COMP SCI EXAM 1
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
Object
a software bundle of related state and behavior often used to model real life behavior.
have states and behaviors. Example: A dog has states - color, name, breed as well as behavior such as wagging their tail, barking, eating. It is an instance of a class
Class
a template/blueprint that describes the behavior/state that the object of its type supports.
Method
basically a behavior. It is a chunk of code that can be called upon or invoked to perform a set of actions. A class can contain many methods. It is in methods where the logics are written, data is manipulated and all the actions are executed
Instance variable
Each object has its unique set of instance variables. An object's state is created by the values assigned to these instance variables. HAs separate copies created for every object.
UML
Notation used to depict objects and to illustrate OO concepts
interface
a contract between objects on how to communicate with each other
Encapsulation
objects encapsulate expertise, attributes and actions that it needs to carry out its role
Information hiding
objects can be designed to hide certain info and implementation details from other objects
Generality
objects are designed as general as possible so it can be applied to multiple similar problems
extensibility
designed to potentially be extended to perform a certain task
Literal value
A value expressed as itself, they are constant. EX: int number = 20;
Case sensitivity
Java is sensitive, which means that Hello and hello are different
Class names
1) First letter should be upper case
2) If several words are present, each inner word’s first letter should be uppercase
EX: public class MyFirstJava
Method names
1) Starts with lower case letter
2)if several words, then each inner word’s first letter needs to be uppercase
EX: public void myMethodName(parameters) {
}
Program file name
1) NEEDS TO MATCH class name , it won’t compile otherwise
2) add .java to the end
3) If public isnt included in the class name then the file can have a different name
main method
public static void main (String[] args) {
}
Identifiers
Names used for classes, variables, and methods
Rules of identifiers
All should begin with a letter (A-Z), currency characters ($), or an underscore(_)
after the first character, there can be any combination of characters
A key word cannot be used
CASE SENSITIVE
EX legal: age, $salary, _value
EX illegal: 123abc, -salary
modifiers
modifies classes and methods
Acess modifiers
default, public, protected, private
Non access modifiers
final, abstract, strictfp
Final
keyword used to define a constant value or method/classes. Its a non-access modifier applicable only to a variable, a method or a class. Once declared the variable can’t be changed when using this keyword.
Extends
Keyword used to inherit the properties of a class
package
Set of classes and interfaces grouped together
static
access modifier and keyword used to create variables that will exist independently of any instances created for the class. The method can be called without using an individual object. Belongs to the class rather than an instance. It is only applicable for methods and variables . Only ONE object which is shared by every object of the class.
Inheritence
Allows you to reuse fields and methods of an exisitng class w/o having to rewrite the code. Classes can be derived from classes. Basically if you need to create a new class and you already have a class that has some of the code you require, then it is possible to derive your new class from the already existing code
Superclass
existing class
Subclass
class made from superclass
Types of variables
local, class (Static), instance(non-static)
Variables
named storage units that the program can manipulate. Each has a specific type, which determines the size and layout of the variables memory
Declare: int a,b,c;
Initialize: a = 2, b = 4, c =5
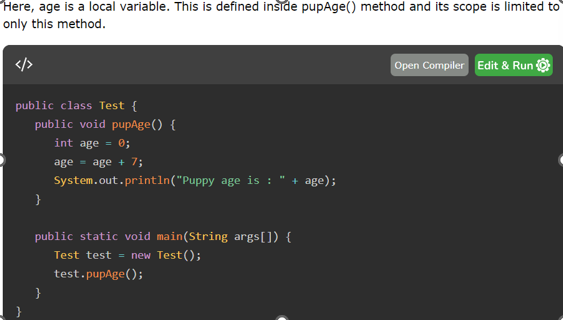
Local
declared in methods. CANNOT have access modifiers
Instance variables
Declared in a class but outside of a method. Created when an object is created with the use of the keyword new and are destroyed when the object is destroyed
They hold values that may be referenced by one or more methods
They can have access modifiers and be declared in the class level before or after use
They have default values
They can be accessed directly by calling the variable name inside the class
Within static methods(if they are given accessibility) they should be called using the full name
Default values:
numbers - 0 , booleans - false, objects - null
Class/Static variables
labeled with the static keyword in a class but outside of a method
There is only ONE copy of each variable per class, regardless of how many objects are created from it.
Created when the program starts and destroyed when the program stops
Data types
primitive and non primitive
primitive data types
byte
short
char
int
long
float
double
boolean
byte
8 bit
short
16 bit
char
16 bit
int
32 bit
long
64 bit
float 32 bit
double
64 bit
Boolean
true/false
Non primitive
Complex data types that store collections of values in various formats rather than just a stingle value
String
Array
Classes
Array
Structures that store multiple values of the same type in a single variable
declaration
int [] arrayName; → ont can be replaced with other data types
arrayName = new int[Array length];
setting and getting an element of an array
int[] numbers = new int [5];
numbers[0] = 10; //setting first element
int firstElement = numbers[0]; //getting first element
Getting length of an array
int length = arrayName.length;
Numeric promotion
converting one type to another type
Type promotion
the smaller type is converted to the larger type before the operand is performed
The smallest value taken is an int. Byte/short will become an int
implicit type conversion
allowed in cases where no information will be lost (narrower to wider) → small to larger, done automatically by Java
Cast operator
Must be used when converting a wider type into a narrower type. This is explicit casting. doing this manually/explicitly, making a larger type become a smaller type
preincrement
++k The operation is done before the operans value is used
EX: k = k + 1; j = k; OUTPUT k = 1, j = 1
postincrement
k++ the operation is done after the operand value is used
EX: j = k; k + 1; OUTPUT k = 1, j = 0;
predecrement (same as preincrement)
-- k
k = k -1; j = k; OUTPUT k = -1, j = -1
Postdecrement (same as postincrement)
k- -
j = k; k - 1; OUTPUT k = -1, j = 0;
Public
An access modifier used for attributes, methods, and constructors, making them accessible from any class
private
access modifier used for attributes, methods, and constructors, making them only accessible within the declared class
Formatting numbers
%n→ names a new line, %07 makes seven spaces where any extra space is a 0. The comma , is used like a decimal
Method overloading
technique used in OOP where multiple methods can have the same name but they need different parameters
Unary vs Binary operations
Unary operation is between one operand like increment/decrement
Binary operation is between two operands, +, - , *, /, and, or
Representation
the objects/characteristics
action
methods/behvaior
class constant
A field that is declared with the static and final keywords, They cannot be changed
class variable
a variable defined in a class of which a single copy exists, regardless of how many instances of the class exist
instance variable
each class has its own copy
Helper method
USed to perform particular repetitive tasks common across multiple classes. A function that is used to assist the main funcion
class method
methods declared within a class, perform specific operations
operator overloading
allows operators to be redefined and used in a way where they have a different meaning based on their operands
method overloading
having two or more methods in a class with the same name but different parameters/arguments
method call
block of code that only runs when it is called
Type conversion/type casting
convert one data to another, this has to be done MANUALLY
Type promotion
Dont naturally, smaller → bigger type
modularity
dividing a program into smaller parts
float is the same as
long
byte is the same as
short
Class Hierarchy
tree like
has one root class, called Object , which is superclass of any class
Each class below the
Objectclass is a subclass (child) of its parent class and can have its own subclasses.Subclasses inherit the characteristics (fields and methods) of their parent classes, allowing them to reuse code and create specialized classes based on the more general ones.
Three types of comments in java
Single-Line Comments for brief notes, Multi-Line Comments for detailed explanations or disabling code, and Documentation Comments for generating JavaDoc.
// single
/* multiline */
/** javadoc
*@Author
*@Param
*@return
*/
Consider the following code
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(args[2]+","+args[0]); S
ystem.out.println(args[2] + ", " + args[0] + " "+args[1]);
System.out.println(args[0]); } //end of main method
}
Name of the file - > MainClass
How to compile and run in CD
javac filename,java
java filename
output if it takes the arguments Alan M.Turin
Turin, Alan
Turin, Alan M
Alan
What does the code do
Reads the index of the argument and prints them whith different delimeters like , and space shown by ““
Math package
java.lang.Math
all methods in the math class are static so you can call them directly like
Math.max(24, 9 , 3, 22);
Using static import in the header class will allow you to invoke the methods and use the fields without writing the class name
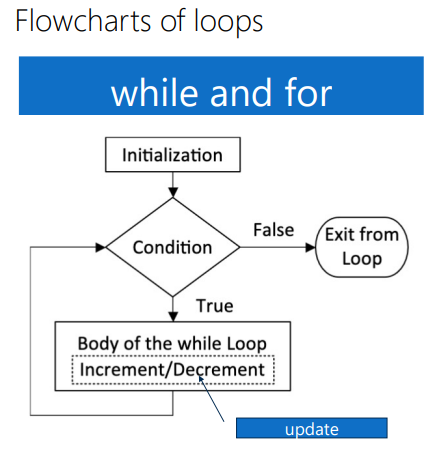
While loops
Used when you dont know how many times youre going to loop through.
Will only enter the body if the condition is met
for loops
used when you do know how many loops you want to do.
for(initialization; continuation statement; update)
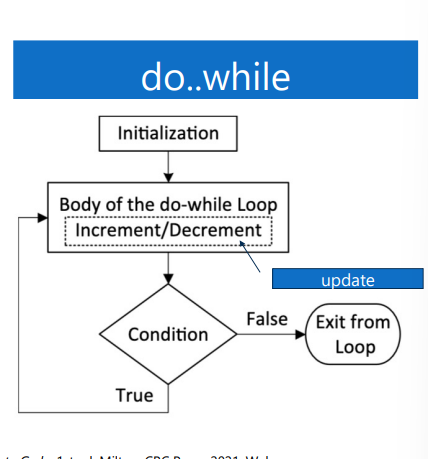
do - While
will always enter the body of the loop and then will check the condition
infinite loop
will run continuously
for(;;){
}
while(true){
}
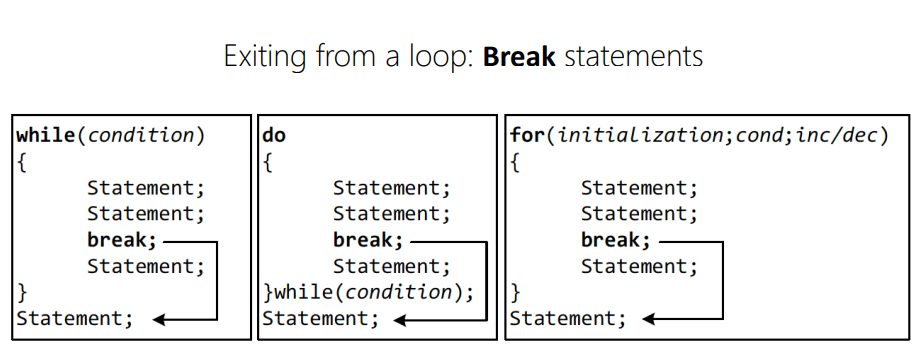
break
terminates any loop
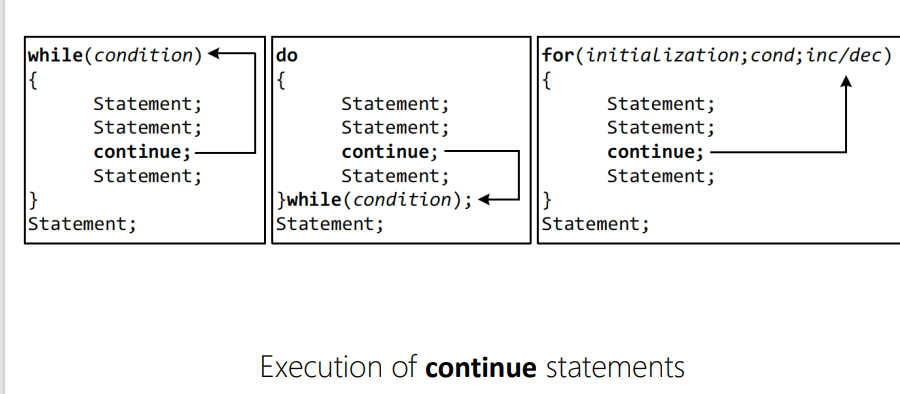
continue
skips the current iteration and continues with the next one
Ternary operator
Works like an if else statement but is more compact
variable = expression ? statement1 : statement2
str = (num > 0,0) ? “Positive” : “Negative”;
Create Array
data_type[] variableName = new data_type[Length];
or
data_type[] variableName = {Comma seperated literal values}
Elements of an array
anArray [i-1]
Elements of anArray are indexed from
0 to (# of elements - 1)
Limitations of arrays
only one type
Fixed size
Off- by -One error
When you are off by one index.
It will create an ArrayOutofBoundsException
value semantics
behavoir where values are copied when assigned, passed as parameters or returned
FOR primitive types
reference semantics
Behvaior where variables actually store the address of an object in memory
FOR objects
Aliasing
having more than one reference to the same object
Traversing an array
int[] data = {2,4,6,8,10};
for(int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.println(data[i]);
}
Array manipulation
java.util.Arrays
copyFrom, indexFrom, indexTo-exclusive
Two arrays are equivalent in values if they have the same
length and same sequence of values
Test if two arrays are equal
.equals
Which of the following would return a random number from 1 to 5 inclusive? - Choose all that apply.
A. (int) (Math.random() 5 )
B. myRandom.nextInt(5) + 1
C. (int) (Math.random() 6 )
D. (int) (Math.random() 5 ) + 1
E. (int)Math.random()5+1
B & D
String
String myStr = “NEW STRING”;
String variableName = new String(“My new String”);
The string class is immutable
String methods return new String objects