Cells Test
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Cell Theory
All organisms consist of cells, All cells come from pre-existing cells through cell division, and Cells are the basis of life
Prokaryotic Organisms
Organisms made up of one cell (bacterial cells)
Eukaryotic Organisms
Organisms made up of more than one cell
Prokaryotic distinctive features
No nucleus, No membrane-bound organelles, DNA in a single circular chromosome
Eukaryotic distinctive features
Nucleus present & Membrane-bound organelle
Animal cells distinctive features
No cell wall, no chloroplast, no vacuole
Plant cells distinctive features
Cell wall, Chloroplast, Vacuole
Cell Wall Structure
Bilayer structure
Cell Wall Function
To provide structural support, shape, and protection
Cytoplasm Structure
A thick solution of water, salts and proteins which fills the cell
Cytoplasm function
To hold the cell’s internal components in place
Ribosomes Structure
Intercellular structure made of both RNA and protein
Ribosomes Function
To synthesise proteins in the cell
Nucleus Structure
Includes the nuclear envelope, nucleolus and nuclear matrix
Nuclear Envelope
Separates the contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm
Nucleolus
Spherical structure which produces the cells ribosomes
Nucleus Function
To store the cell’s DNA
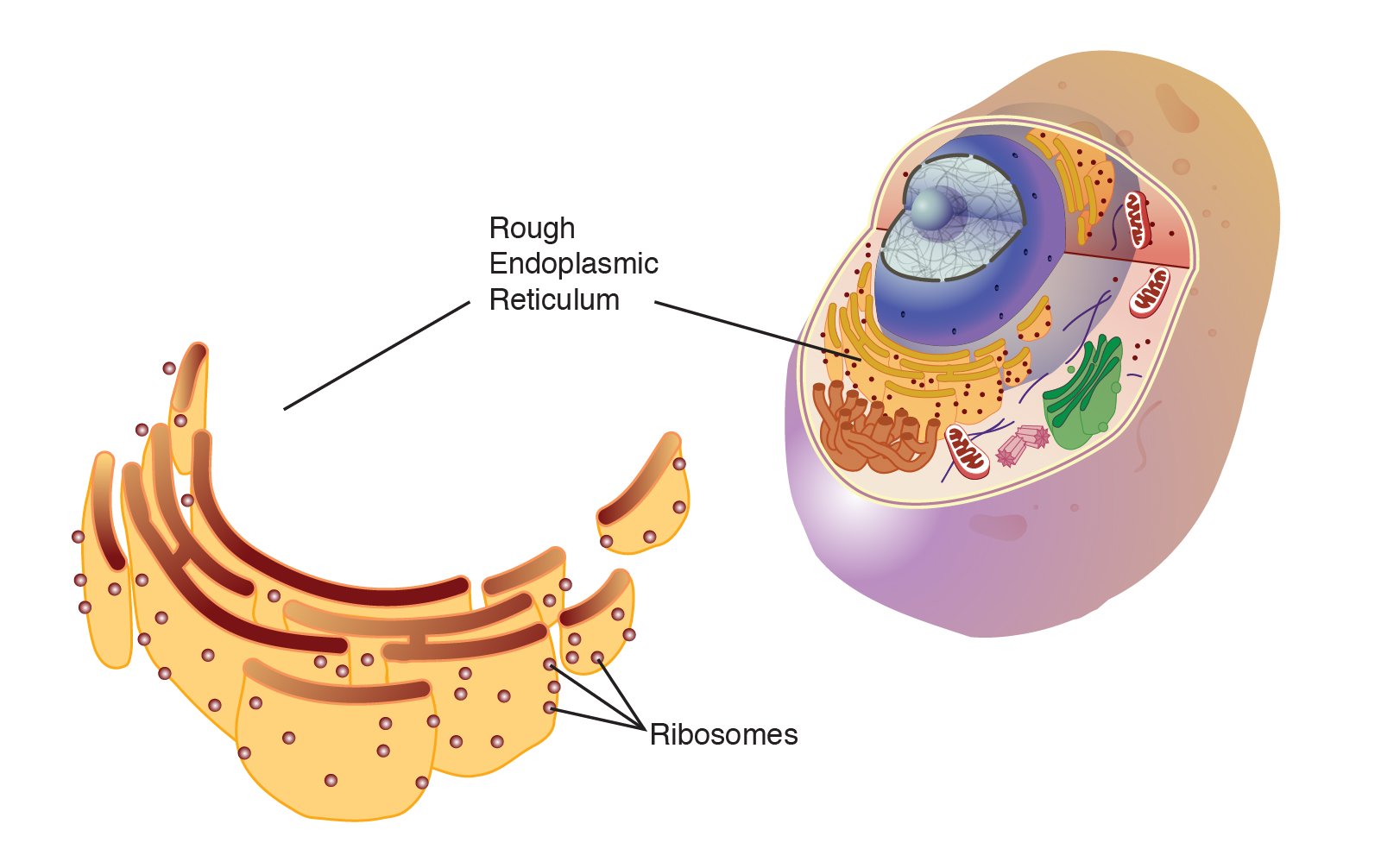
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure
Ribosomes and composed of many tissue folds (SA:V) for chemical reactions to take place.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Function
To produce proteins vital for the cell to function
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure
A tubular membrane vesicles with no ribosomes present
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Function
To synthesize essential lipids such as phospholipids and cholesterol
Golgi Body Structure
Central intracellular and membrane-bound
Golgi Body Function
Helps process and package proteins and lipid molecules
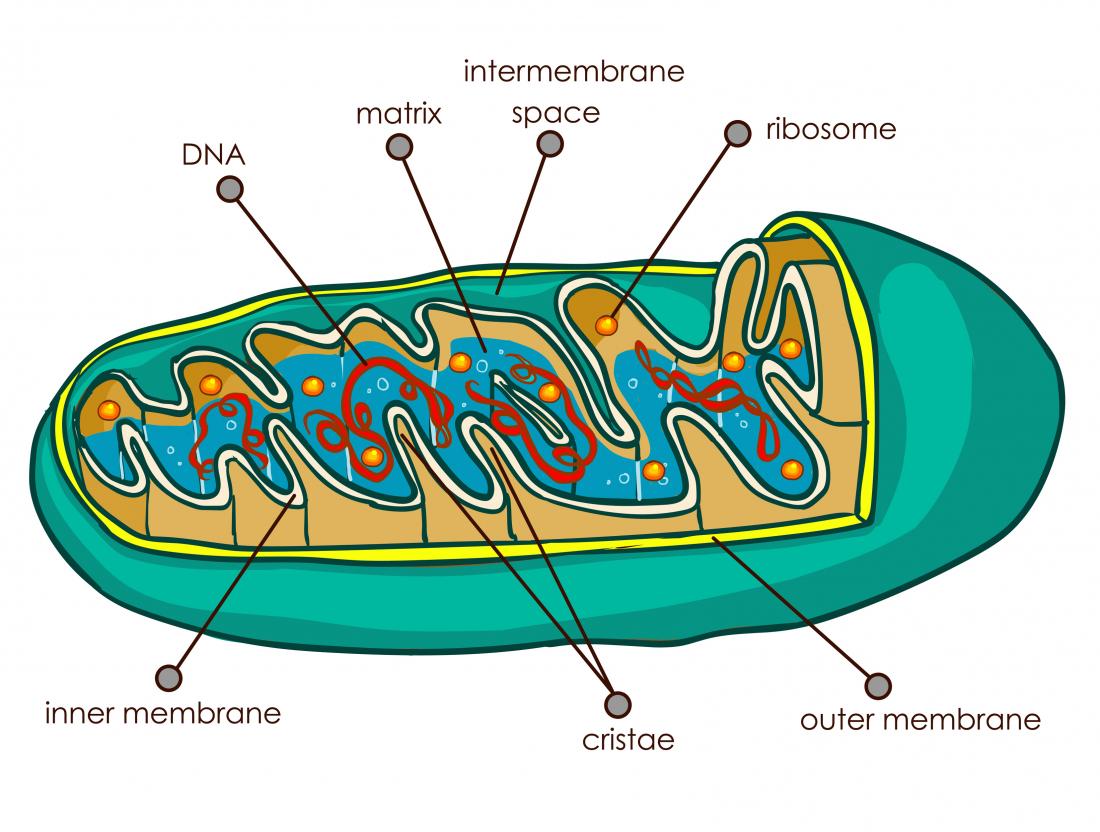
Mitochondrion Structure
Double-membrane bound, with outer and inner membrane which forms cristae and within the matrix
Mitochondrion Function
To generate ATP energy which is necessary for the cell’s survival
Vacuole Structure
Membrane bound sacs
Vacuoles Function
To store the cells materials
Chloroplast Structure
Large organelles with a double membrane called the chloroplast envelope
Chloroplast Function
To produce glucose and water which is used for cellular respiration
Purpose of the cell division
To produce two identical daughter cells to allow growth and repair
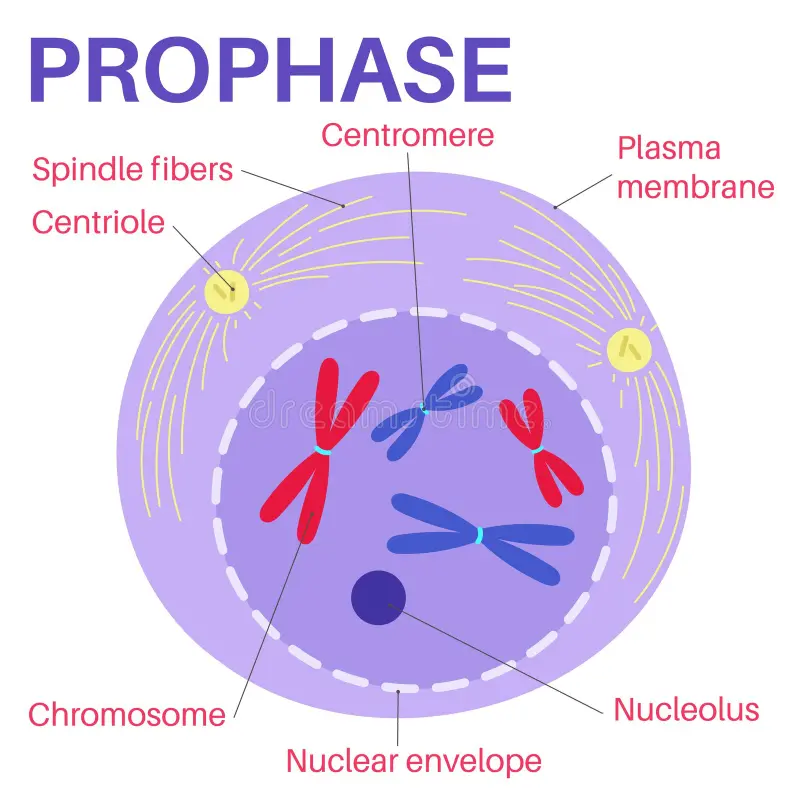
Prophase
Cell membrane disintegrates, chromosomes condense, centrosomes become spindle fibers
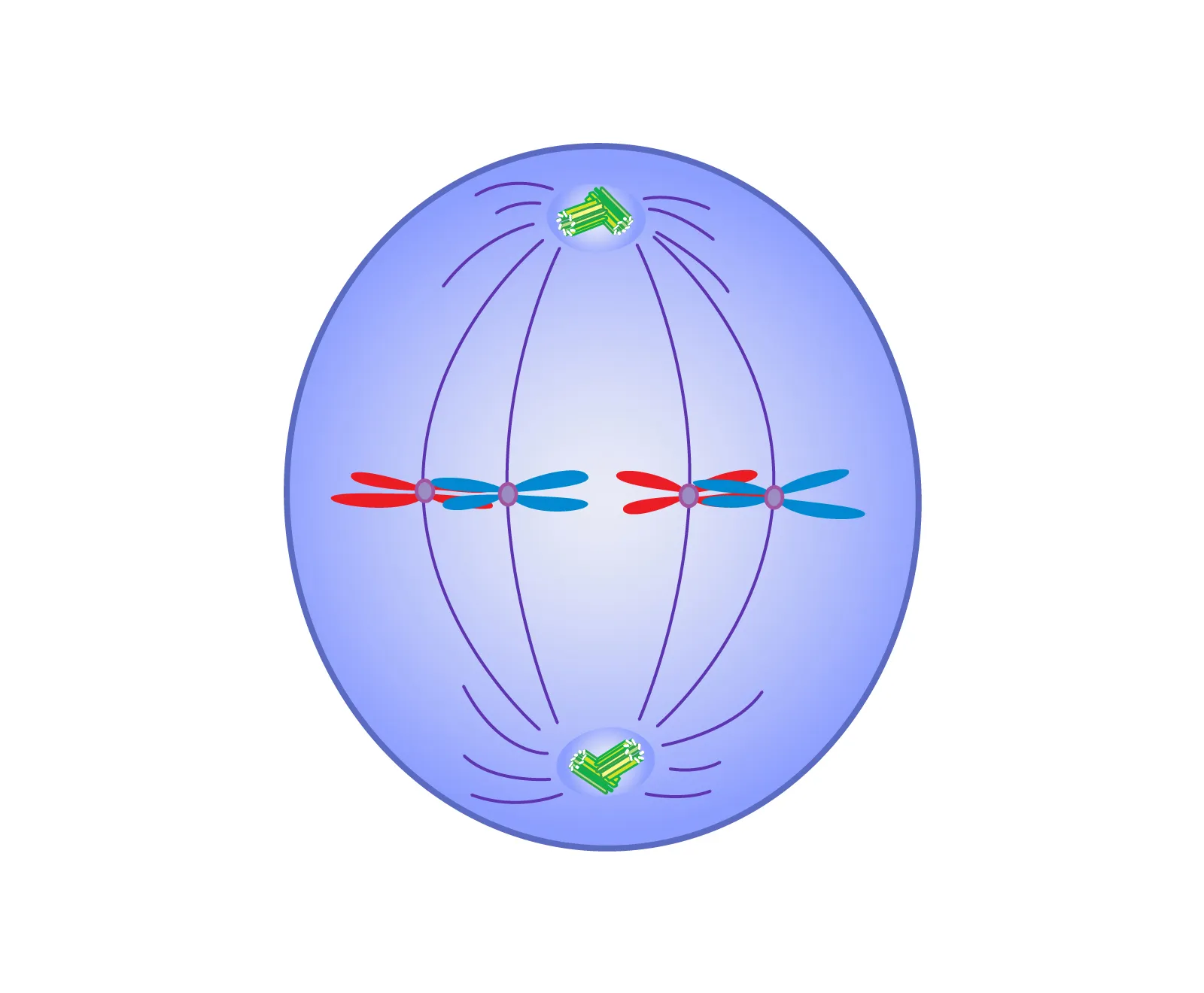
Metaphase
Through the spindle fibers, the chromatids line up the cell’s midline
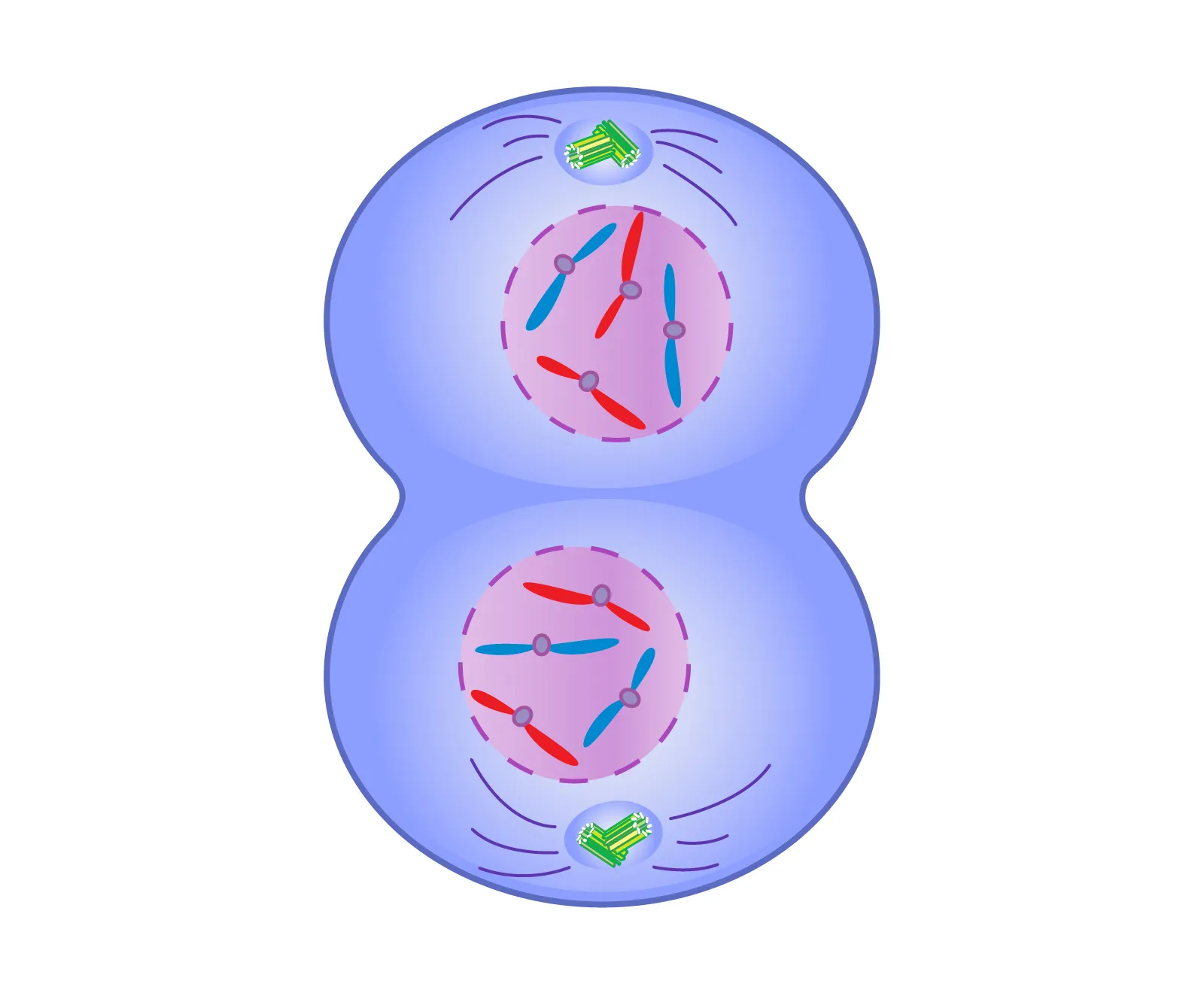
Telophase
The spindle fibers disappers and the nucleus begins to form
Cytokinesis
The physical process of cell division, cytoplasm is divided
Interphase
Cell Growth in G1, DNA replication in S phase, Preparation for Mitosis in G2
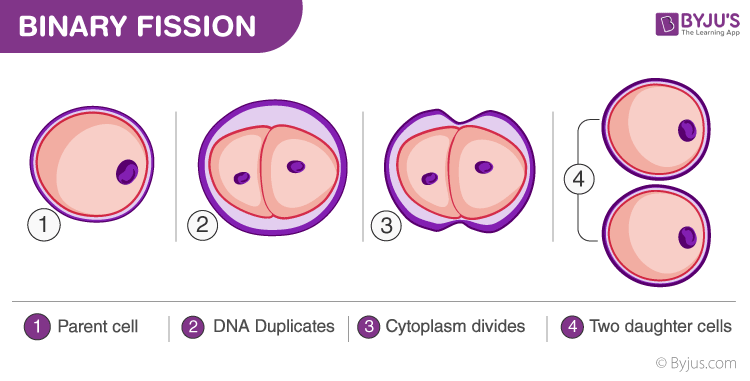
Binary Fission in prokaryotic cells
The process of one bacterial cell dividing into two
Equation of Photsynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O ~ C6H12O6 + 6O2
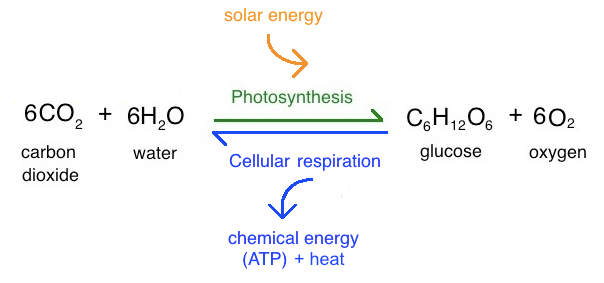
Process of Photosynthesis
Sunlight is captured, using water and carbon dioxide to create glucose and oxygen used within the cell
Equation of Cellular Respiration
C6H12O6 + O2 ~ 6CO2 + 6H2O
Process of cellular respiration
The glucose synthesized from photosynthesis is used to create ATP which when broken, releases energy
Equation of Fermentation
C6H12O6 ~ 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Process of Fermentation
Process which converts glucose to anaerobically release energy
Cell Membrane Structure
Fluid mosaic model made of a phospholipid bilayer with phosphate heads and lipid tails
Glycoproteins
A molecule made of proteins and carb chains
Glycolipids
Lipids with a carbohydrate, which maintain the cell membrane
Cholesterol
Ring structure, which makes the membrane thicker and impenetrable
Passive Transport
Transport which does not require energy to move substances across the cell membrane
Simple Diffusion
The process where molecules diffuse through the semi-permeable membrane down a concentration gradient (hi to low)
Facilitated Diffusion
The diffusion of solutes through carrier proteins due to charge, polarity or molecular size
Osmosis
The movement of molecules, down a concentration gradient from high to low concentration
Hypertonic Solution
Solution has higher solute concentration
Hypertonic Net movement of water
Water will move out of the cell
Isotonic Solution
Water outside the cell = Water within the cell
Isotonic net movement
No net movement of water will take place
Hypotonic Solution
Low Solute and High water concentration compared to the cell
Hypotonic Net Movement of Water
Water will move into the cell, causing it to become turgid
Active Transport
Transport of molecules across a cell membrane which requires energy
Endocytosis
The ingestion of large particles into the cell
Exocytosis
The process of moving large molecules out of the cell