EXAM TOMORROW RADIOLOGY
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Compton Effect
Compton Effect / Scatter
■ occurs when an incident x-ray photon strikes a target atom and uses a portion of its energy to eject
an outer shell electron
■ occurs at energy levels throughout the diagnostic x-ray range of KVp
■ travels in all directions
- most scattered photons move in forward direction
- some directed back towards the x-ray tube are termed BACKSCATTER
■ extremely important because it is responsible for occupational worker
exposure to radiation.
Photoelectric Effect
secondary radiation
- In PE interaction, the photons are totally absorbed in the process, creating an
ABSORBED DOSE in the patient.
- less prevalent in the diagnostic energy range than Compton interactions.
- DECREASES with INCREASED KVp (opposite to Compton effect)
Scatter Radiation
Scatter radiation increases with:
1. Increased KVp
2. Increased Field size
3. Increased patient thickness (volume and density of tissue)
■ Scatter radiation is controlled by use of:
1. Beam restricting devices – limits field size to smaller area thus reducing scatter
radiation
2. Grids – absorb scatter radiation before it reaches the film
3. Air-gap technique – gap between pt and film decreases scatter radiation
How MRI works
A cross-sectional imaging modality where a strong
magnetic field forces protons in the body to align with
that field to produce images in multiple planes
A radiofrequency current causes the protons to be
stimulated, and spin out of equilibrium, straining them
against the pull of the magnetic field.
When the radiofrequency field is turned off, the
MRI sensors detect the energy released as the protons
realign with the magnetic field.
Contrast agents (e.g., Gadolinium) may be given to
increase the speed at which protons realign with the
magnetic field. The faster the protons realign, the
brighter the image.
Distortion (1) Can magnify areas of anatomy (1)
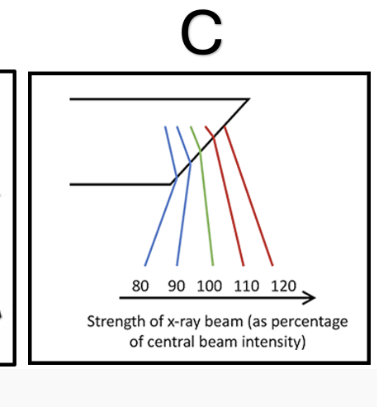
Anode Heel Effect (1) Can cause over AND under exposure on one image if anatomy is of high and low density (1)
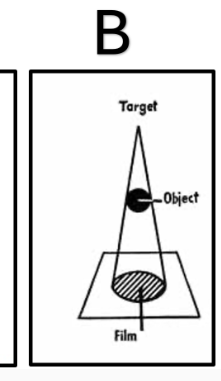
Focal Spot Blur OR Penumbra (1) Can cause a region of blurring on the image
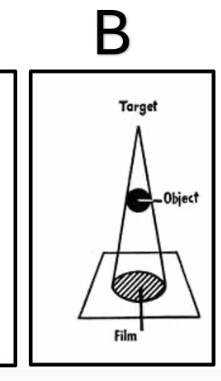
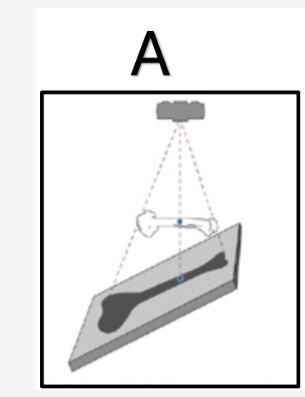
Please state how to counteract the geometric factor shown in Image B
Increase Source to Image Distance (SID) (1) Decrease Object to Image Distance (OID)
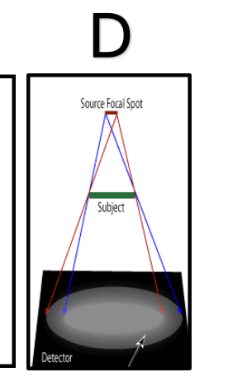
Please state which attenuation interaction is demonstrated here
Photoelectric Absorption/Effect
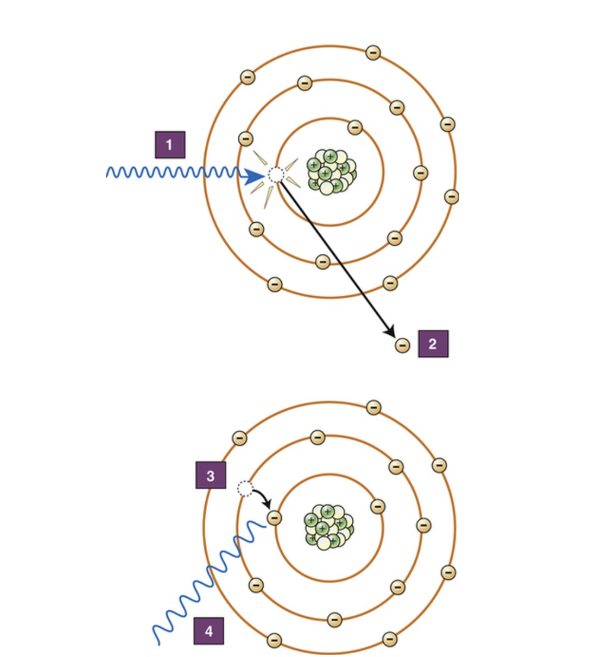
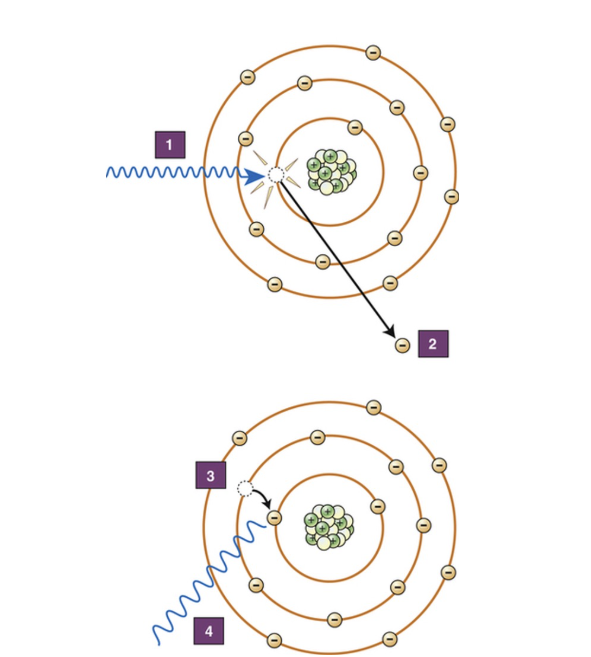
Please describe what occurs at stages 1-4 on the diagram adjacent.
Incident photon interacts with inner shell electron, Inner shell electron is ejected from the atom, There is a vacancy in the inner shell, As the electron fills the vacancy drops down it emits its excess energy as a secondary photon.
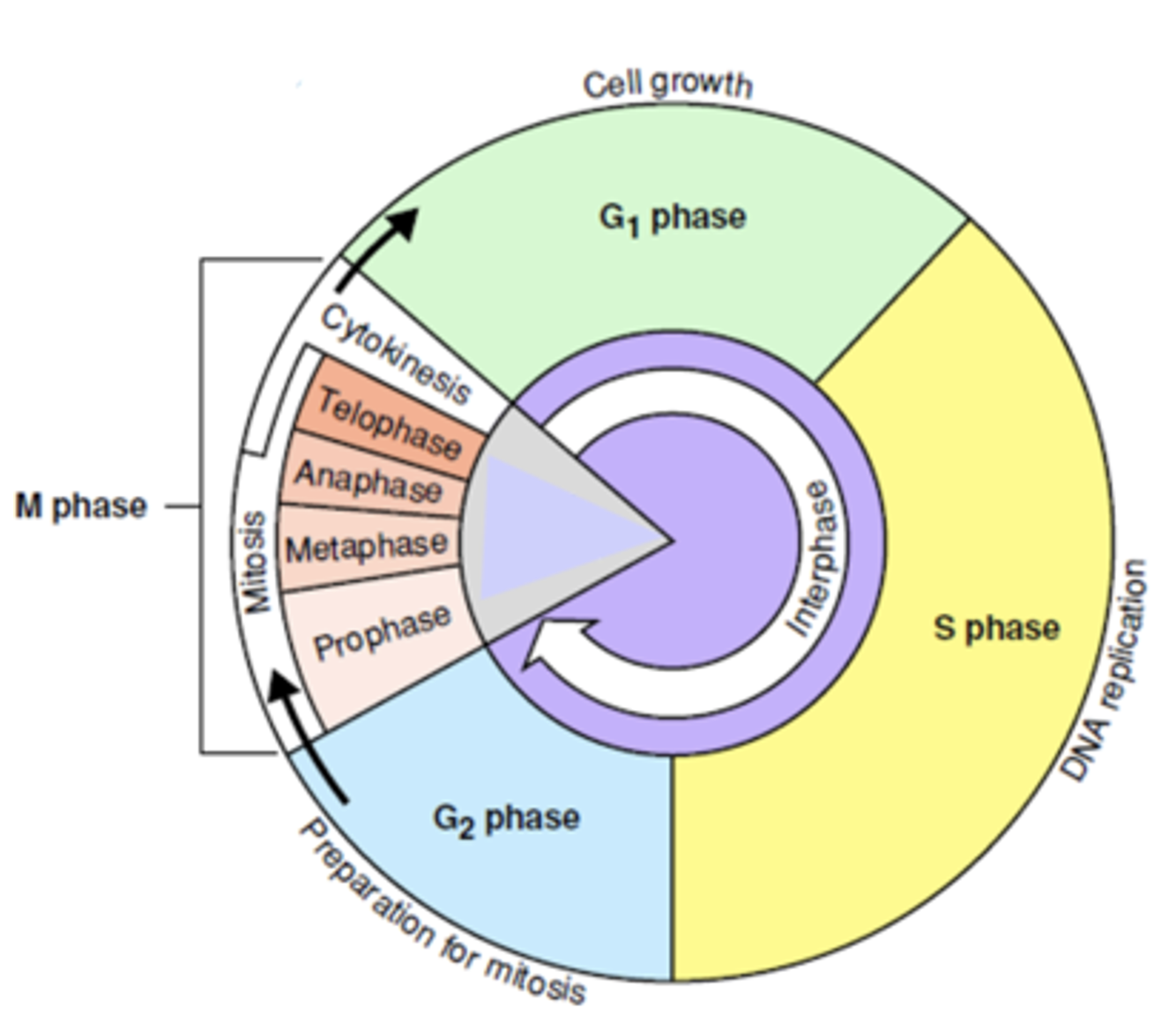
TRUE or FALSE:
a) The ‘M’ phase of the cell cycle is part of the cycle when a cell is at its most radiosensitive.
b) The ‘S’ phase of the cell cycle is part of the cycle when a cell is most radioresistant.
c) Apoptosis is the programmed survival process a cell experiences when exposed to radiation.
d) Cell cycle time of malignant cells is shorter than that of normal cells.
e) Blood and bone marrow have long cell cycles.
TRUE
TRUE
FALSE
TRUE
FALSE
5 pro’s and 5 con’s to Computed Tomography as an imaging modality
Pros: Quick
Widely available
Ideal for whole body trauma scanning
Few restrictions
Comprehensive
Accurate
Painless
Planning Ability
Reconstructions
Cons:
Uses ionising radiation
Contrast Risk
Unsuitable for pregnant patients
Expensive
Misdiagnosis
Please state the 4 main factors that influence the degree of attenuation of an x-ray beam
Thickness of Tissue (2)
Energy of the Beam (2)
Density of material (2)
Atomic Number of Material (2)
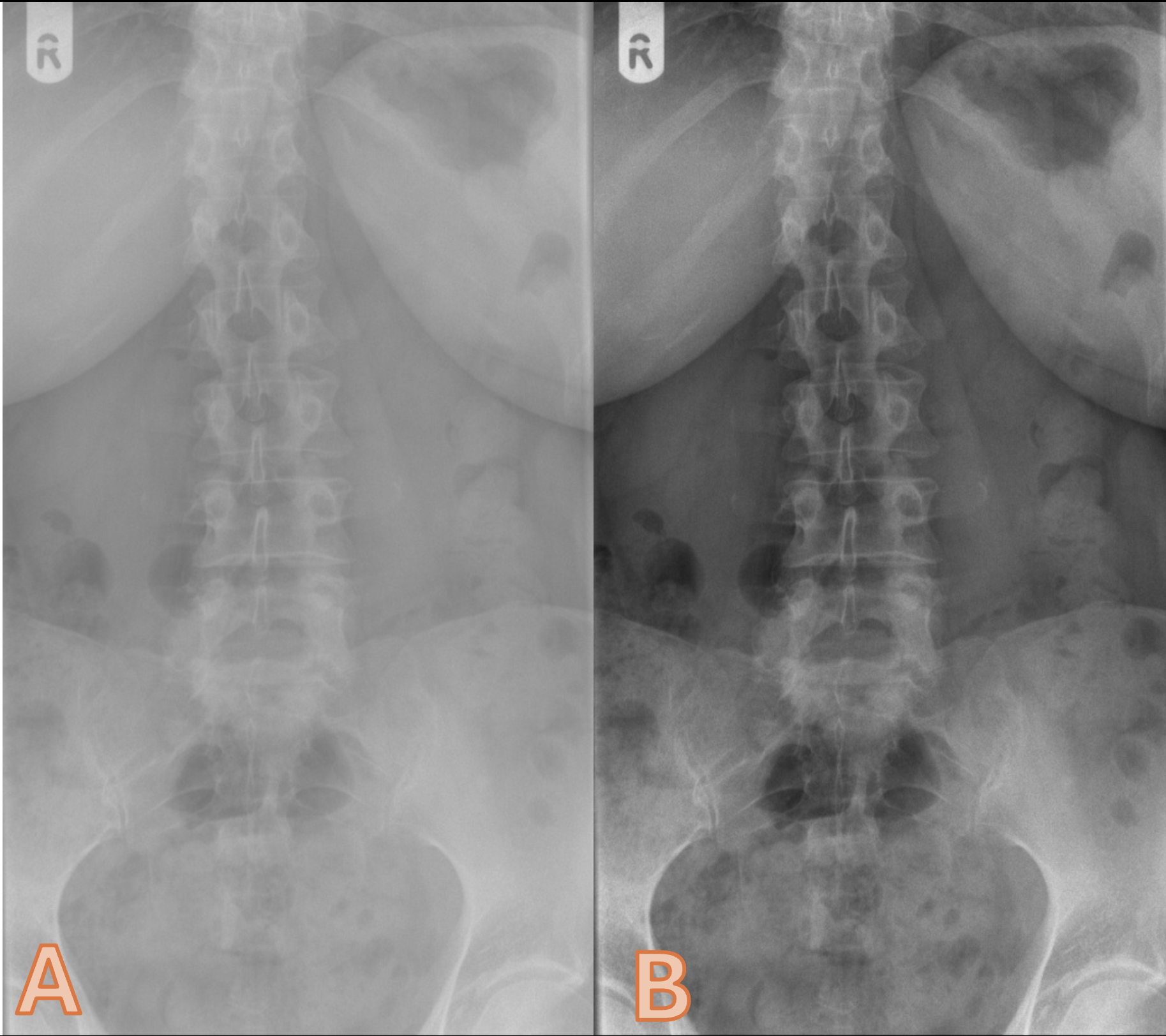
Please discuss Image A and B in relation to image contrast
Image A has poor contrast (1) and Image B has higher contrast (1)
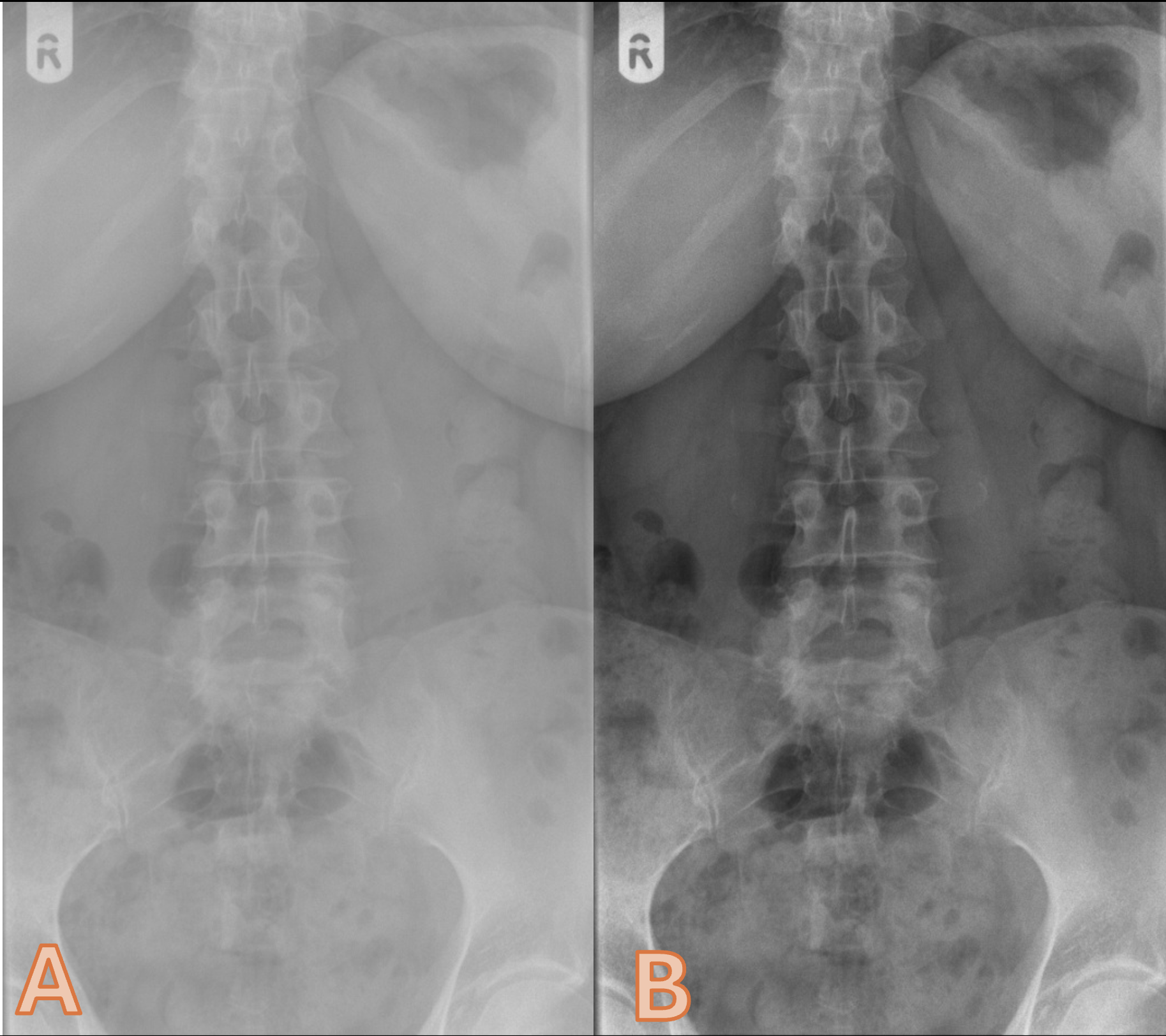
Please list 4 factors that can influence image contrast
mAs
Focal spot size
Anode heel effect
Distance
Filtration
Beam restriction
Anatomical part
Image receptor
Processing
Use of grids
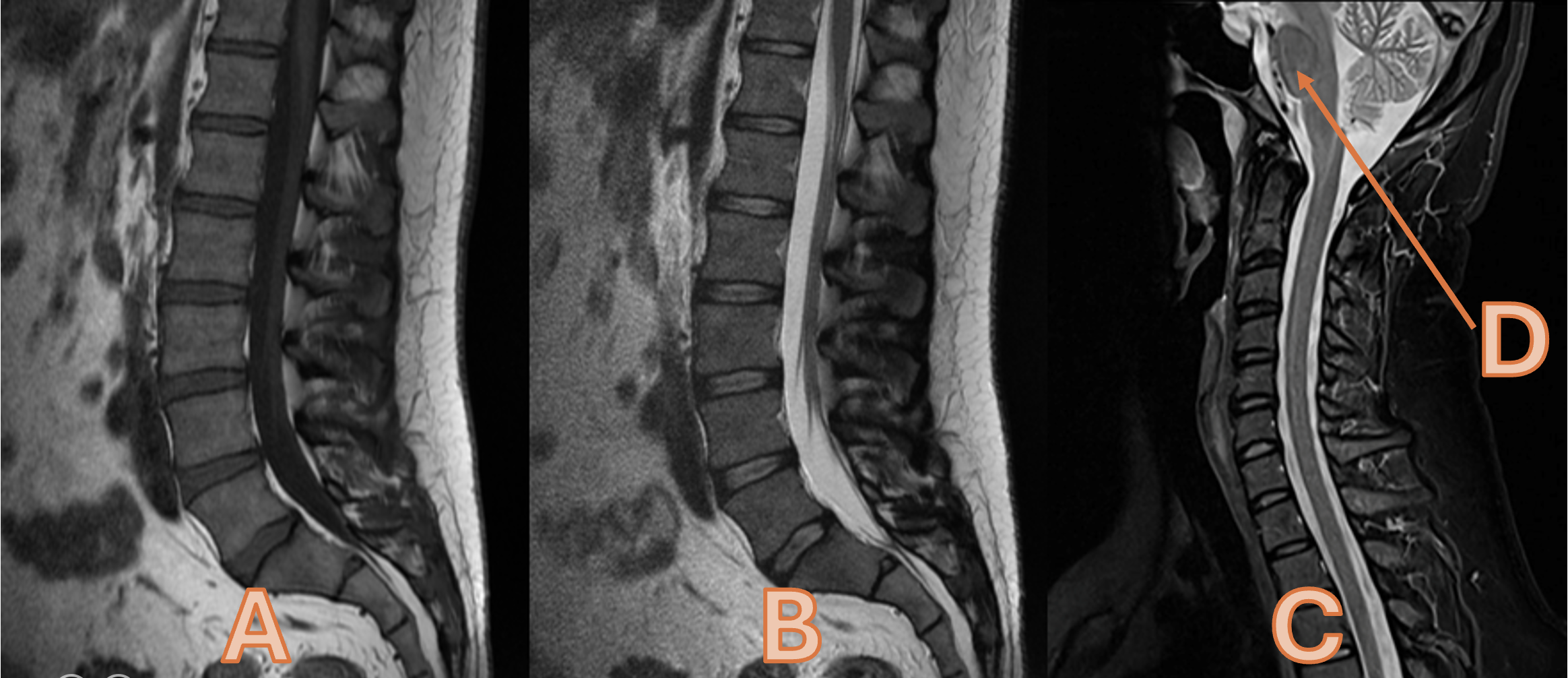
Please state the image weightings for Images A, B and C
A = T1 Weighted (1) B = T2 Weighted (1) C = STIR OR Short Tau Inversion Recovery
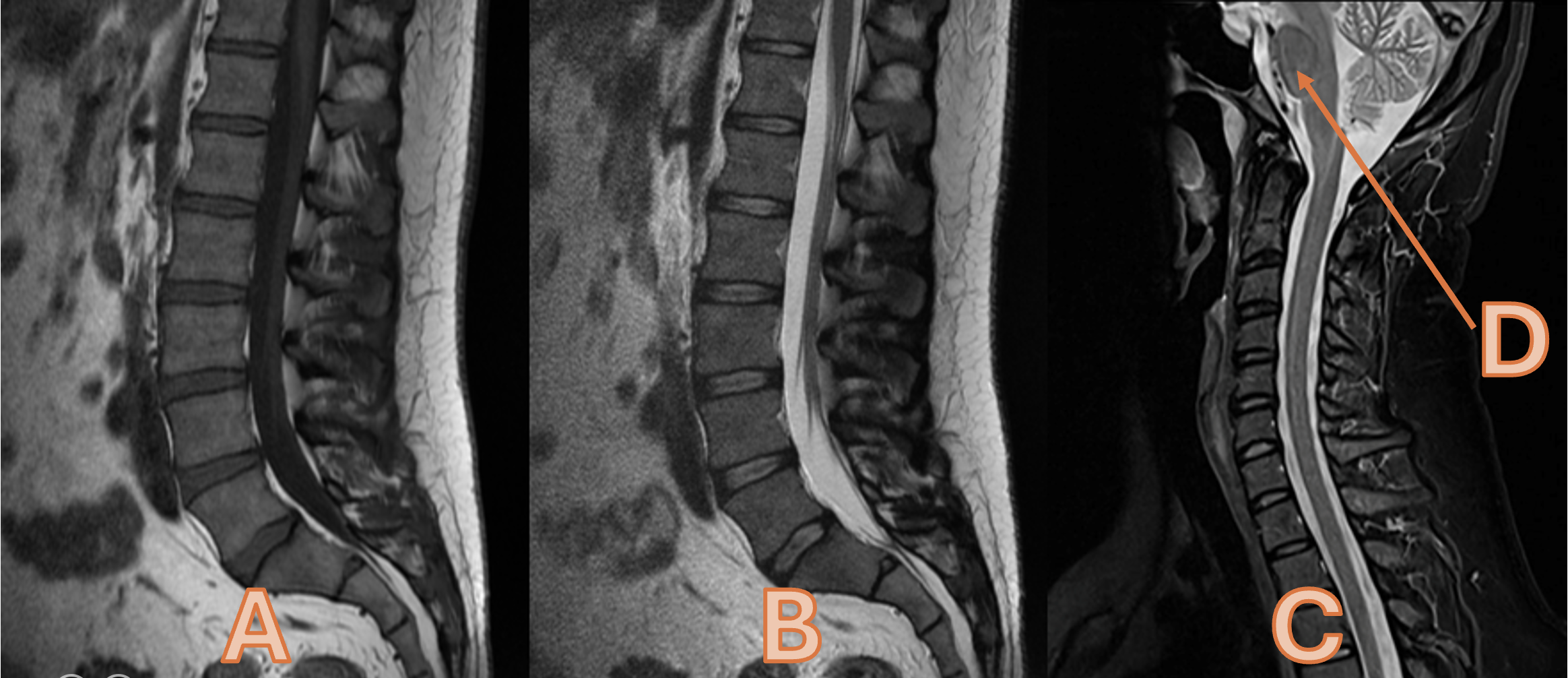
Please state the appearance of fat Images A, B and C
A = Hyperintense (1) B = Hyperintense (1) C = Hypointense
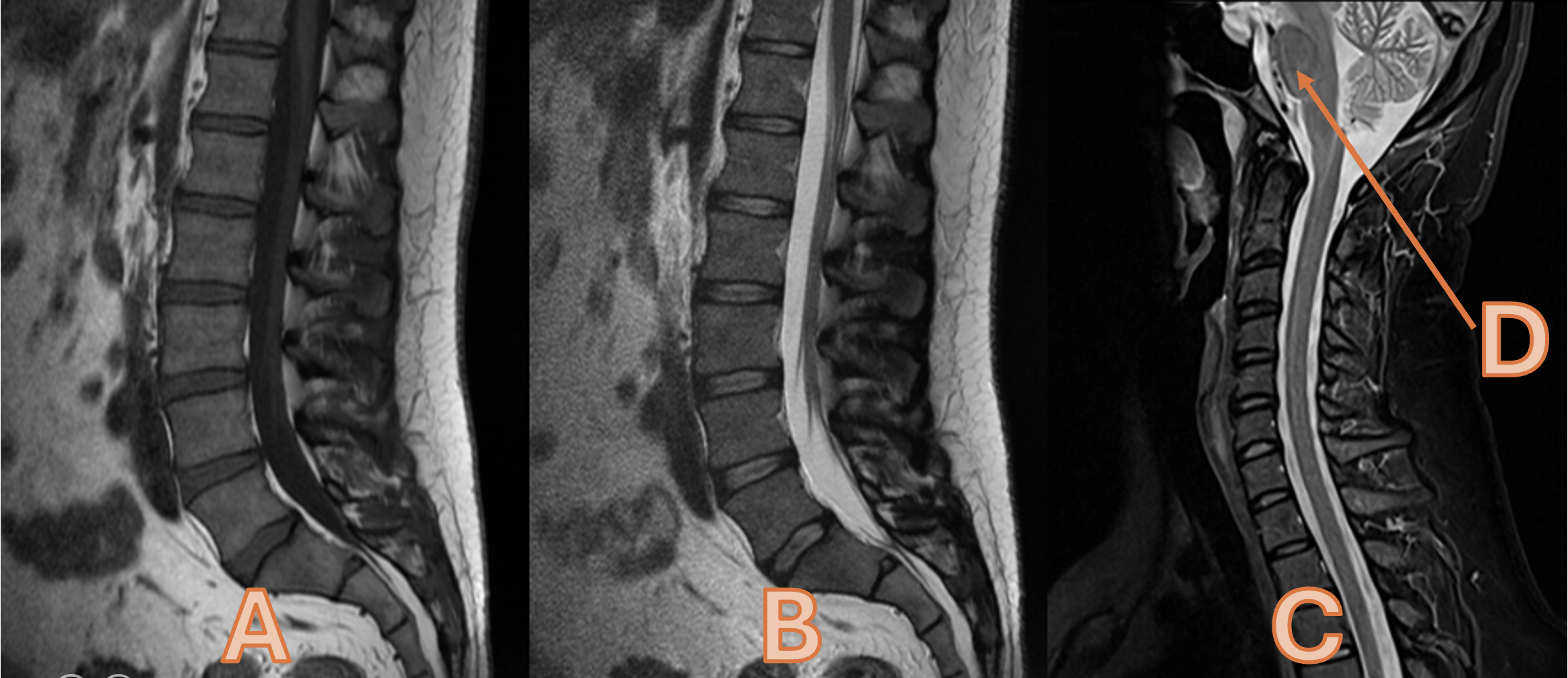
Please state the appearance of fluid for Images A, B and C
A = Hypointense B = Hyperintense C = Hyperintense
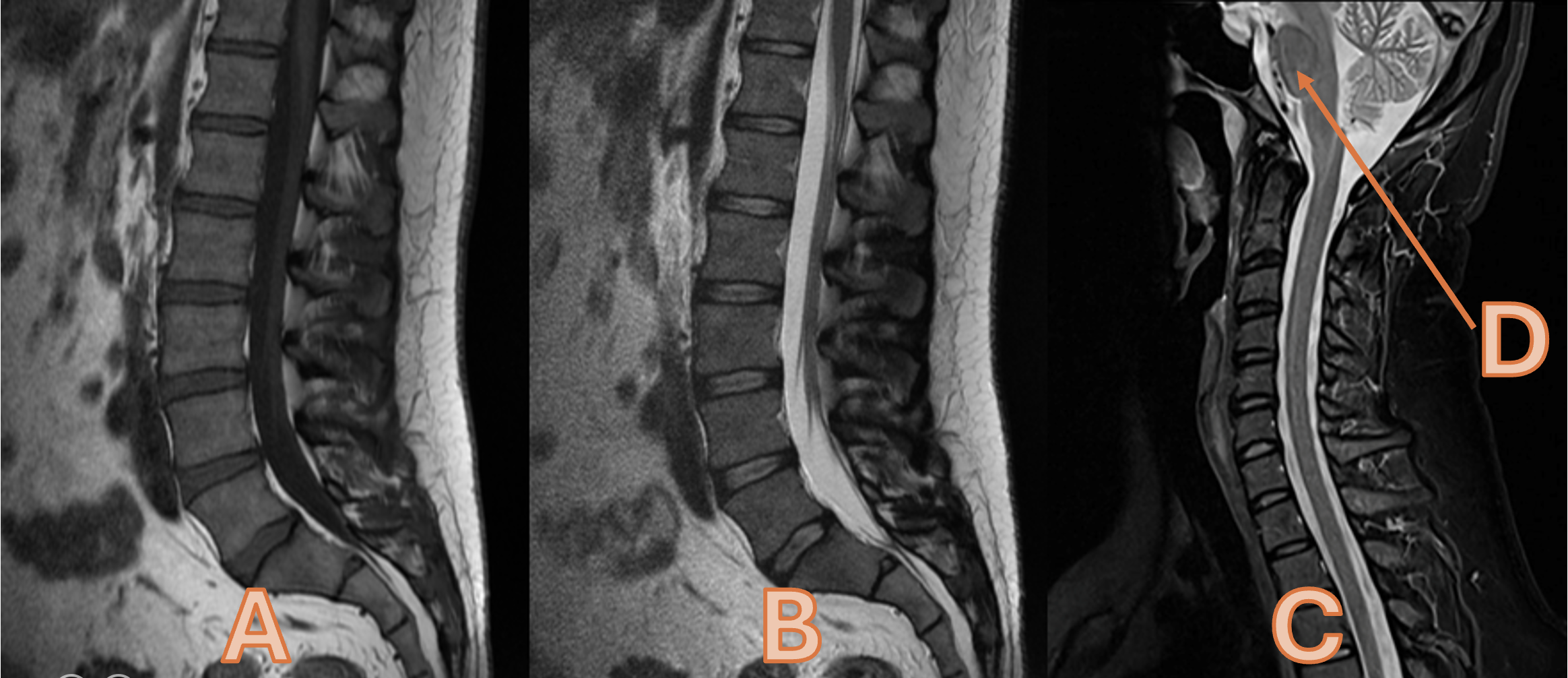
. Please state the anatomy labelled as ‘D’
Pons
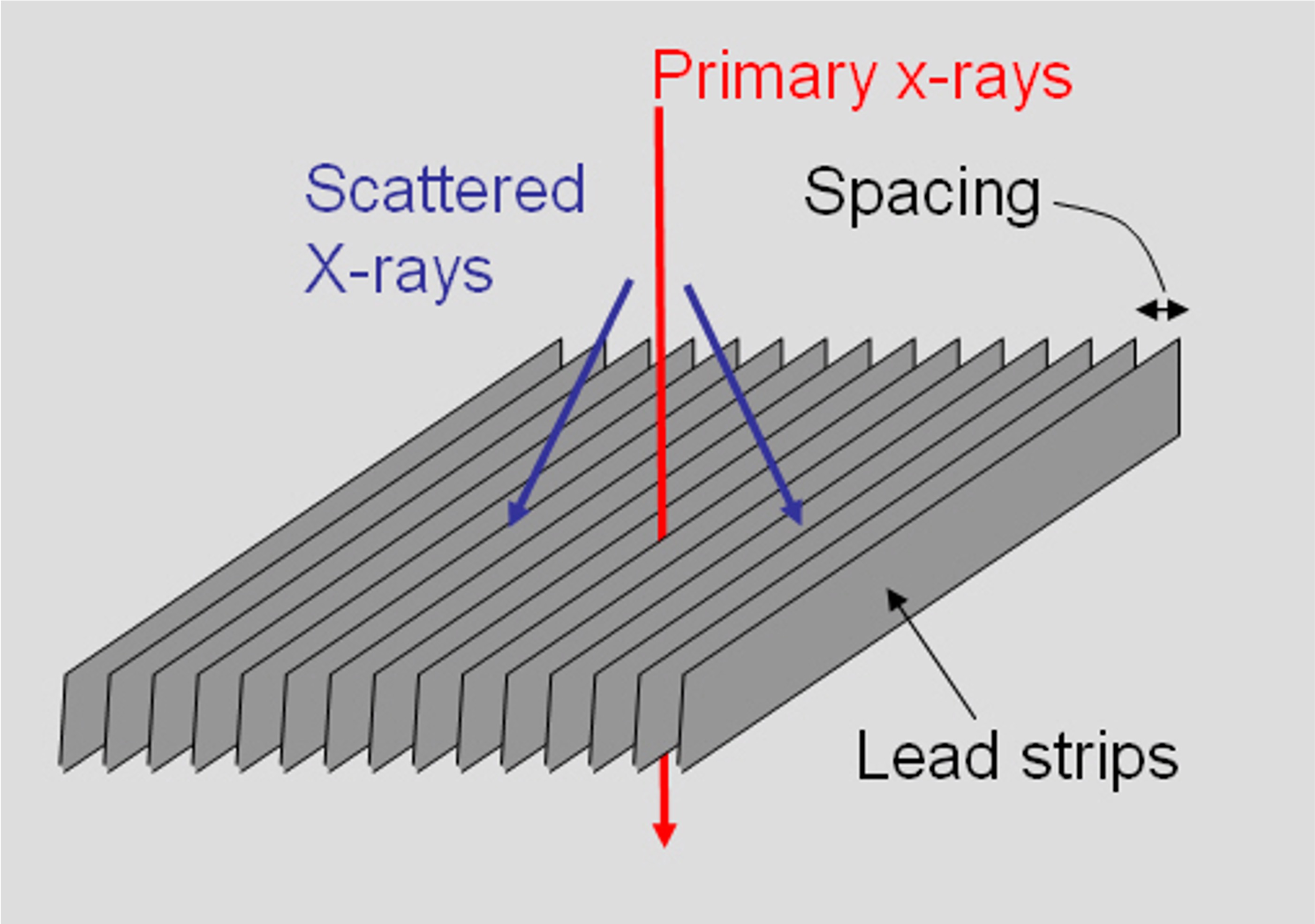
Please state the name of the equipment demonstrated
Anti (1) Scatter (1) Grid
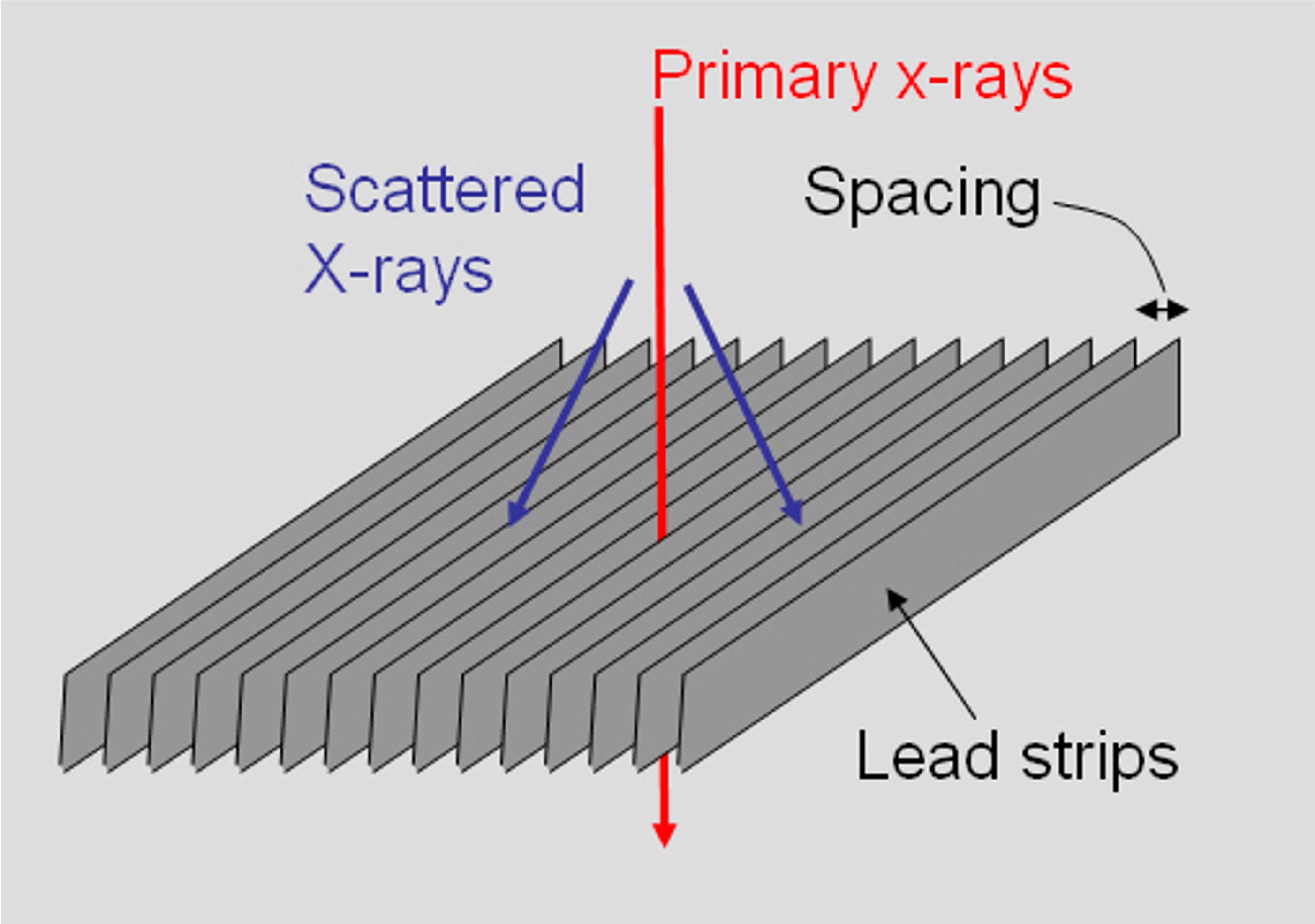
What is the main function of this bit of equipment?
. Reduce the quantity of scatter radiation (1) reaching the image receptor (1) improve image contrast (1) or quality (1) reduce scatter fog
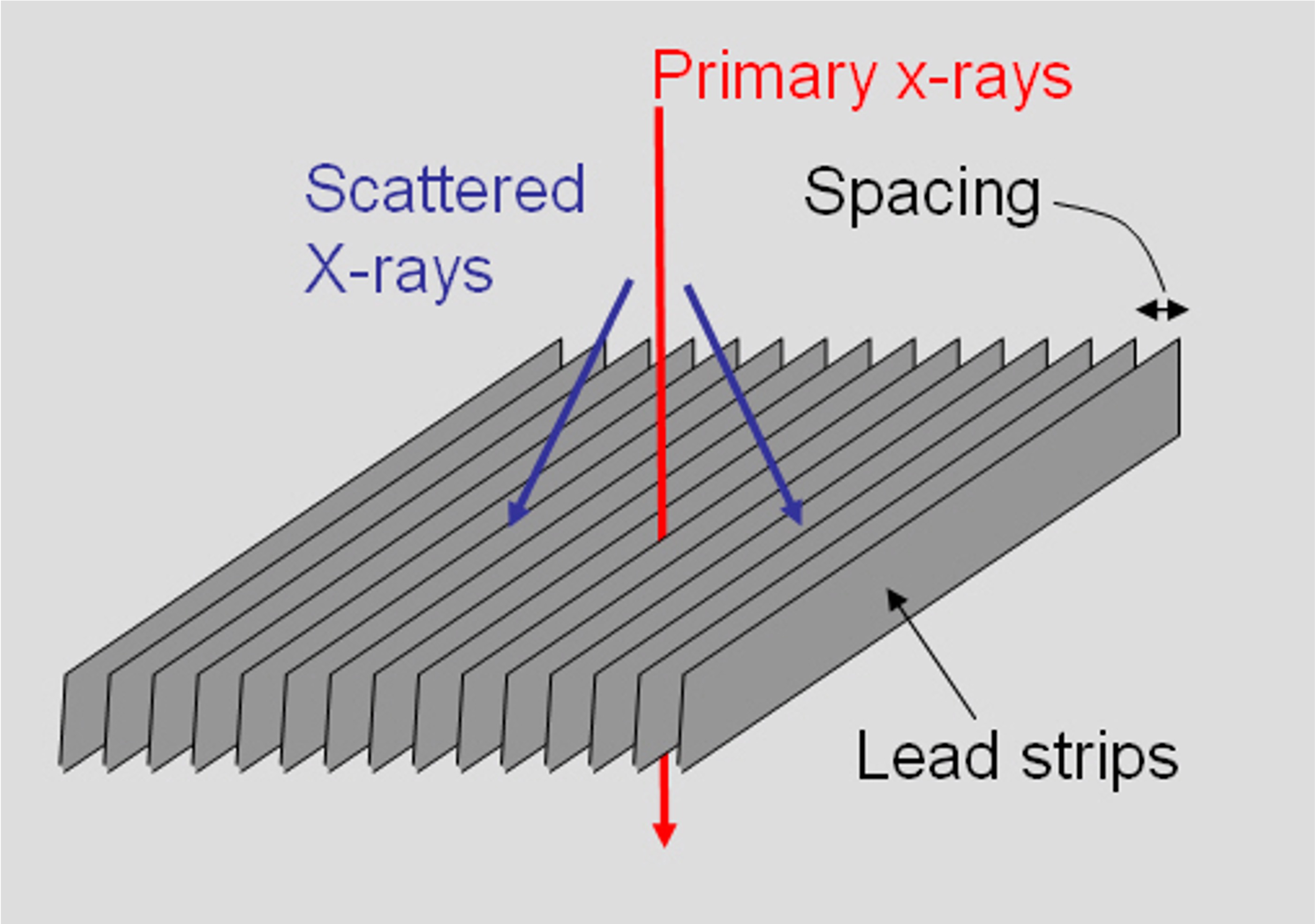
Please describe how this bit of equipment functions
Primary x-ray photons will pass through the interspaces (1) and scattered x-ray photons will be absorbed (1 – must have absorbed for second mark) by the interspace material
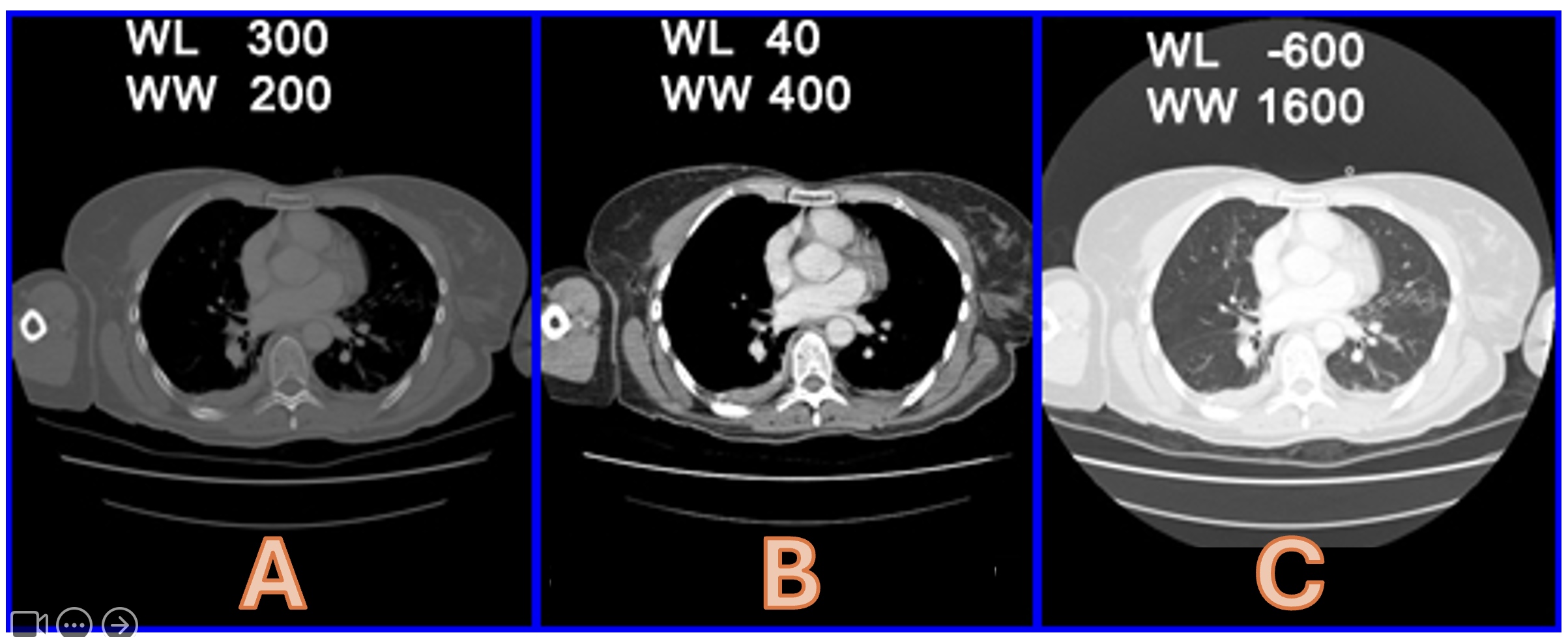
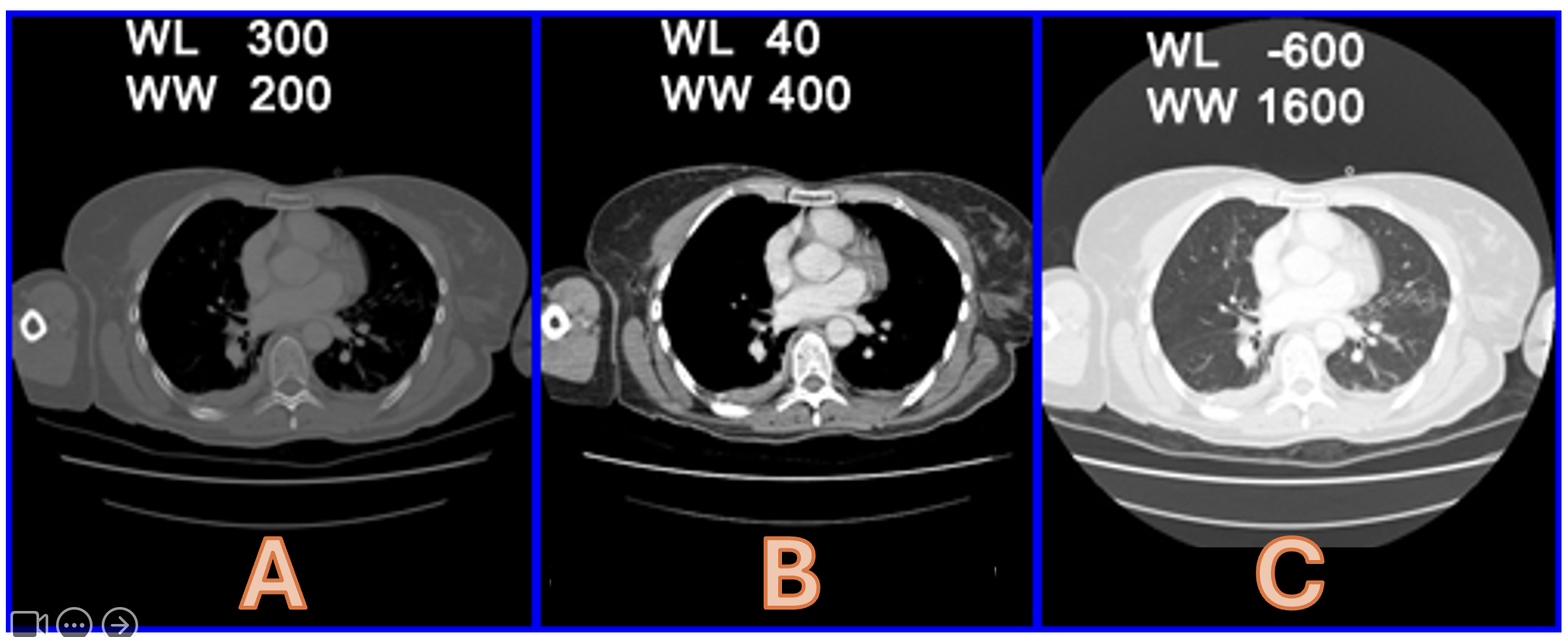
Please state the windowing of Images A-C
Bone Window (1) B = Soft Tissue Window (1) C = Lung Window
Please state the Hounsfield Units for the following (5 marks):
a) Air b) Fat c) Water d) Blood e) Bone
a = -1000 (1) b = -70 (1) c = 0 (1) d = 70 (1) e = 1000
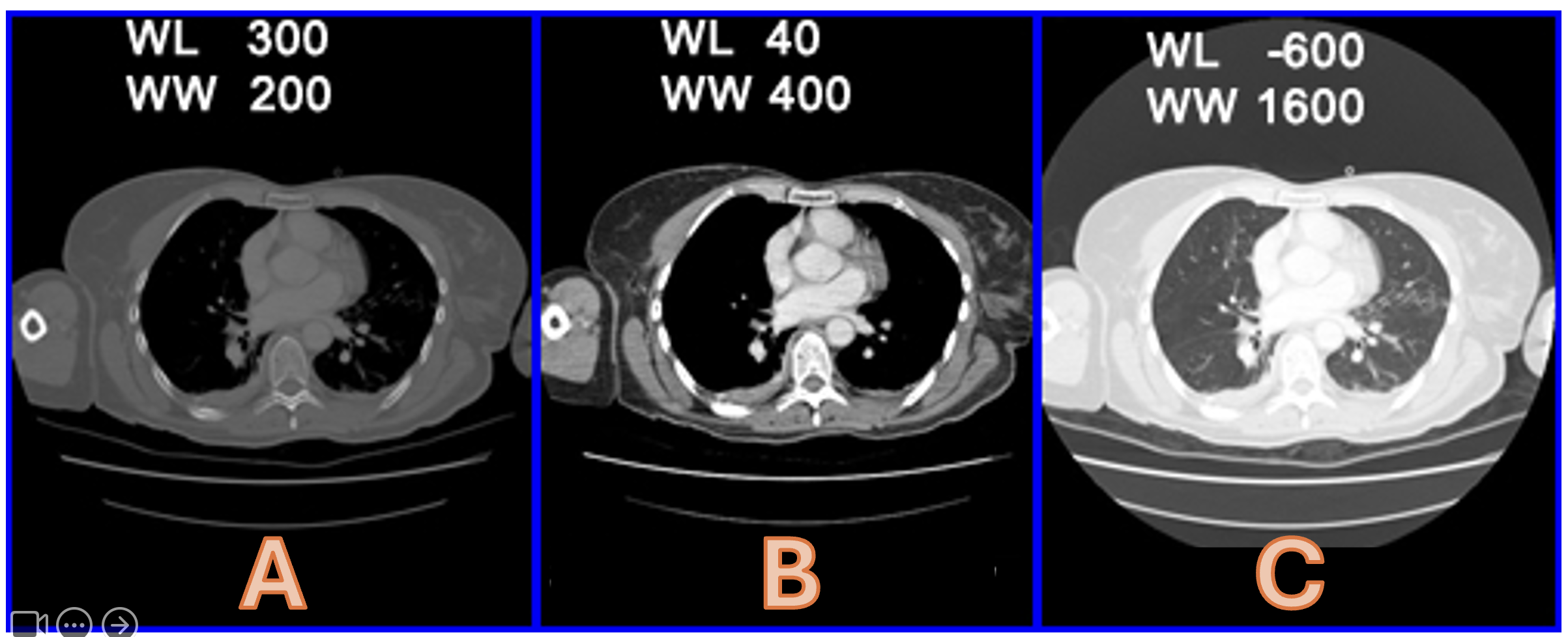
What do ‘WL’ and ‘WW’ stand for in the images below?
Window Width (1) and Window Level
Please state the 4 main factors that influence the degree of attenuation of an x-ray beam
Thickness of Tissue (2)
Energy of the Beam (2)
Density of material (2)
Atomic Number of Material
What exposure factor controls beam quantity?
mAs
What exposure factor controls beam quality
kVp
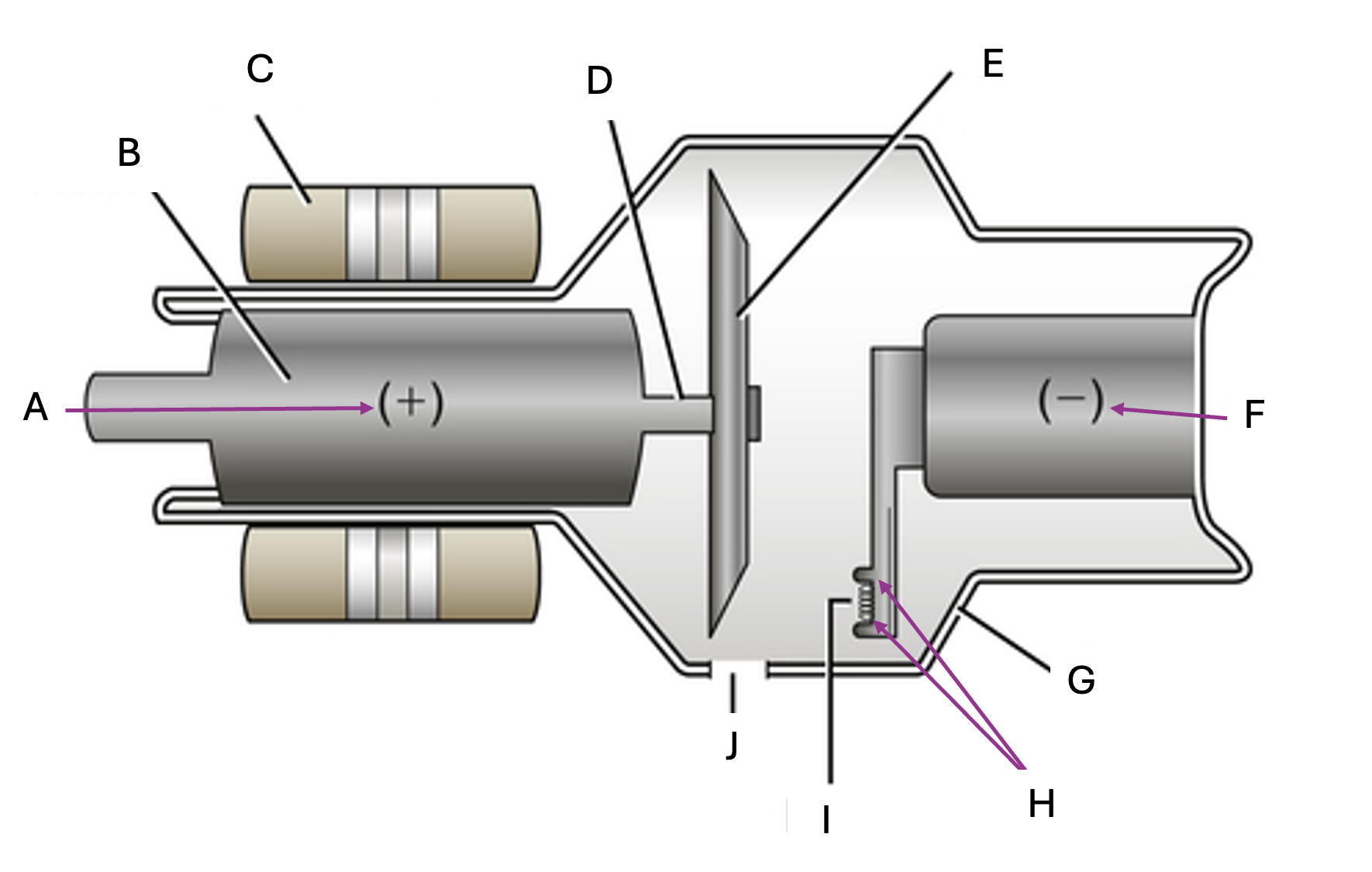
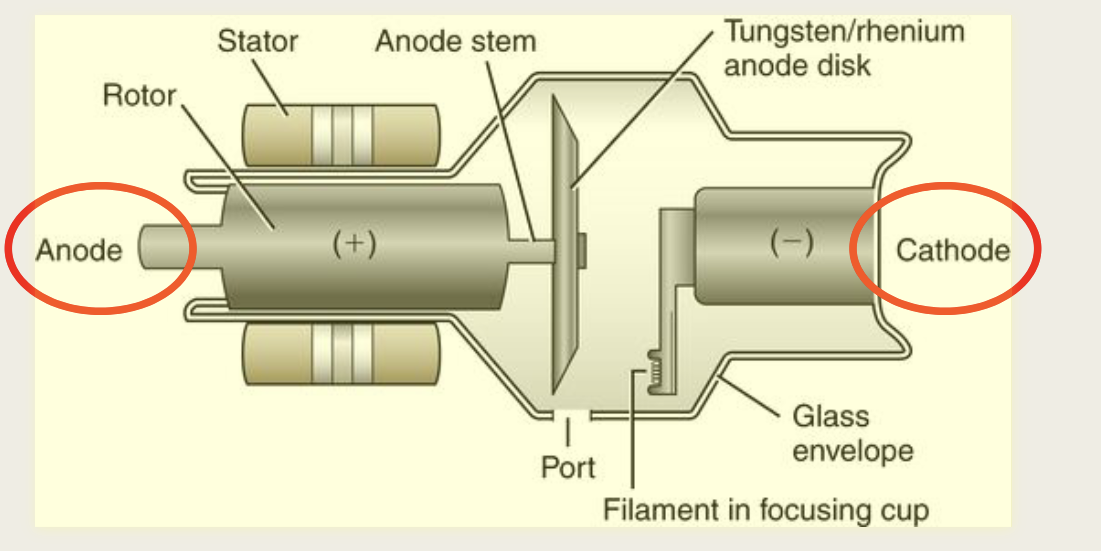
What are the two main components of xray tube
the cathode and anode
Is Filament a subcomponent of
Cathode or Anode
cathode
what are some of the imaging accessories.
Filters – Regular QA
■ Body measure – TLD
Badge
■ Lead protection
■ Stabilisation devices –
foam pads, sandbags
■ Body marker
■ Vertical cassette holder
■ Xray reference ball –
25mm ball diameter
■ Image detectors – CR / DR
What are the three types of interactions that occur when radiation is absorbed by matter?
Coherent scattering , Compton Effect, Photoelectric Effect
Increased KVp increases scatter radiation
Increasing field size
Increases scatter
TRUE
TRUE
Which modalities use ionising radiation.
CT, XRAY, DEXA
What modalities can be used for musculoskeletal imaging?
MRI
US
CT
XRAY