Digestive System - Anatomy and Physiology
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
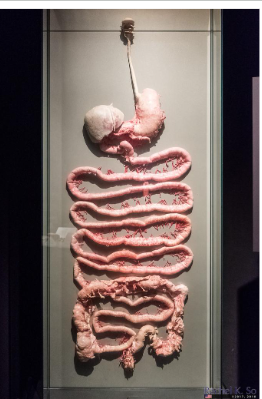
Alimentary Canal/GI Tract
the whole passage where food passes through the body through mouth to anus
includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach (small duodenum, jejunum, ileum) intestine and large intestine/colon (ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid, cecum, appendix), rectum, anus
Accessory Structures
organs that aid in breaking down food
salivary glands, gallbladder, liver, pancreas, peritoneum (mesentery)
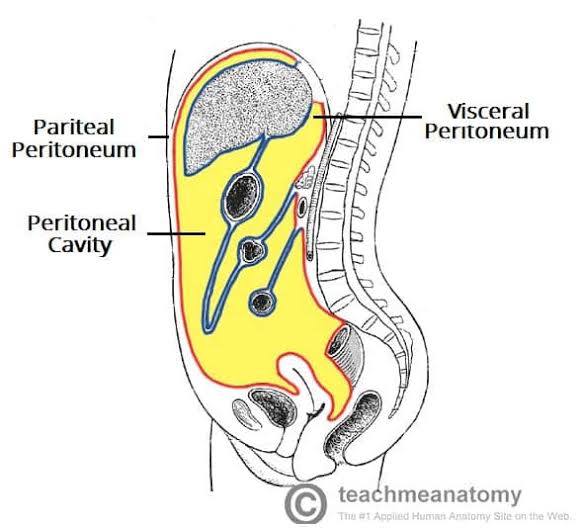
Peritoneum/Mesentary
large structure lining the abdominal cavity
serous membrane (type of membrane it is)
mesentary is folds that attaches to the intestine
Mouth
where digestion starts
responsible for chewing, ingestion, and mechanical processing
Saliva
contains chemical compounds that break down food in mouth
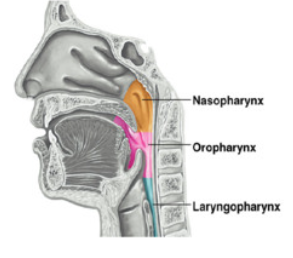
Pharynx
bolus passes through this passageway (bolus is softened food from chewing)
also known as throat
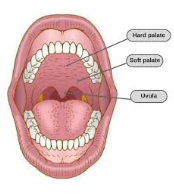
Uvula
folds back to block food from going down nose and into the laryngopharynx
Epiglottis
flap of tissue that closes opening to the larynx and trachea
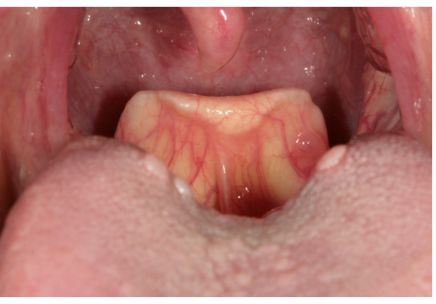
Peristalsis
wave like involuntary muscle movement that helps bolus pass through pharynx and esophagus
Stomach
first place where chemical digestion takes place
food enters through cardiac sphincter (helps prevents food from going back UP into esophagus)
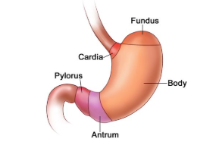
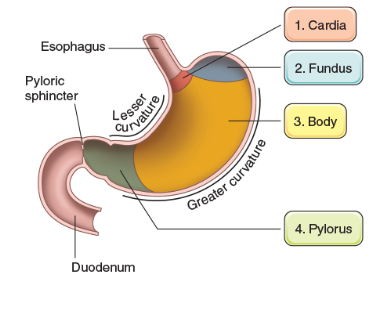
Cardia
attached to both esophagus and stomach and helps produce mucus
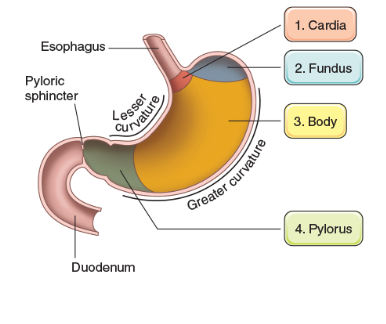
Fundus
located on top of the stomach that produces pepsin and HCl (hydrogen chloride)
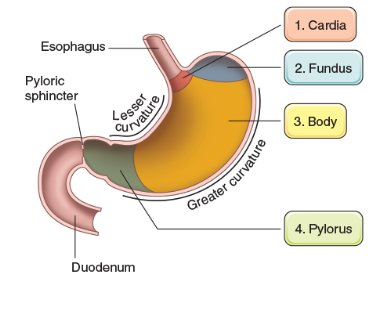
Body
main part of the stomach that helps produce pepsin and HCl (hydrogen chloride)
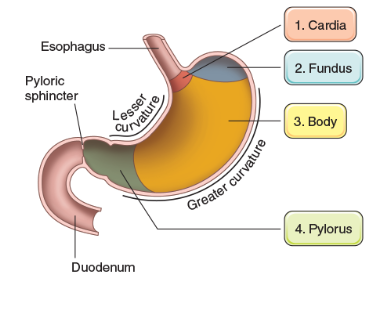
Plyoric
bottom part of stomach that attaches to the duodenum and helps produce mucus
Chyme
partially digested food inside the stomach
made of acid, mixture of food, and mucus
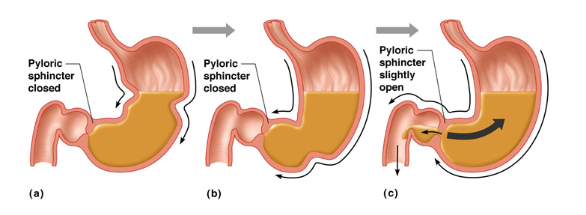
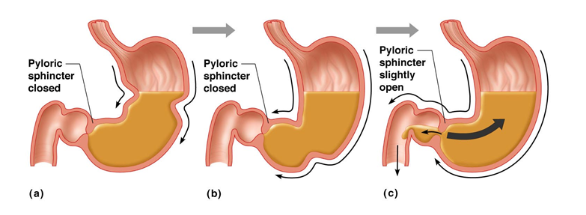
Pyloric sphinter
helps opening region between small intestine and stomach and opens and closes to release chyme into small intestine
Duodenum
where most digestion occurs in small intestine
RECIEVES secretions from gallbladder and pancreas
Jejunum
apart of small intestine
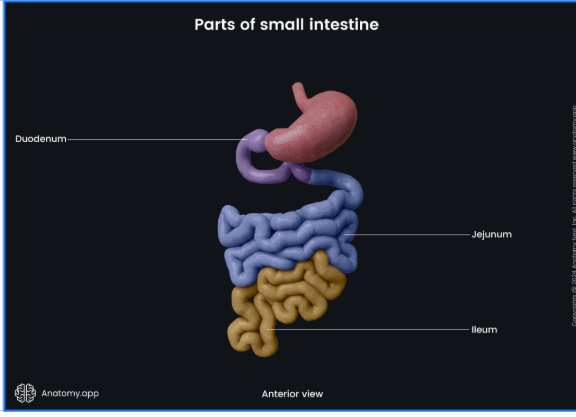
Ileum
last segment of the small intestine
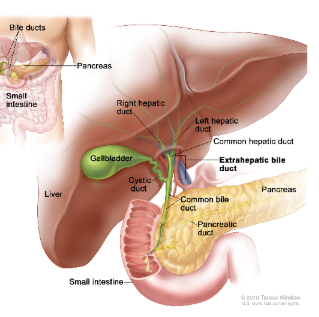
Liver
produces bile salts
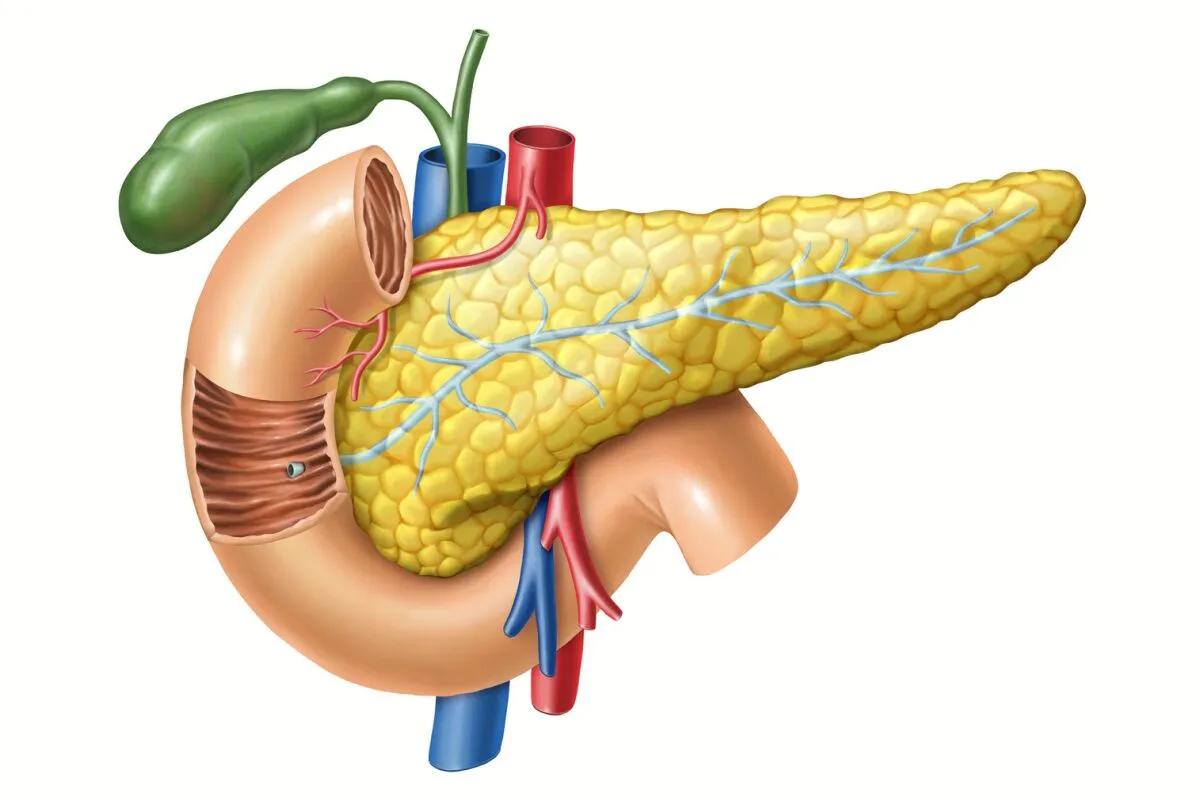
Pancreas
large gland behind stomach (skinny in frogs)
secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum
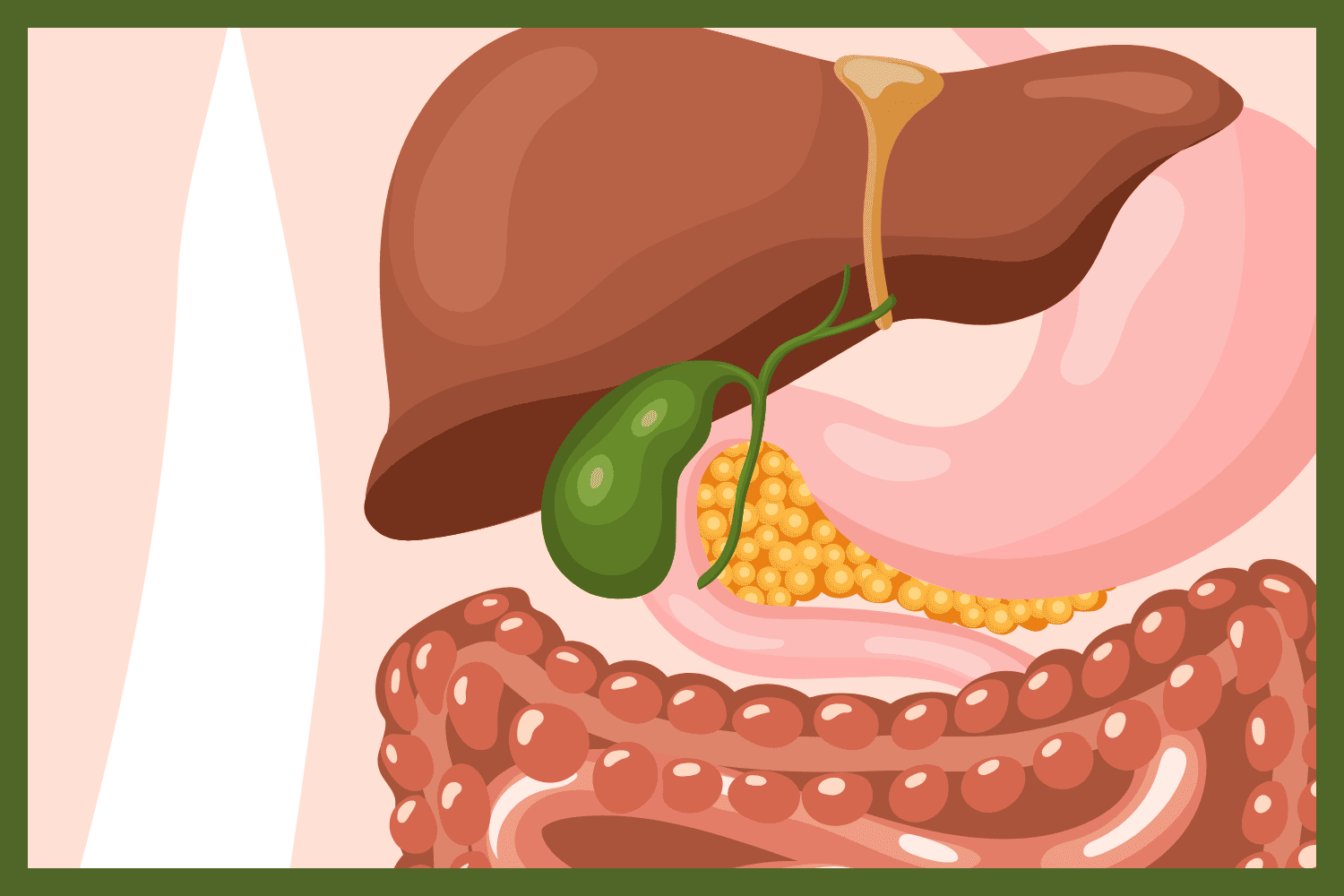
Gallbladder
STORES bile in pouch located under liver
Cecum
pouch in the first part of the large intestine and attached to the “thin” appendix
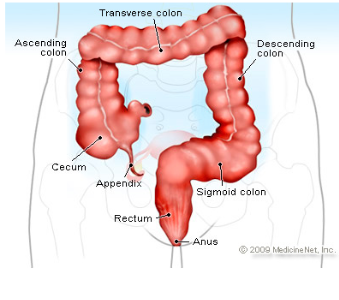
Appendix
dead end pouch that looks like a snake/thin structure attached to cecum
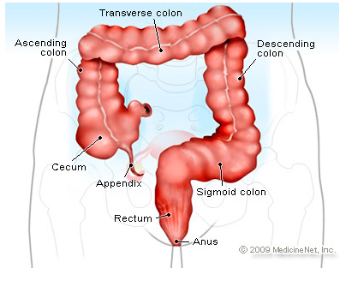
Ascending colon
attached to the cecum and below the right colic flexure
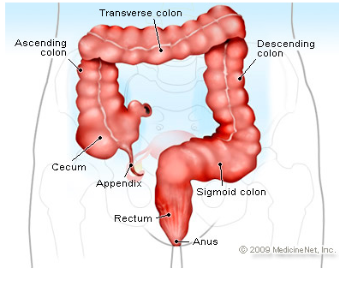
Transverse Colon
above and parallel to the rectum and anus and after right colic flexure
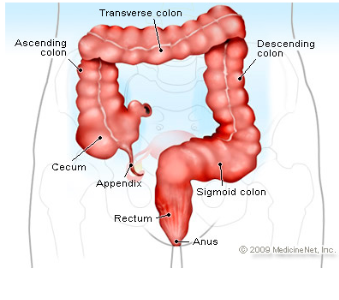
Descending Colon
connected to the left colic flexure and after the transverse colon
going down—> “hence the name DESCENDING!”
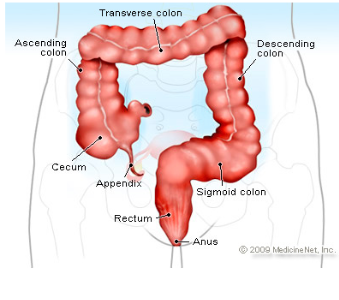
Sigmoid colon
the last part of the large intestine before it reaches the rectum
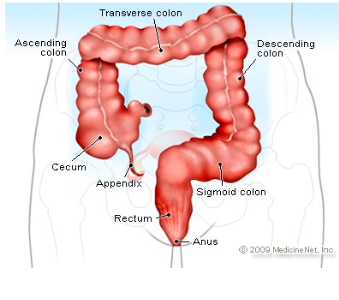
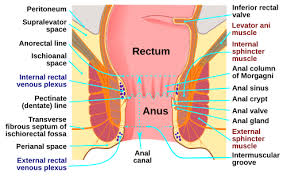
Rectum
final section of large intestine where colon travels through
stores feces
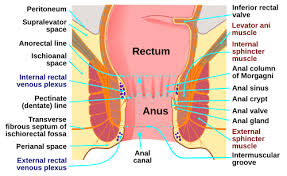
Anus
opening where solid mass leaves the body at the end of the GI tract
Q: Which parts of the alimentary canal or GI tract are specifically functioning to absorb contents and nutrients?
small intestine and stomach
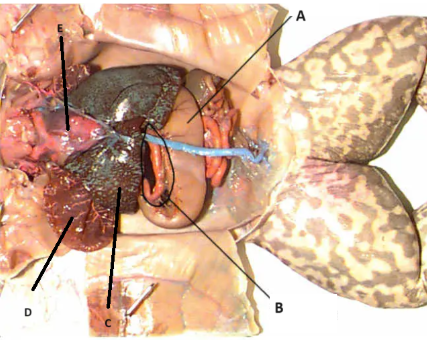
A
stomach
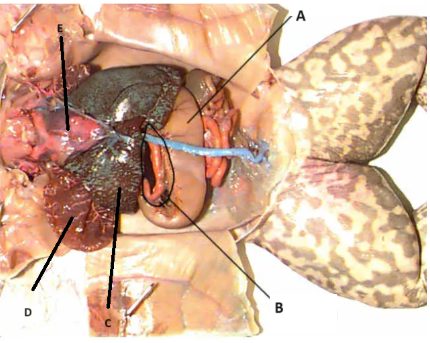
B
Pancreas
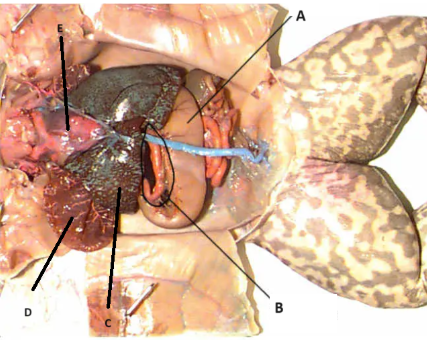
C
Liver
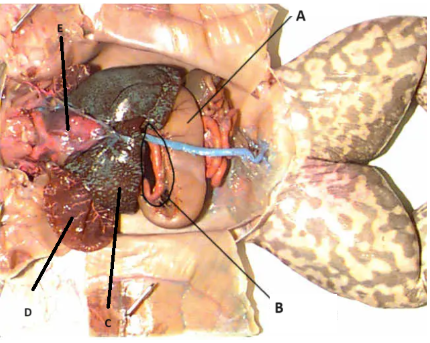
D
Lungs
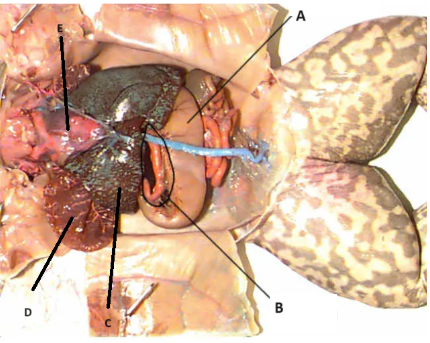
E
Heart
What is the name of the sphincter that regulates the exit of food from the stomach to the duodenum?
Pyloric Sphinter
What is stored in the gallbladder and what is its function?
The gallbladder stores bile and helps break down fat
What is the cloaca?
The cavity at the end of the GI tract
Explain where in the digestive tract proteins are broken down and which enzymes are used. Give 2 examples.
The stomach breaks down the enzyme pepsin and the duodenum breaks down enzymes such as lactase, sucrase, and maltase
The SMALL INTESTINE mainly absorbs…
nutrients

The LARGE INTESTINE mainly absorbs…
water
