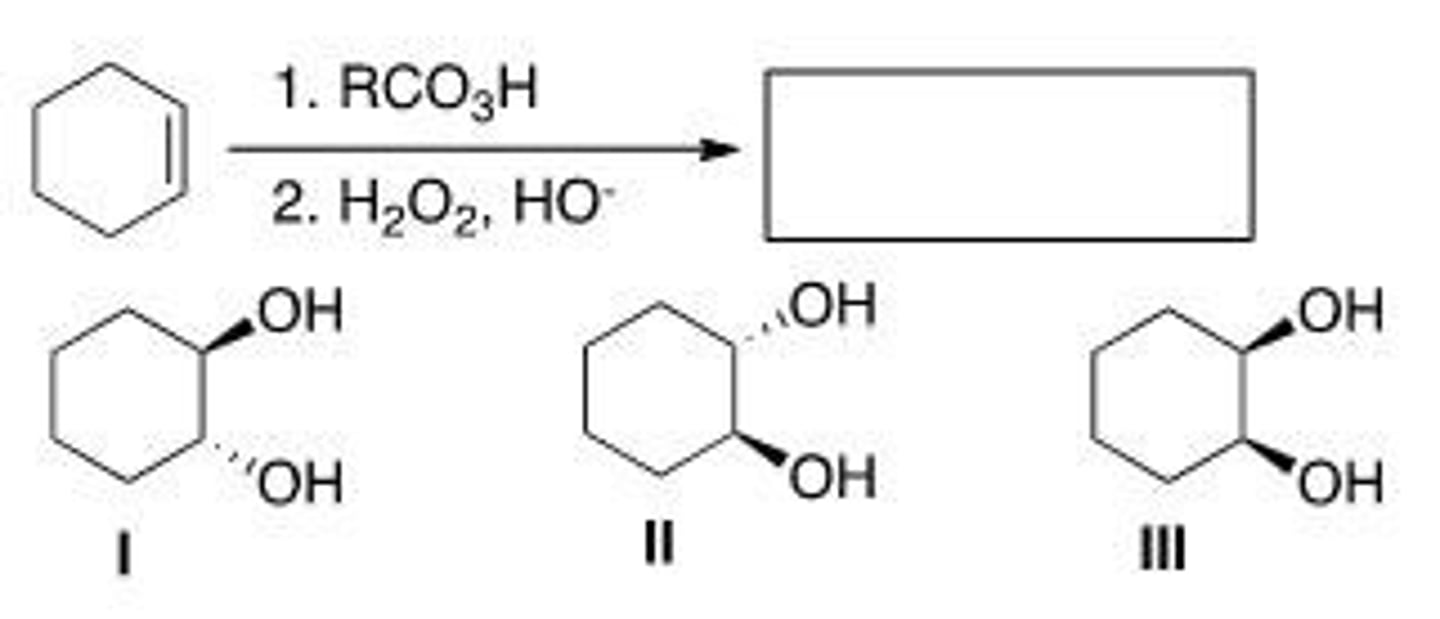
C
Determine the product of the following reaction, ignoring stereochemistry.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
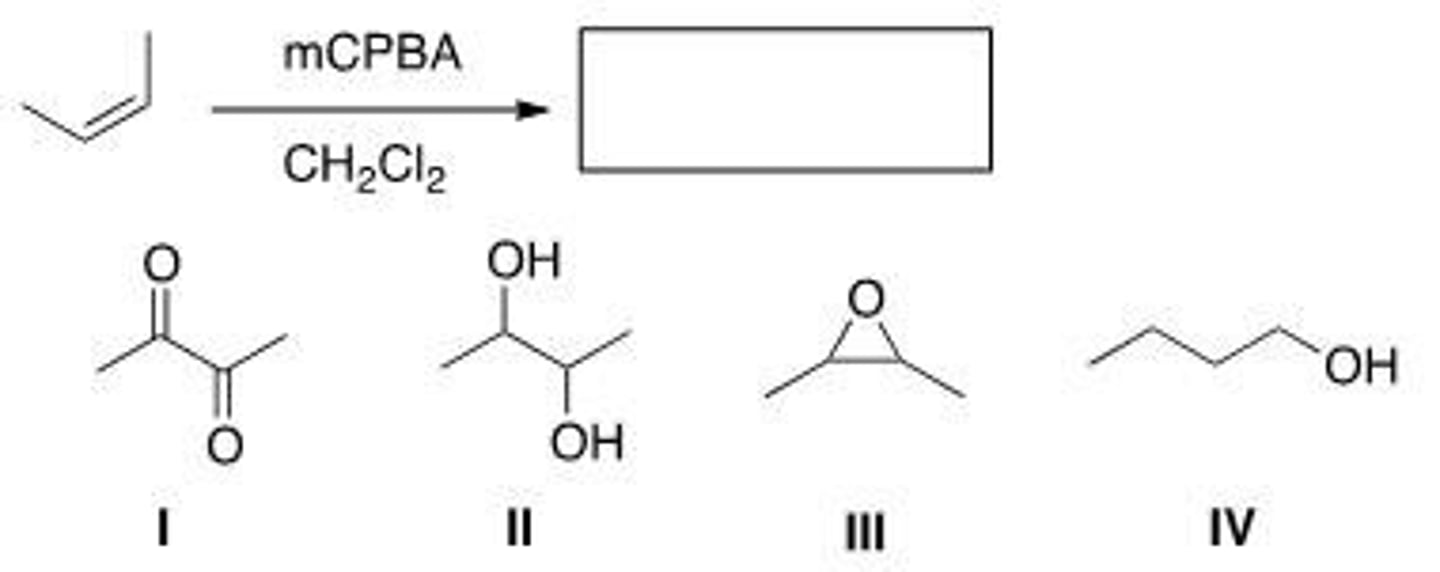
C
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
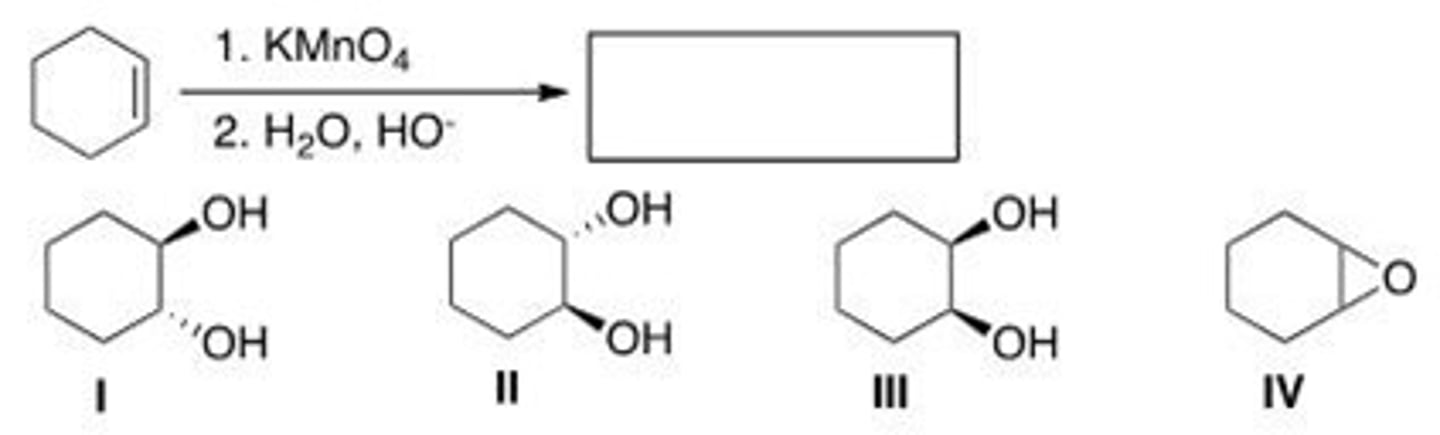
B
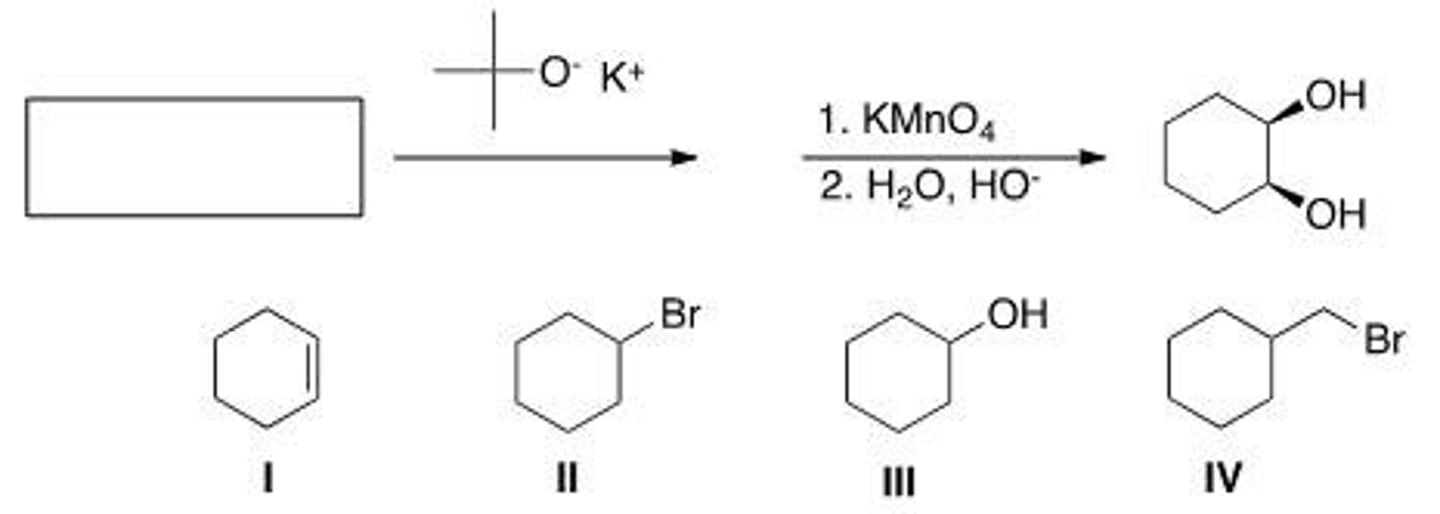
What is the reagent required to accomplish the following transformation?
A.
LiA1H4
B. [1] OsO4; [2] NaHSO3, H2O
C. RCO3H, H2O/HO-
D.
PCC/CH2Cl2
![<p>What is the reagent required to accomplish the following transformation?</p><p>A.</p><p>LiA1H4</p><p>B. [1] OsO4; [2] NaHSO3, H2O</p><p>C. RCO3H, H2O/HO-</p><p>D.</p><p>PCC/CH2Cl2</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2955c93c-1ca9-4e69-b9a6-9ab63d83e230.jpg)
C
What is the reagent required to accomplish the following transformation?
A. [1] OsO4; [2] NaHSO3, H2O
B. KMnO4, H2O/HO-
C. RCO3H/H2O/HO-
D.PCC/CH2Cl2
![<p>What is the reagent required to accomplish the following transformation?</p><p>A. [1] OsO4; [2] NaHSO3, H2O</p><p>B. KMnO4, H2O/HO-</p><p>C. RCO3H/H2O/HO-</p><p>D.PCC/CH2Cl2</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/00d9311d-a739-4385-92a0-4b85f967c2b9.jpg)
D
Determine the product of the following reaction.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
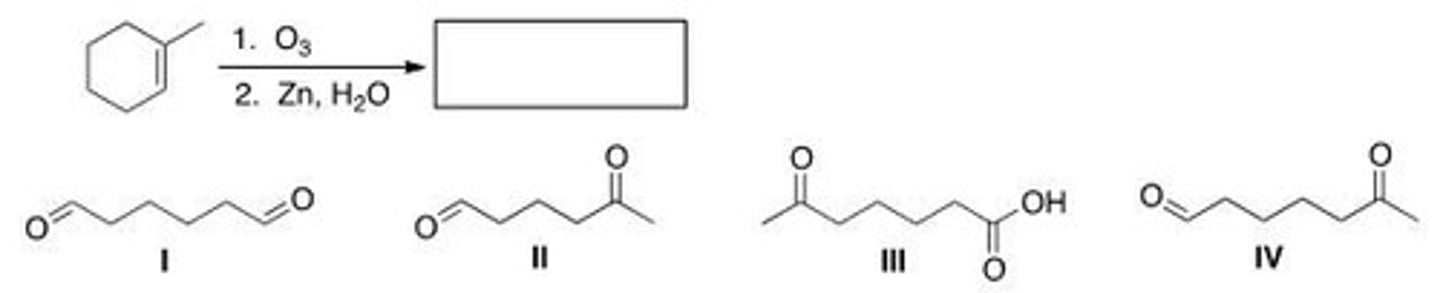
A
After ozonolysis and treatment of the unstable ozonide with CH3SCH3, compound A was converted to the compound below. What is the structure of compound A?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
B
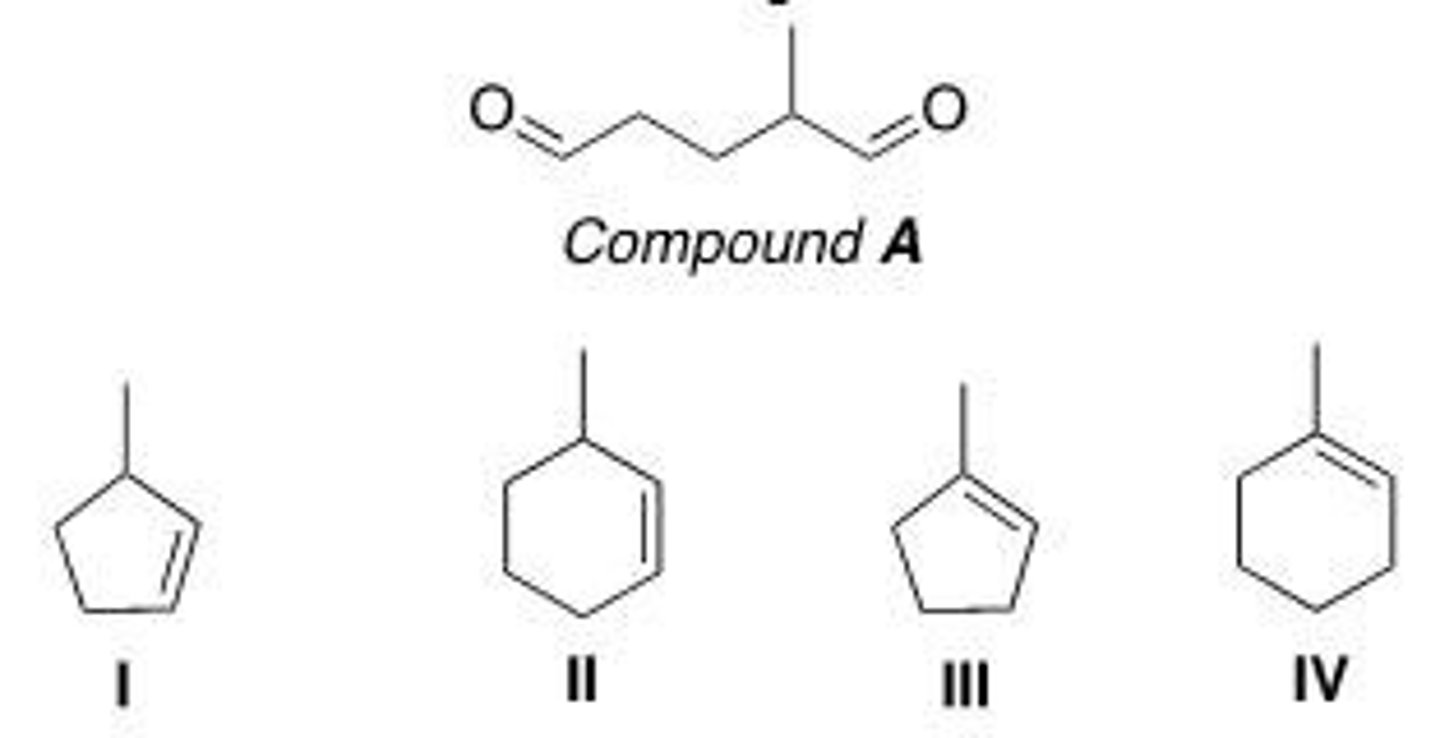
What is the starting material in the following sequence of reactions?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
C
Which of the following is (are) formed by ozonolysis of compound A?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. Only I and II
D. I, II, and III
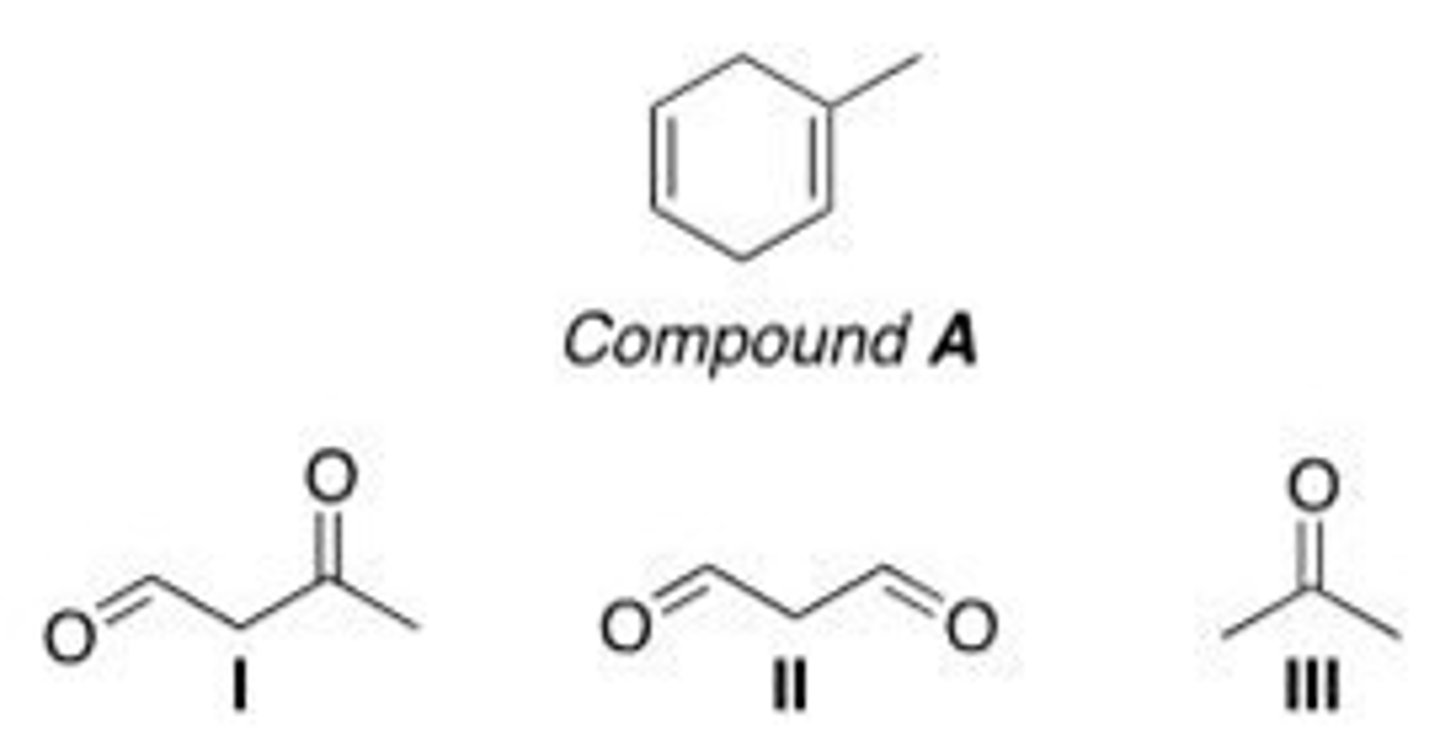
C
Which of the following is (are) formed by ozonolysis of compound A?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. I and II
D. I, II, and III
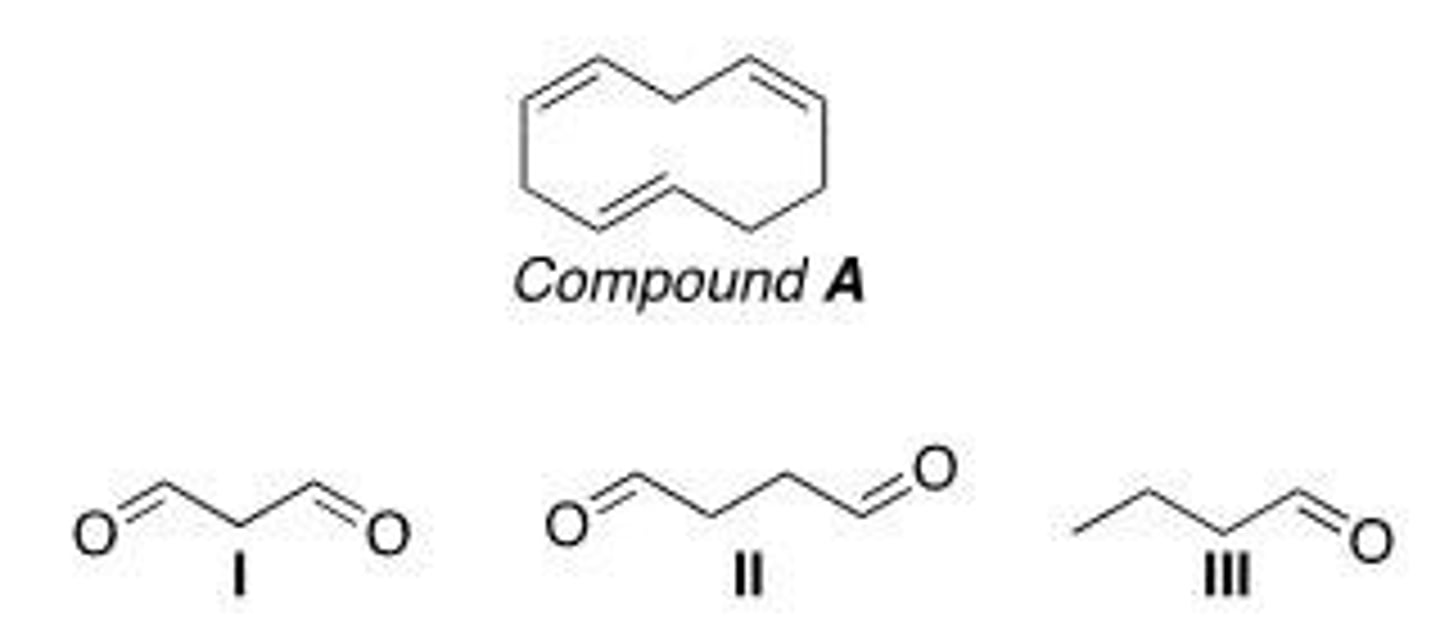
A
Which of the following is (are) formed by ozonolysis of the following alkyne?
A. Only I and II
B. Only III and IV
C. Only I and IV
D. Only II and III
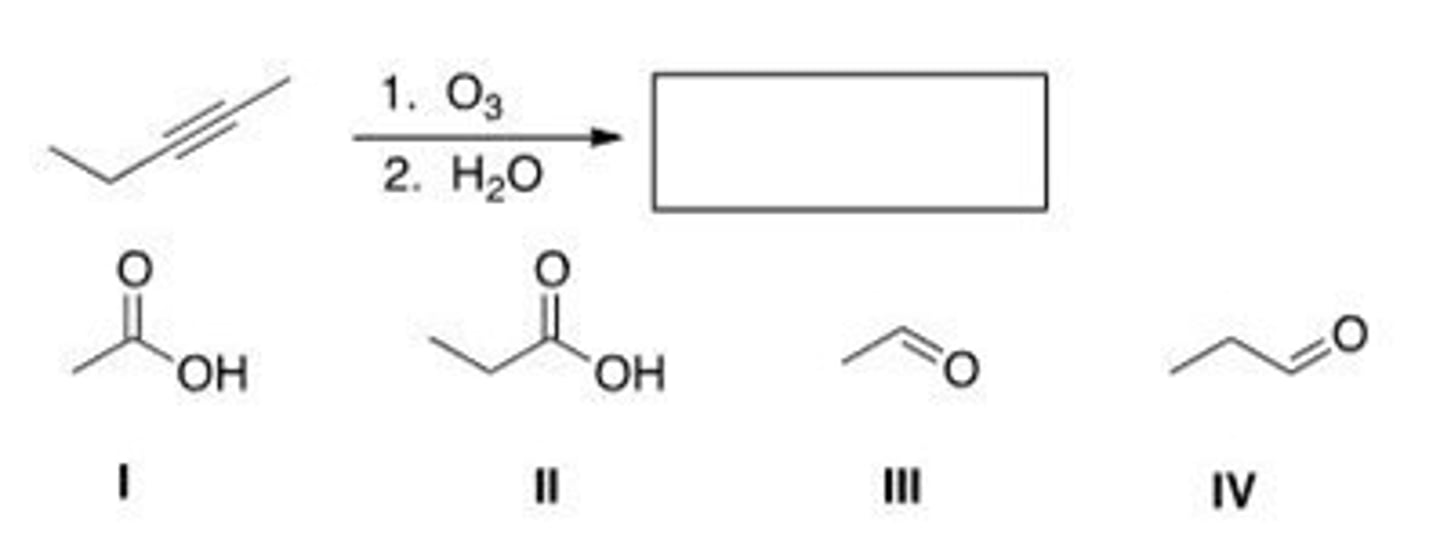
A
Which of the following is (are) formed by ozonolysis of the following alkyne?
A. Only I
B. Only II
C. I and II
D. I, II, and III
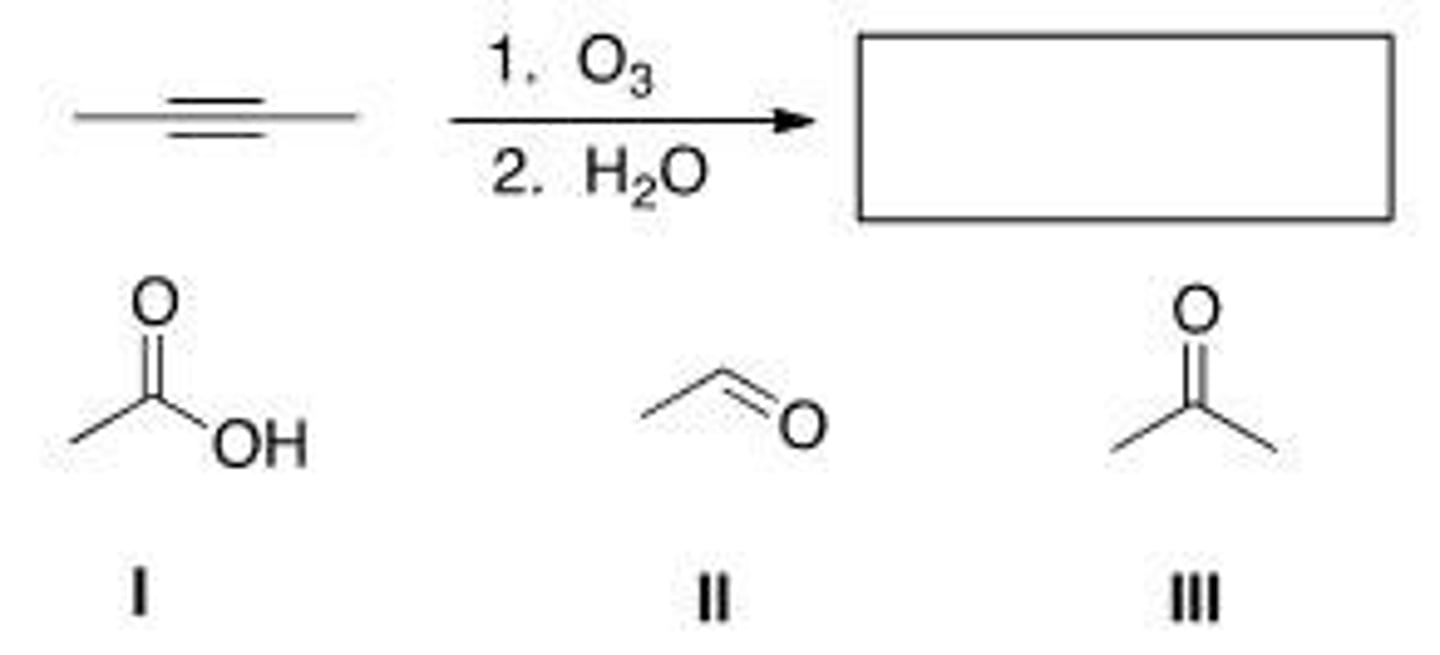
D
Determine the product of the following reaction.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
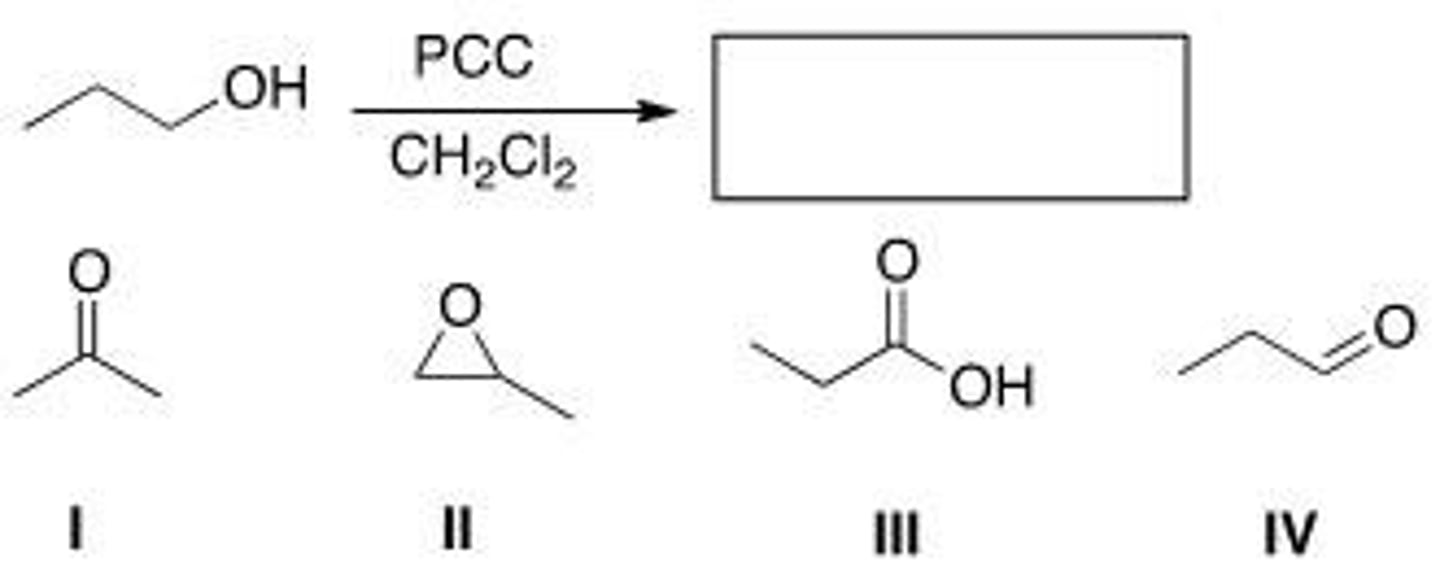
D
Determine the product of the following reaction.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
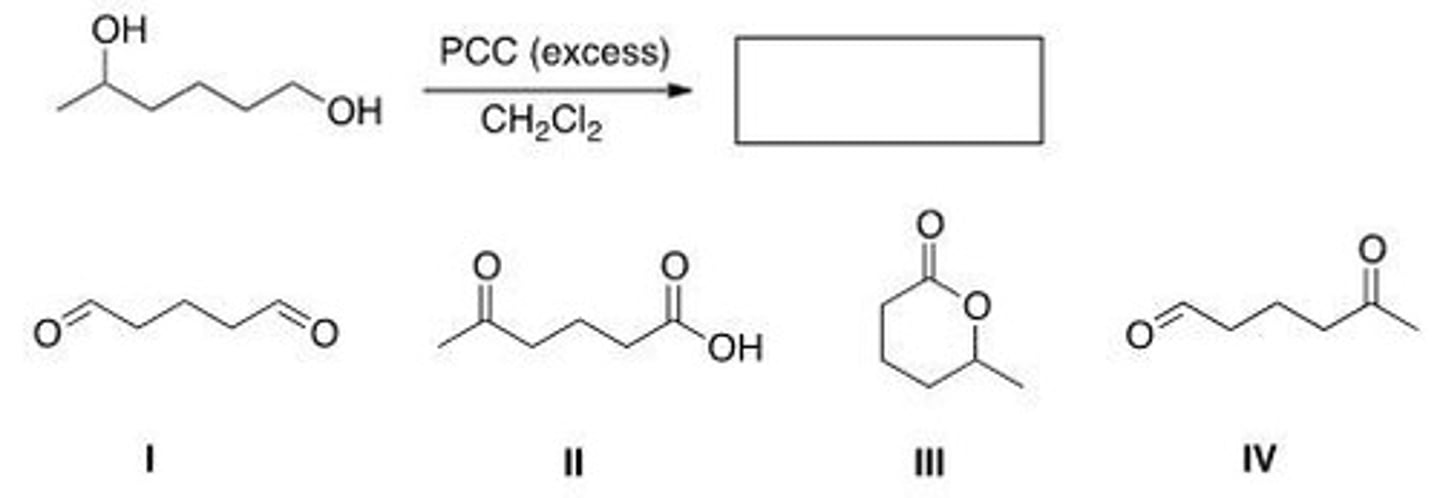
B
What is the product of the following reaction?
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
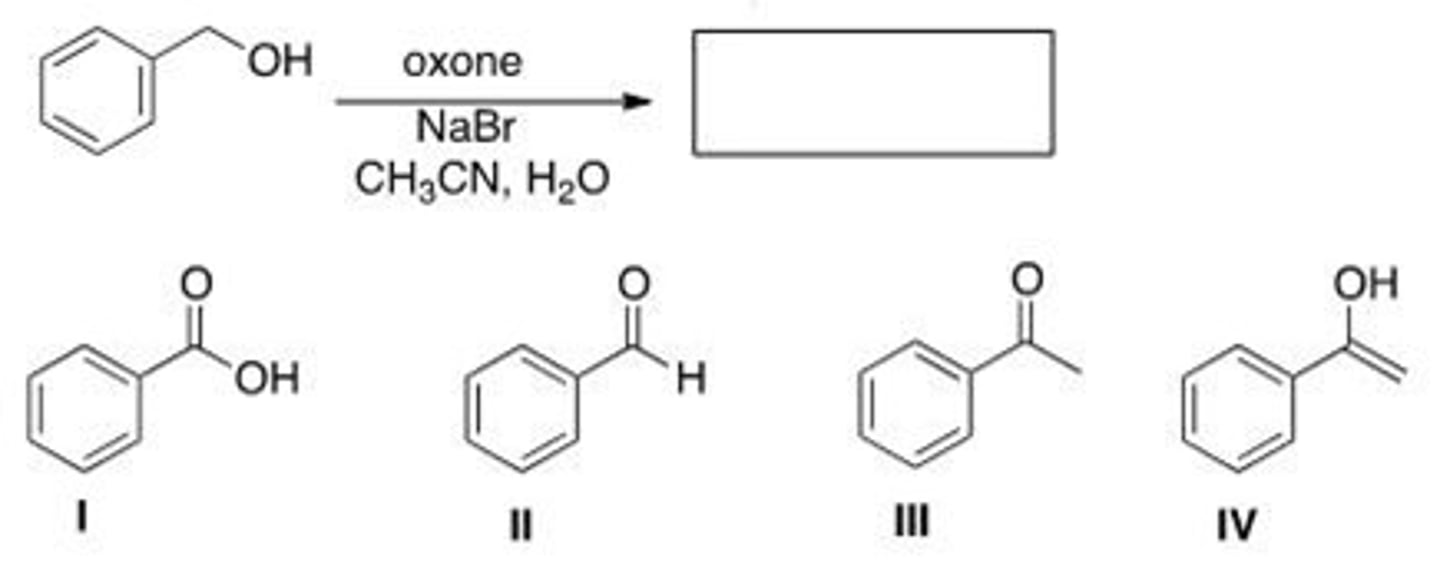
A
Predict the major product of the following reaction.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV
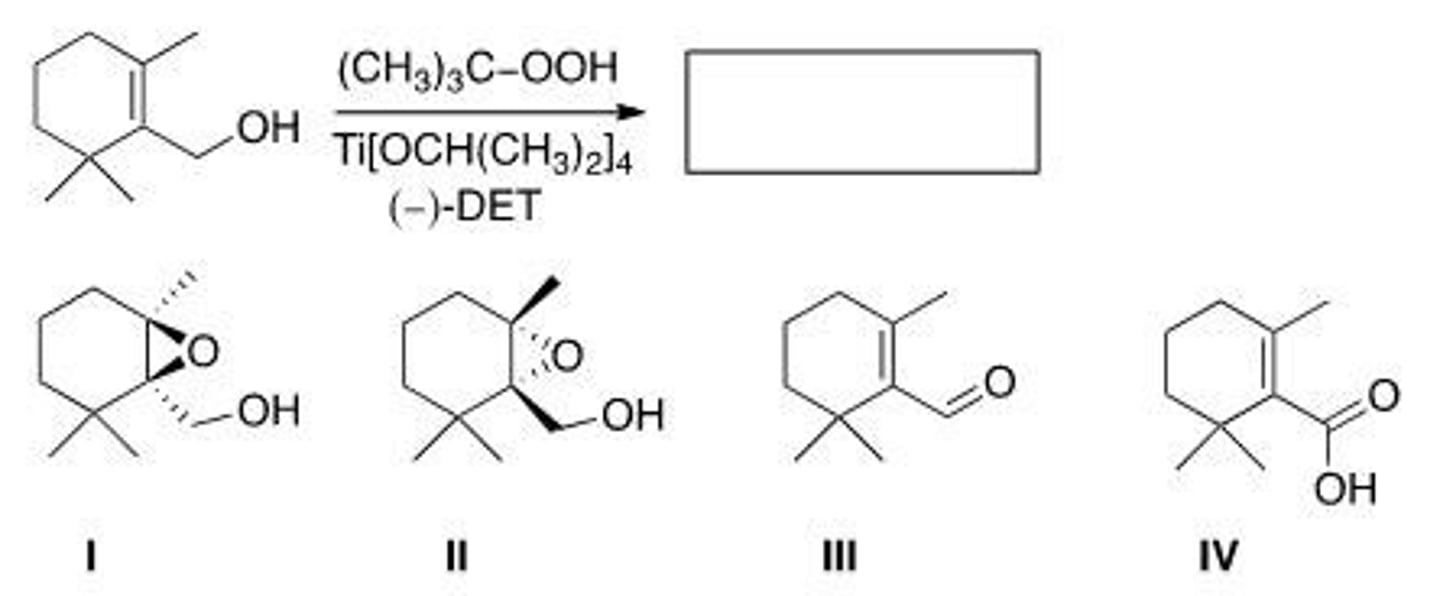
A
Predict the major product of the following reaction.
A. I
B. II
C. III
D. IV