Haitian Revolution
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
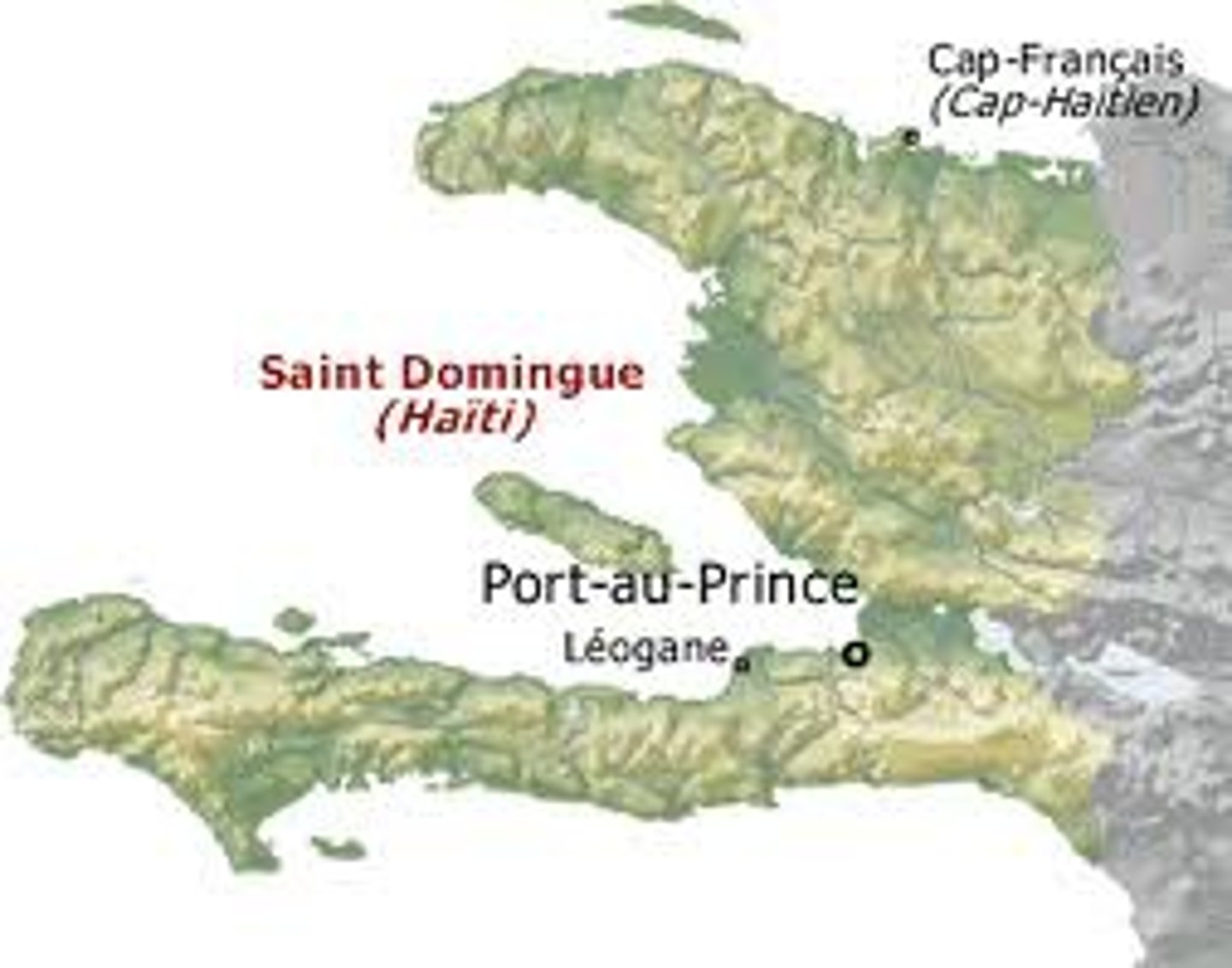
Saint-Domingue
Now referred to as Haiti, this was a former French colony. It is part of the western part of an island in the Caribbean called Hispaniola. "Hayti" was the original name of the island in the language of the Taino people and it was renamed Haiti by Jean-Jacques Dessalines and his government upon declaring the country's independence from France.
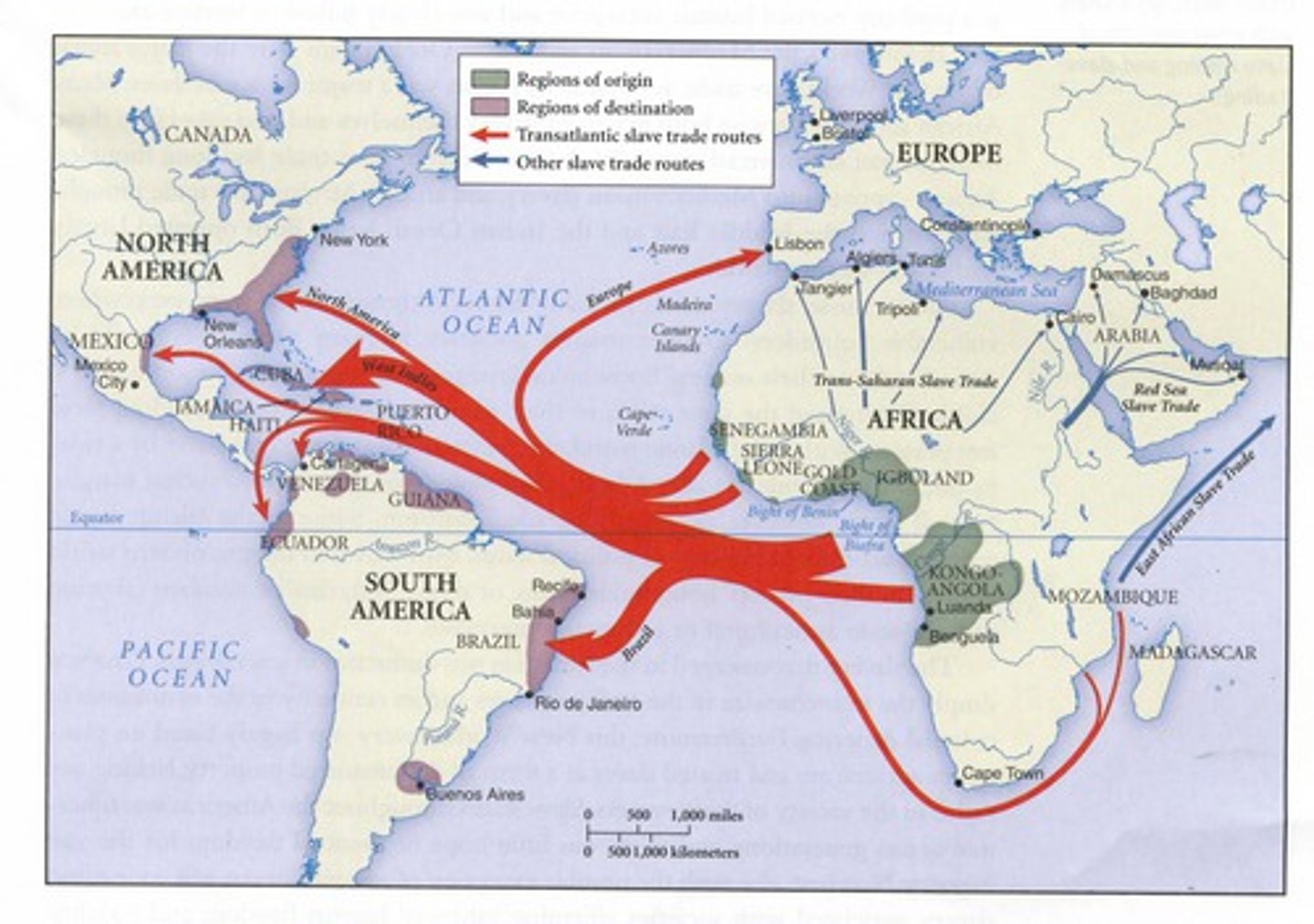
Transatlantic Slave Trade
The brutal system of trading enslaved people kidnapped from Africa to the Americas. It changed the economy, politics, and the environment of multiple continents--impacting Africa, Europe, and the Americas. The use of enslaved people was used for the creation of a whole new economic system--one set upon racial hierarchy and dehumanization. Slavery is defined as a crime against humanity by the International Criminal Court.
Grand Blancs (Big Whites)
Wealthy, white slave owners with plantations. Typically French men who left France to seek new economic opportunities.
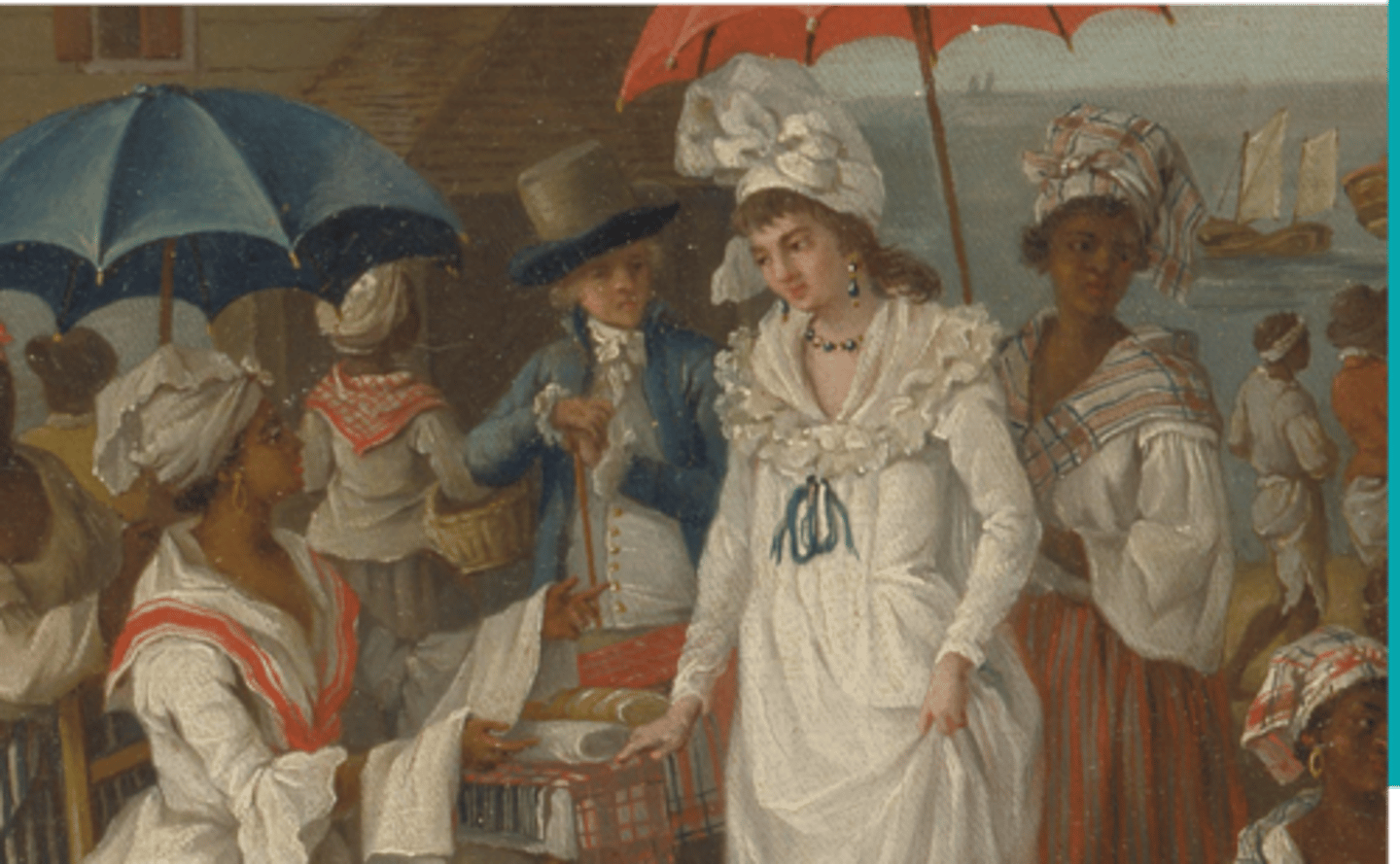

Petit Blancs (Little Whites)
Poorer than Grand Blancs, but still toward the top because of skin color. They have a variety of occupations such as carpenters, farmers, butchers, tailors, etc.

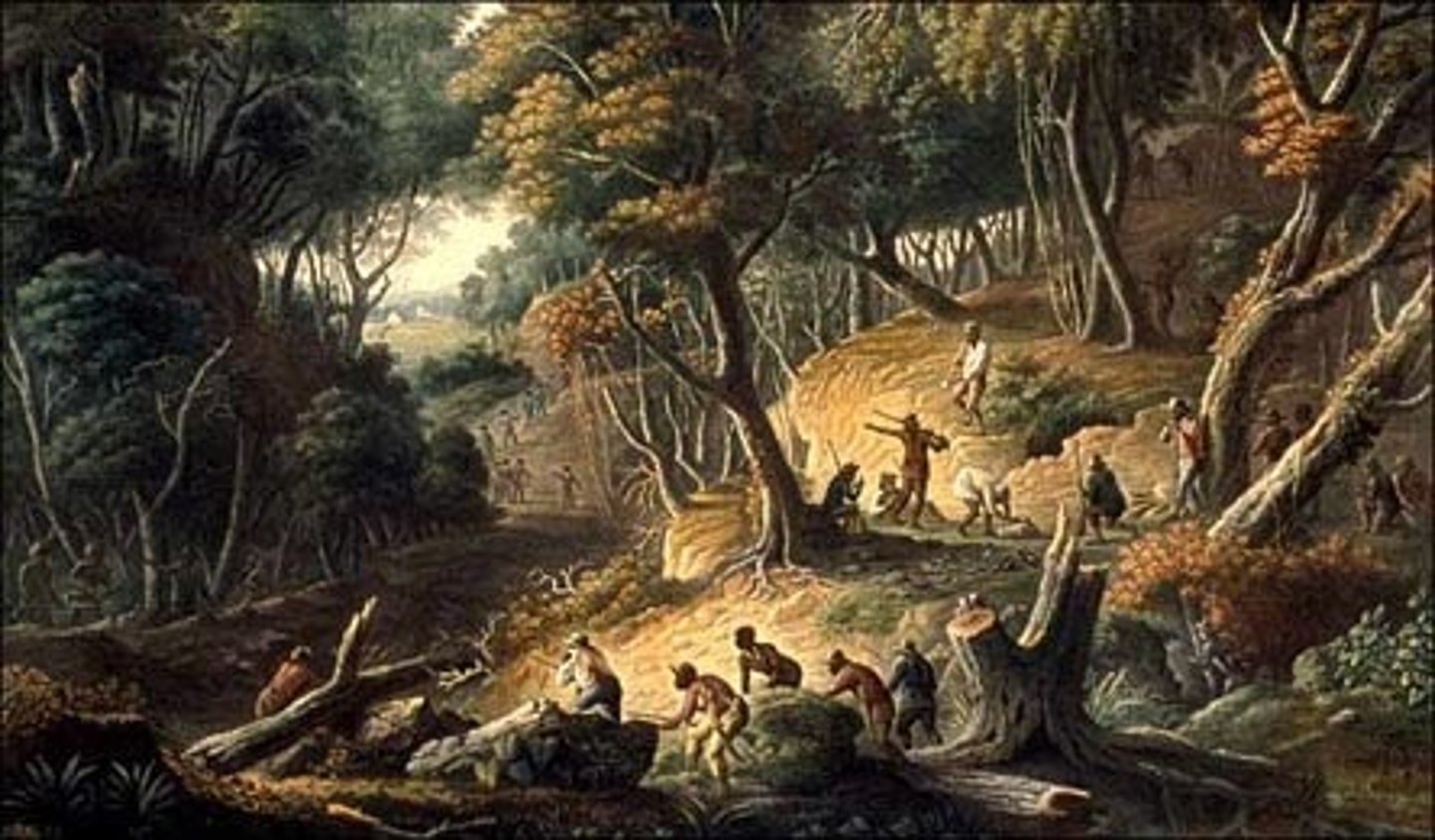
Gens de couleur
Meaning "People of Color" in French, these were mixed race citizens that were free. Some were wealthy and enslaved people on their own plantations.
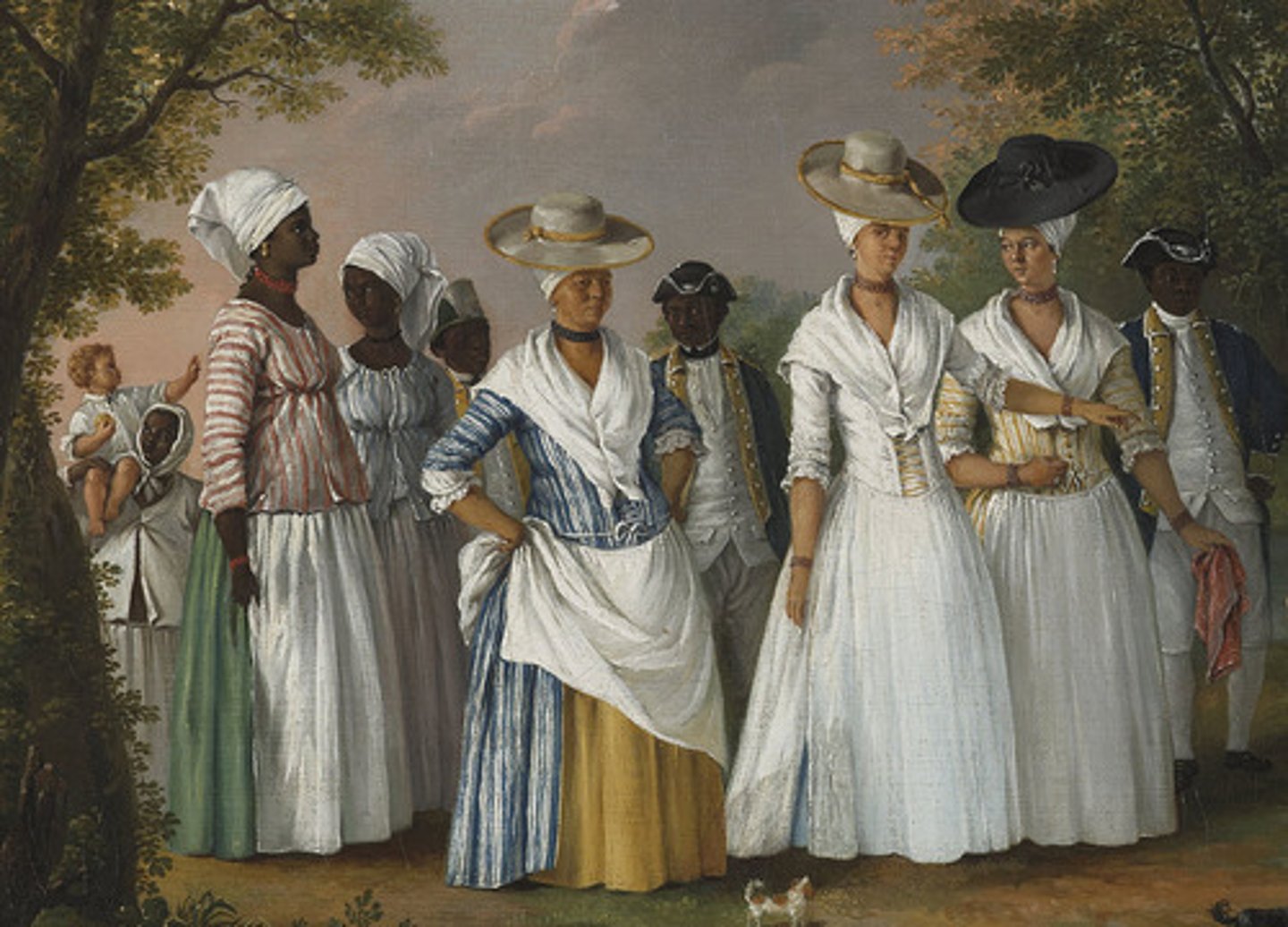
Maroons
Formerly enslaved Africans who had escaped and lived in groups in the mountains.

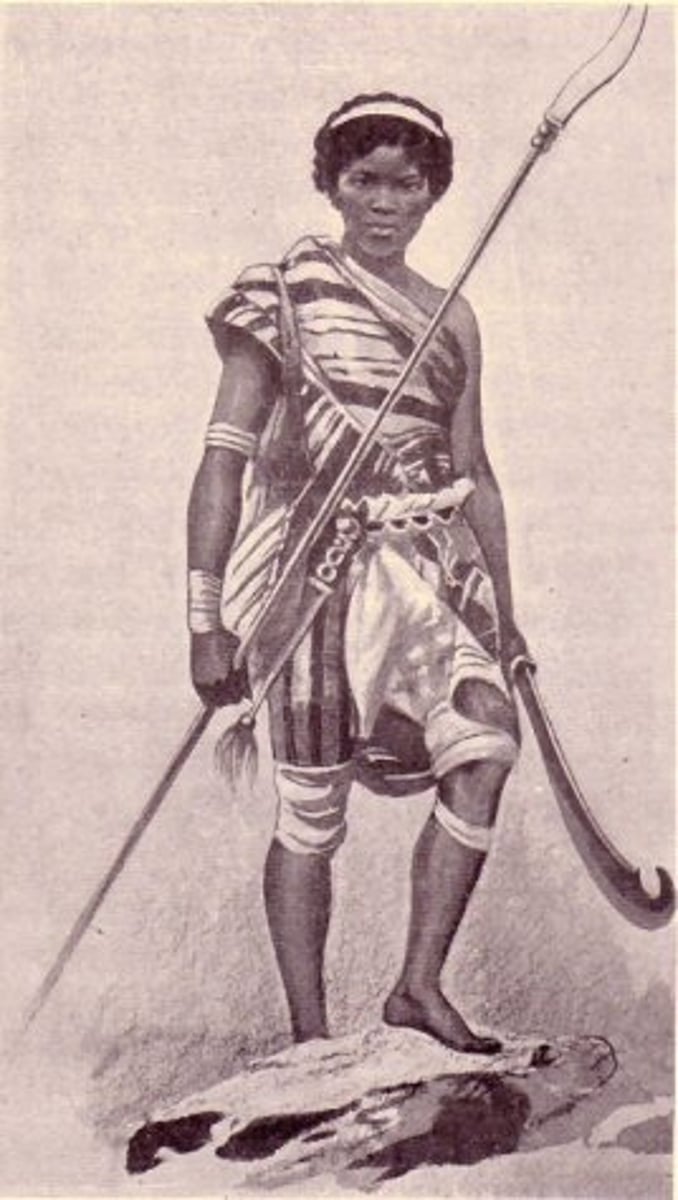
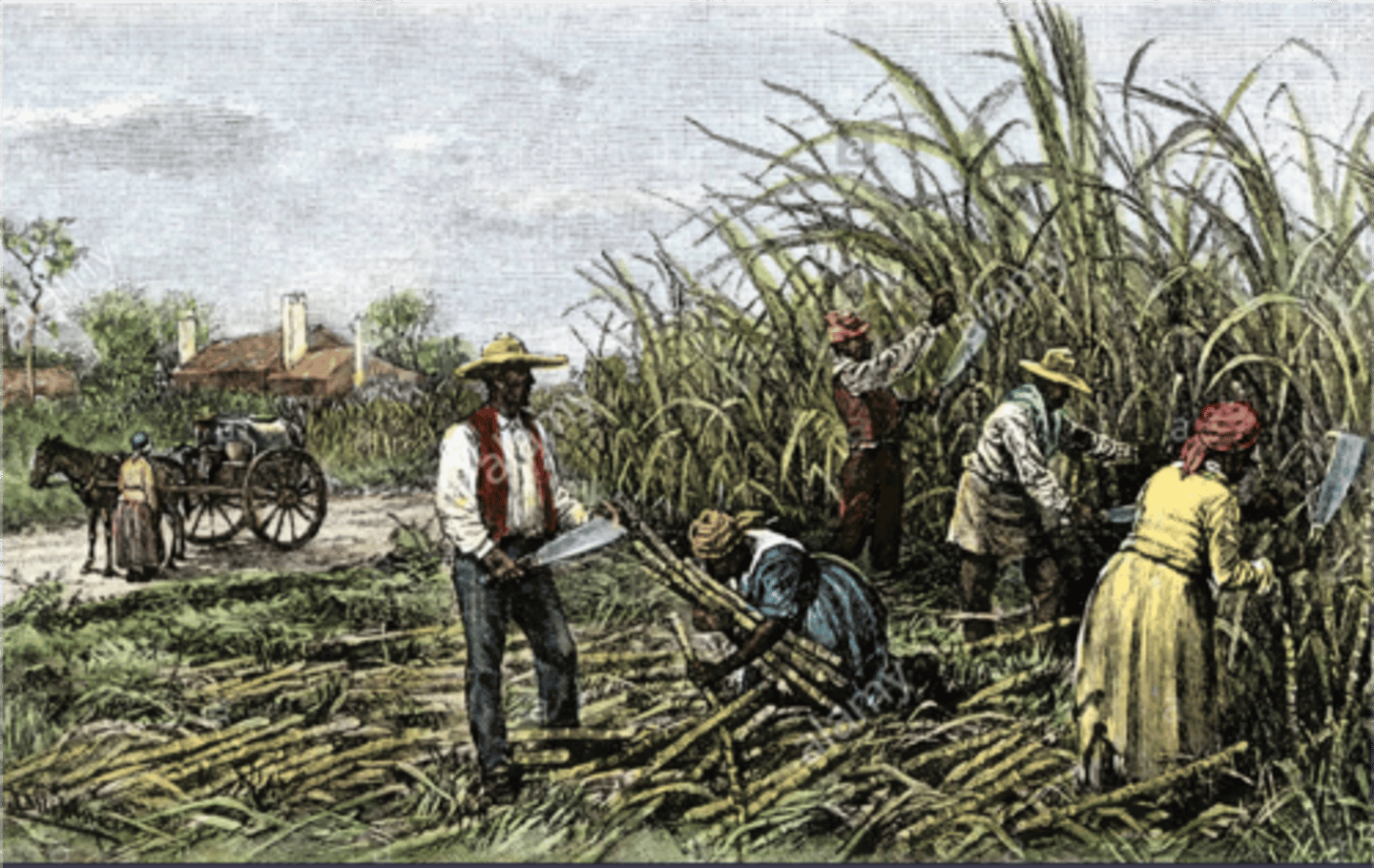
Enslaved people
Mostly Africans (Bossal/Congoes), some creoles, and a few remaining Taino Indigenous people born in Haiti. Restricted to doing hard, manual labor.

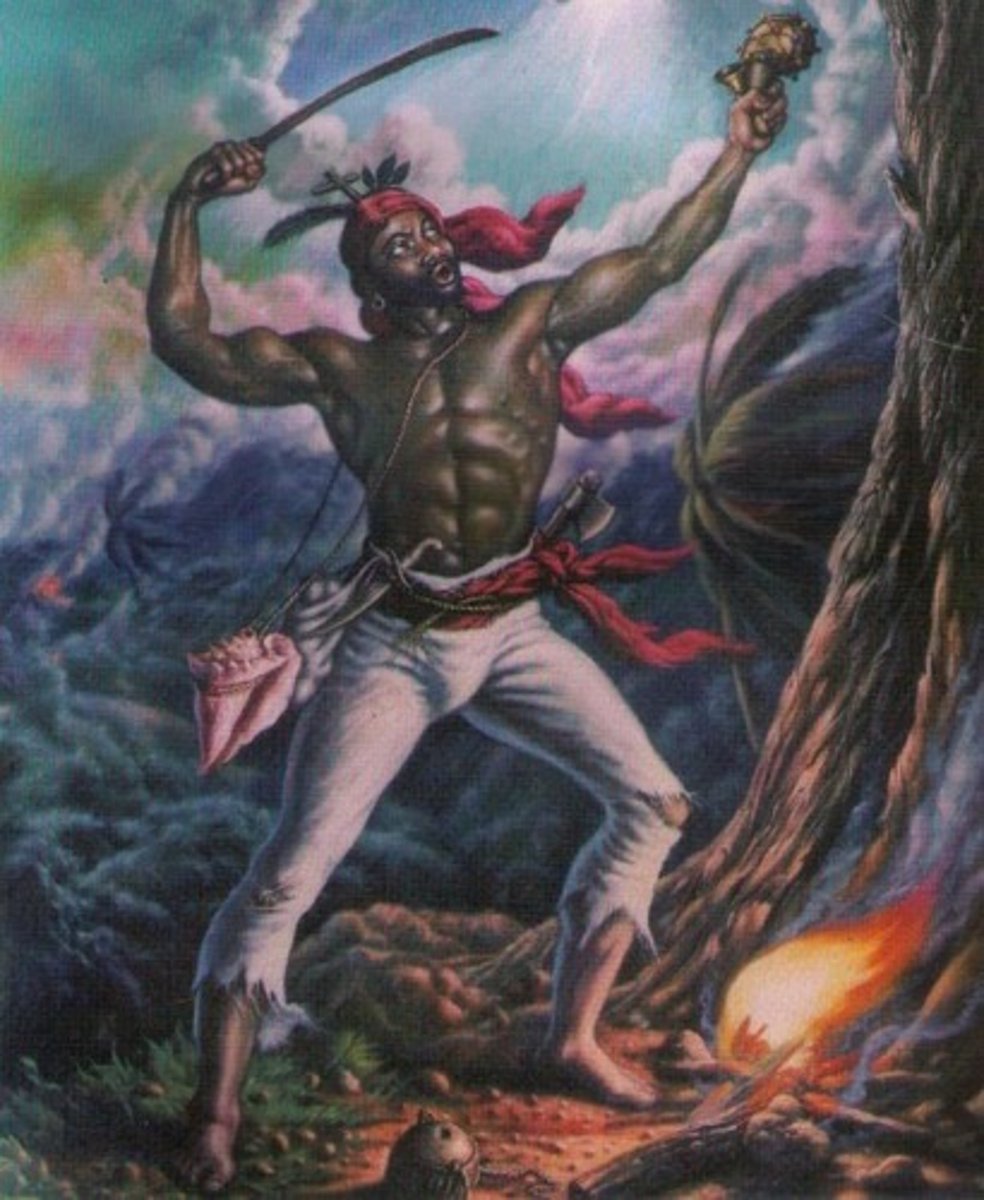
Boukman Dutty
An escaped slave and voodoo priest who held a religious ceremony and persuaded the slaves to rebel against plantation owners for the first time in 1791.

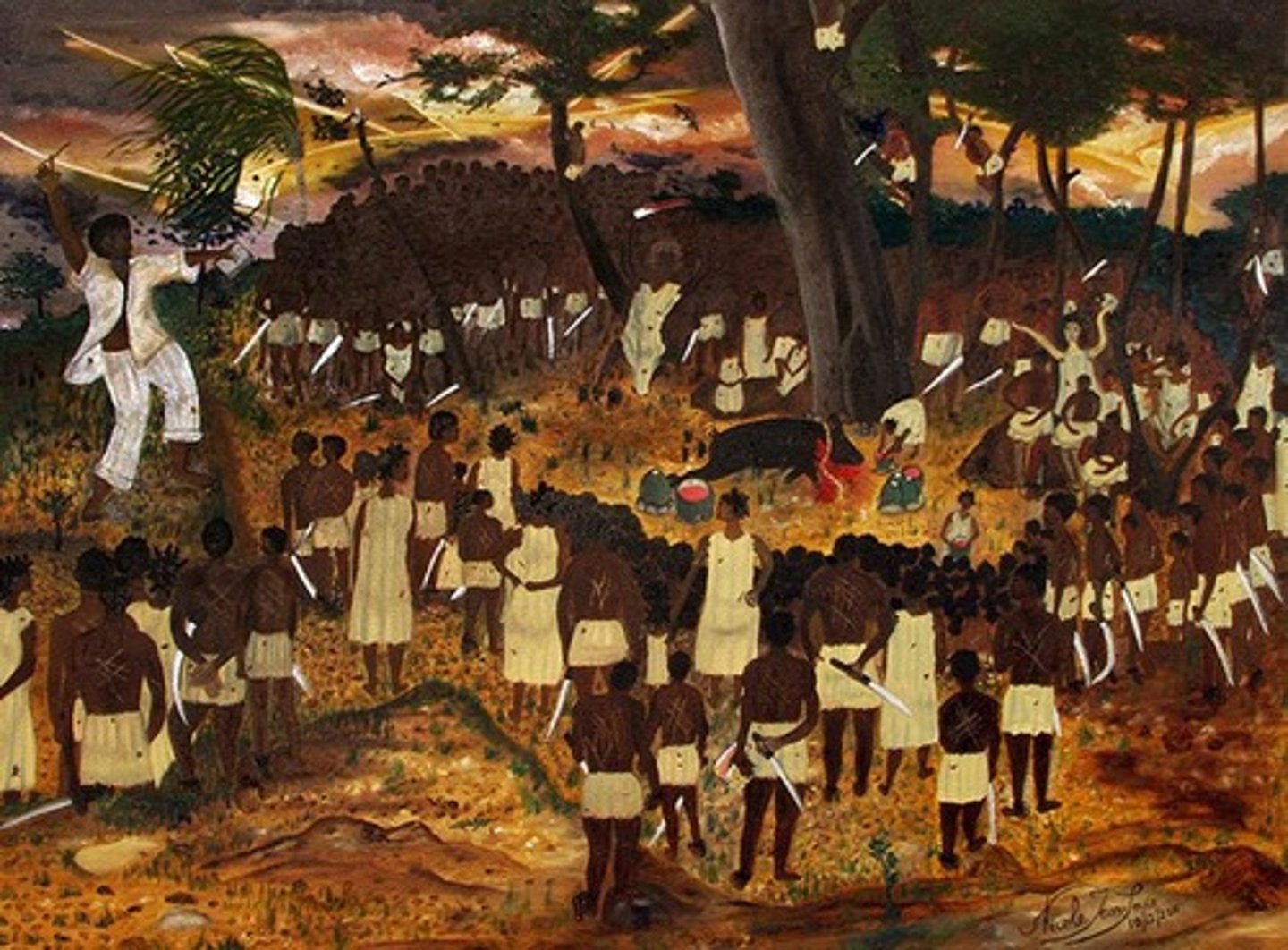
Boukman's Rebellion
(1791) Enslaved people and maroons revolted, destroying plantations and killed many Grand Blancs (rich whites). It was one of the first acts of violence from the rebelling black population toward the white population in the Haitian Revolution.

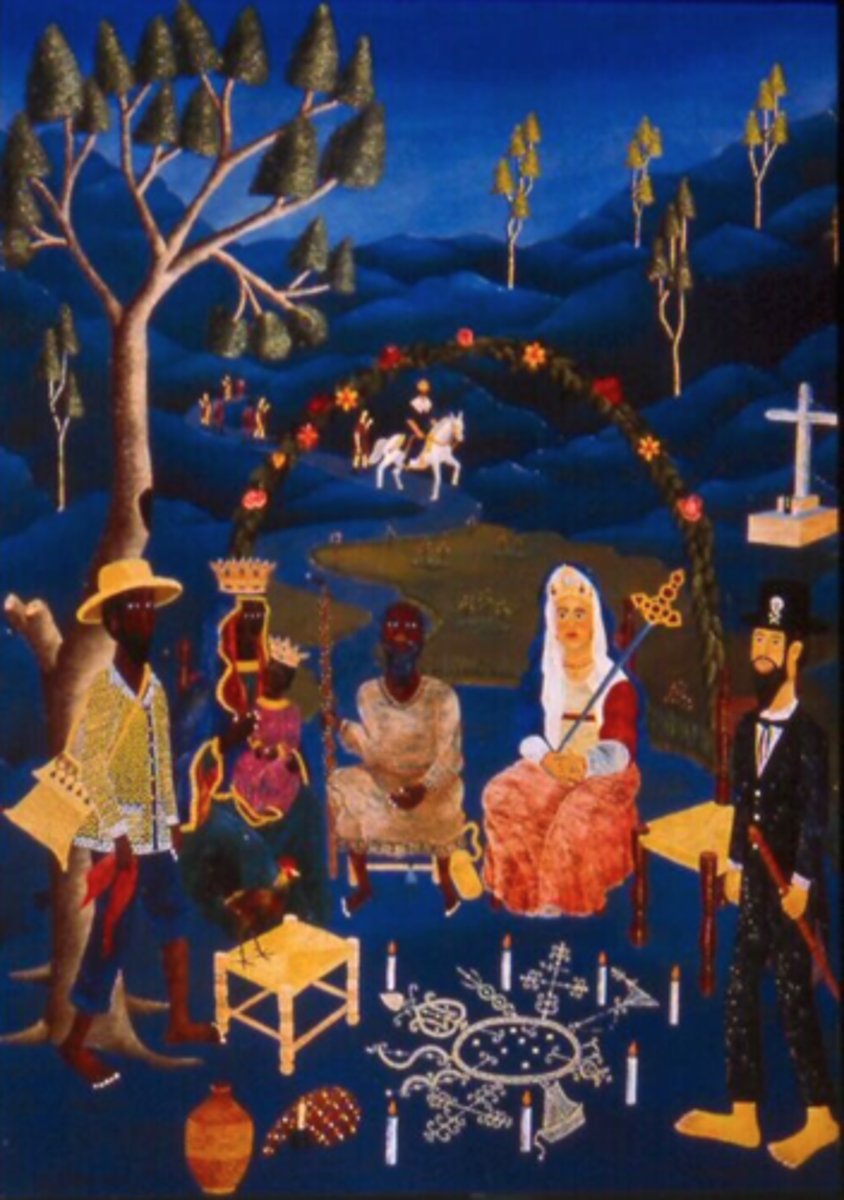
Vodou/Voudou
A West African religion mixed with some Catholic traditions practiced among people of African descent--both enslaved and maroons.

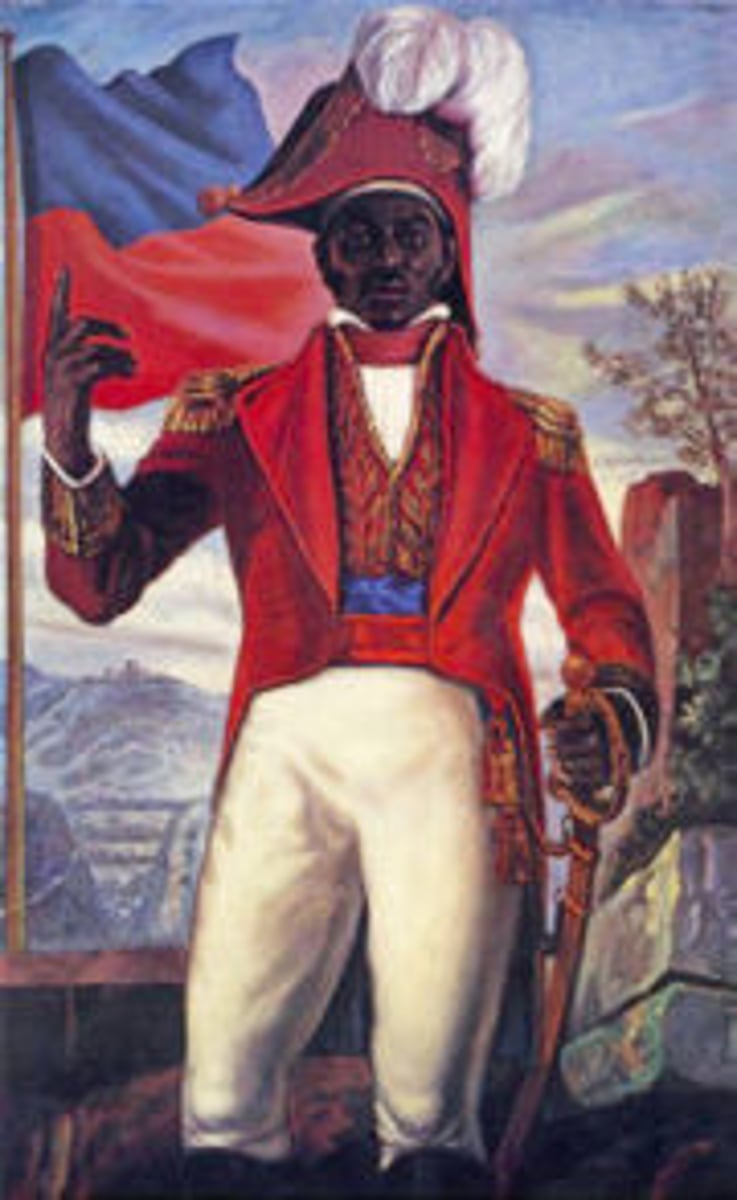
Toussaint L'Ouverture
A former slave who became a war general and leader of the Haitian Revolution. He wrote Haiti's Constitution of 1801 without Napoleon's approval and made himself governor for life. Napoleon had him tricked, arrested, and brought to France on charges conspiracy to commit treason. He died in a French prison before Haiti achieved independence.

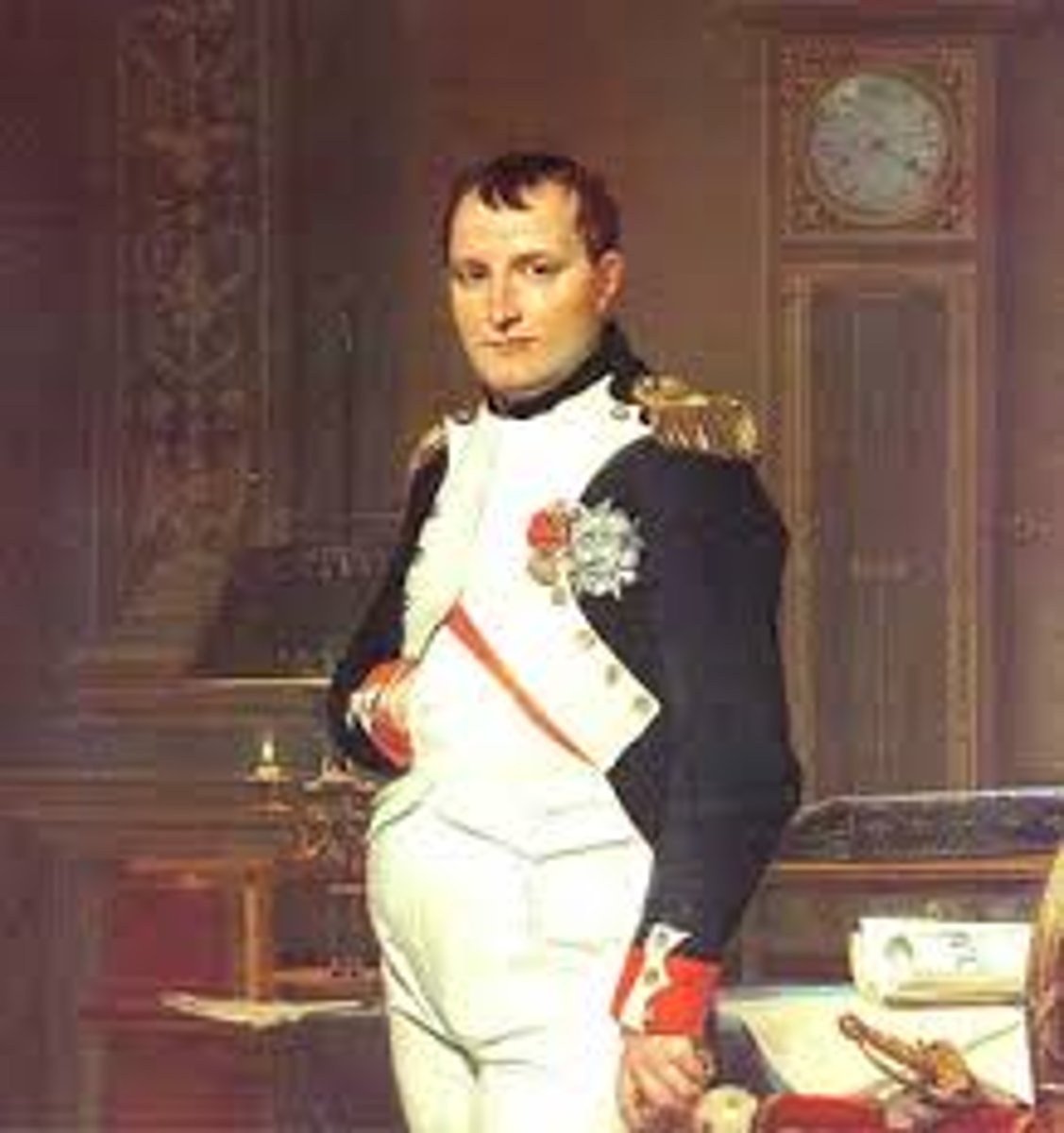
Napoleon's Reaction to Constitution of 1801
Napoleon was very unhappy with Toussaint about the constitution and wanted to impose slavery on Saint-Domingue. He sent 80,000 French troops and 408 ships to Saint-Domingue to take control of the colony and capture Toussaint L'Ouverture. Toussaint surrendered but was tricked by Napoleon's general and brought back to France where he died in captivity.
Haitian Independence 1804
Haiti declared independence from France in 1804.

Hispaniola
The name of the entire island that now has modern day Haiti and the Dominican Republic.
Caste System
a set of rigid social categories that determined not only a person's occupation, race, and economic potential but also their position in society
Napoleon Bonaparte
French general who became emperor of France and wanted to restore slavery in the French colonies.

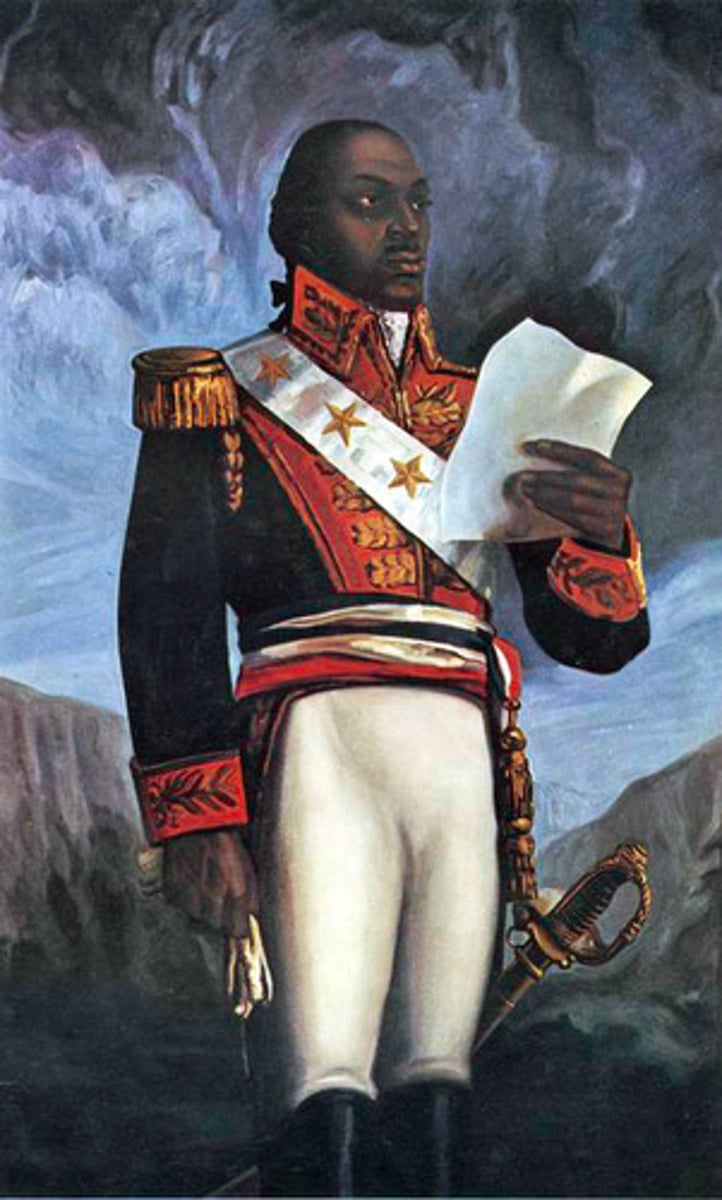
General Jean-Jacques Dessalines
A general under Toussaint L'Ouverture, he took over as successor during the Haitian Revolution. In 1804 he declared the former colony of Saint-Domingue to be the new independent state of Haiti once the rebels kicked the French out of the colony once and for all. He took the title Emperor Jacques I when Haiti declared independence.

Taino
The Indigenous people who inhabited Hayti/Hispanola and many Caribbean islands surrounding the area. The Tainos were the first people Columbus encountered after making landfall in the New World and the first people Europeans enslaved there. Originally there were up to 3 million Tainos on the island of Hayti/Hispanola. Just 25 years after the Spanish had come to the island, the population of Tainos had dropped to less than 50,000 people due to the brutality of the Spanish and the diseases they brought from Europe.
African resistance to slavery
These included building fortresses around their villages, trying to escape, refusing to eat, and committing suicide. Africans also revolted but revolts were less common.
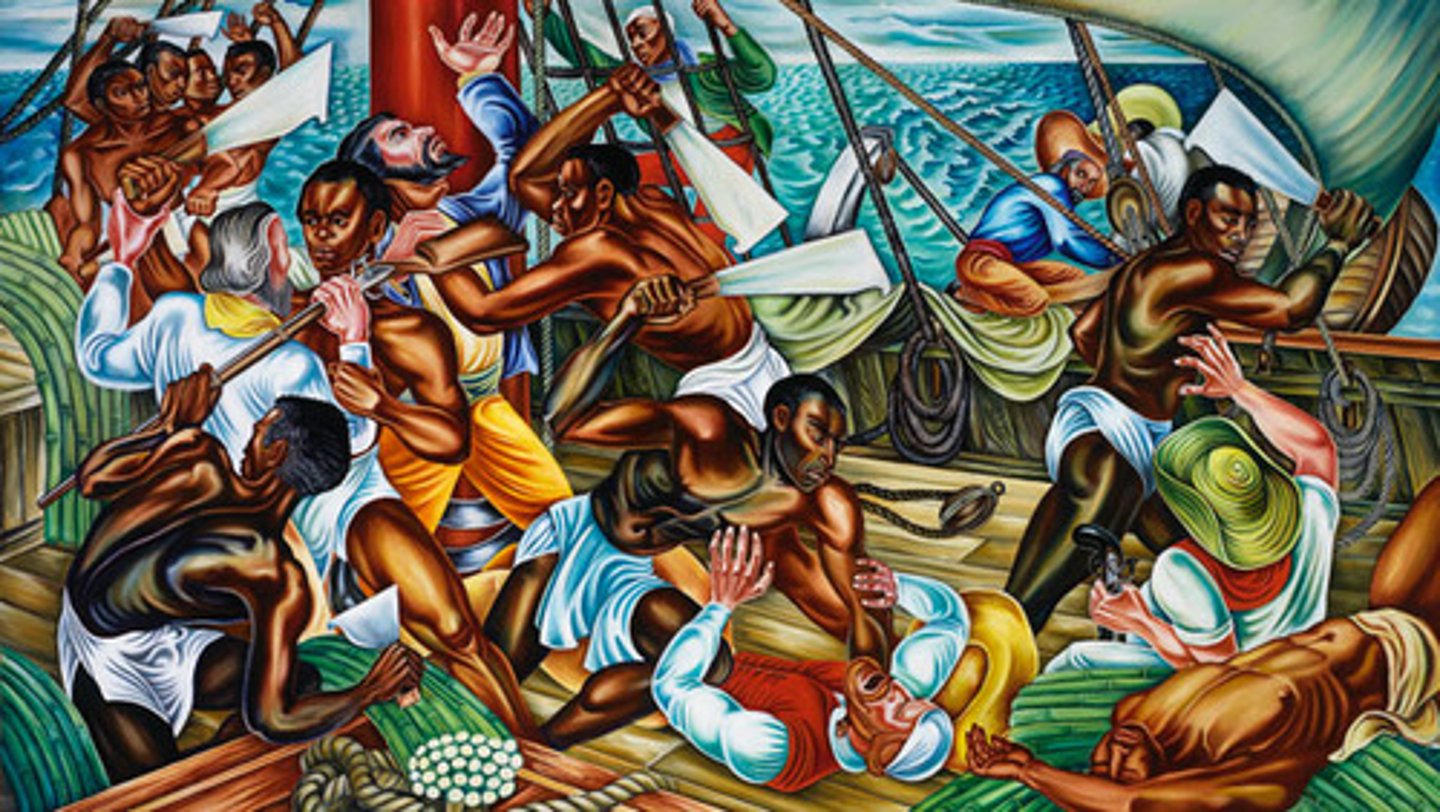

Racial Slavery
When slavery becomes associated with a particular race and becomes something that follows people for generation after generation.
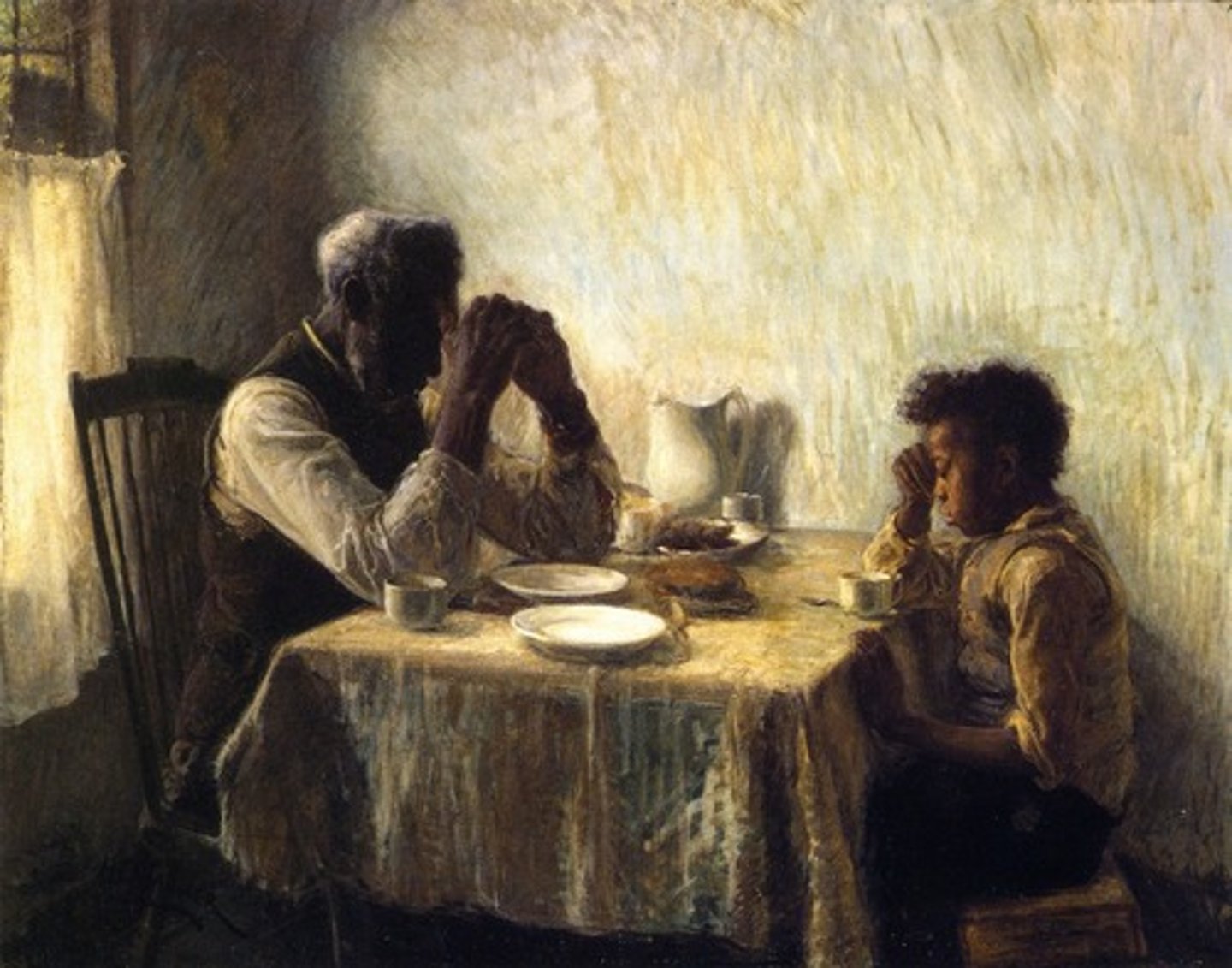

Creoles
In Saint-Domingue, Creoles were enslaved blacks born on the island (not born in Africa)

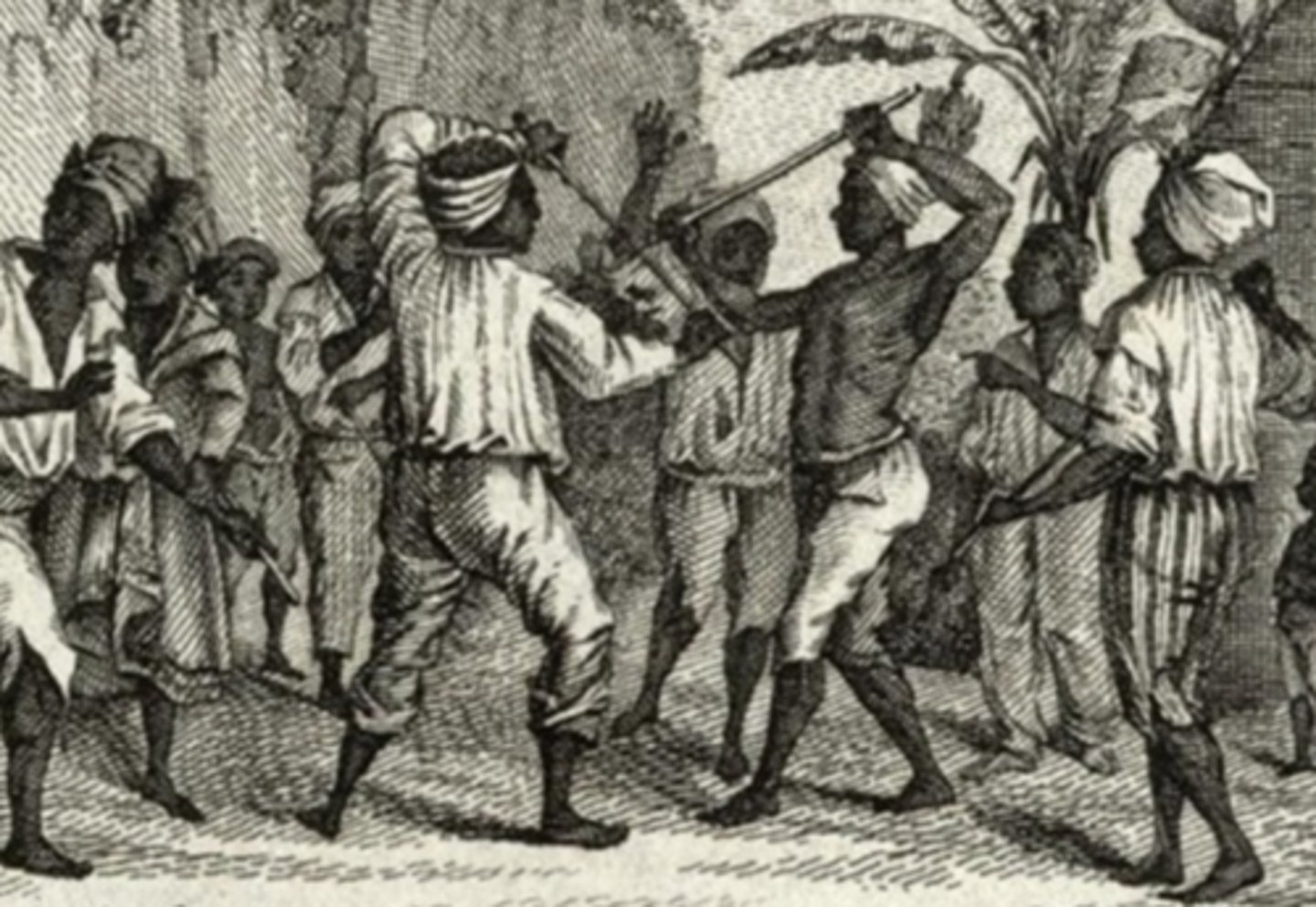
Congoes & Bossales
Enslaved peoples from Africa. Congoes from the area of Central Africa made up the majority. Bossal were from West Africa.

Cecile Fatiman
Vodou priestess who led the ceremony at Bois Caiman

Adbaraya Toya (Gran Toya)
Godmother to Jean-Jacques Dessalines. Former Dahomey warrior who was captured from West Africa (present-day Benin) and enslaved on Saint-Domingue.
