Primer Design and Cloning Strategies in Synthetic Biology
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
GC Clamp
Two or more G/C nucleotides on primer's 3' end.
Melting Point (Tm)
Temperature where 50% of DNA strands are double-stranded.
Primer Length
Primers should be 20-25 nucleotides long.
Uniqueness
Primers must bind only once in DNA sequence.
High GC Content
Primers should have >60% GC for stability.
High AT Content
Primers can have >80% AT, affecting annealing.
Hairpin
Self-complementary structure in primers, causing issues.
Palindromes
Sequences that read the same forwards and backwards.
Slipping
Runs of identical nucleotides in primer sequences.
Transformation Efficiency
Circular plasmids transform better than linear ones.
Cytotoxicity
Toxic effects from certain DNA sequences or proteins.
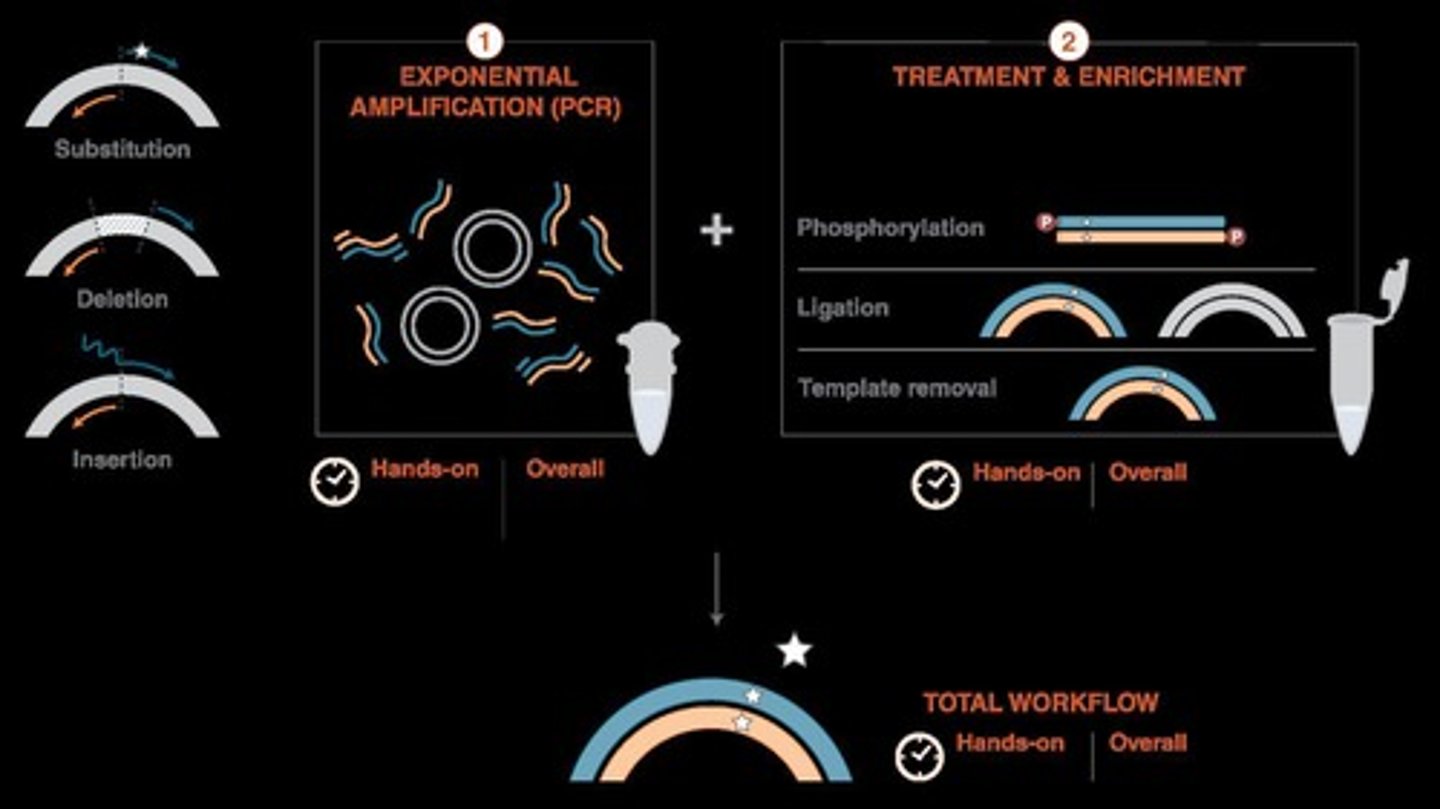
Site-Directed Mutagenesis
Introducing specific mutations at defined positions.
Deletions
Removing specific amino acids or nucleotides from sequences.
Insertions
Adding specific amino acids or nucleotides to sequences.
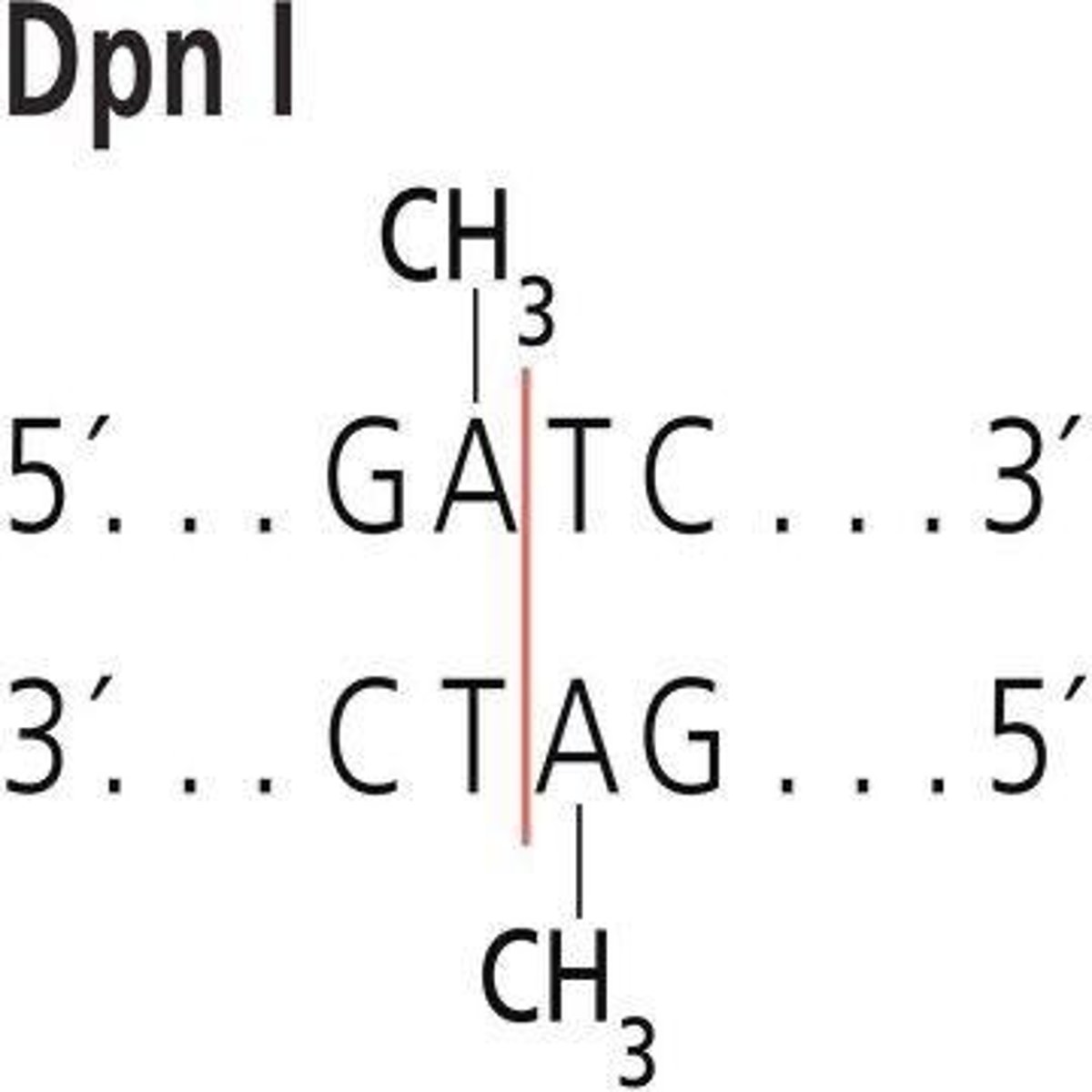
DPN1 Enzyme
Digests methylated DNA, removing template plasmid.
T4 Ligase
Enzyme that ligates DNA fragments together.
PNK Enzyme
Phosphorylates DNA ends for ligation.
Complementary Strands
Strands that pair according to base pairing rules.
Forward Primer
Matches target DNA sequence in 5' to 3' direction.
Reverse Primer
Complementary to the target DNA, designed in reverse.
Reverse Complement
Complement of the reverse strand for primer design.
Substitution Primer Design
Mutation placed at 5' end of forward primer.
Overhang
Extra nucleotides added before mutation in primers.
E→G mutation
A specific nucleotide change from E to G.
ADE mutation
A specific deletion mutation affecting adenine.
CAT mutation
An insertion of CAT sequence into DNA.
FAT CAT mutation
A large insertion mutation of ≥10 nucleotides.
Chimeras
Fusion of different proteins not found naturally.
Fusions
Concatenation of two proteins into one.
Gibson Assembly
Technique using nuclease for DNA assembly.
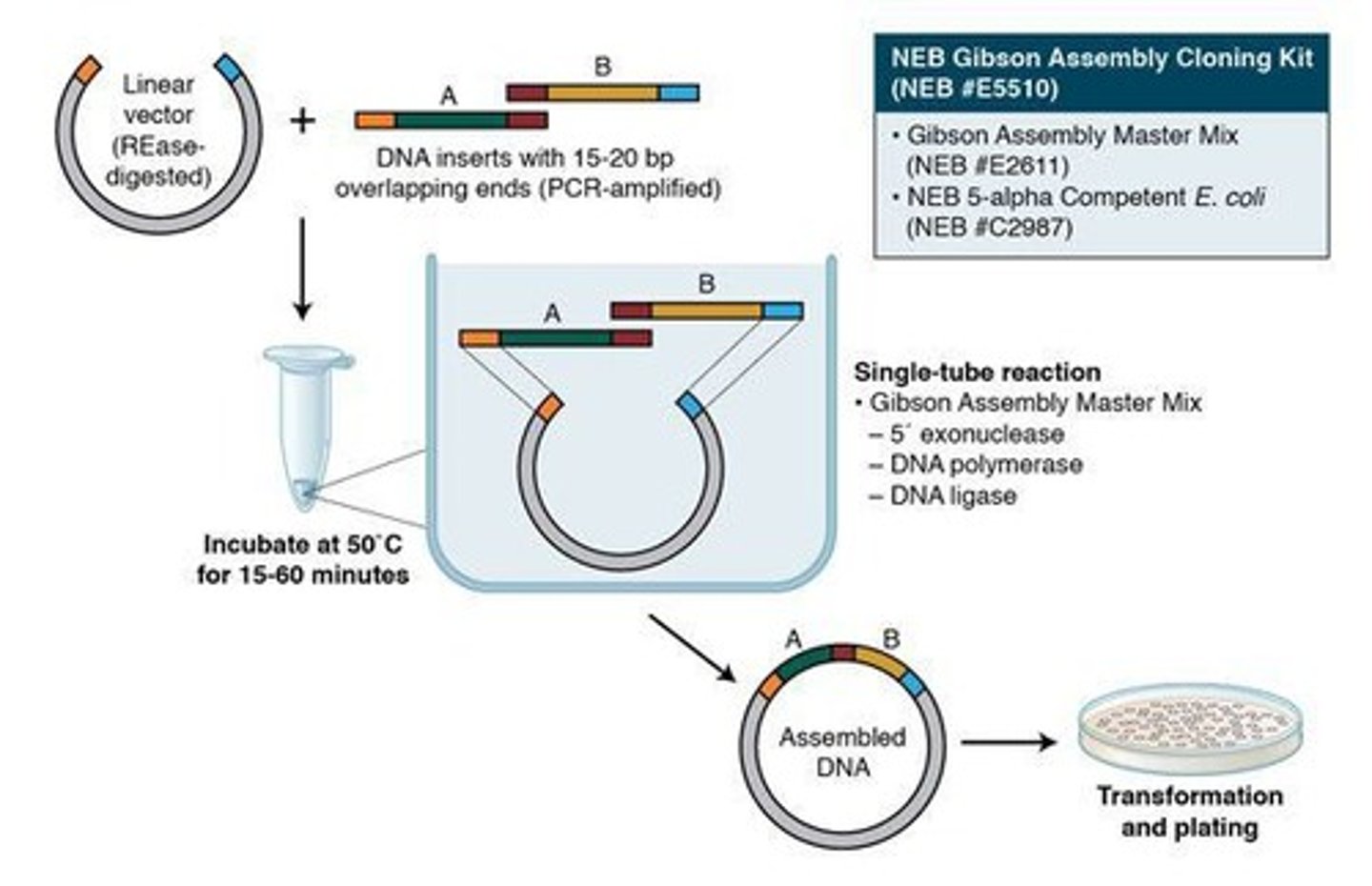
Gibson Primer Design
Primers designed with ~25-50 nucleotide overlap.
Gblocks
Synthetic inserts used in genetic engineering.
Codon
Triplet of nucleotides coding for an amino acid.
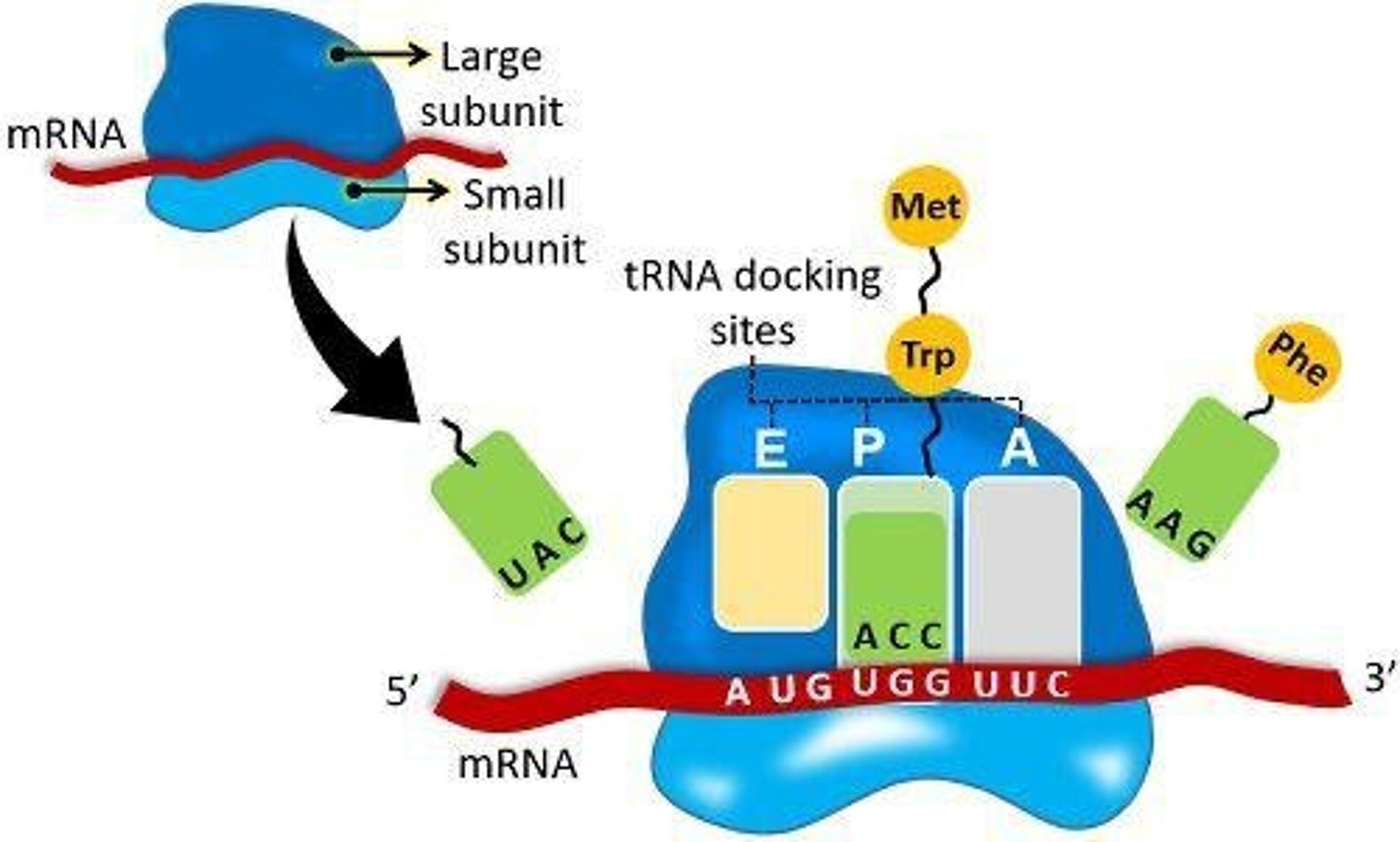
tRNA
Transfer RNA carrying amino acids to ribosomes.
Anticodon
tRNA sequence that base pairs with mRNA codon.
A site
Ribosomal site where tRNA first binds.
P site
Ribosomal site for amino acid polymerization.
E site
Ribosomal site where tRNA exits.
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
Transcription
Synthesis of mRNA from a DNA template.
Reverse Transcription
Conversion of RNA back to DNA.
Frameshifts
Mutations causing misreading of codons.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs)
Variations at a single nucleotide position.
Monocistronic genes
Genes coding for a single protein.
Polycistronic genes
Genes coding for multiple proteins.
Central Dogma
Flow of genetic information: DNA → RNA → Protein.
Wobble Position
Last anticodon nucleotide pairs flexibly with mRNA.
Codon Degeneracy
Multiple codons can specify the same amino acid.
Start Codon
AUG; initiates protein synthesis with methionine.
Stop Codons
Signals termination of protein synthesis; varies by organism. UAA, UAG, and UGA
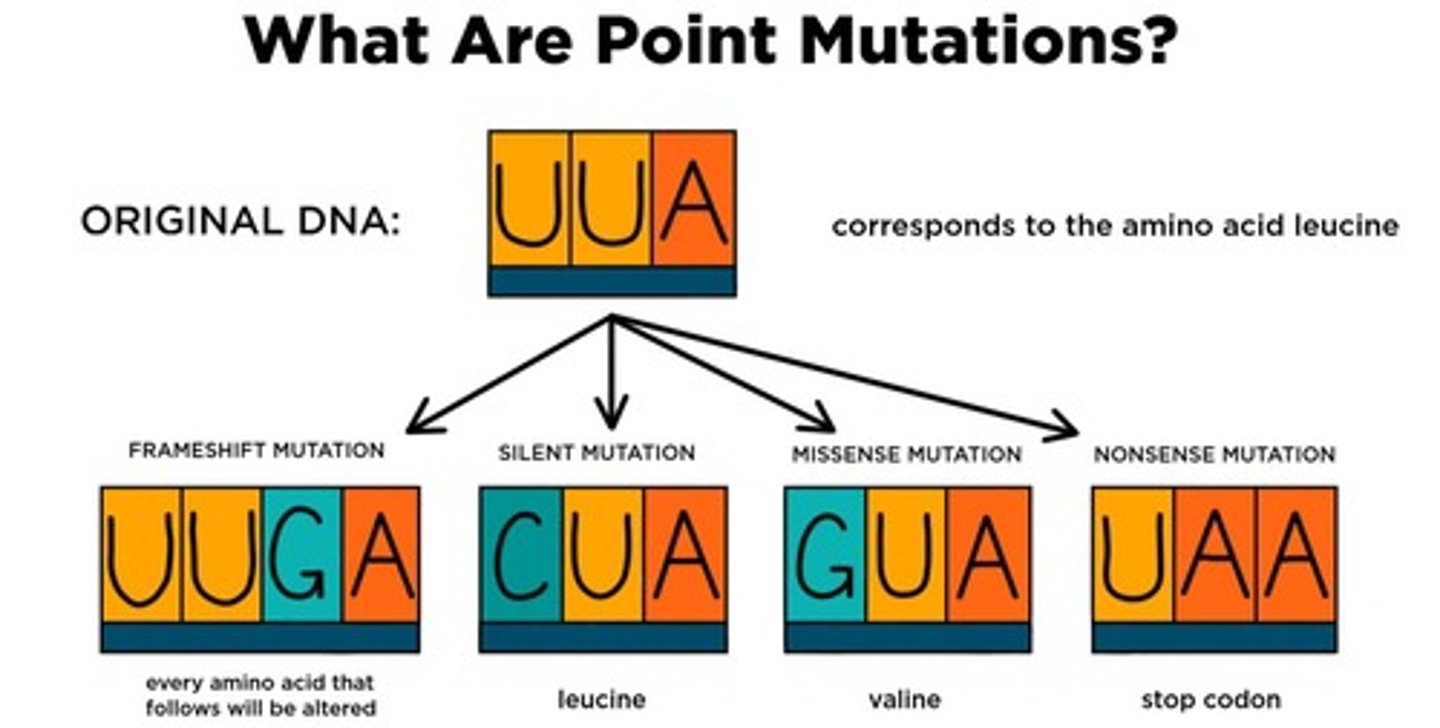
Frameshift Mutation
Nucleotide shift alters downstream translation reading frame.
+1 Frameshift
One nucleotide addition shifts reading frame by one.
+2 Frameshift
Two nucleotide addition shifts reading frame by two.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
Single nucleotide change; may or may not alter amino acid.
Silent Mutation
No amino acid change despite nucleotide alteration.
Point Mutation
Single nucleotide change results in different amino acid.
Insertions
Addition of nucleotides; can cause frameshifts if not in multiples of three.
Deletions
Removal of nucleotides; can cause frameshifts if not in multiples of three.
In-Frame Deletion
Deletion maintains reading frame; fewer amino acids produced.
Out-of-Frame Insertion
Insertion disrupts reading frame; alters downstream translation.
Monocistronic Genes
One gene codes for one protein.
Polycistronic Genes
One gene codes for multiple proteins.
Non-Coding DNA
DNA that does not code for proteins; often regulatory.
Human Genome Project
Initiative to map all human genes and their functions.
CRISPR-Cas9
Bacterial immune system used for gene editing.
NHEJ Pathway
Non-Homologous End Joining; DNA repair mechanism.
HR Pathway
Homologous Recombination; DNA repair using homologous sequences.
GMO Definition
Genetically Modified Organism; lab-altered organisms.
Dolly the Sheep
First cloned mammal; significant in genetic research.

Cas9
Endonuclease that creates double-stranded DNA breaks.
CRISPR
DNA sequences targeted by Cas9 in gene editing.
gRNA
Guide RNA processed from DNA sequences for targeting.
HR
Homologous recombination; uses templates for DNA repair.
NHEJ
Non-homologous end joining; ligates DNA without templates.
Rad51
Protein involved in homologous recombination repair.
BRCA1/2
Genes linked to DNA repair and cancer risk.
TdT
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase; involved in NHEJ.
Artemis
Nuclease that processes DNA ends in NHEJ.
Cas12a
Endonuclease with simpler RNA targeting and sticky ends.
Cas13
Targets RNA instead of DNA for gene regulation.
Casgevy
FDA approved therapy for Sickle Cell Anemia.
Point mutants
Genetic mutations causing specific diseases.
Cystic Fibrosis
Disease affecting mucus membranes due to mutations.
Tay-Sachs Disease
Neurodegenerative disorder affecting brain and spinal cord.
Down syndrome
Genetic disorder causing developmental delays and abnormalities.
Spinal muscular atrophy
Progressive muscle wasting due to genetic mutations.
Crohn's disease
Chronic inflammatory bowel disease with severe symptoms.
Polycystic kidney disease
Genetic disorder leading to kidney failure.
ALS
Neurodegenerative disease with multiple genetic causes.
Knockout mouse
Mouse with a nonfunctional gene for research.
Knock-in
Modification of a gene, often with GFP.
Electroporation
Technique to introduce DNA into cells using electricity.
Blastocyst
Stage of embryo development for stem cell injection.
Homozygous population
Genetically uniform group with specific gene modifications.
Global Alignment
Aligns entire sequences from start to end.
Local Alignment
Aligns specific regions within sequences.
Pairwise Alignment
Compares two sequences for similarity.
BLAST
Basic Local Alignment Search Tool for sequence comparison.
Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
Aligns three or more sequences simultaneously.
ClustalW
Progressive alignment tool for multiple sequences.