Drug Delivery Quiz/Exam
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
In which type of dispersion, homogenous or heterogenous, is the dispersed phase physically distinguishable from the medium in which it is dispersed?
a. Homogenous dispersion
b. True solution
c. Heterogenous dispersion
d. None
c. Heterogenous dispersion
Which of the following is an example of solid in liquid dispersion?
a. Cream
b. Suppositories
c. Suspension
d. Gels
c. Suspension
A physician has two injection vials, A and B, which are unlabeled. One is saline, and the other albumin-containing solution. They look very similar. A pharmacist is consulted to identify vials A and B.The pharmacist shines light through the two vials. Solution A does not scatter light when light passes through. Solution B scatters light when light passes through.Which of the following statements is true regarding vials A and B?
a. Vial B is a saline solution
b. Vial A is an albumin solution and Vial B is a saline solution
c. Vial A is saline solution and Vial B is albumin solution
d. Vial A contains colloidal particles
c. Vial A is saline solution and Vial B is albumin solution
Which of the following is an example of liquid in solid dispersion?
a. Solid foams
b. Suppositories
c. Gels
d. Liquid spray
c. Gels
Which of the following is an example of a solid in solid emulsion?
a. Cream
b. Suppositories
c. Gels
d. Pediatric suspension
b. Suppositories
Creams and lotions are examples of a(n)
a. Foam
b. Emulsion
c. Suspension
d. Aerosol
b. Emulsion
Creams tend to separate from the dispersion medium by rising.
a. True
b. False
a. True
The light scattering properties of colloidal systems is called
a. Brownian effect
b. Tyndall effect
c. Rising
d. Sedimentation
b. Tyndall effect
Insulin and albumin are examples of
a. Hydrophobic colloids
b. Hydrophillic colloids
c. None
b. Hydrophillic colloids
Ibuprofen suspension is an example of
a. Colloidal dispersions
b. Coarse dispersion
c. None
b. Coarse dispersion
According to Stoke's equation, an increase in the crystal particle size of a coarse suspension ___________ the sedimentation rate of the suspension:
a. Increases
b. Decreases
c. Contains constant
a. Increases
A bottle of milk is an example of
a. None
b. Coarse dispersion
c. Colloidal dispersion
d. Molecular dispersion
c. Colloidal dispersion
If the length of the bar, L, is 5 cm and the mass required to break a soap film is 0.50 g, what is the surface tension of the soap solution? Recall that the downward force equals the mass multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity. With g=9.81 m/s^2= 981 cm/s^2 1 dyne/cm= 1 g/s^2
a. 40 dynes/cm
b. 25 dynes/cm
c. 49 dynes/cm
d. 35 dynes/cm
c. 49 dynes/cm
According to Stoke's equation, an increased viscosity of a coarse suspension ___________ the sedimentation rate of the suspension:
a. Increases
b. Contains constant
c. Decreases
c. Decreases
What are the two phases in contact for emulsion, creams, and lotions?
a. Solid and liquid
b. Liquid and gel
c. Liquid and liquid
d. Gels and solid
c. Liquid and liquid
A liquid-solid interface is found in a(n)
a. Emulsion
b. Suspension
c. Aerosol
d. Powder particle in contact
b. Suspension
What is an anti-foaming agent's Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance (HLB) range?
a. 13-15
b. 2-3
c. 3-6
d. 7-9
b. 2-3
When water-loving groups in a surfactant are predominant, the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance is
a. High
b. Low
c. Balanced
a. High
When oil-loving groups in a surfactant are predominant, the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance is
a. High
b. Balanced
c. Low
c. Low
The properties of the molecules forming the suspension interface are sufficiently different from those in the bulk of each phase.
a. True
b. False
a. True
What is the HLB of Polysorbate 80, NF, (Tween 80), for which S=50 and A=200?
a. 5
b. 10
c. 15
d. 20
c. 15
How much B=Span 80 (HLB=4.3) and A=Tween 80 (HLB=15) do we need for a requires HLB of 10?
a. 47% and 53%
b. 62% and 38%
c. 35% and 65%
d. 73% and 27%
a. 47% and 53%
Which of the following is not a component of creams or lotions?
a. Water
b. Oil
c. Surfactant
d. Interfacial tension enhancers
d. Interfacial tension enhancers
What is the essential first step in a solid dosage form dissolution process?
a. Disintegration
b. Wetting
c. Absorption
d. Diffusion
b. Wetting
Viscosity is the study of the resistance to flow of (_____________________)
a. Liquids
b. Solids
c. None
a. Liquids
What is the definition of the term "η" is the Newton equation of flow?
a. Viscosity
b. Fluidity
c. Diffusion
d. Rate of shear
a. Viscosity
What is the definition of the term "Φ" is the Newton equation of flow?
a. Viscosity
b. Fluidity
c. Diffusion
d. Rate of shear
b. Fluidity
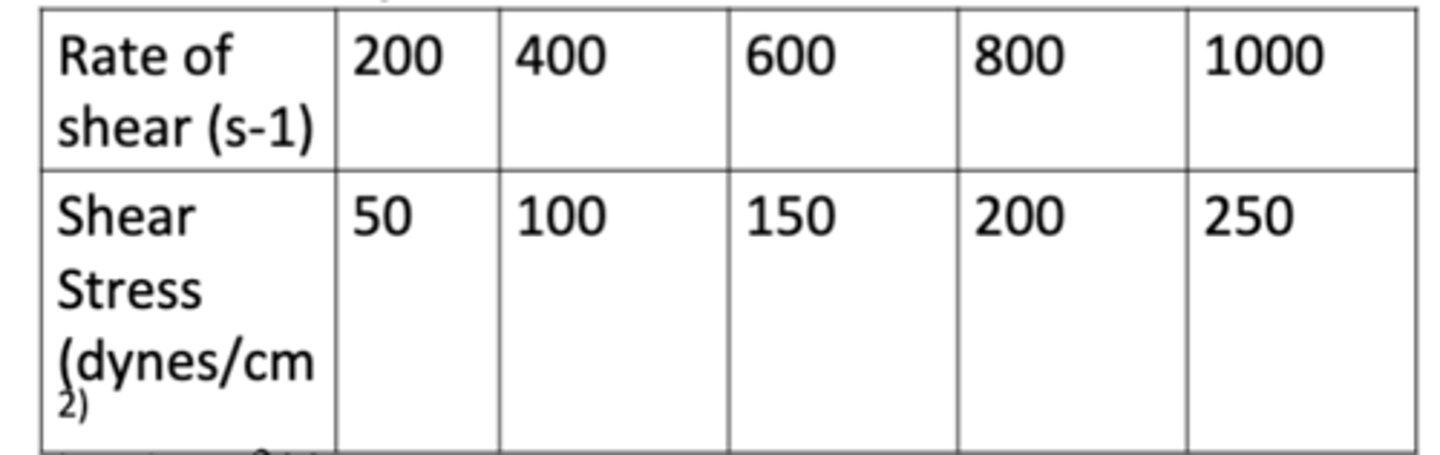
The following data show the rate of shear as a function of shear stress for a Newtonian fluid at 25C (77F). Determine the fluidity of the fluid.
a. 1 cm^2/dynes
b. 4 cm^2/dynes
c. 8 cm^2/dynes
d. 10 cm^2/dynes
b. 4 cm^2/dynes
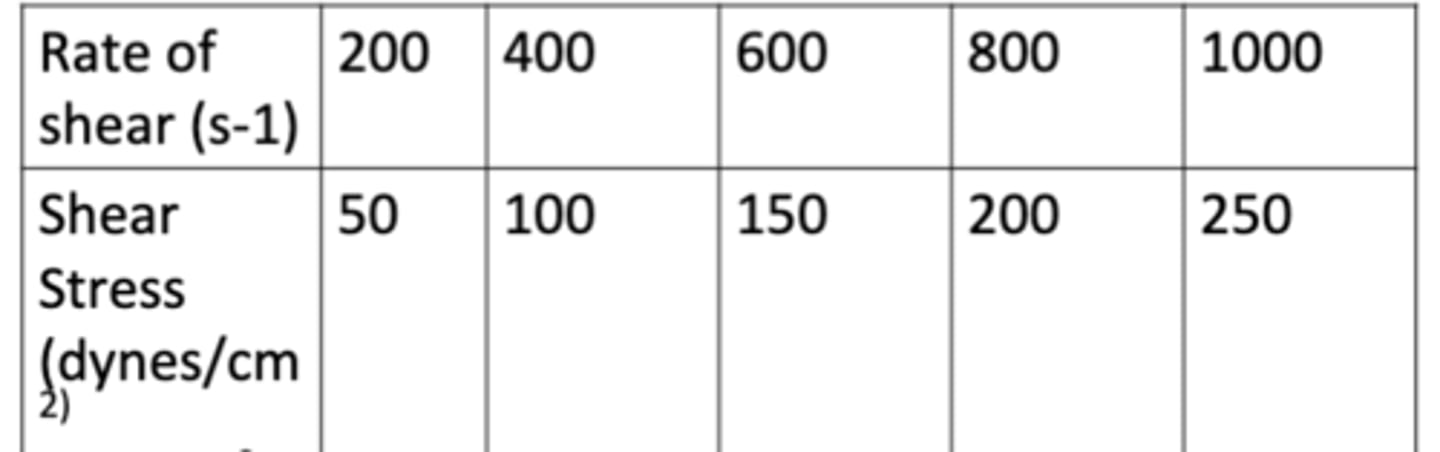
The following data show the rate of shear as a function of shear stress for a Newtonian fluid at 25C (77F). Determine the viscosity of the fluid in cps.
a. 15 cps
b. 10 cps
c. 25 cps
d. 10 cps
c. 25 cps
The viscosity of Newtonian fluids ____________ with increasing temperature.
a. Increases
b. Decreases
c. Remains constant
d. None
b. Decreases
A pharmacist prepares a micelle by adding an amphiphilic molecule in water. Then the measured size of the micelle at the critical micelle concentration was 80 nanometers. The pharmacist concludes that he has successfully prepared a (_______________).
a. Coarse dispersion
b. Colloidal dispersion
c. True solution
d. None
b. Colloidal dispersion
An aqueous solution of insulin and albumin are examples of (_______________).
a. Hydrophillic colloids
b. Hydrophobic colloids
c. Lipophobic colloids
d. None
a. Hydrophillic colloids
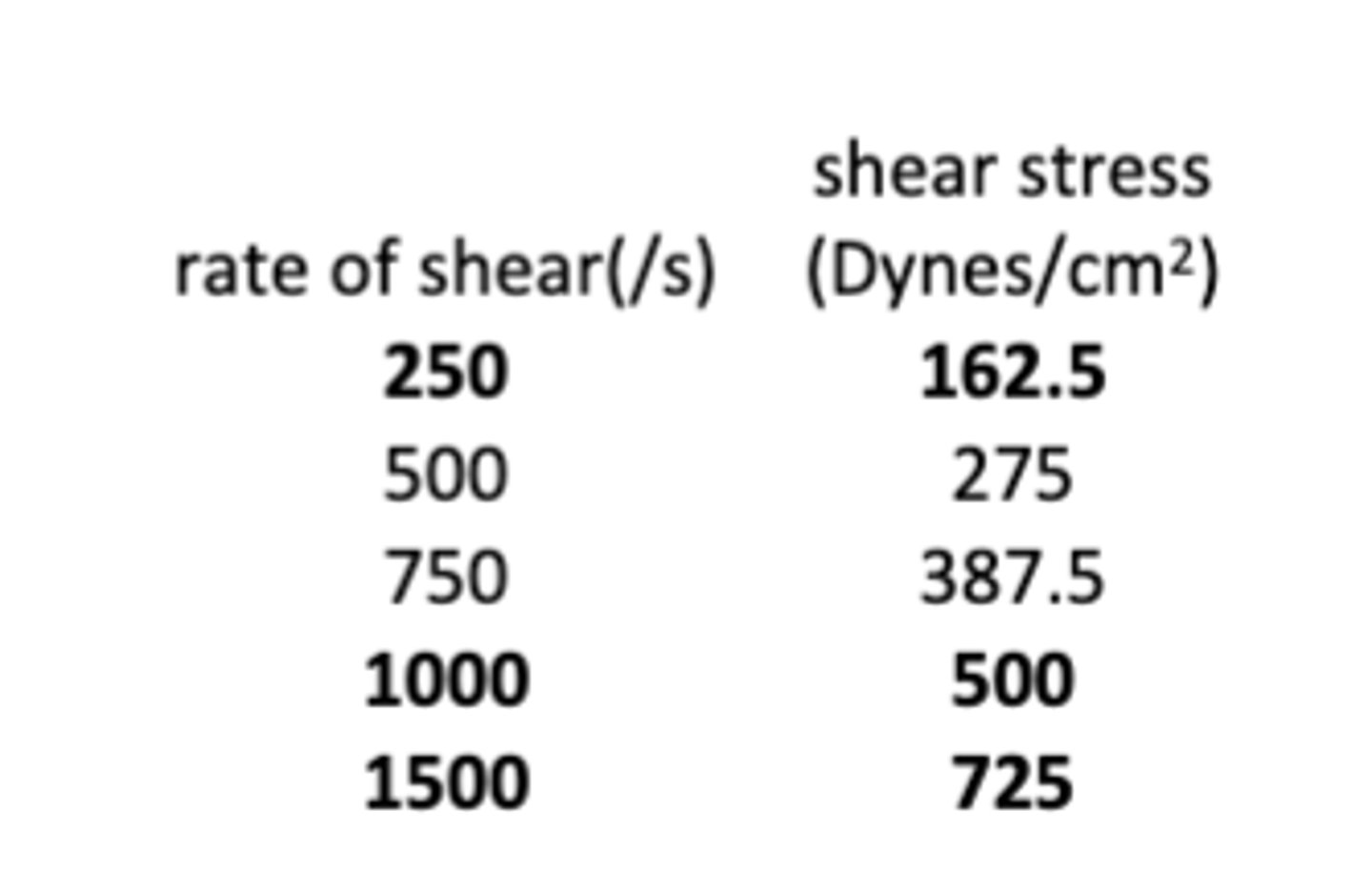
The following data show the relationship between the shear and shear stress rate for a topical formulation that exhibits plastic rheology. What is the yield value of the formulation?
a. 20 dynes/cm2
b. 50 dynes/cm2
c. 75 dynes/cm2
d. 100 dynes/cm2
b. 50 dynes/cm2
What is the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid if the activation energy is 4.25 x 10^3 cal/mole, the gas constant R=1.987 and A = 1.21 x 10^-3 cps and the temperature = 25C?
a. 1.58 cps
b. 2.54 cps
c. 2.34 cps
d. 1.24 cps
a. 1.58 cps
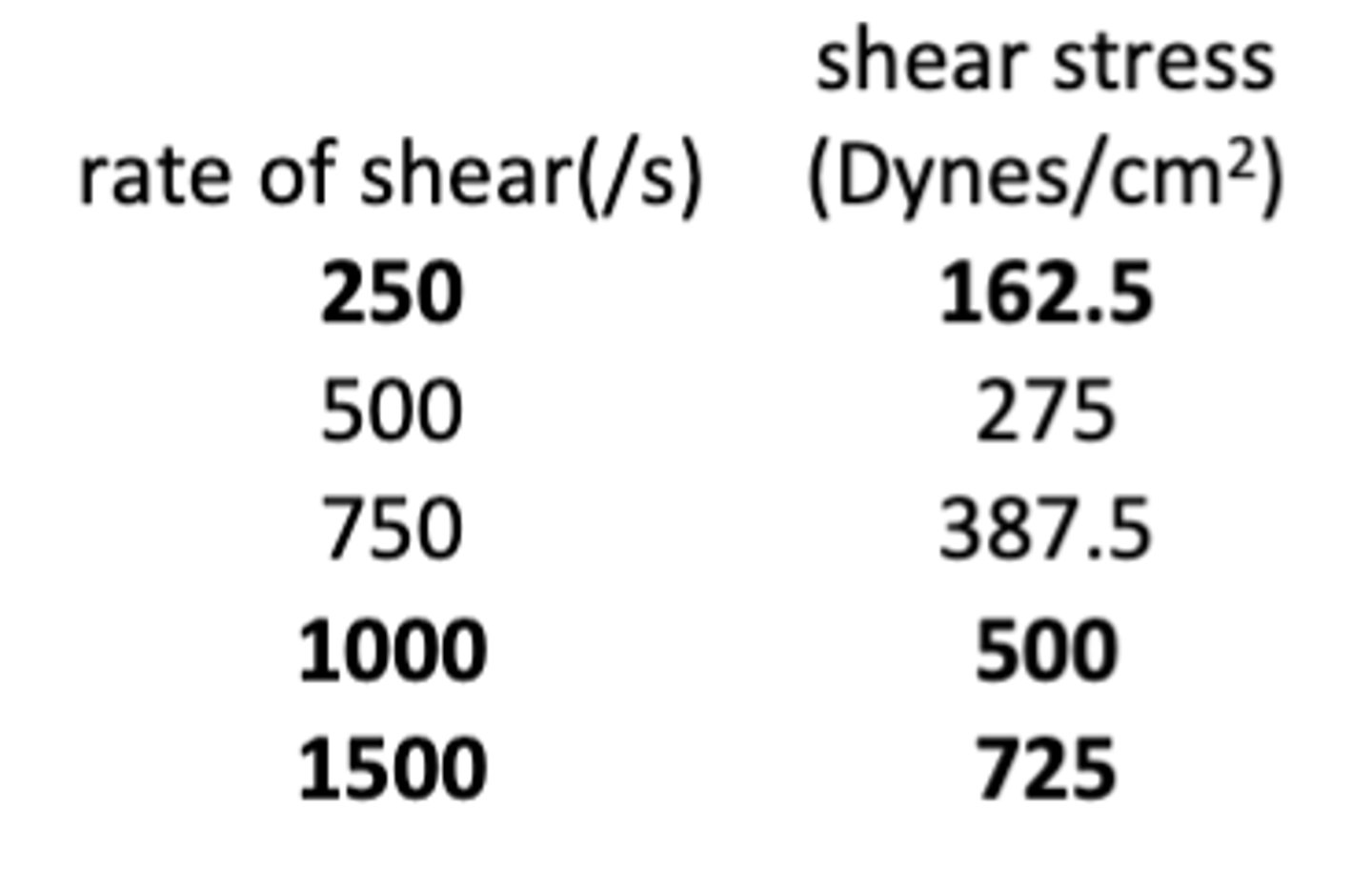
The following data shows the relationship between the rate of shear and shear stress for a topical formulation that exhibits plastic rheology. What is the plastic viscosity of the formulation?
a. 35 cps
b. 40 cps
c. 45 cps
d. 50 cps
c. 45 cps
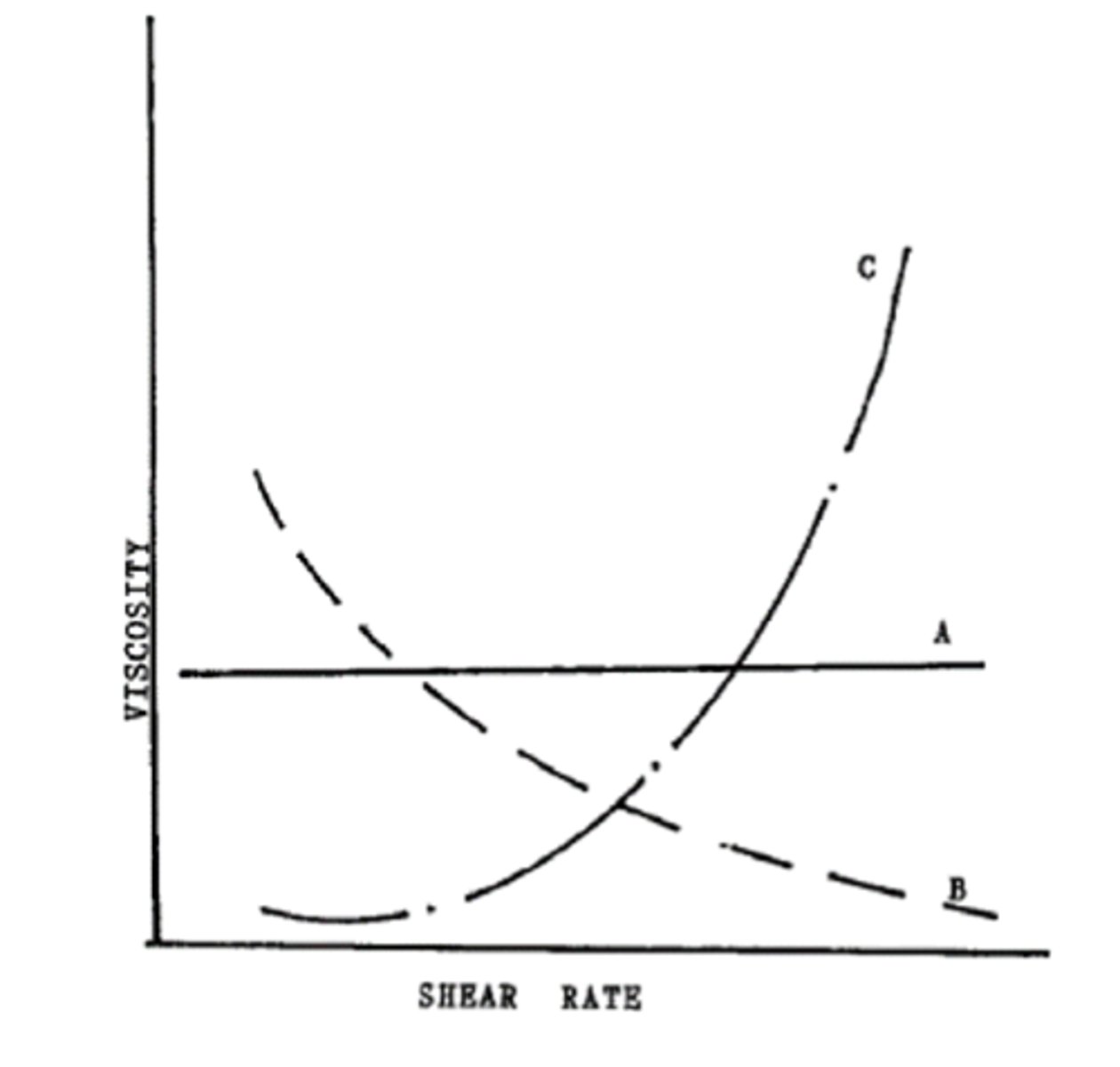
The following graph depicts the viscosity of different rheology system vs the shear rate. Which of the following curve is a dilatant or shear thickening system?
a. Curve A
b. Curve B
c. Curve C
c. Curve C
Mineral oil was dispersed as globules in an oil-wateremulsion to form a total surface area of globules of 10^8c m^2. If the presence of emulsifying agent results in aninterfacial tension between oil and the water phase of 5 erg/cm^2, what is the total surface free energy of the systemin calories, in SI units?
a. 50.2 joule
b. 40.6 joule
c. 78.3 joule
d. 38.8 joule
a. 50.2 joule
The HLB of polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate(Tween 20), for which S = 45.5 and A = 276, is
a. 15.8
b. 19.2
c. 16.7
d. 20.1
c. 16.7
Calculate the HLB value of polyoxyethylene 20 sorbitanmonolaurate (Tween 20) which has a MW = 1226? The hydrophilic portion of this molecule consists of sorbitan (MW=164=> P) and 20 moles of ethylene oxide (MW= 880=>E).
a. 18
b. 17.03
c. 20.4
d. 15
b. 17.03
How much Span 80 (HLB = 4.3) and Tween
80 (HLB = 15) do we need for a required HLB of 12 for a stable prescription (Rx).
A) 72% Tween 80 and 28% Span 80
B) 28% Tween 80 and 72% Span 80
C) 25% Tween 80 and 75% Span 80
D) 75% Tween 80 and 25% Span 80
A) 72% Tween 80 and 28% Span 80
Calculate the rate of shear applied by a patient in rubbing a 200-μm-thick film of ointment on the skin surface at a rate of 10 cm/s.
a. 300 /s
b. 400 /s
c. 500 /s
d. 600 /s
c. 500 /s
Use an Ostwald viscometer at 20 ºC the time for the flow of waterthrough the apparatus is 297.3 seconds. When the instrument wascalibrated with carbon disulfide (density 1.2632 g/mL), the time offlow was 85.1 sec. The density and the viscosity of water at 20ºC are0.9982 g/mL and 1.002 cp, respectively. What is the viscosity of carbon disulfide at 20 ºC?
a. 0.454 cps
b. 0.363 cps
c. 0.545 cps
d. 0.672 cps
b. 0.363 cps
The time for water to flow through an Ostwald pipette at 20ºC was 297.3 sec. The density of water at 20 ºC is 0.9982g/mL and the density of a sample of olive oil is 0.910g/mL. The viscosity of water at 20 C is 1.002 cp and the viscosity of the sample of olive oil is 84.0 cps. How long will it take for the olive oil to flow through the Ostwald pipette at 20 ºC?
a. 455.65 minutes
b. 312.72 minutes
c. 537.84 minutes
d. 404.92 minutes
a. 455.65 minutes