MidYear ALL TERMS
1/336
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
337 Terms
nature v nurture
whether genetics or environment have greater influence on outcome of person; natural selection
Transduction
Process where sensory stimuli is converted into neural signals in brain
(Converts physical energy (light or sound) into electrical signals, nervous system can understand)
Absolute threshold
min level of stimulation needed for a person to detect stimulus;
when stimulus can be detected 50% of time across multiple trials (like faintest light, or quietest sound you can hear)
Just-noticeable difference
minimum amount stimulus needs to change for a person to reliably detect a difference; point where person can notice change 50% of time (difference threshold)
Weber’s law
The ratio of the JND is dependent on how big or intense the stimulus itself is
(change on small paper vs change on 5 story tall mattress - harder to see change)
Sensory Adaptation
process where sensory neurons become less responsive to constant stimulus over time, results in diminished perception of stimulus
Sensory Interaction
phenomenon where one sense influences or alters perception of another sense, meaning that our different senses work together to create a complete understanding of our environment (how smell can influence taste when eating food)
Synesthesia
neurological condition where stimulation of one sense (seeing a color) automatically triggers a perception in another sense (tasting something), causing blending of sensory experiences
Accommodation
individual completely changes their existing mental frameworks (schemas) / beliefs to accommodate new knowledge
Afterimages
visual sensation that persists even after the original stimulus has been removed, lingering image that appears in your vision after looking away from object
Prosopagnosia
neurological condition: "face blindness,"
Gate Control Theory of Pain
theory that explains pain perception by suggesting a "gate" mechanism in the spinal cord that can either allow or block pain signals from reaching the brain
Vestibular Sense
sensory system that provides info about balance + spatial orientation, allowing us to perceive our body's position in space, thru organs located w/in the inner ear; our equilibrium/posture
Kinesthesis
Sense that provides info about position and movement of one's body parts thru receptors located in muscles, tendons, and joints, allowing for coordinated movement even with eyes closed
Occipital Lobes
Brain’s Visual Processing Center; Back Of Brain/Cerebral Cortex
Optic Nerve
cranial nerve that transmits the electrical signals made by light from retina (in eye) to brain, allowing us to see
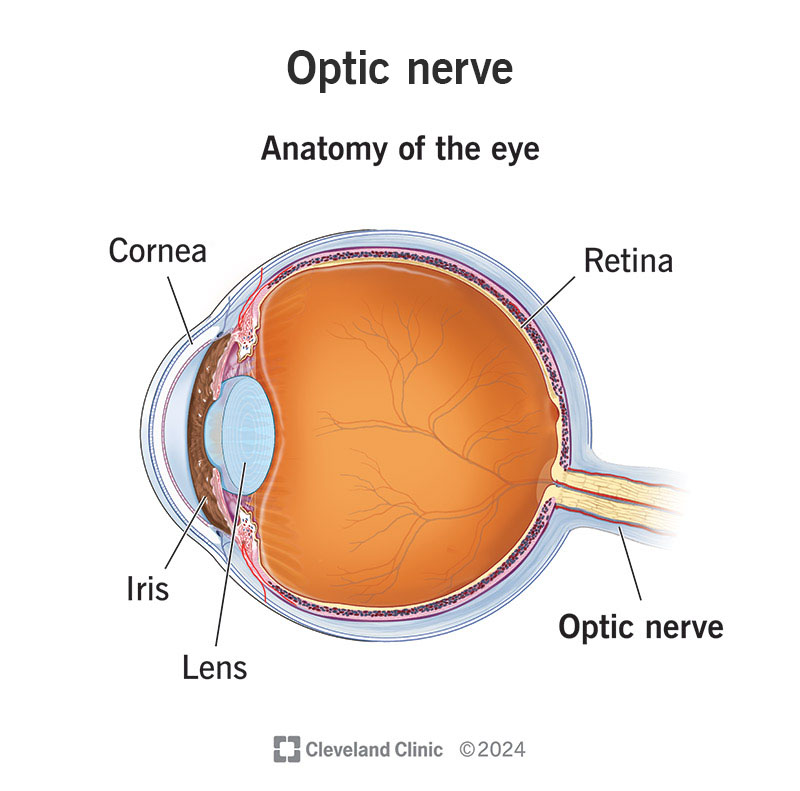
Retina
cranial nerve that carries electrical signals made by light to brain: allowing us to see
Blind Spot
area in visual field we cannot see
(image falls on optic disk, points where optic nerve leaves eye, and lacks light sensitive receptor cells; so we can’t see)
Lens
transparent structure w/in eye that changes shape to focus light onto the retina, allowing for clear vision at different distances (acts like lens in camera to focus images on light-sensitive part of the eye)
Rods
located in retina, detects shades of gray, what we shift to in dark
Cones
photoreceptor cell located in retina:
Responsible for color + detailed vision in bright light Allow for sharp central vision
Concentrated in Fovea (central part of retina)
Fovea
small pit located in center of retina:
highest concentration of cone cells, Responsible for sharp central vision + detailed visual acuity (sharpness), Part of eye where you focus on an object directly
Ganglion Cells
Neurons located in retina, receive visual info from bipolar cells (receive signals from rods and cones), then transmit that info to brain via optic nerve (final relay point for visual signals before they leave eye to visual cortex)
Cornea
eye’s clear, protective outer layer: covers pupil + iris
Iris
ring of muscle tissue that forms colored portion of the eye around pupil: controls size of the pupil opening.
Bipolar Cells
Neuron found in retina: transmits signals from photoreceptor cells (rods + cones) to ganglion cells (which then send this info to the brain)
Pupil
adjustable opening in center of eye thru which light enters
Temporal Lobes
Section of brain located near temples, responsible for:
Processing Auditory Info, Memory Encoding, Language Comprehension (Wernicke’s Area here)
Ear Drum
Protects Middle Ear + Transmits sound waves effectively
Maintains Balance of air pressure b/w outer + middle ear
Thin Cone Shaped Membrane that separates outer ear from middle ear
Hammer/Anvil/Stirrup
Three tiny bones in middle ear that transmit vibrations from eardrum to inner ear: then sent to the brain as sound
Oval Window
Oval-shaped-opening in inner ear needed for the hearing-membrane-covered opening in inner ear. Transmits sound energy to middle ear, to fluid-filled cochlea, to electrical signals for brain to interpret
Cochlea
coiled, bony, fluid-filled tube in the inner ear; sound waves travel thru the cochlear fluid & trigger nerve impulses
Hair Cells
sensory cells in inner ear that convert sound waves + head movements into neural signals sent to brain
Semicircular Canals
Three fluid-filled, looped tubes located w/in inner ear, responsible for:
Detecting head movements, sense of balance, Body’s awareness of orientation + movement (VB sense)
Auditory Nerve
Eighth cranial nerve that carries sensory info from inner ear to brain; Responsible for hearing + balance (vestibulocochlear nerve)
Cochlear Nerve
Carries auditory information from the cochlea, the spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear that converts sound vibrations into electrical signals
Vestibular Nerve
Carries balance info from semicircular canals and vestibule, located in the inner ear
Gustatory Cells
Taste bud cells that use chemicals dissolved in saliva to send these taste signals to brain (sweet, sour, bitter, salty, umami, oleogustus)
Skin Sensory Receptors (Nociceptors)
Sensory Neurons that detect potentially damaging stimuli & alert the body to injury, triggered by: extreme temps, pressure, injury-related chemicals, converting these stimuli into electrical signals sent to brain to create sensation of pain
blue
short wavelengths of light
green
medium wavelengths of light
red
long wavelengths of light
trichromatic theory
human color vision relies on three types of retinal cones—sensitive to short (blue), medium (green), and long (red) wavelengths—which combine signals to perceive all colors
opponent-process theory
posits that human perception and emotion are governed by opposing, antagonistic systems (e.g., red-green, pleasure-pain). In vision, it explains that seeing one color (e.g., yellow) inhibits its opposite (blue), creating afterimages
color vision deficiencies
sseeing colors differently, most commonly struggling with red-green shades due to genetic issues with retinal cones
Dichromatism
a type of partial color blindness where the eye contains only two, rather than the typical three, types of functional cone photopigments
Monochromatism
rare, genetic form of total color blindness where individuals lack functioning cone cells, seeing the world in shades of gray (black, white, and gray)
Blindsight
neurological condition where individuals with damage to the primary visual cortex can respond to visual stimuli in their "blind" field without consciously perceiving them.
wavelength of sound
pitch
amplitude of wave
loudness
place theory
states that pitch perception is determined by the specific location (place) along the basilar membrane of the cochlea that vibrates in response to different sound wave frequencies (best explains high pitched sounds)
frequency theory (with the volley principle)
theory of pitch perception stating that the frequency of auditory nerve impulses (firing rate of hair cells in the cochlea) directly matches the frequency of a sound wave, allowing us to hear pitch (best explains low pitched sounds)
sound localization
ability to determine the origin, direction, and distance of a sound source in one's environment
conduction hearing loss
type of hearing impairment caused by the failure of sound waves to reach the inner ear (cochlea) due to physical obstructions or damage in the outer or middle ear (earwax buildup, infections, fluid, perforated eardrums)
sensorineural hearing loss loss
hearing impairment from damage to inner ear (cochlea's hair cells) or auditory nerve, disrupting sound-to-brain signal transmission impacts communication + perception (aging, genetics, loud noise exposure, head/ear trauma)
Olfaction
sense of smell
Gustation
physiological and psychological process of detecting chemical substances dissolved in saliva via receptors on the tongue and palate
Thalamus
paired, egg-shaped, gray-matter structure located deep within the center of the brain's diencephalon, serving as the main relay and processing station for sensory and motor signals traveling between the body and the cerebral cortex; consciousness, alertness, sleep regulation, emotional responses
Pheromones
chemical substances secreted externally by animals—and potentially humans—that trigger social, behavioral, or physiological responses in members of the same species
hot = warm and cold receptor activation
brain gets a mixed message from the adjacent warm and cold spots, and that mixed signal translates to the feeling of intense heat.
phantom limb syndrome
the subjective sensation that an amputated or missing limb is still present, often accompanied by sensations like tingling, itching, or, most notably, severe chronic pain
Bottom Up Processing
analyzing sensory info from environment w/ no prior knowledge to form a complete perception of things, “what you see is what you get” approach
Top Down Processing
where your brain uses existing knowledge, expectations, and context to interpret new info. instead of solely relying on sensory input; higher-level mental functions to interpret things
Selective Attention
the capacity to react to and process certain stimuli selectively when multiple things happen at the same time
Cocktail Party Effect
ability to focus on a single conversation or auditory stimulus while filtering out background noise; demonstrates selective attention where brain prioritizes certain sounds over others (being able to hear your name called
across a crowded room at a party)
inATTENTIONal Blindness
when someone can’t to perceive a visible stimulus because their attention is focused on something else; missing things in plain sight
CHANGE Blindness
when a person fails to notice a big & obvious chance in their vision because their attention is focused on something else
Perceptual Set
the mental predisposition to perceive stimuli in a certain way based on past experiences, expectations, & context; where we notice certain aspects of sensory info while ignoring others due to our preexisting beliefs
Schema
a structured framework or blueprint for organizing and connecting info
Gestalt
school of thought that highlights how our brains process info in overall structures rather than individual elements; states "the whole is greater than the sum of its parts"
Binocular Cue
Visual cues that require use of both eyes to perceive depth
Depth Perception
BINOCULAR ability to perceive the relative distance of objects
Convergence
BINOCULAR inward movement of both eyes when focusing on a nearby object; muscles in eyes turn inwards to align on a close target
Retinal Disparity
slight difference in image received in each eye when viewing an object; used by brain to perceive depth + distance; greater the difference b/w images, closer object appears to be
Monocular Cue
Visual cues that allow us to perceive depth using only one eye
Relative Clarity
objects that appear sharp and clear are perceived as closer than objects that appear hazy or blurry
Relative Size
monocular depth cue used to determine how far away an object is based on its apparent size compared to another object (further away if appears smaller, closer if appears bigger)
Texture Gradient
visual perception cue: objects seem denser and have finer details when close; objects seem to have less detail and appear more spread out when farther
Linear Perspective
MONOCULAR depth cue where parallel lines appear to converge as they recede into the distance, creating the perception of depth on a flat Surface
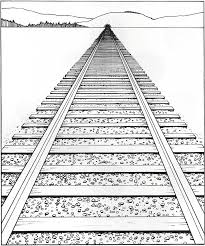
Interposition
MONOCULAR depth cue where one object partially blocks another, causing the partially blocked object to be perceived as farther away
Sensory Adaptation
after a long time of intake of certain stimuli, sensory receptors adjust by becoming less sensitive to them
Habituation
Lowered response to a stimulus after repeated exposure to it; organism becomes less responsive to a familiar stimulus (getting less shocked when someone yells at 7am each morning)
Sensory Adaptation v Habituation
Sensory adaptation is an automatic, physiological process in sensory receptors where response to a constant stimulus decreases; habituation is a learned, psychological process where the brain learns to ignore a repetitive stimulus, requiring more conscious control
Perception
process of interpreting and organizing sensory information
received from the environment, essentially how our brains make sense of the raw data
gathered by our senses,
Context
the surrounding circumstances, environment, or situation that influences behavior, perception, and memory
Figure & Ground
The visual perception concept where our brain
distinguishes a main object (the "figure") from its surrounding background (the
"ground"),
Proximity
People tend to perceive objects that are physically close together as
belonging to the same group,
Similarity
tendency to categorize things based on shared characteristics.
Closure
Gestalt principle where the brain tends to perceive incomplete
figures as complete by filling in the missing information, essentially "closing the gaps"
Perceptual Constancy
our brains interpret objects as consistent despite variations in
sensory input.
Apparent Motion
visual illusion where a stationary object appears to
be moving,
Visual Cliff (ced unit 3)
place glass right after checkered surface in frnt of babies to see if they have depth perception and fear of heights
Cognition
mental processes involved in acquiring, processing, and applying knowledge; encompasses memory, perception, attention, reasoning, language, etc.
Concept
idea or abstract principle that helps explain human behavior and mental processes; encompasses memory, perception, learning, motivation, personality, and social influence
Prototype
best/most typical example of a category, being the mental representation for making judgments about other things. People categorize new items by comparing them to this idealized prototype (fruit is mentioned = apple usually thought of first)
Schema
a structured framework or blueprint for organizing and connecting info
Assimilation
cognitive process of incorporating new info into existing mental frameworks (schemas) without changing them; how people fit new experiences into their current understanding of the world
Accommodation
Cognitive process of adjusting existing mental frameworks (schemas) by changing them when new info does not fit with current understandings rather than simply being assimilated into existing ideas
Convergent Thinking
cognitive process where a person analyzes info to arrive at a single, well-defined solution to a problem, typically considered the "correct" answer; relies on logic and critical evaluation
Divergent Thinking
cognitive process where a person generates multiple, creative solutions to a problem by exploring many different possibilities; "thinking outside the box"