Y11 Biology Subject Matter
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is the cell theory?
All organisms are made of cells. The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of life, and all cells come from other cells.
What is the hierarchical organisation of the cell structural levels? (order molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, and systems from smallest to largest)
Molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems.
What are 3 differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane bound organelles, are significantly smaller than eukaryotes, and usually have a single circular chromosome. Whereas, eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles and have linear chromosomes.
What are 3 similarities between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Both have cell membranes, genetic material, and ribosomes.
What is the role of the chloroplast?
Site of photosynthesis.
What is the role of the mitochondria?
Site of cellular respiration, which results in energy (ATP) production.
What is the role of the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
A transport system for substances e.g. proteins through the cytoplasm.
What is the role of the ribosomes?
Site of protein production.
What is the role of the golgi apparatus?
Proteins are packaged into vesicles that are ready for use.
What is the role of the vacuoles?
Storage site of the cell.
What is the role of the cell membrane?
Provides a selectively permeable barrier that controls what enters and leaves the cell.
What is the role of the nucleus?
Serves as the control center of the cell, contains the cell's genetic material (DNA).
What is the role of the centrioles?
Direct chromosome movement during cell division.
What is epithelial tissue?
Tissue that covers external or lines internal structures, where the cells are tightly packed. Involved in absorption, secretion, and protection.
What is connective tissue?
Tissue where cells are loosely packed in obvious extracellular matrix. Involved in connecting, supporting, and storage.
What is nervous tissue?
Tissue where cells are irregularly shaped. Involved in sensing stimuli and transmitting signals.
What is muscle tissue?
Tissue where cells are elongated and change shape (contractile). Involved in movement.
What is the formula for diameter of field of view?
field number (18) / objective magnification.
What is the magnification of the scanning objective?
x4
What is the magnification of the low power objective?
x10
What is the magnification of the high power objective?
x40
What is the formula for real life size?
Diameter FoV (um) / no. of cells that fit across FOV
What are light microscopes?
Use light to produce image, specimen can be alive or dead, relatively small, total magnification (1000 - 1500x), and relatively poor resolution.
What are electron microscopes?
Use electrons in a vacuum to focus image on a photographic plate or a fluorescent screen, specimen must be dead, relatively large total magnification (100,000 – 250,000x) and very good resolution.
What is the formula for determining the magnification of biological drawings?
size of drawing (um) / RLS (um)
How do you calculate total magnification?
eyepiece power (10X) x the objective used (4X, 10X, or, 40X)
What is photosynthesis?
An enzyme-controlled series of chemical reactions that occurs in the chloroplast in plant cells and uses light energy to synthesise organic compounds (glucose).
What is the word equation for photosynthesis?
carbon dioxide + water —> glucose + oxygen
What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H20 —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
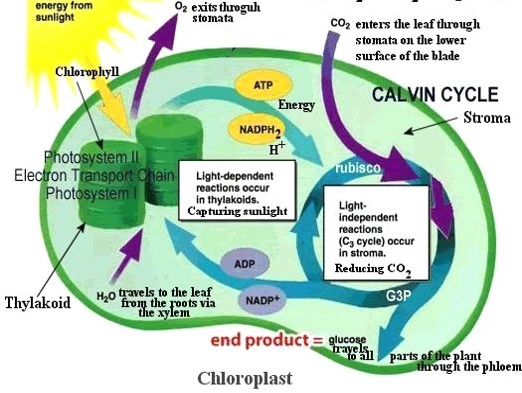
What is the light-dependent reaction involved in photosynthesis?
Requires the presence of light, occurring in the gronum inside chloroplasts. Here pigments (e.g. chlorophyll a and b) absorb sunlight energy and use this energy to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen, and produce some ATP molecules.
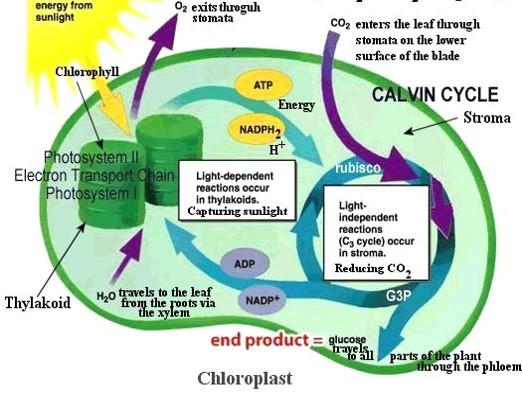
What is the light-independent reaction involved in photosynthesis?
Does not require light, occuring in the stroma inside chloroplasts. Here ATP is used to combine carbon and oxygen (from carbon dioxide) with hydrogen (from water) to produce 3C organic molecule called triose phosphate. This involves a complex series of reactions called the Calvin Cycle. An important enzyme called Rubisco is used in this process. Triose phosphate molecules are then combined together to form glucose
How does levels in carbon dioxide impact the rate of photosynthesis in organisms?
As levels of this substance increase, the rate of photosynthesis increases. This is because carbon dioxide is a reactant for this process.
How does light intensity impact the rate of photosynthesis in organisms?
As levels of this increase, the rate of photosynthesis increases. This is because above a certain light intensity level chlorophyll molecules become ‘saturated’ (ie. cannot absorb higher levels of solar energy).
How does temperature impact the rate of photosynthesis in organisms?
As levels of this increase, the rate of photosynthesis increases. However, above a certain temp the rate of photosynthesis decreases. This is because at high temps, the plant stroma closes which limits gas exchange for photosynthesis.
How does water impact the rate of photosynthesis in organisms?
Low water levels will cause the plant stroma to close which limits gas exchange for photosynthesis.
How does changes in light colour impact the rate of photosynthesis in organisms?
Because plants' light-absorbing pigments, like chlorophyll, primarily absorb specific wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum. Red and blue light are most effectively utilised, while green light is often reflected rather than absorbed