L5: Immune Cell Communication and Activation: Cytokines
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering cytokine and receptor families, PRR-mediated cytokine production, TNF and Interleukin-1 signaling, other interleukins, cytokine functions, immune cell differentiation, pro-inflammatory, anti-inflammatory, and reparative cytokines.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What key processes are modulated by cytokines in immunity?
Immune cell maturation/differentiation
Stimulating cell adhesion during recruitment
Inflammation
ROS/NO production
Degranulation, apoptosis, and resolution/repair.
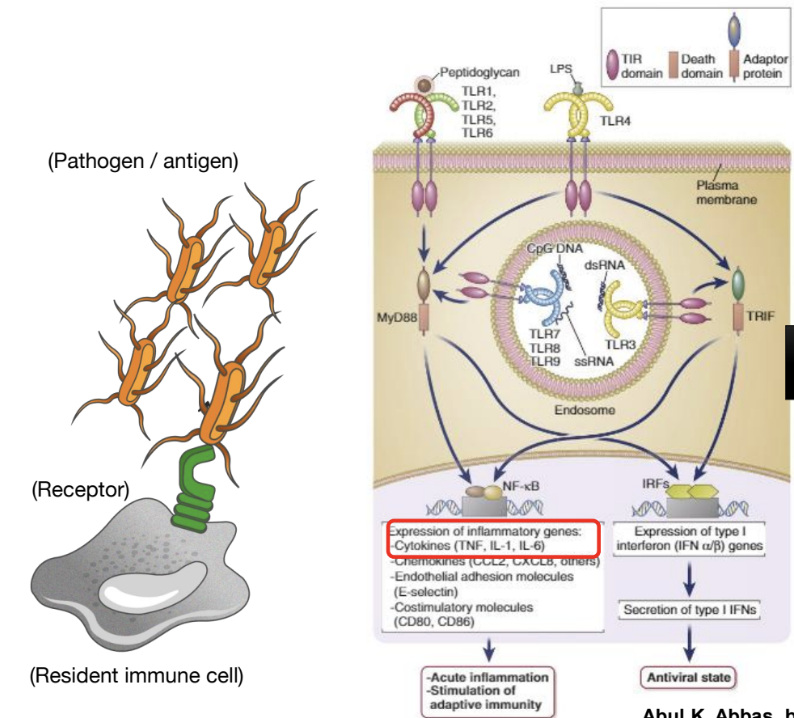
Toll-like receptors induce ______ responses which are _________
NF-kB responses , which are transcription factors that regulate immune gene expression.
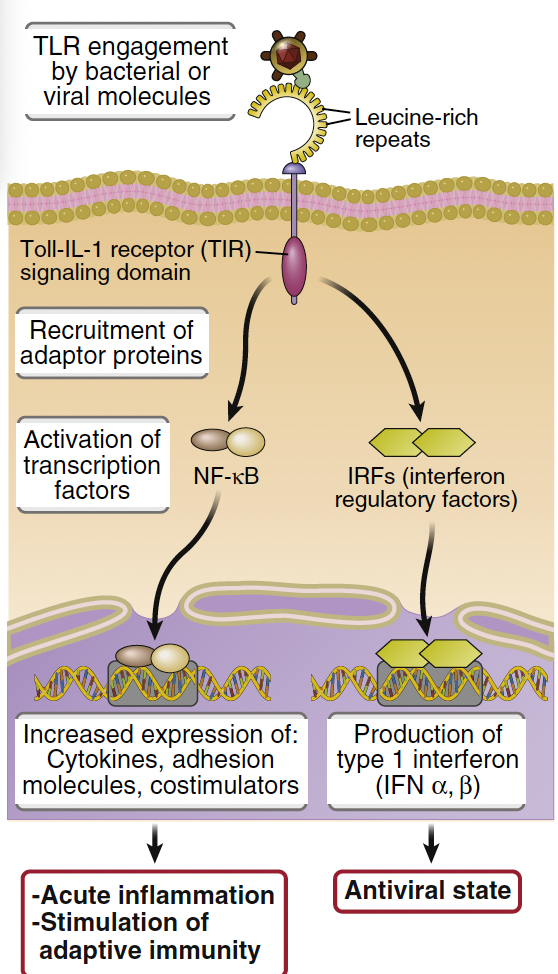
What is Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) and its role in immune response?
NF-κB is a master regulator of the immune response, constitutively bound to IκB in the cytoplasm.
TLR engagement induces IκB degradation, allowing NF-κB subunits with transcriptional activity to move to the nucleus
This induces inflammatory cytokines like TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6.
What are 3 key inflammatory cytokines?
TNFα
IL-1β
IL-6
What are cytokines?
A group of proteins that regulate immune-related processes that ‘communicate' to immune cells on what functions to perform:
• Maturation of immune cells i.e DC from their naïve or progenitor counterparts.
• Activation of inflammatory responses.
• Induction of integrin and adhesion molecule expression.
• Promoting apoptosis of damaged, old and also cancer cells.
• Promoting resolution of inflammation.
• Induction of immune “memory”.
What are the key functions and receptors of Interleukins (ILs)?
Interleukins are involved in;
Immune cell activation & maturation
Promotion of cell adhesion
Resolution of inflammation
Binding to ILRs (e.g., IL-1R, IL-4R, IL-6R).
In innate immunity what are the main sources of cytokines?
dendritic cells, macrophages, and mast cells that are activated by recognition of microbes,
Recognition of PAMPs like GN cell wall component LPS and peptidoglycan by TLRs + recognition of microbial nucleic acids by TLRs, RLRs, and CDSs are powerful stimuli for cytokine secretion by innate immune + some epithelial cells.
Cytokines are secreted in ________ in response to an external stimulus and bind to _________ on target cells
small amounts, bind to high affinity receptors
How can cytokines act in a paracrine, autocrine and endocrine manner?
Paracrine signaling affects nearby cells
Autocrine signaling acts on the cells that secrete them
Endocrine signaling involves cytokines entering the bloodstream to target distant cells i.e. by large amounts of activated MP and DC producing large amounts of cytokines
What are the key functions and receptors of the TNF superfamily (TNFSFs)?
TNFSFs mediate:
Inflammation
Immune cell adhesion, fever, pain
Leukocyte production
Apoptosis
Binding to TNFSFRs (e.g., TNFR1 and 2, HVEM, LTbR, Fn14).
What are Hematopoietins?
Cytokines with the ability to stimulate the differentiation of immune cells at different stages (e.g., IL-2, IL-3, GM-CSF, M-CSF, G-CSF, TSLP).
What are Chemokines (review) ?
Chemotactic cytokines that attract immune cells and strengthen integrin binding, binding to CCRs and CXCRs (e.g., CCL2, CCL5, CXCL1, CXCL8).
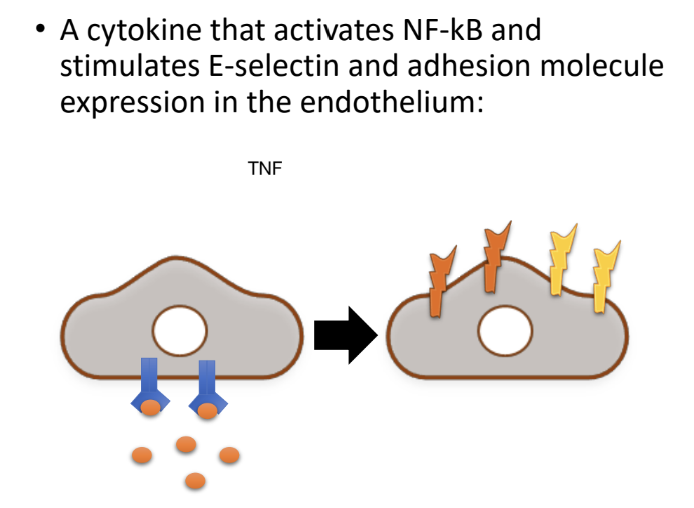
What is TNF's main role in inflammation?
TNF is an early-response cytokine mainly produced by MPs that is key in initiating inflammation:
Promoting fever and pain
Stimulating leukocyte production in bone marrow
Facilitating immune cell migration e.g induction of E-selectin and adhesion molecules on endothelium.
Induces (other) cytokine and chemokine production,
Promotes apoptosis of cancer cells.
What are the two TNF receptors and their signaling outcomes?
TNFSFR1A (TNFR1) : Engagement can mediate apoptosis or inflammation (NF-κB or caspase activation)
TNFSFR1B (TNFR2) : Engagement primarily drives inflammation BUT NOT apoptosis.
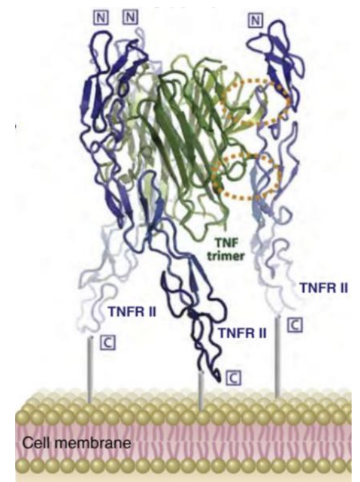
What can high concentrations of TNF-a lead to?
Can lead to septic shock, characterised by widespread inflammation, low blood pressure, increased vascular permeability, and potential organ failure.
What are Anti-TNF therapies?
(one of the 1st biologics developed)
Medications designed to inhibit the action of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), reducing inflammation and promoting remission in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease.
Done by monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins that block TNF-TNFR interaction
what are monoclonal anitbodies?
Lab-made molecules engineered to bind to specific antigens, often used in therapies to target diseases.
They are produced from identical immune cells that are clones of a unique parent cell.
What are Interleukin-1 (IL-1) subtypes and their general roles?
2 subtypes: IL-1α and IL-1β, produced by MPs, endothelial, and epithelial cells.
Bind to IL-1R1, are early response pro-inflammatory cytokines, promote the release of other cytokines, activate immune cells, and are thought to promote iNOS expression.
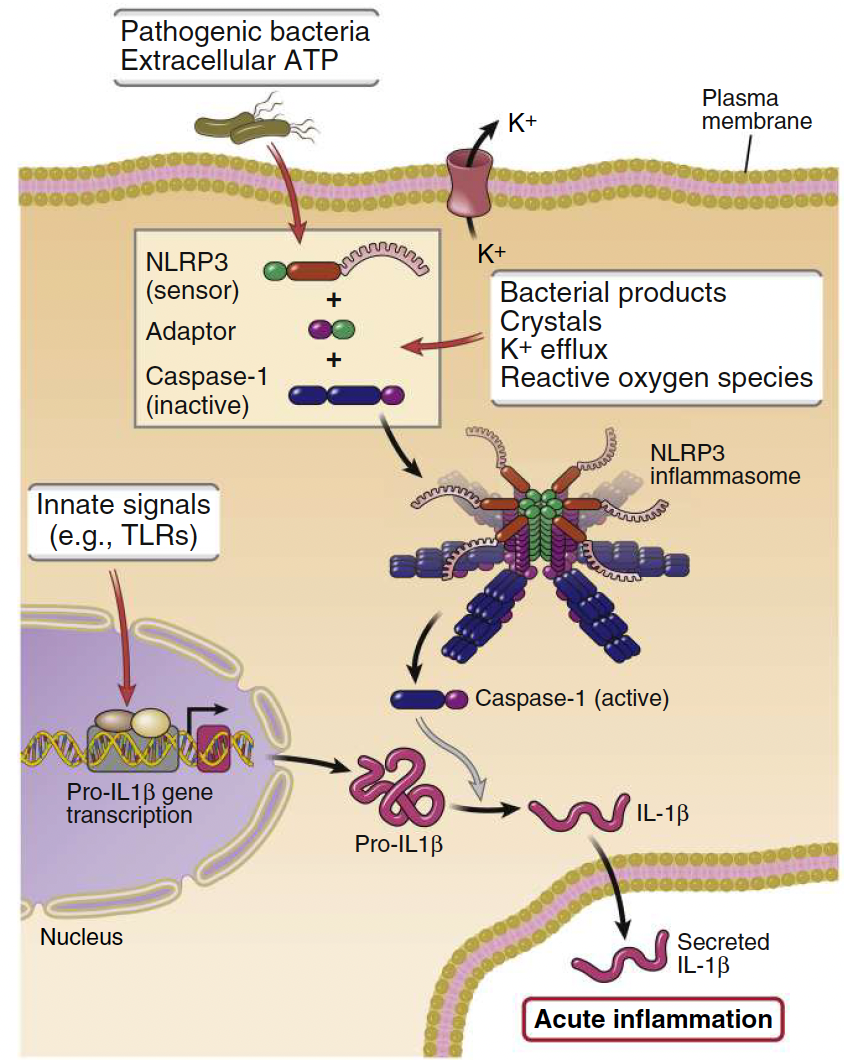
How is Interleukin-1 (IL-1) activated?
An inactive precursor (pro-IL1β) must be cleaved by caspase-1 for activation.
Facilitated by inflammasomes, which processes pro–interleukin-1β (pro–IL-1β) to active IL-1.
The synthesis of pro–IL-1β is induced by various PAMPs or DAMPs.
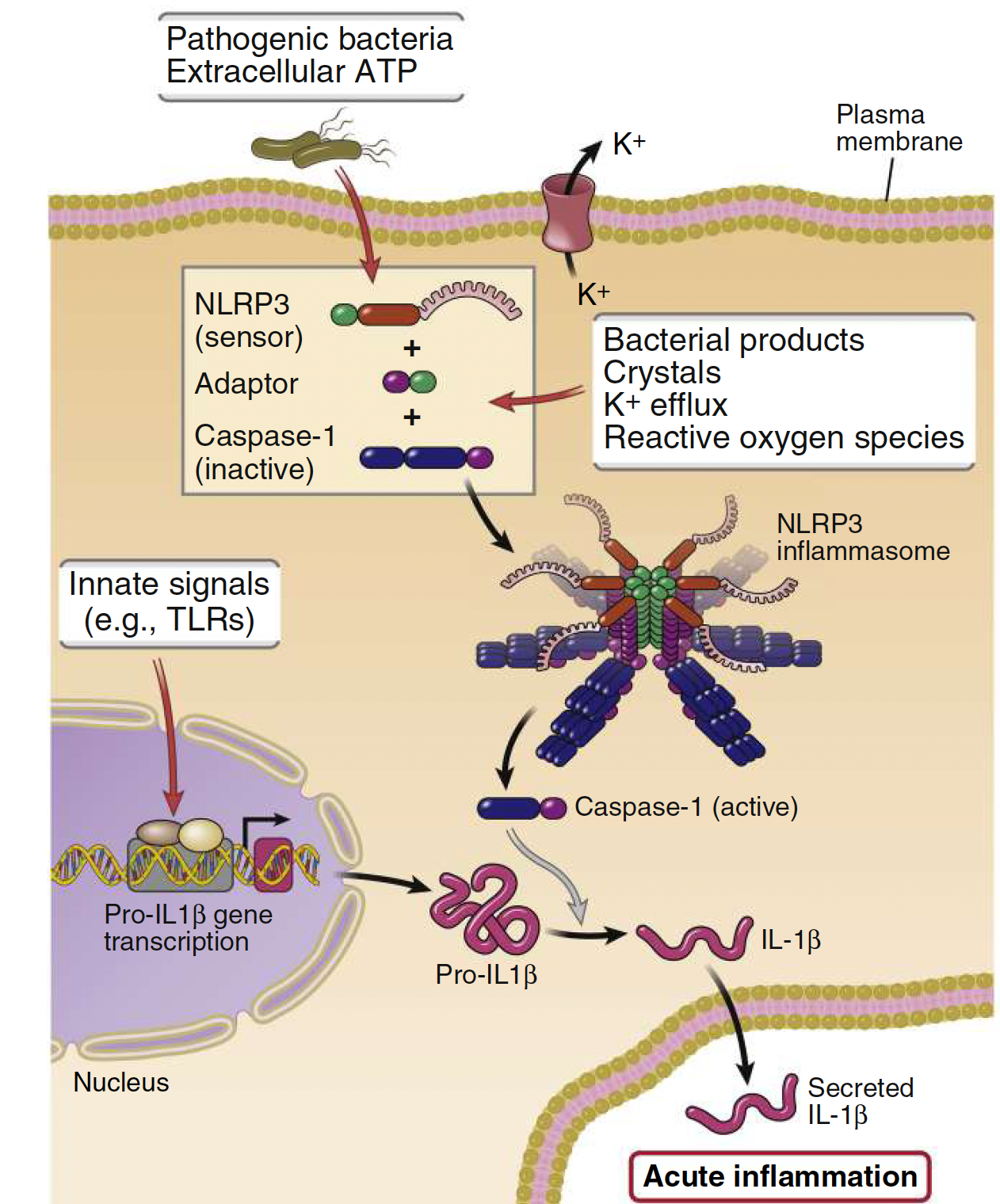
What are inflammasomes?
Protein complexes that form in the cytosol in response to infection or injury and trigger IL-1 proteolytic cleavage:
• Formed of adaptors (NLRPs) and caspase-1.
• NLRPs are NOD-like receptors.
• ATP, Flagellin or LPS (PAMPs) can trigger inflammasomes resulting in secretion of active IL-1
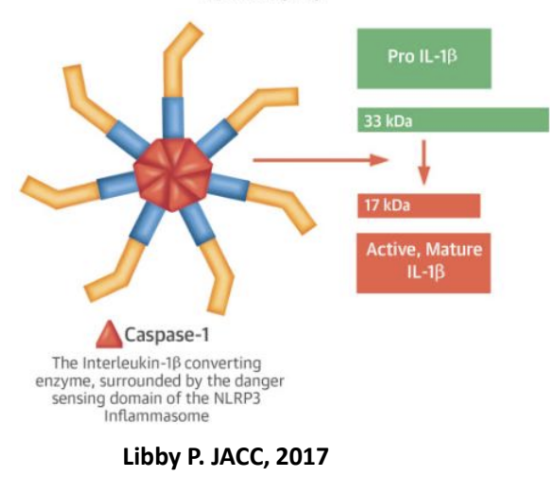
Cleaved ___ binds the __ to trigger inflammation
IL-1β binds the ILRI
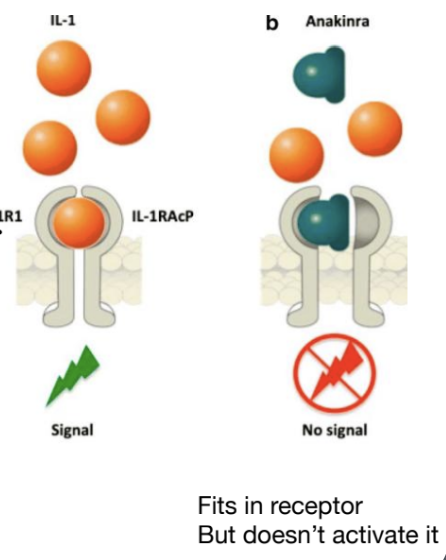
What is Anakinra and its mechanism of action?
Anakinra is a drug developed to block the IL-1 pathway by binding to IL-1RI without activating signalling, thus treating inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Why are interleukins considered pleiotropic?
pleiotropic = affecting multiple cell types and functions because they can influence various immune responses and cellular activities.
Name some interleukins examples that reflect their pleiotropic nature:
IL-3 and IL-2 promote innate and adaptive immune cell maturation
IL-5 promotes eosinophil activation and degranulation
IL-12 activates the adaptive immune system.
Colony-stimulating factors (CSFs)
Cytokines that promote the expansion and differentiation of bone marrow progenitor cells.
Essential for the maturation of RBC, granulocytes, monocytes, and lymphocytes.
Examples include granulocyte-monocyte colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), and IL-3.
Which cytokines are involved in the development of granulocytes?
G-CSF and GM-CSF are involved in the development of granulocytes.
*G stands for granulocyte.
CSF stands for colony-stimulating factor.
M stands for macrophage.
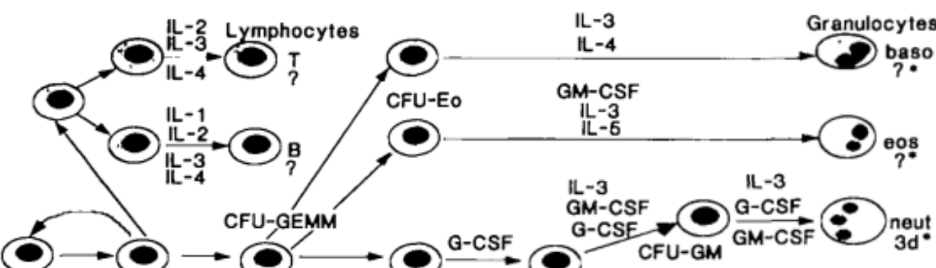
Which cytokines promote the transition from progenitor to monocyte?
GM-CSF and M-CSF promote the transition from progenitor to monocyte.
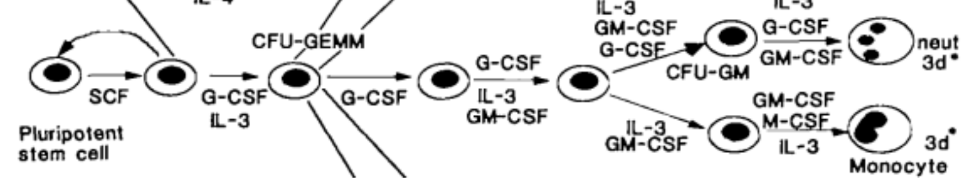
Which cytokines promote the transition of naive T lymphocytes to mature T lymphocytes?
IL-2 and IL-3 promote the transition of naive T lymphocytes → mature T lymphocytes.
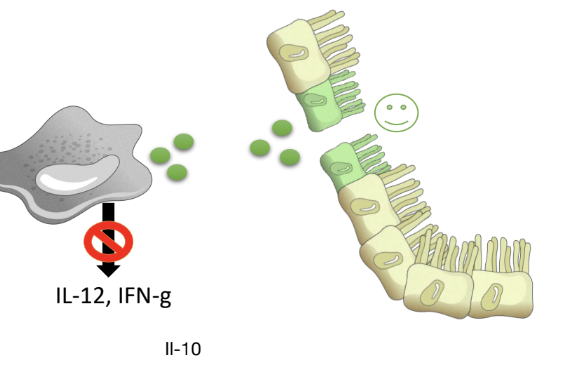
What is the role of IL-10 in immunity?
IL-10 is a cytokine produced by MPs with profound anti-inflammatory effects, binding the IL-10R
Inhibits production of some pro-inflammatory cytokines,
Inhibits antigen presentation by MPs and DCs
Promotes epithelial barrier repair and differentiation.
Mutations of IL-10 and IL-10R are strongly linked to ____
Colitis: infants with such mutations develop colitis before the age of 1
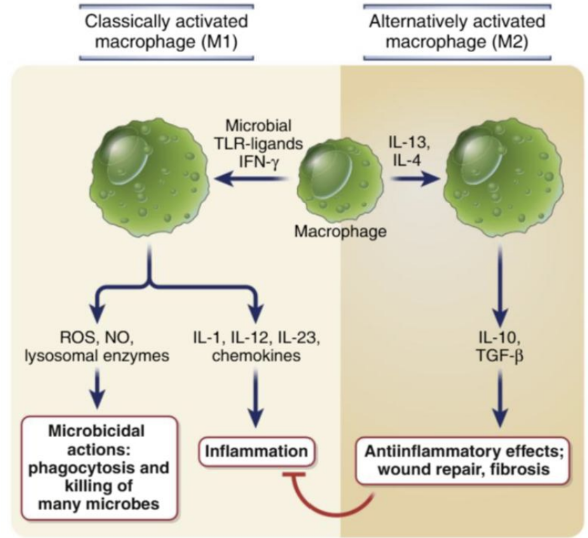
How can a MPs function be switched from the classically activated state (M1) to repair?
By increasing IL-10 and TGF-β1 production.
*Need to differentiate into an anti-inflammatory profile
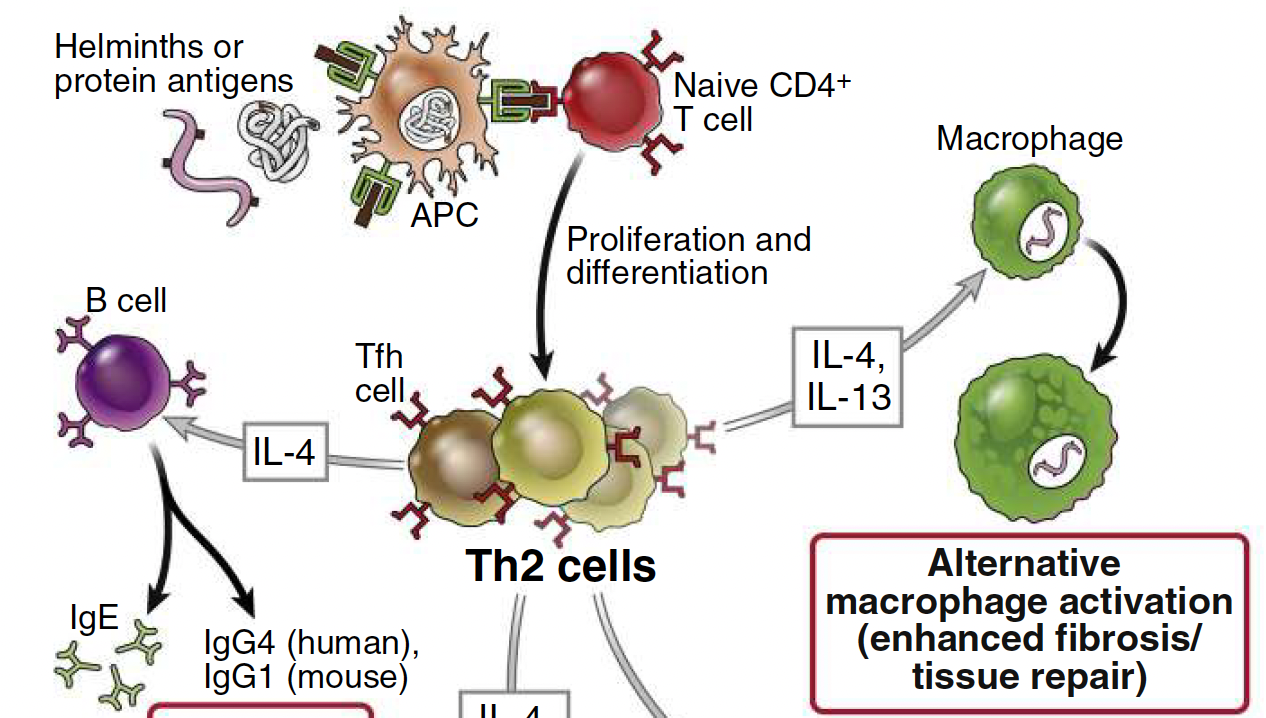
What cytokines can induce an alternative anti-inflammatory macrophage activation state?
IL-4 and IL-13 (produced by Th2 cells) can induce an alternative anti-inflammatory macrophage activation state and promote tissue repair via secretion of growth factors that act on fibroblasts to increase collagen synthesis and induction of fibrosis.
Which receptor recognizes the bacterial product LPS?
TLR4 - a PRR
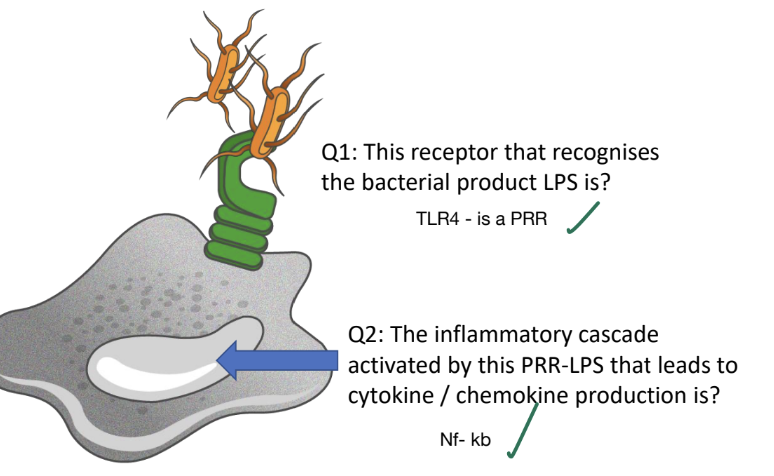
Which inflammatory cascade is activated by PRR-LPS engagement leading to cytokine/chemokine production?
NF-κb pathway is activated, resulting in the transcription of cytokines, adhesion molecules and costimulators
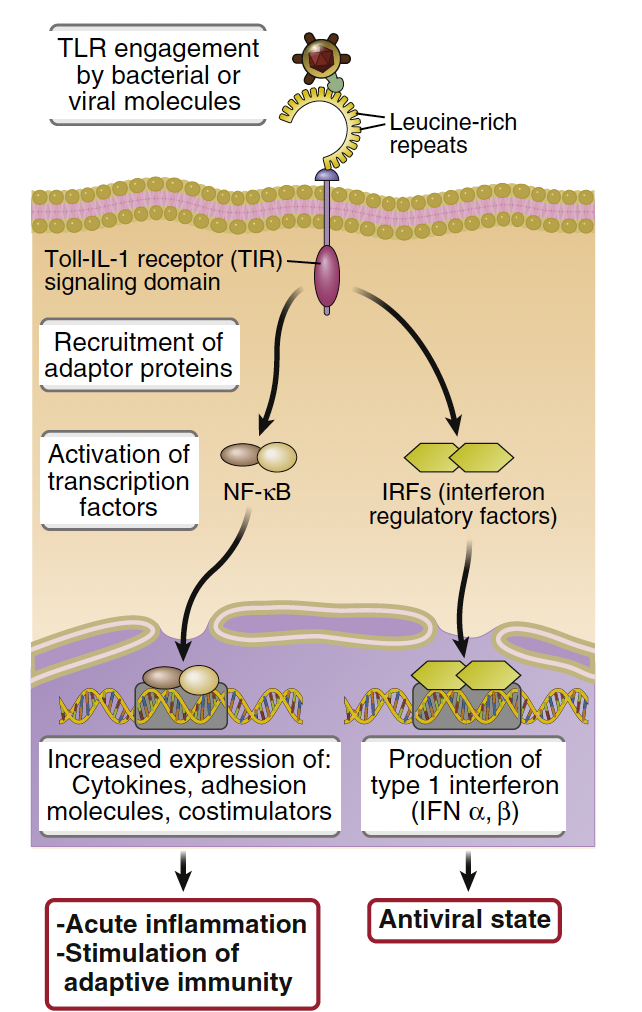
Name two early response cytokines produced during initial immune cell activation by a pathogen.
IL-1 and TNF-α are key early response cytokines that promote inflammation and recruit immune cells.
Which cytokine activates NF-κB and stimulates E-selectin and adhesion molecule expression in the endothelium?
TNF α is the cytokine that activates NF-κB
A cytokine that is produced as a precursor and has to be cleaved by inflammasomes to be released:
IL-1β is a cytokine that is produced as a precursor and has to be cleaved by inflammasomes to be released.
A cytokine that turns OFF inflammation and promotes tissue repair:
IL-10 is a cytokine that turns OFF inflammation and promotes tissue repair.
2 cytokines that promote maturation of monocytes?
GM-CSF, M-CSF