Levers, Newton's Laws, Kinematics and Kinetics (copy)
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sports science HL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
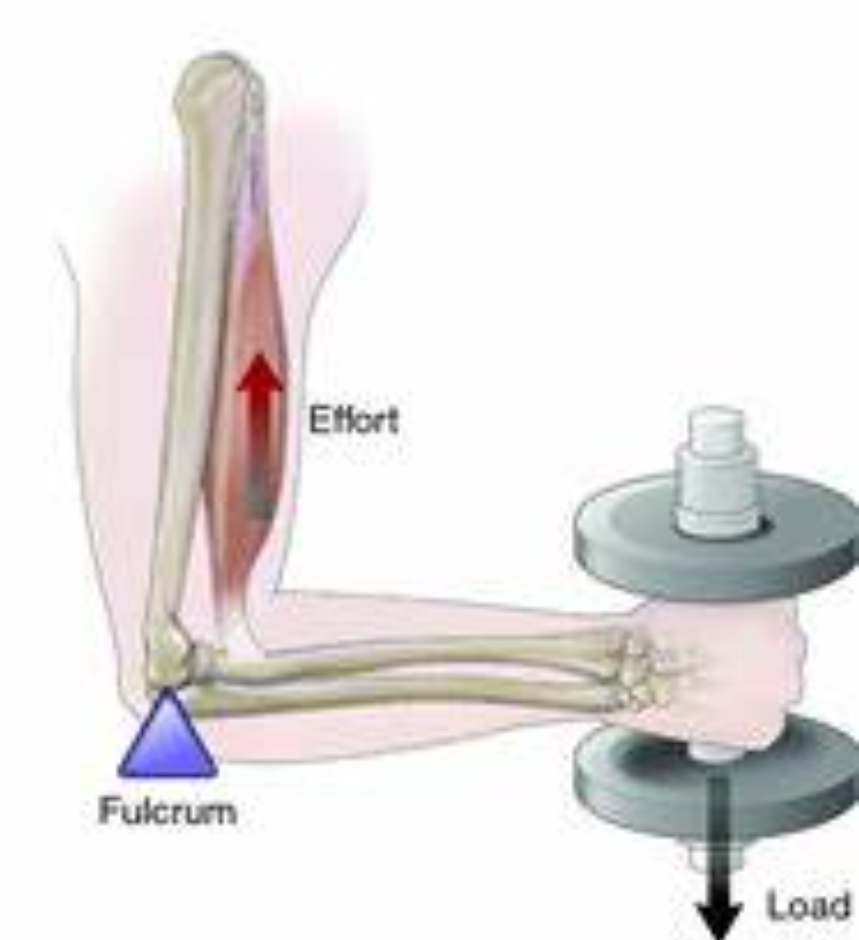
First class lever
Resistance——Fulcrum——Effort
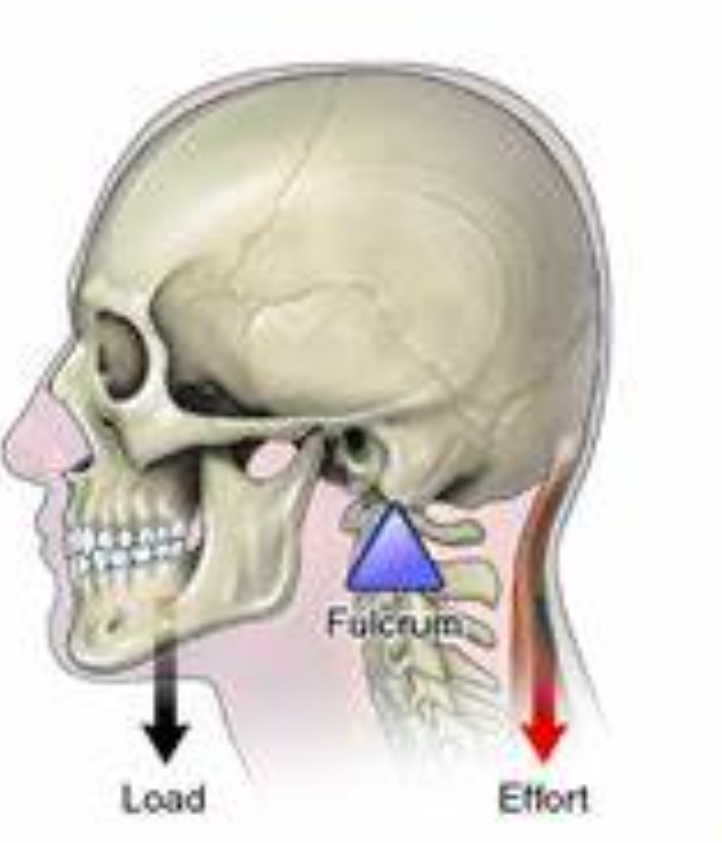
Second class lever
Fulcrum——Resistance——Effort
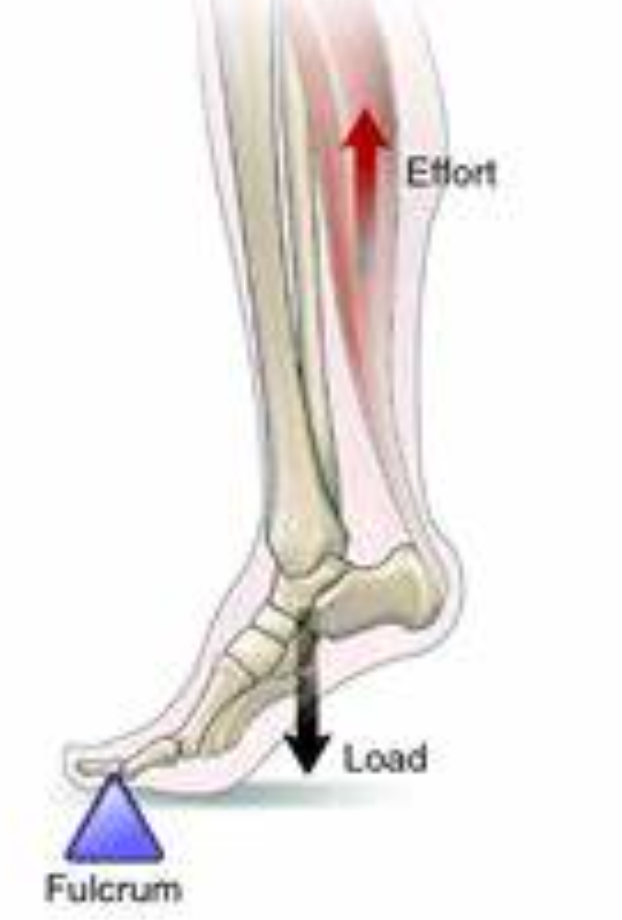
Third class lever
Fulcrum——Effort——Resistance
mechanical advantage
class 2 lever. when effort arm>resistance arm, it gives more power
mechanical disadvantage
Class 3 lever. when effort arm<resistance arm, it gives more speed but is harder to move
Newton’s first law
Law of inertia. an object will remain at rest or continue with constant velocity unless acted on by an unbalanced force
Newton’s second law
Law of acceleration. Force= mass×acceleration
Newton’s third law
Law of reaction. For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction force applied.
inertia
a property of matter that causes it to resist changes in velocity (speed/direction)
Center of Mass (CoM)
mathematical point around which the mass of a body is evenly distributed.
CoM and stability
the CoM must be in the Base of Support (BoS)to have balance. The lower the CoM the more stable the object is
Summation of Forces
Normally the strongest and lowest body parts around the center of gravity move first, followed by the weaker, faster, and lighter extremities. The order reflects the best techniques.
Kinematics
study of motion
Kinetics
study of forces that cause motion
Scalor
size
Vector
size+direction
displacement
The distance from the starting point. Has size+direction
distance
has only size but no direction
angular kinematics
movement around an axis (spinning)
momentum
The force of a moving object. measured in newtons. p=mv
Impulse
force applied in a certain timeframe. I=Ft
Impulse momentum principle
total momentum before impact =total momentum after impact
moment
a force that is rotational (spins around CoM)
Angular momentum
the force of rotation and is based on the moment of inertia and angular velocity
moment of inertia
the property of an object to resist spinning, or to resist not spinning. the more mass an object has the harder it is to start spinning, the harder it is to stop spinning
factors affecting the amount of spinning
size of the applied force
direction of the applied force
how far from the axis of rotation the force is applied
the conservation of angular momentum
when an object is freely rotating (in the air), the amount of angular momentum is conserved. If the moment of inertia changes, the angular velocity will be affected.
conservation of momentum
the total momentum of a closed system remains constant, provided no external forces are acting on it
coefficient of restitution
a measure of how elastic a collision is between two objects, between 0 and 1
work
W=Fs, forced applied on an objects and the resulting displacement
Power
The measure of how much Work is being done, measured in Watts (J/s)
Kenetic energy
the energy of an object in motion
Potential energy
stored energy an object has due to its position/state
chemical energy
energy stored in bonds between atoms and moleules.