Gas Exchange
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Gas Exchange in Alveoli (Gas Laws) 2
Dalton’s and Ficks
Dalton’s law of partial pressures
Total pressure of the mixture is sum of pressures of individual gases
Each gas exerts the same pressure as it would exert alone
Fick’s law of diffusion
Amount of a gas that diffuses across membrane determines by
Partial pressure difference
Total surface area
Respiratory pigments: Oxygen transport Function
Combine reversibly with oxygen and Increase amount of oxygen transported in fluid
Types of respiratory pigments
-Hemoglobin [contains iron]: In vertebrates and some invertebrates and ~99% of O2 in human blood transported by hemoglobin
-Hemocyanin [contains copper]: In hemolymph of many species of mollusks and arthropods
-Myoglobin: In muscle fibers (form of hemoglobin): extracts oxygen from hemoglobing and delivers to muscle tissue
O2 carrying capacity
Maximum amount of O2 that can be transported by hemoglobin
O2 content
Actual amount of O2 bound to hemoglobin
Percent O2 saturation
how much could you carry vs how much you are carrying
Normal curve
Bohr Effect (pH
Acidic (7.2): shift curve to right
: Under acidic conditions, what does hemoglobin want to do?
Donate Hydrogen (Vice Versa)
Why is curve shifting right under high amount of CO2
higher partial pressure to get saturated
As CO2 levels rise in blood, which way will it shift?
Right, Acidic
Equation for Bohr Effect with Carbonic Anyhrase
CO2 + H2O <-> H2CO3 <-> H+ +HCO3-
Haldane Effect
For Haldane Effect what happens to curve when there is high vs low CO2
High=acidic= shift right
Low=Basic=Left
Temperature Effect
Why is right shift combined relates to?
Excersise (temp, CO2, O2, pH)
Cooperative binding:
if one binds, two binds easier than one, three binds even easier
Carbonic anhydrase reaction
Rev. rxn Carbonic Acid Bicarbonate Ion
CO2 + H2O <-> H2CO3 <-> H+ + HCO3−
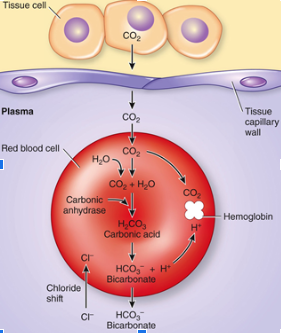
Carbon dioxide transport at tissue level
into rbc > carbinic anhydrase reaction runs> Bicarbonate ion produced and moves into blood-> Cl- taken out of blood (one in one out) -> Hydrogen provides acidic environment for hemoglobin
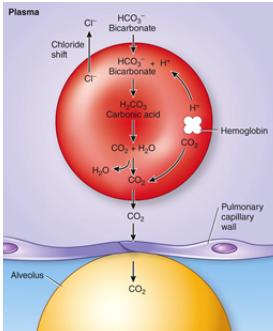
Carbon dioxide transport at lung level
Lungs:CO2 from lung into alveoli
- Bicarbonate into cell >Cl out -> carbonic anhydrase opposite direction to produce CO2 and H2O -> increases PP on blood side -> diffuse over to alveoli
- O2 high into alveolus diffusing in-> displaces H2 and CO2 from hemoglobin