Comptia A+ 220-1201 flashcards (2.0 Networking - 23%)
1/3
Earn XP
Description and Tags
23% of the exam section 2.0 Networking
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
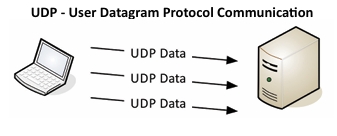
TCP and UDP
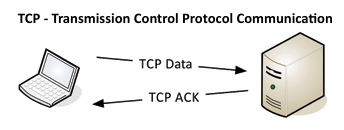
• Transported inside of IP– Encapsulated by the IP protocol • Two ways to move data from place to place– Different features for different applications • OSI Layer 4– The transport layer • Multiplexing– Use many different applications at the same time– TCP and UDP TCP - Transmission Control Protocol Communication TCP – Transmission Control Protocol • Connection-oriented– A formal connection setup and close • “Reliable” delivery– Recovery from errors– Manages out-of-order messages or retransmissions • Flow control– The receiver can manage how much data is sent UDP - User Datagram Protocol Communication © 2025 Messer Studi
UDP – User Datagram Protocol
• Connectionless - No formal open/close to the connection • “Unreliable” delivery– No error recovery, no reordering of data or retransmissions • No flow control– Sender determines the amount of data transmitted
Why would you ever use UDP?
• Real-time communication– There’s no way to stop and resend the data– Time doesn’t stop for your network Server Ethernet Trailer Ethernet Trailer Ethernet Trailer Ethernet Trailer • Connectionless protocols– DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)– TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) • The data might not get through– The application keeps track
Communication using TCP
• Connection-oriented protocols prefer a “return receipt”– HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure)– SSH (Secure Shell) • The application doesn’t worry about out of order frames or missing data– TCP handles all of the communication overhead– The application has one job