Nervous System: Brain Anatomy, Development, and Functions
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
What are the four major regions of the brain?
Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Brainstem, Cerebellum
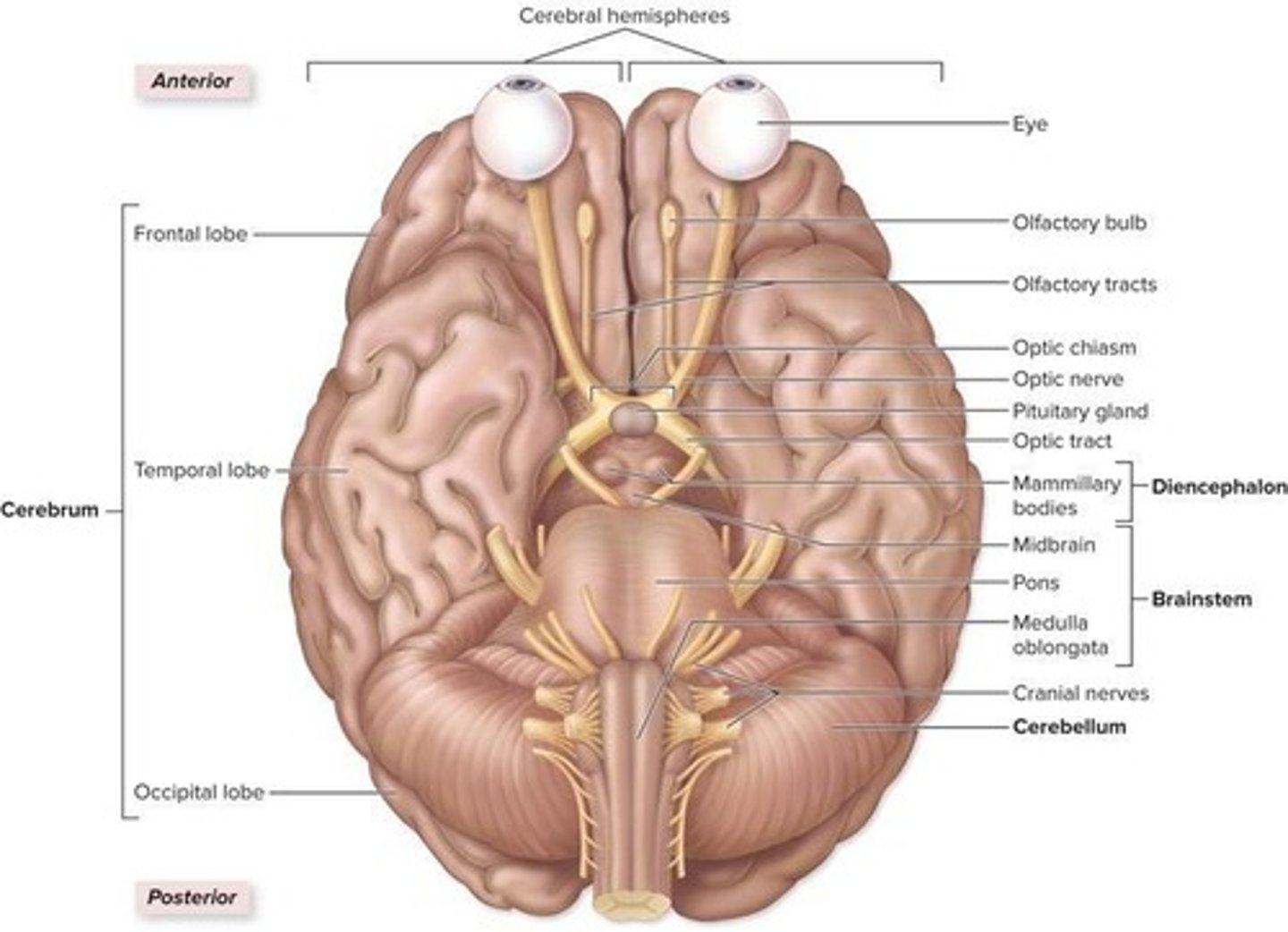
What is the outer surface of the brain composed of?
Gyri (ridges) and Sulci (depressions between ridges)
What is the function of the corpus callosum?
It connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres, facilitating communication between them.
What are the three main functions of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
1) Provides a liquid cushion for the brain, 2) Circulates nutrients and removes waste, 3) Maintains intracranial pressure.
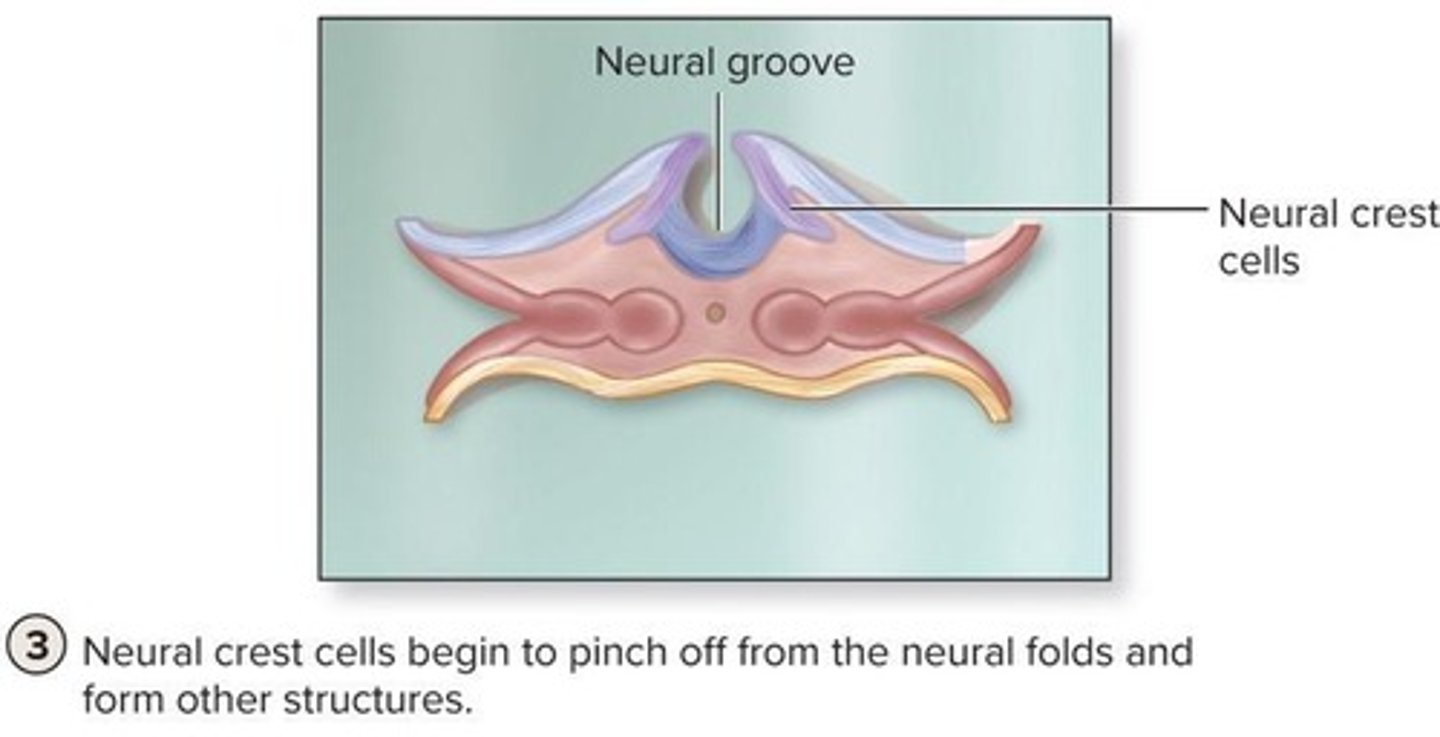
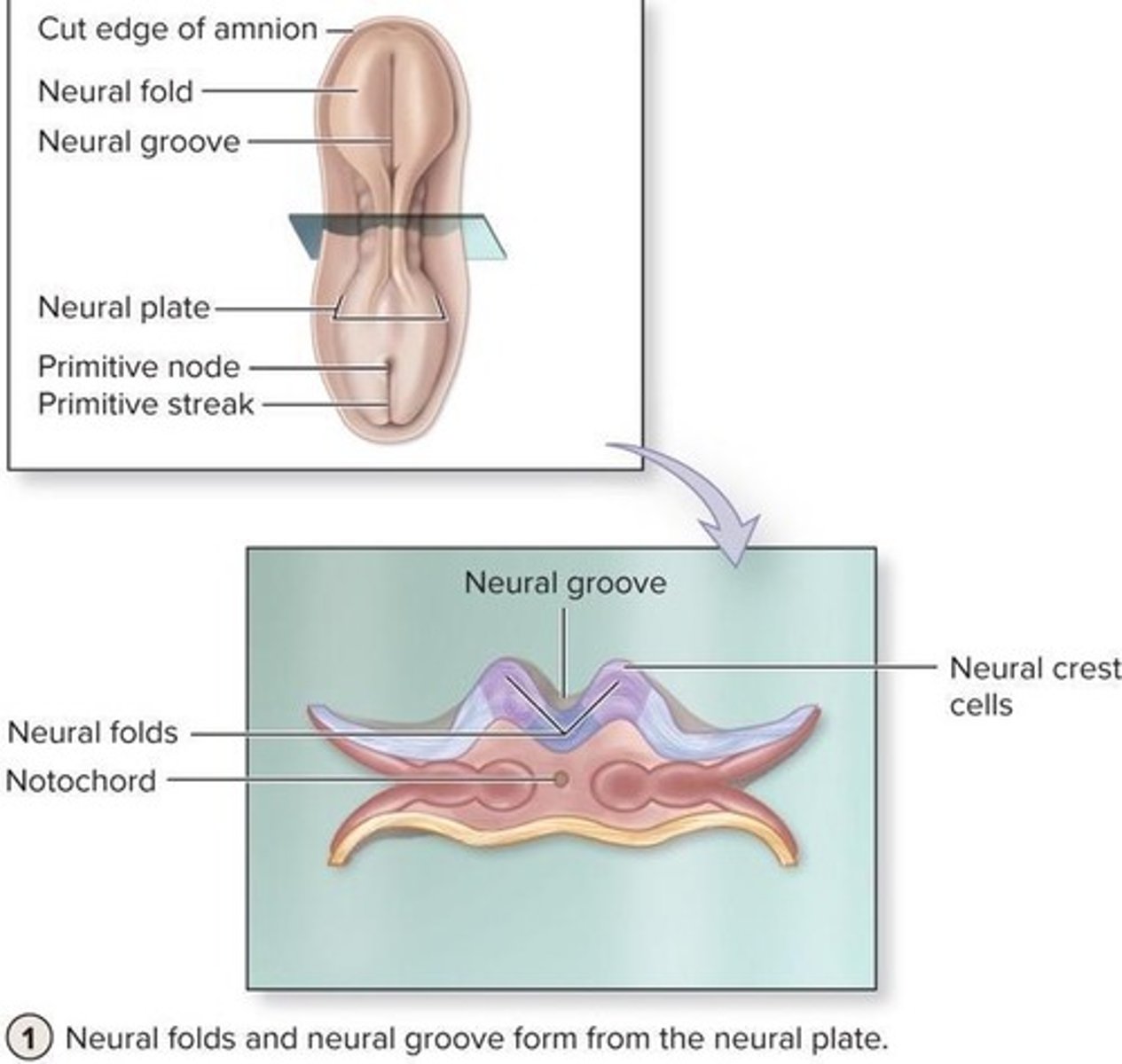
What is neurulation?
The process of forming nervous tissue, beginning in the 3rd week of embryonic development.
What are the five secondary brain vesicles?
1) Telencephalon, 2) Diencephalon, 3) Mesencephalon, 4) Metencephalon, 5) Myelencephalon.
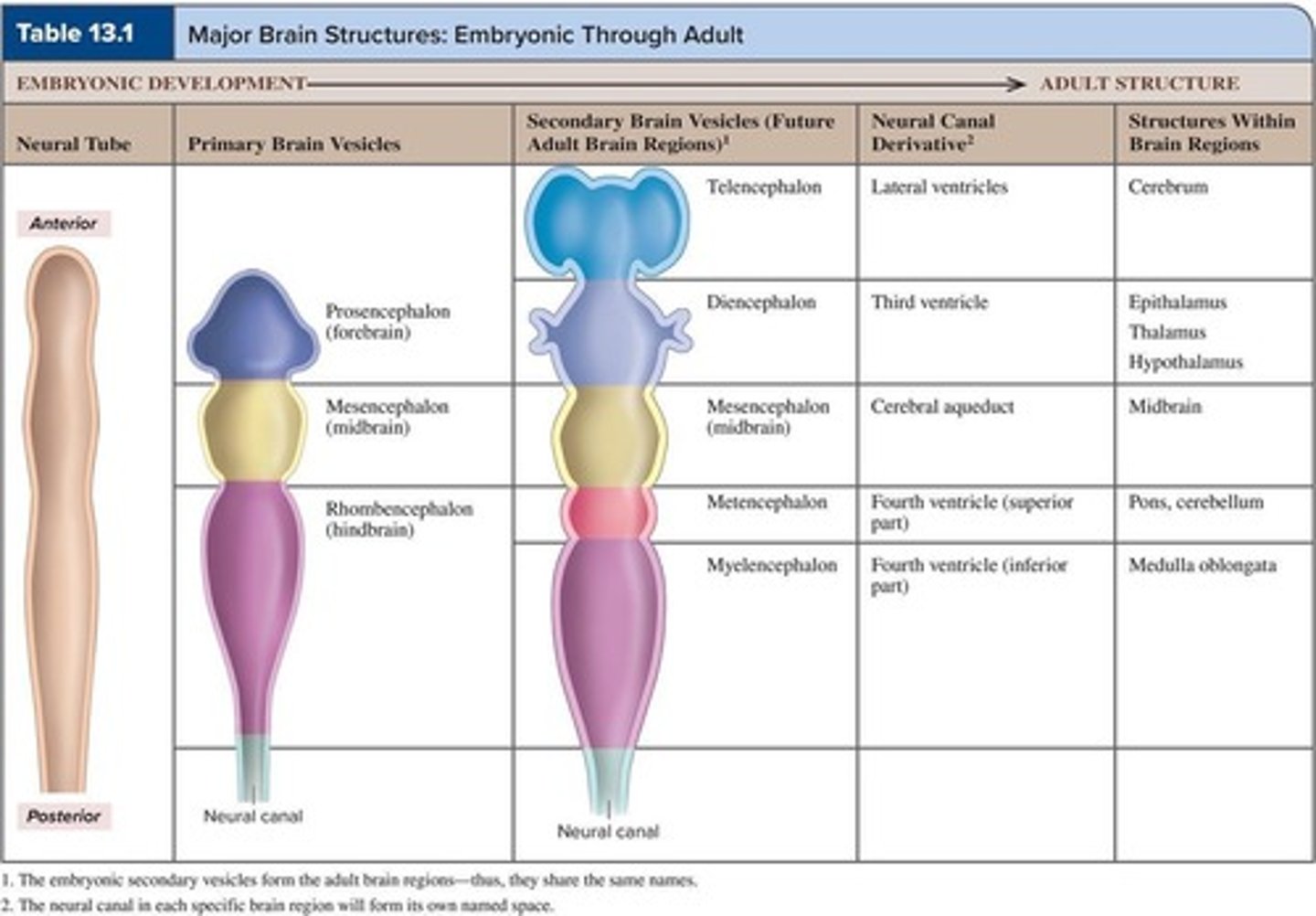
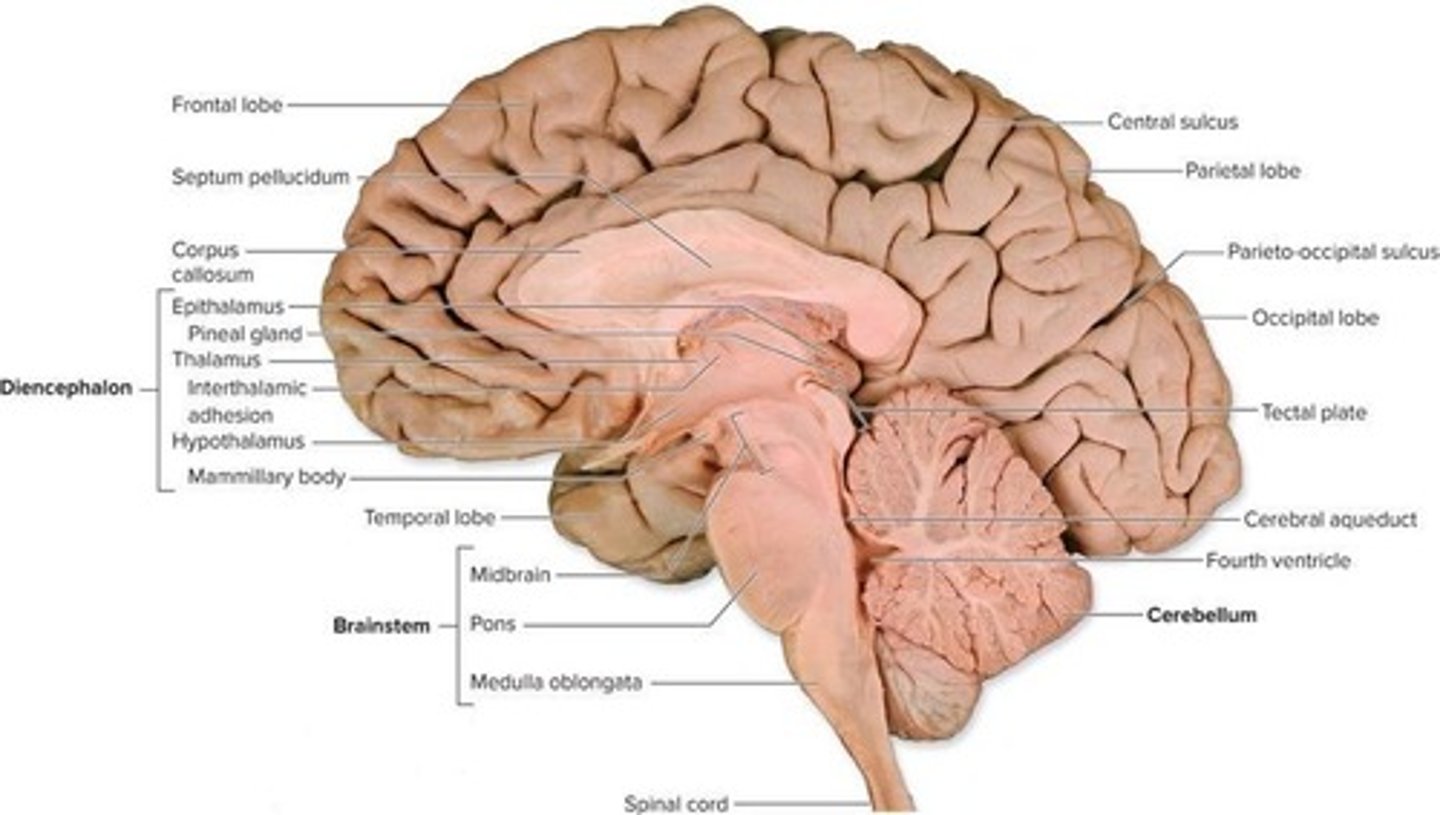
What adult brain structures are formed by the telencephalon?
Cerebrum.
What adult brain structures are formed by the diencephalon?
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Epithalamus.
What adult brain structures are formed by the mesencephalon?
Midbrain.
What adult brain structures are formed by the metencephalon?
Pons and Cerebellum.
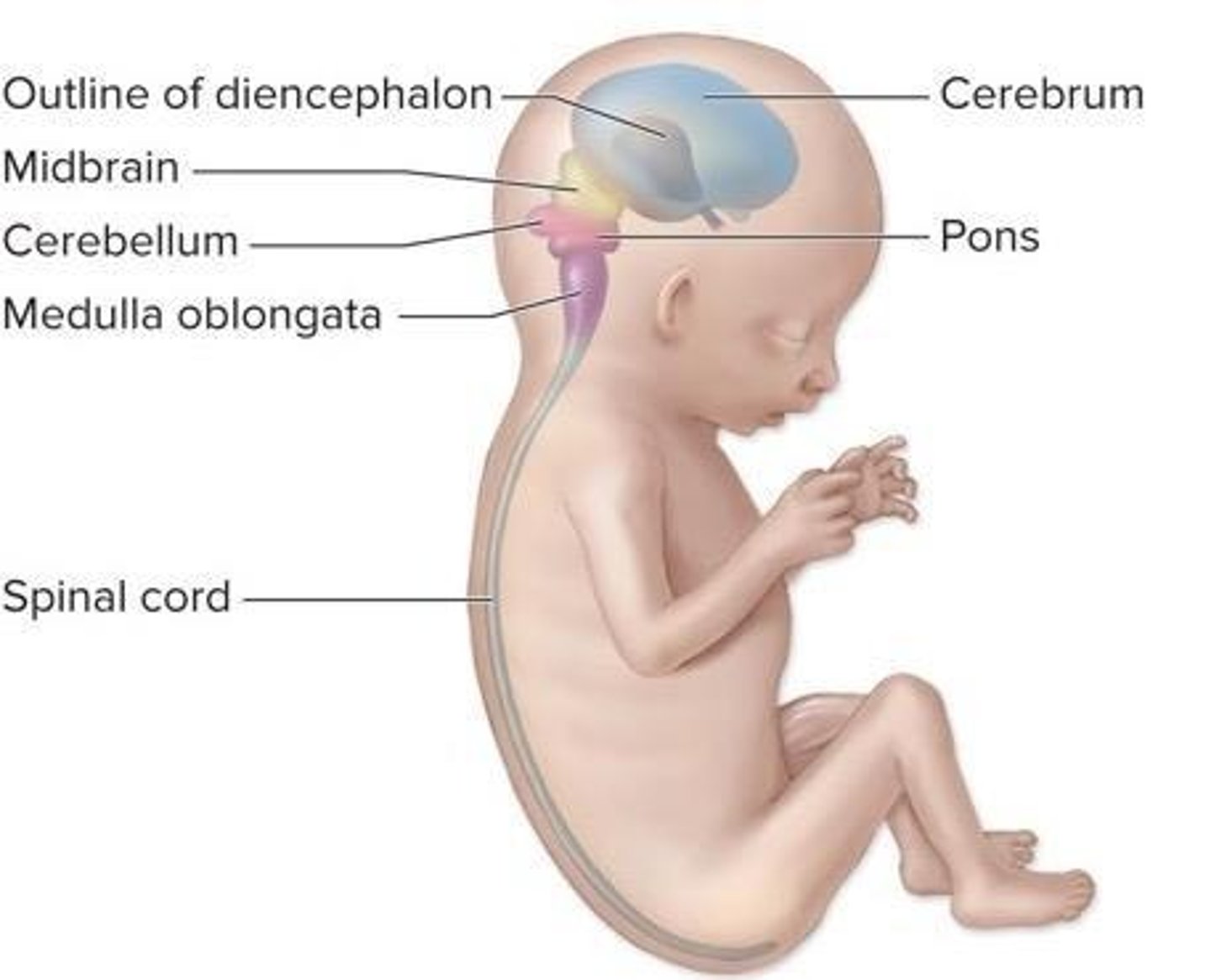
What adult brain structures are formed by the myelencephalon?
Medulla oblongata.
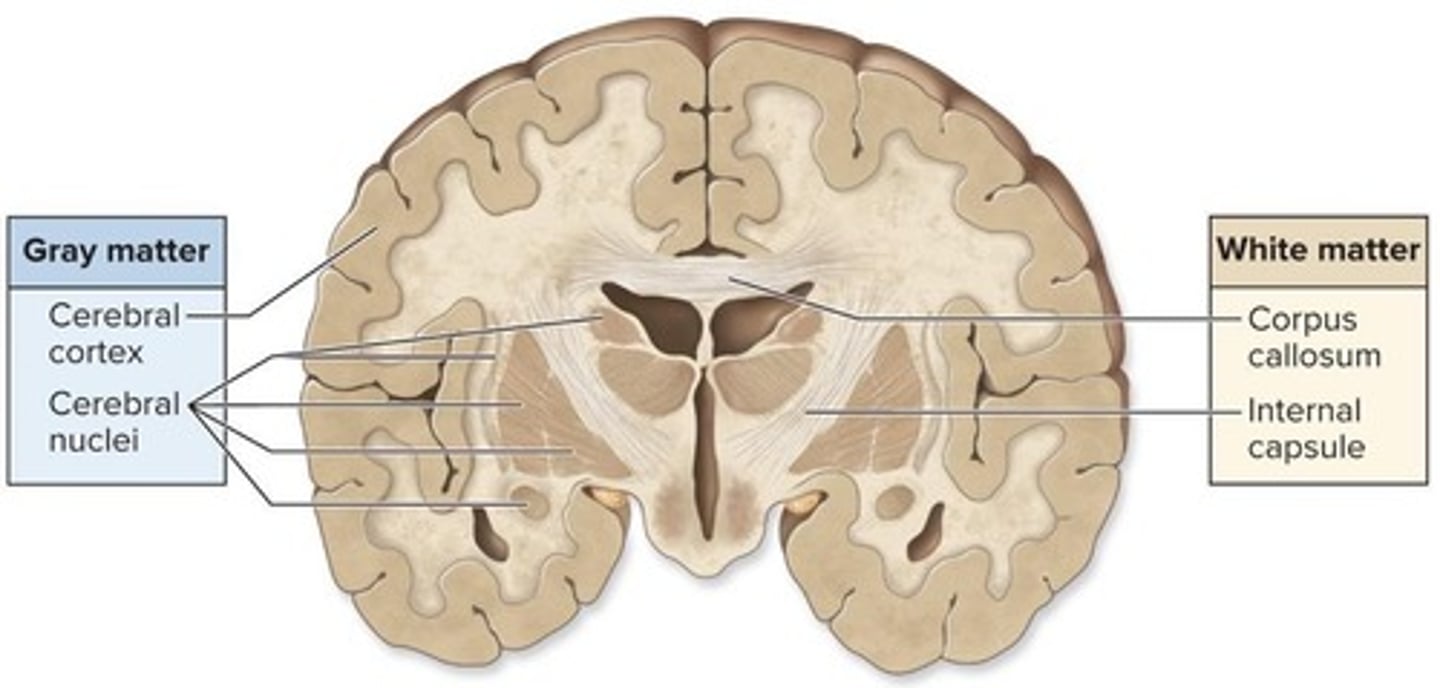
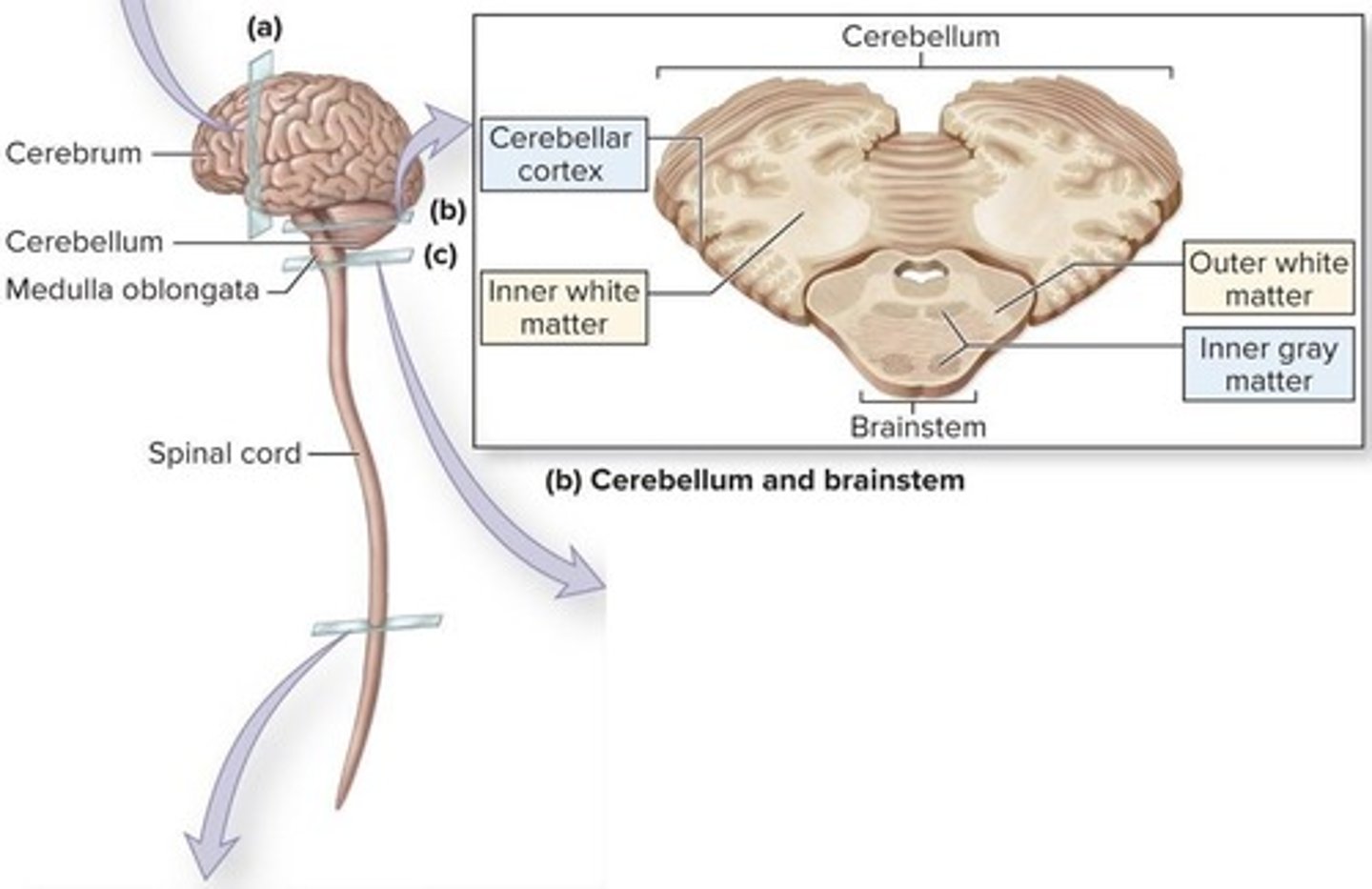
What is the difference between gray matter and white matter?
Gray matter consists of neuron cell bodies and unmyelinated axons, while white matter consists of myelinated axons.
What are the three layers of meninges?
Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, Pia mater.
What is the role of the blood-brain barrier?
It controls what substances can pass from the blood into the brain, protecting it from harmful substances.
What happens if the cranial and caudal neuropores do not close?
Neural tube defects such as Anencephaly or Spina bifida may occur.
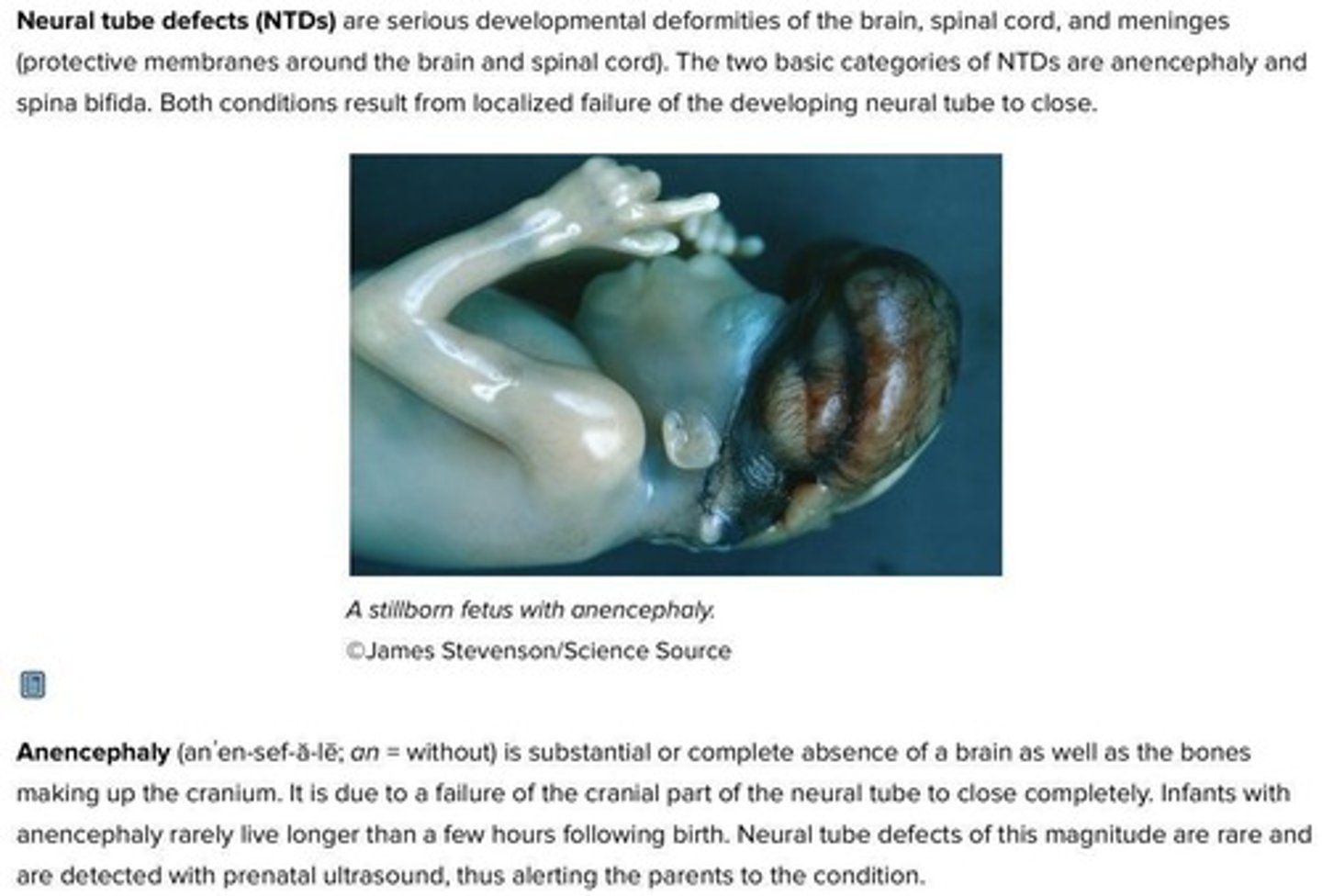
What is Anencephaly?
A serious condition where there is a substantial or complete absence of a brain, leading to infant death shortly after birth.
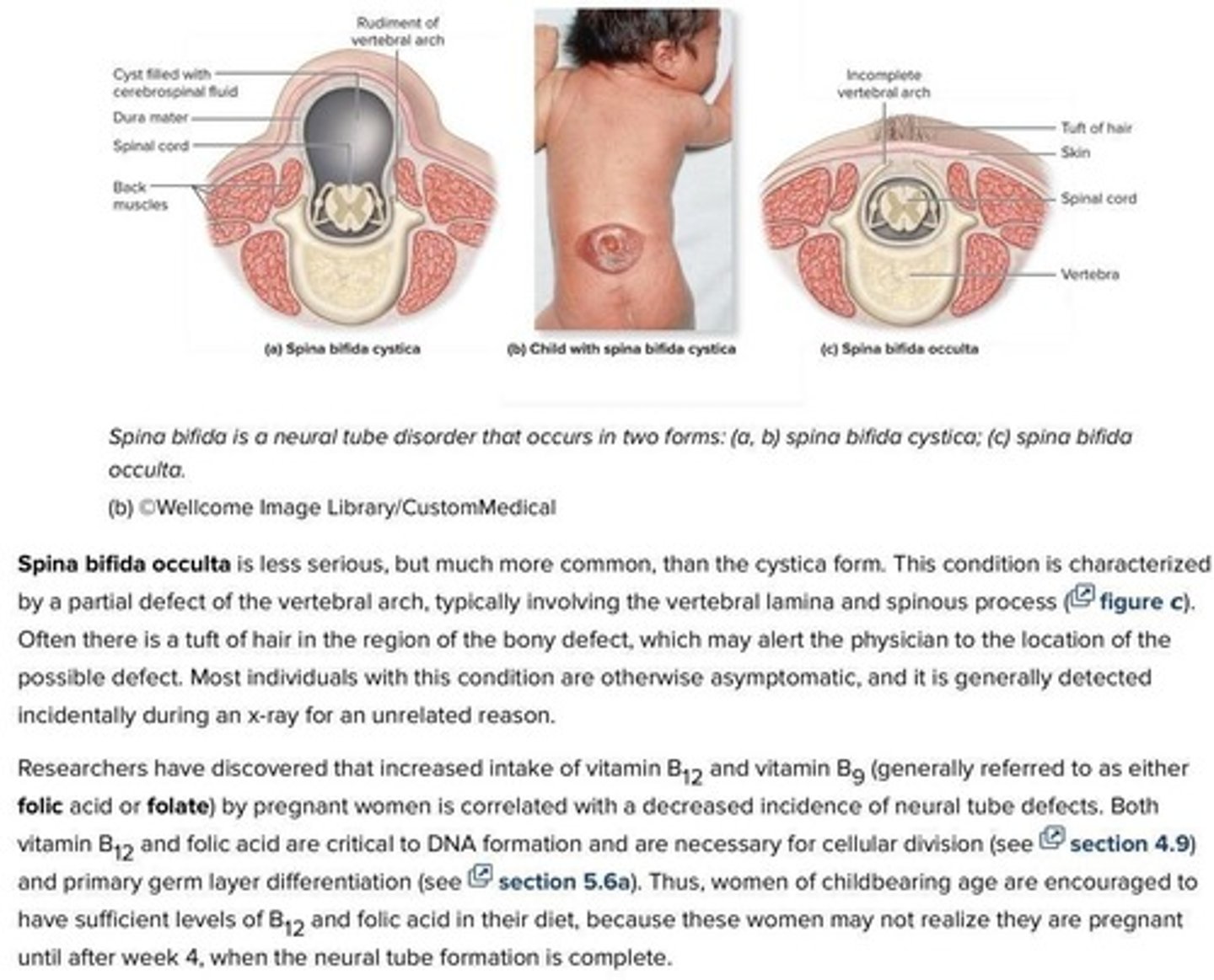
What is Spina bifida?
A defect where the caudal portion of the neural tube fails to close, leading to varying degrees of spinal cord damage.
What is the significance of taking Vitamin B12 and folate during pregnancy?
It lowers the risk of neural tube defects.
What is a concussion?
The most common type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) characterized by temporary loss of consciousness and other symptoms.
What is a contusion?
Bruising of the brain due to trauma.
What is second impact syndrome?
A condition where a second injury occurs before the first one resolves, leading to severe brain swelling.
What are gyri and sulci?
Gyri are ridges on the brain's surface, while sulci are the depressions between those ridges.
What is the significance of the neural crest cells?
They develop from the tips of the neural folds and contribute to the formation of various structures in the body.
What is the role of the prefrontal cortex?
It is involved in complex behaviors such as decision making, social behavior, and personality expression.
What are the functions of the Wernicke area?
It is involved in language comprehension.
What are the three connective tissue layers of the meninges?
Pia mater, Arachnoid mater, and Dura mater
What is the function of the meninges?
They separate and support soft tissue of the brain, enclose and protect blood vessels, and help contain and circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
What is the Pia mater?
The innermost layer of the meninges, adhering to the brain surface and made of thin areolar connective tissue.
What is the Arachnoid mater?
The layer external to the Pia mater, made of a web of collagen and elastic fibers, containing the subarachnoid space.
What is found in the subarachnoid space?
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
What is the Dura mater?
The tough outer membrane of the meninges, made of dense irregular connective tissue in two layers.
What are the two layers of the Dura mater?
The meningeal layer (deeper) and the periosteal layer (more superficial).
What is the function of cranial dural septa?
They form partitions between brain areas and provide support.
Where is the falx cerebri located?
In the midline, projecting into the longitudinal fissure between cerebral hemispheres.
What does the tentorium cerebelli separate?
It separates the occipital and temporal lobes from the cerebellum.
What is an epidural hematoma?
A pool of blood in the epidural space of the brain, usually due to a severe blow to the head.
What is a subdural hematoma?
Hemorrhage in the subdural space, typically from ruptured veins due to fast rotational head movement.
What are brain ventricles?
Cavities within the brain lined with ependymal cells that contain cerebrospinal fluid.
How many ventricles are there in the brain?
Four ventricles: two lateral ventricles, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle.
What is the function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Provides buoyancy, protection, and environmental stability for the brain.
How is cerebrospinal fluid formed?
By the choroid plexus in each ventricle, involving ependymal cells and blood capillaries.
What happens to excess cerebrospinal fluid?
It flows into arachnoid villi and drains into dural venous sinuses.
What is hydrocephalus?
A condition of excessive cerebrospinal fluid that can lead to brain distortion.
What is the blood-brain barrier (BBB)?
A selective barrier that regulates which substances enter the brain's interstitial fluid.
What are the components of the blood-brain barrier?
Specialized capillaries with endothelial cells connected by tight junctions and wrapped by astrocytes.
What is the role of the falx cerebelli?
It runs vertically in the midsagittal plane, separating the left and right cerebellar hemispheres.
What is the smallest dural septa?
Diaphragma sellae, which forms a roof over the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone.
What is the function of the choroid plexus?
To produce cerebrospinal fluid.
How does the blood-brain barrier protect nervous tissue?
By preventing exposure to harmful substances such as drugs and wastes.
What is the role of the interventricular foramen?
It connects each lateral ventricle to the third ventricle.
Where does the fourth ventricle connect?
It connects to the third ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct and opens to the subarachnoid space.
What is the primary function of the cerebrum?
Origin of all complex intellectual functions, including reasoning, thought, memory, and voluntary muscle control.
What separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres?
The longitudinal fissure.
What is cerebral lateralization?
The phenomenon where some higher-order functions are primarily controlled by one side of the brain.
What are the five lobes of the cerebrum?
Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, and insular lobes.
What is the primary function of the frontal lobe?
Motor control, concentration, verbal communication, decision making, planning, and personality.
Where is the primary motor cortex located?
In the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe.
What sensory functions does the parietal lobe serve?
General sensory functions, including evaluating shape and texture of objects.
What is the main function of the temporal lobe?
Hearing and smell.
What does the occipital lobe primarily process?
Vision and visual memories.
What is the function of the insula?
Memory and sense of taste.
What is the primary somatosensory cortex responsible for?
Receiving somatic sensory information from proprioceptors, touch, pressure, pain, and temperature receptors.
What is the role of the Wernicke area?
Involved in language comprehension, recognizing and understanding spoken or written words.
What is the function of the prefrontal cortex?
Complex thought, judgment, personality, planning, and decision-making.
What are the three types of cerebral white matter tracts?
Association tracts, commissural tracts, and projection tracts.
What do commissural tracts connect?
Regions in different hemispheres of the brain.
What is the primary function of the basal nuclei?
Help regulate motor output.
What is the significance of the corpus callosum?
It connects the two hemispheres of the brain.
What is a cerebrovascular accident (CVA)?
A reduced blood supply to part of the brain, potentially causing brain tissue death.
What are common symptoms of a stroke?
Blurred vision, weakness, headache, dizziness, and walking difficulty.
What is the difference between a stroke and a transient ischemic attack (TIA)?
A TIA is a brief episode of reduced blood supply that does not cause permanent damage.
What is the role of the primary auditory cortex?
Receives, processes, and stores auditory information.
What does the primary gustatory cortex process?
Taste information.
What is the function of the primary visual cortex?
Receives, processes, and stores visual information.
What is the role of the auditory association area?
Integrates and interprets sounds..
What is the function of the somatosensory association area?
Integrates touch information allowing us to identify objects by feel.
What is the significance of the motor homunculus?
It reflects the amount of cortex dedicated to each body part for motor control.
What is the role of the lentiform nucleus?
Composed of putamen and globus pallidus, it helps control movements at a subconscious level.
What is the function of the amygdaloid body?
Functions in mood and emotions.
What is the clinical view of autism spectrum disorder?
Characterized by social and communication difficulties, severity varies across the spectrum.
What is the primary function of the corpus striatum?
Regulates motor output and has a striated appearance due to its internal capsule.
What is the difference between nuclei and ganglia?
Nuclei refer to cell bodies within the CNS, while ganglia refer to cell bodies external to the CNS.
What are common characteristics of Parkinson's disease?
Affects muscle movement and balance, causing stiff posture, slow voluntary movements, and resting tremor.
What is Huntington's disease?
A hereditary disease affecting cerebral nuclei, leading to rapid, jerky involuntary movements and intellectual deterioration.
What is the primary function of the temporal lobe?
Hearing and smell.
What does the occipital lobe primarily function in?
Vision and visual memories.
What is the insula's role in the brain?
Memory and sense of taste.
What is the function of the Wernicke area?
Involved in language comprehension, recognizing and understanding spoken or written words.
What is a motor homunculus?
A distorted representation of the body reflecting the amount of cortex dedicated to each body part's motor control.
What is the difference between association tracts and commissural tracts?
Association tracts connect regions within the same hemisphere, while commissural tracts connect regions in different hemispheres.
What does the corpus callosum do?
Connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
What is the categorical hemisphere specialized for?
Language abilities, categorization, and analytical tasks, typically located in the left hemisphere.
What is the representational hemisphere concerned with?
Visuospatial relationships, imagination, and artistic skills, typically located in the right hemisphere.
What is the role of the basal nuclei?
Help regulate motor output and are associated with involuntary movements.
What is the primary function of the primary auditory cortex?
Receives, processes, and stores auditory information.
What is the function of the primary gustatory cortex?
Receives, processes, and stores taste information.
What are the symptoms of a transient ischemic attack (TIA)?
Brief episodes of blurred vision, weakness, headache, dizziness, and walking difficulty.
What is the significance of the caudate nucleus?
Helps produce the pattern and rhythm of walking movements..
What is the clinical view of epilepsy?
A neurological disorder characterized by neurons transmitting action potentials too frequently and rapidly.
What is the primary function of the somatosensory association area?
Integrates touch information allowing us to identify objects by feel..