Comprehensive Geography: Maps, Data, Culture, Politics, Agriculture, Cities, Industry
1/323
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
324 Terms
Reference Maps
Designed for people to refer to for general information about places.
Thematic Maps
Used as a communications tool to tell us how human activities are distributed.
Isoline
A type of thematic map that uses lines to connect points of equal value.
Proportional Symbol
A thematic map that uses symbols of different sizes to represent data.
Cartogram
A thematic map that distorts the size of areas to represent data values.
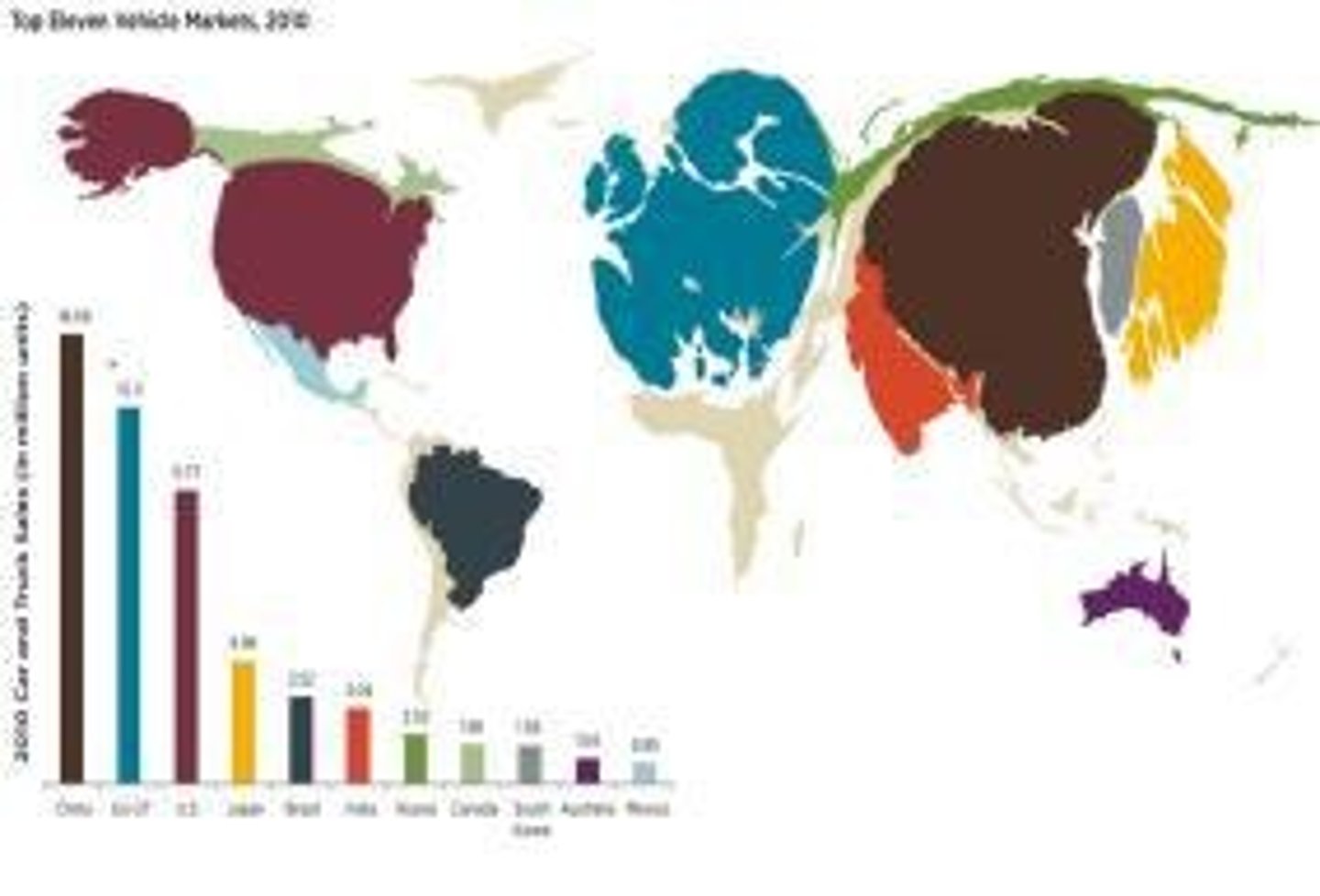
Choropleth
A thematic map that uses different shades or colors to represent data.
Dot Density
A thematic map that uses dots to represent the presence of a feature.
Clustering
A spatial pattern where features are grouped or bunched together.
Dispersal
A spatial pattern where features appear to be distributed over a wide area.
Elevation
Using levels to indicate how high or low something is located on land.
Absolute Distance
The exact measurement of distance between two points.
Relative Distance
The distance between two points in relation to other locations.
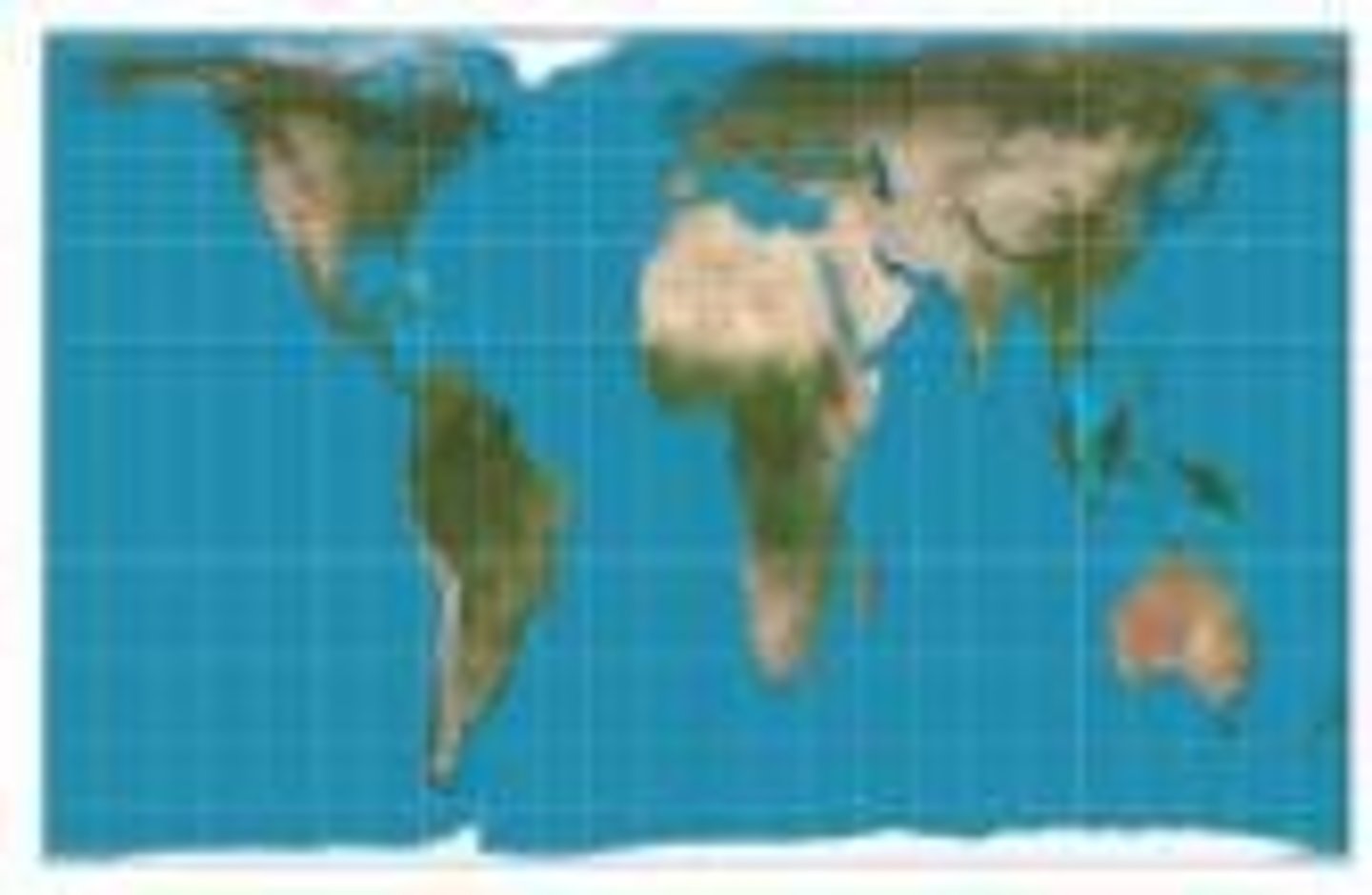
Robinson Map
A map projection where everything is distorted in small amounts.
Gall Peters
A map projection that distorts the shape of countries, especially near the equator.
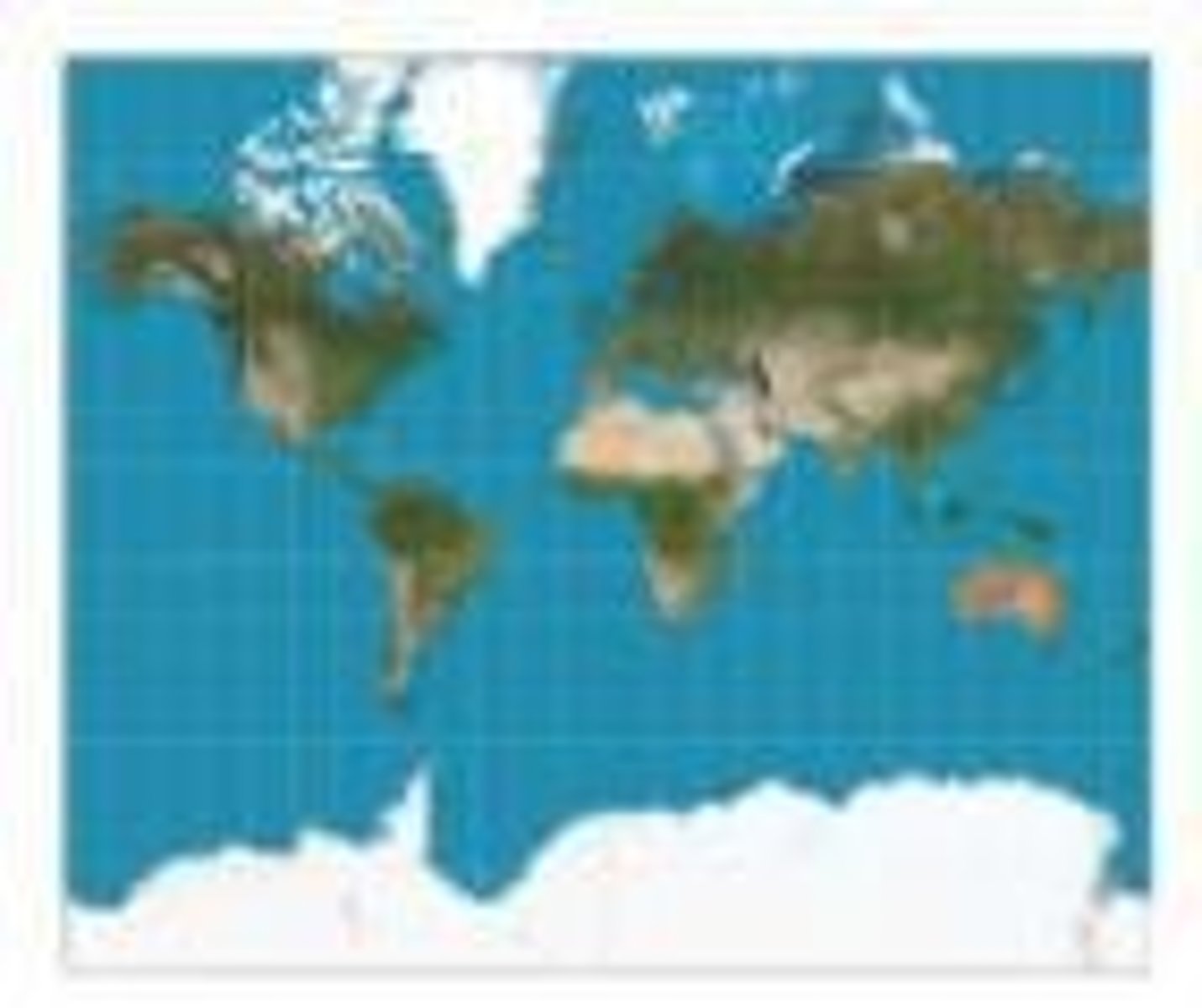
Mercator Map
A map projection where the shape and directions of countries are fairly accurate but greatly distorted toward poles.
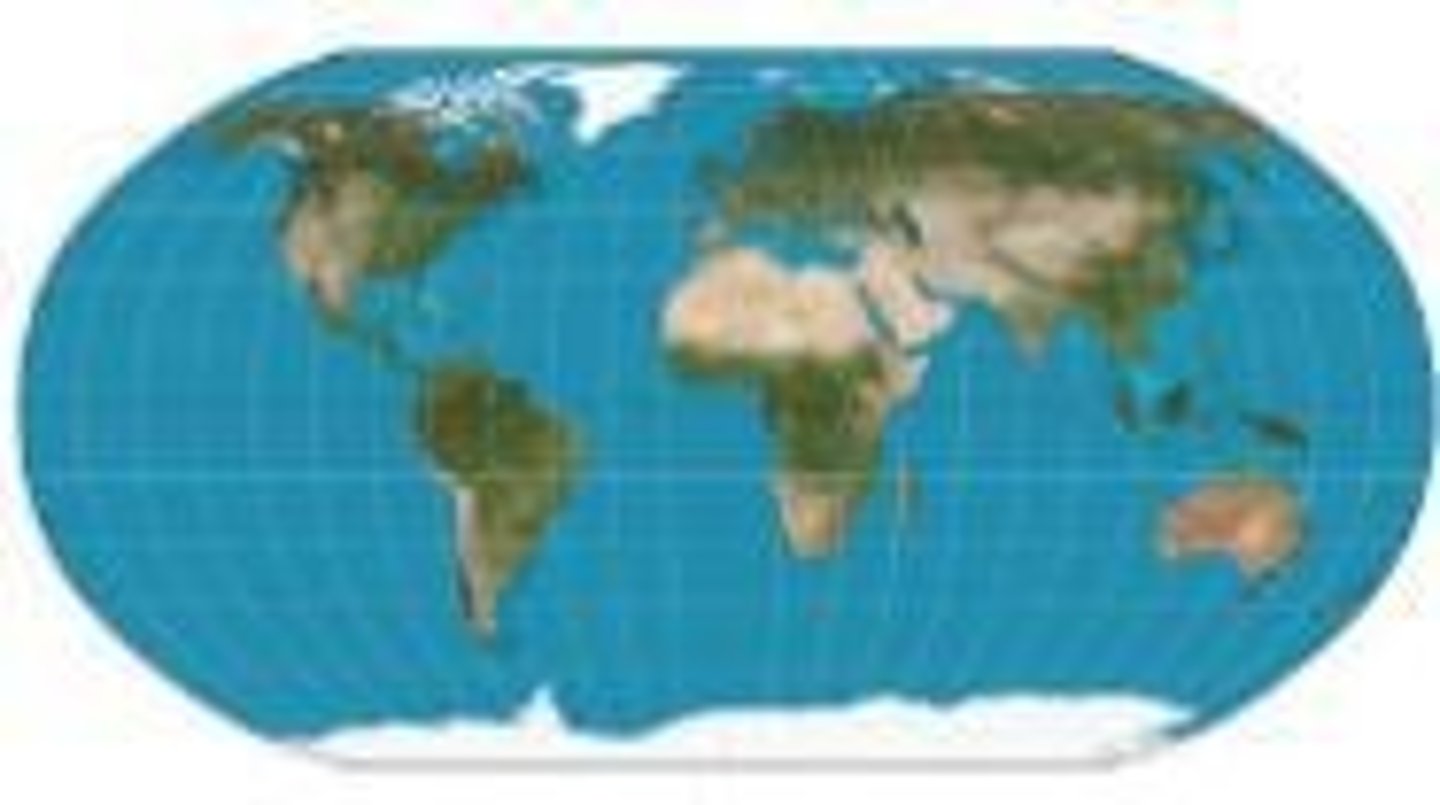
Goode Map
A map projection that accurately portrays continent sizes but distorts directions and distances.
Geospatial Data
All information including physical features and human activities.
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth's surface.
GPS
Geographic Positioning System, which uses data from satellites to pinpoint a location on Earth.
Remote Sensing
The process of taking pictures of the Earth's surface from satellites or airplanes.
Census Data
An official count of individuals in a population, occurring every 10 years in the USA.
Absolute Location
The precise spot where something is located.
Relative Location
Where something is in relation to other things.
Space
The extent of an area, which can be in a relative and absolute sense.
Place
Refers to the specific human and physical characteristics of a location.
Distance Decay
A geographical term that describes the effect of distance on cultural or spatial interactions.
Time-Space Compression
The increasing sense of connectivity that seems to bring people closer together despite physical distances.
Pattern
The geometric or regular arrangement of something in an area.
Sustainability
The goal of reaching equilibrium with the environment while meeting present needs and leaving resources for future generations.
Natural Resources
Physical materials constituting part of Earth that people need and value.
Environmental Determinism
The theory that the physical environment determines social development.
Possibilism
The theory that the physical environment may limit some human actions, but people can adjust to their environment.
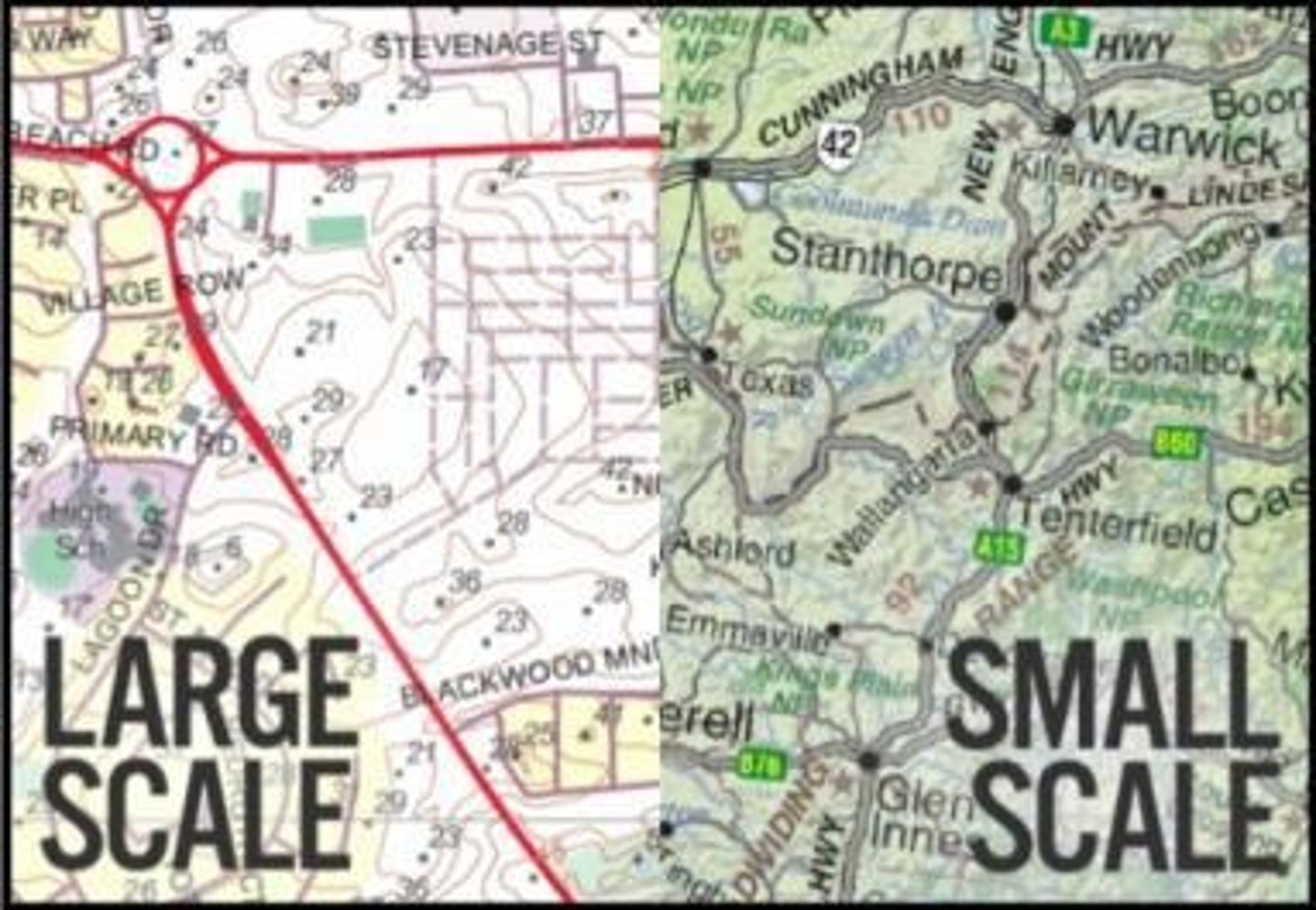
Scale
The relationship between distance on the ground and the corresponding distance on a specific map.
Formal Region
A region based on quantitative data that can be documented or measured.
Functional Region
A region based around a node or focal point.
Vernacular (Perceptual) Region
An area that shares a common qualitative characteristic, defined by people's beliefs.
Ecumene
The term used by geographers to mean where people are settled on Earth.
Arithmetic Density
Total number of objects in an area.
Physiological Density
Number of people supported by a unit area of arable land.
Agricultural Density
Ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land.
Carrying Capacity
The maximum population size of a species that the environment can sustain.
Overpopulation
When there are not enough resources in an area to support a population.
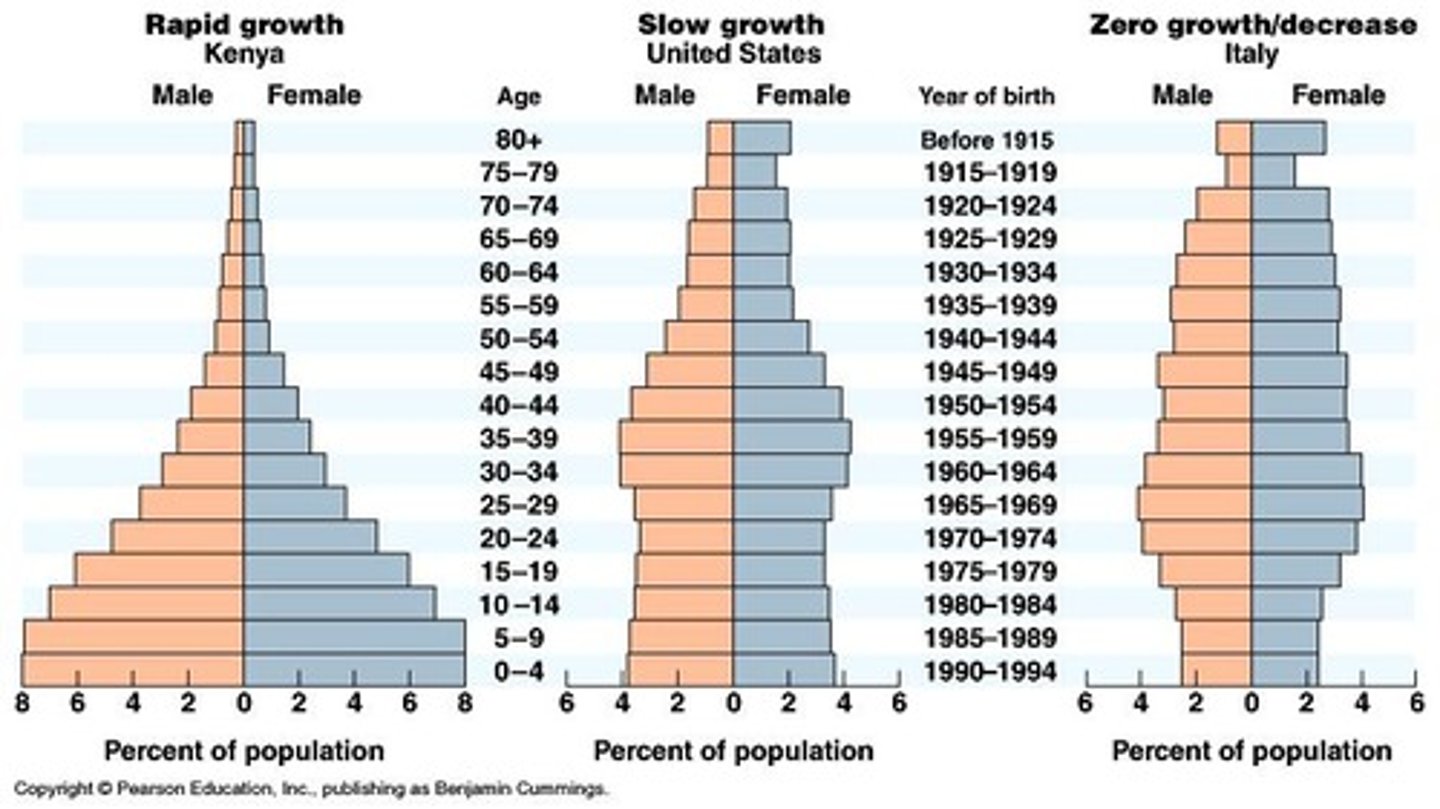
Age/Sex Ratio
Comparison of the numbers of males and females of different ages.
Population Pyramid
A graph of the population of an area by age and sex.
Demography
The study of population
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The number of live births per one thousand people in the population
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The number of deaths per one thousand people in the population
Doubling time
The time period it takes for a population to double in size
Fertility
The number of live births occurring in a population
Infant mortality rate (IMR)
The number of children who don't survive their first year of life per 1000 live births in a country
Mortality
The number of deaths occurring in a population
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI)
(birth rate - death rate)/10 - a positive NIR means a population is growing and a negative NIR means a population is shrinking
Total fertility rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman is predicted to have in her child bearing (fecund) years
Antinatalist policies
When a country provides incentives for people to have fewer children
Pronatalist policies
When a country provides incentives for people to have more children
Push Factors
Force that drives people away from a place (no jobs, slavery, political instability, no water)
Pull Factors
Force that draws people to immigrate to a place (jobs, to be near family)
Intervening opportunity
The presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away
Intervening obstacle
A force or factor that may limit human migration
Asylum seeker
A person seeking residence in a country outside of their own because they are fleeing persecution
Chain migration
A series of migrations within a group that begins with one person who pulls people to migrate to the same area
Step-migration
Migration to a far away place that takes place in stages
Forced migration
When people migrate not because they want to but because they have no other choice
Guest worker
A legal immigrant who is allowed into the country to work, usually for a relatively short time period
Internally displaced persons
A person forced to flee their home who remains in their home country
Refugee
A person who flees their home country and is not able to return
Transhumance
Moving herds of animals to the highlands in the summer and into the lowlands in the winter
Transnational migration
Moving across a border into another country
Voluntary migration
People choosing to migrate (not being forced)
Dependency ratio
The ratio of the number of people not in the workforce (dependents) and those who are in the workforce (producers)
Life expectancy
The average number of years a person born in a country might expect to live
Cultural Relativism
The culture should be judged based on its own standards, not based on another culture
Ethnocentrism
Judging other cultures based on the rules of your culture
Taboo
Something that is forbidden by a culture or a religion
Cultural landscapes
The forms superimposed on the physical environment by the activities of humans. Example: Street lights, rice fields, churches, cemeteries, etc.
Ethnic Neighborhoods
Neighborhood, district or suburb which retains some cultural distinction from a larger surrounding area.
Indigenous people
A culture group that constitutes the original inhabitants of a territory, distinct from the dominant national culture, which is often derived from colonial occupation.
Indigenous community
The community of indigenous people living together working to keep their culture alive.
Sense of place
A strong feeling of identity that is deeply felt by inhabitants and visitors of a location.
Language
A set of mutually intelligible sounds and symbols that are used for communication (Soda vs Pop).
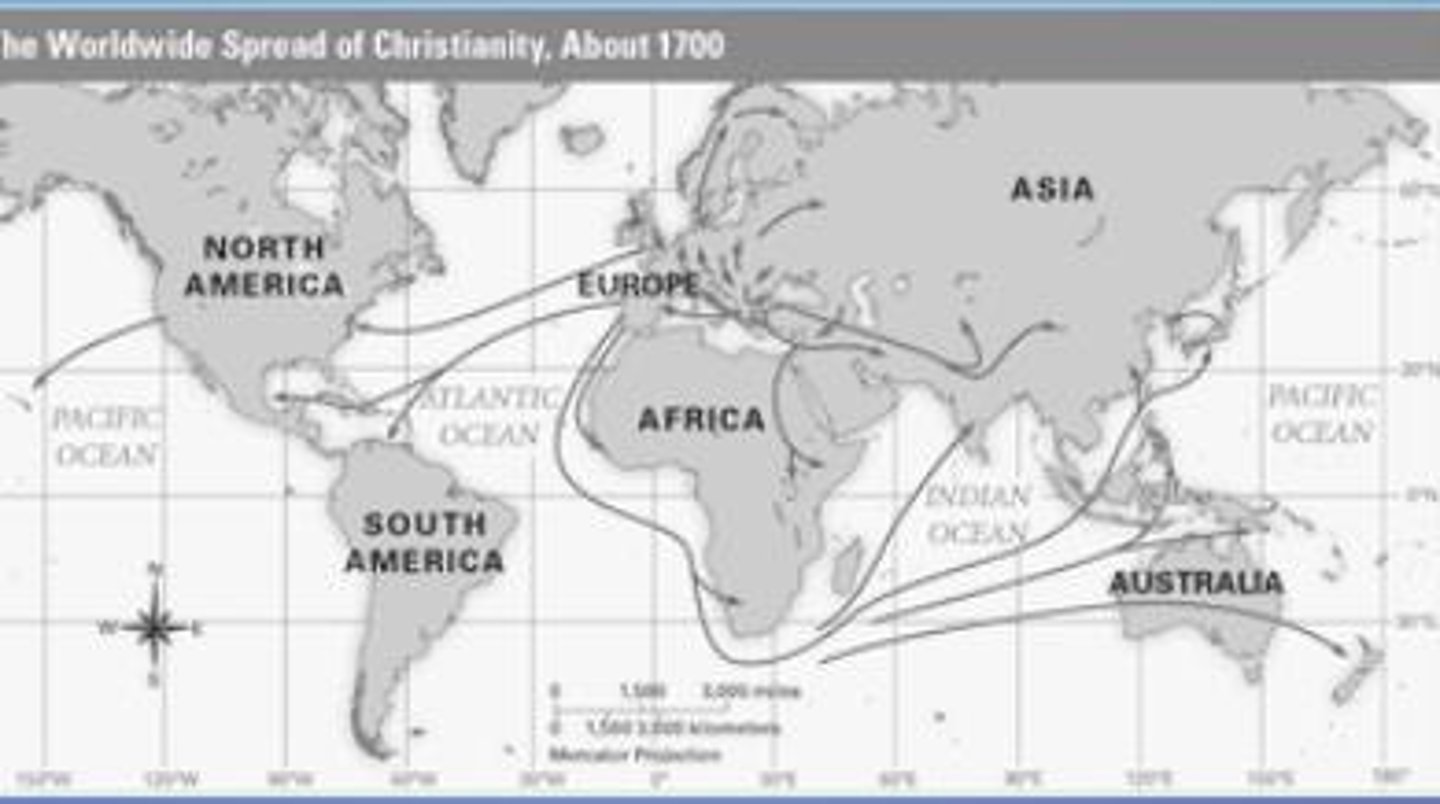
Religion
The belief in and worship of a superhuman controlling power, especially a personal God or gods (Church and Mosque).
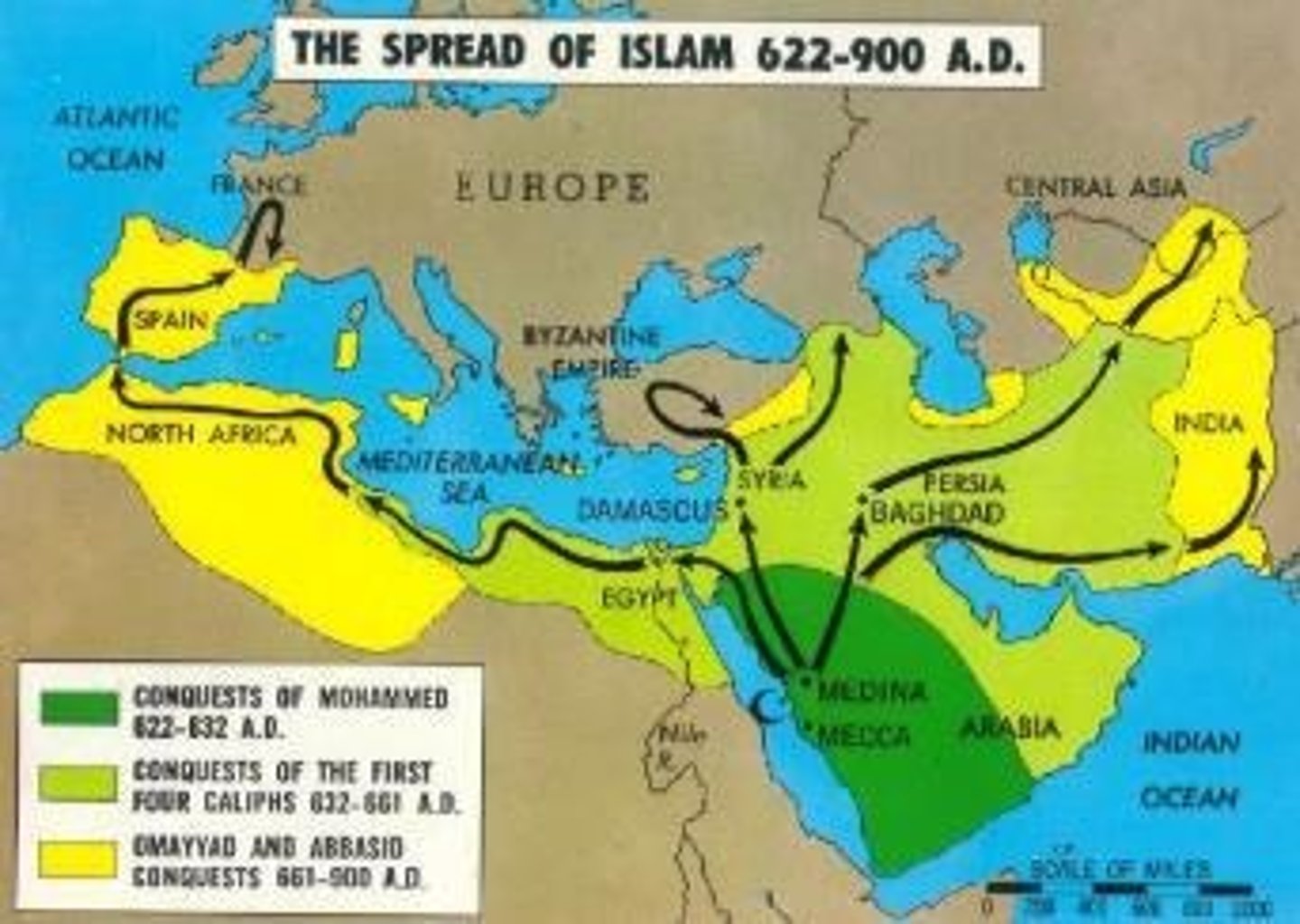
Ethnicity
The fact or state of belonging to a social group that has a common national or cultural tradition. (China Town).
Gender
Refers to the cultural differences in how men are treated differently than women.
Relocation Diffusion
A form of diffusion where the ideas being diffused are transmitted by their carriers as they migrate to new areas.
Expansion Diffusion
The spread of an idea through a population in a way that the number of those influenced becomes continuously larger.
Contagious diffusion
Transmission of a phenomenon through close contact with nearby places, like diseases.
Hierarchical diffusion
An idea spreads by passing first among the most connected individuals, then spreading to other individuals.
Reverse Hierarchical diffusion
Diffusion up a hierarchy, such as from a little city to a big one.
Stimulus diffusion
A form of diffusion in which a cultural adaptation is created as a result of the introduction of a cultural trait from another place.
Creole or creolized language
A language that began as a combination of two other languages and is spoken as the primary language of a group of people.
Lingua Franca
Mutually understood & commonly used by people who have different native languages.
Colonialism
An effort by one country to establish settlement in a territory and to impose its political, economic, and cultural principles on that territory.
Imperialism
The policy of extending a country's influence through political or military force to areas already developed by an indigenous people.
Globalization
World interaction and integration among the people, companies, and governments, a process driven by international trade and investment and aided by information technology.
Time-Space Convergence
The decline in travel time between geographical locations as a result of transportation, communication, and related technological and social innovations.
Cultural Convergence
Different cultures acquire common ideas, products, and traits, becoming more similar.
Cultural Divergence
Different parts of a cultural region are exposed to different influences and become dissimilar.
Indigenous language
A language that is native to a region and spoken by indigenous people.
Language extinction
A language that is no longer spoken by anyone as their native language.
Dialect
Different forms of the same language used by groups that have some different vocabulary and pronunciations.