Lecture 7: RNA processing and interference
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
3 steps in eukaryotic mRNA processing
5’ end capping- methyl guanosine is added,
3’ end polyadenylation- addition of poly A tail,
Splicing- noncoding introns are removed.
mRNA definition
RNA that will be translated into protein. Has 5’ cap and 3’ poly A sequence. Has coding and noncoding regions. Starts as primary transcript in nucleus and is modified and exported to the cytoplasm.
Co-transcriptional processes
RNA processing steps are coupled to transcription
All associate with the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase 2
5’ end capping factors, polyadenylation/3’ end cleavage factors, sliceosome
CTD of RNA polymerase 2
C-terminal Domain, serves as scaffold for organization of pre-mRNA processing factors
Functions of 5’ 7-methyl Guanosine cap on mRNAs
prevents degredation at 5’ end by exonucleases, assists in moving the mRNA out of the nucleus, serves as recognition site for initiation of translation, helps in splicing.
Purpose of the Poly A tail
regulated mRNA stability and prevents degradation of 3’ end by exonucleases, Regulated nuclear exports, utilized in protein translation, useful to scientists for isolating mRNAs by hybridization with poly dT column.
3’ end of the mRNA processing
poly a recognition site is encoded in RNA, functions as recognition site for assembly of 3’ end processing complex, 3’ end of primary transcript is cleaved by exonuclease (~20nt downstream of poly A), poly A is added after the cut site.
Poly A recognition site
AAUAAA
Poly A polymerase (PAP)
Adds poly A tail
Addition of PolyA tail
CPSF cleaves primary transcript to shorten 3’ UTR, PAP adds poly A tail, Poly A binding proteins bind tail, additional poly A binding proteins added in cytoplasm.
CPSF
Cleavage and Polyadenylation Specificity Factor- cleaves primary transcript to shorten 3’ UTR
Up to __ % of genes are alternatively spliced
90
__% of inherited diseases result from incorrect splicing
15
Introns are processes from ____.
pre-RNA
RNA splicing
allows multiple mRNAs and multiple proteins to be produced from a single gene. Process must occur precisely.
RNA splicing is coordinated by a protein/ small nuclear complex (____) called a ____.
snRNA; spliceosome
The average human gene contains __ introns (comprising __% of the transcription unit.
9; 90
Exons
Average size in humans is 150 nt; always recombined in the same linear order
Introns
average size in humans is 3500 nt
pre-mRNA
same sequence as DNA, matches the DNA sequence of the 5’ strand. Uses U’s instead of T’s. Multiple mRNAs can be produced from pre-mRNA by different combinations of exons. has unique combination of exons.
Spliceosome
recognizes specific sequences in the intron, introns are removed by formation of lariat and ligation of the 2 adjoining exons.
Small nuclear RNAs
required for splicing.
U1snRNP
binds to conserved 5’ splice site
U2AF1snRNP
binds to conserved 3’ splice site
snRNP
facilitates 2 transesterification events to remove intron as a lariat
RNA interference
Method of down-regulating gene expression, regulation occurs through binding of an RNA to another RNA molecule and targeting the RNA for degradation or preventing translation. Also known as RNA silencing
siRNA
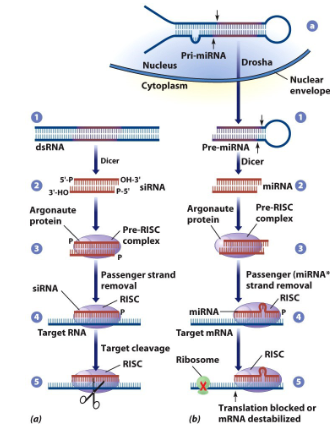
Small interfering RNA, short (20-25nt) double stranded RNA molecules, Exogenous to mammalian cells, have short (2-3) bp overhang on 3’-OH end. Interferes with expression of specific genes to prevent synthesis of a protein. (targets mRNA for degradation or prevents translation of mRNA)
Dicers
Double stranded RNA from viruses can be cleaved by dicer to make siRNA in lower eukaryotic organisms. Eukaryotic organisms also recognize siRNAs that don't require processing by Dicer. Endoribonuclease that can cut a ds DNA to make an siRNA
siRNA
Small interfering RNAs, small ds rnas that can target mRNAs for degradation, inhibit translation of mRNA into protein. Dicer is endoribonuclease that can cut a ds DNA to make an siRNA
siRNAs target ___ for degradation
mRNAs
Small interfering RNAs
Mechanism for reducing protein levels through RNA regulation. Mech. is the same for miRNA after initial steps
miRNA
microRNA, endogenous evolutionarily conserved non coding RNA that regulate gene expression. 20-23nt ds non coding RNAs that are encoded into genome. can function when sequences are not 100% match with target mRNA. typically regulates multiple genes.
miRNA function
Decrease gene expression by inactivating mRNA to reduce protein levels
miRNA can be encoded with___
introns, within the antisense orientation within a gene or in intergenic region.
miRNAs are transcribed by
RNA Pol 2
Endogenous
mechanism for interfering with protein production
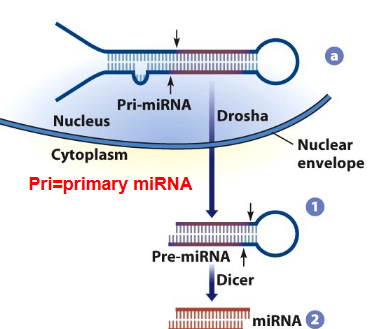
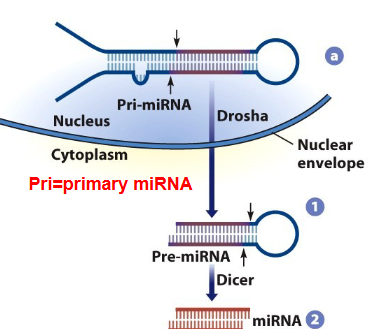
pri-miRNA
processed into miRNAs
DROSHA
cleaves pri-miRNA to make pre-miRNA
1
Pre-miRNAs are exported out of the nucleus
2
Pre-miRNA is cleaved by Dicer in cytoplasm to make an miRNA
miRNAs can block translation of mRNAs
miRNA + argonaut
pre-RISC complex
Argonaut
Removes passenger strand of DNA
If guide RNA is not a perfect match
No translation occurs; Typical for miRNA
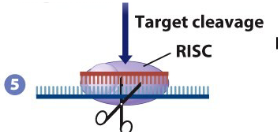
If guide RNA is a perfect match
it targets mRNA for degradation
Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)
200nts, can be transcriptional units or transcribed from within enhancers, promotors, introns or pseudogenes
lncRNA functions
occurs in many different cellular processes but it’s still poorly understood
piRNAs function
small RNAs that suppress the movement of transposable elements in the germline.
piRNAs
piwi-interacting RNAs, longer than other small RNAs- 24-32 nt. Interact with piwi proteins to silence mobile genes known as transposons and can participate in the RISC complex to participate in gene sliencing.
formation of piRNAs
does not involve the formation of dsRNA precursors or cleavage by the Dicer.
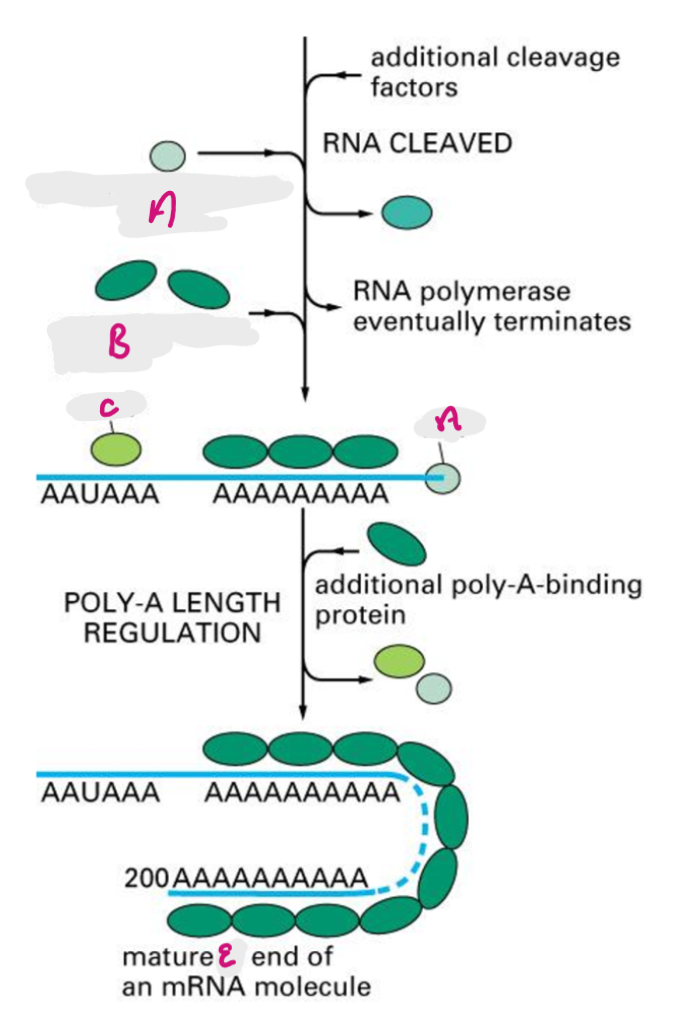
A
Poly-A polymerase (PAP)
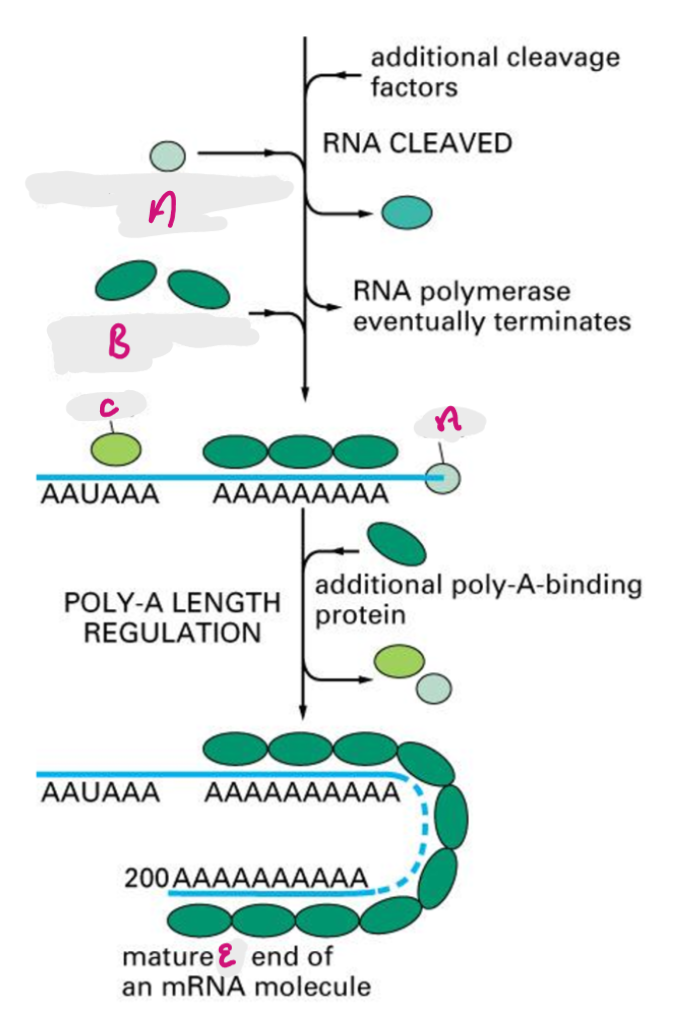
B
Poly-A binding protein (PABP)
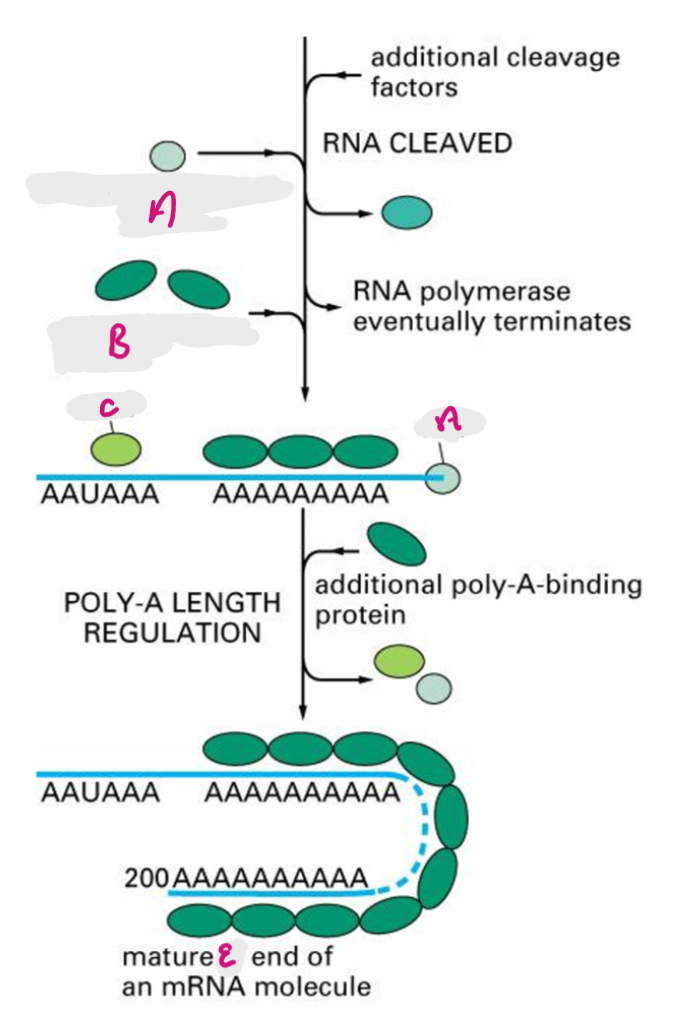
C
Cleavage and Polyadenylation Specificity Factor (CPSF)
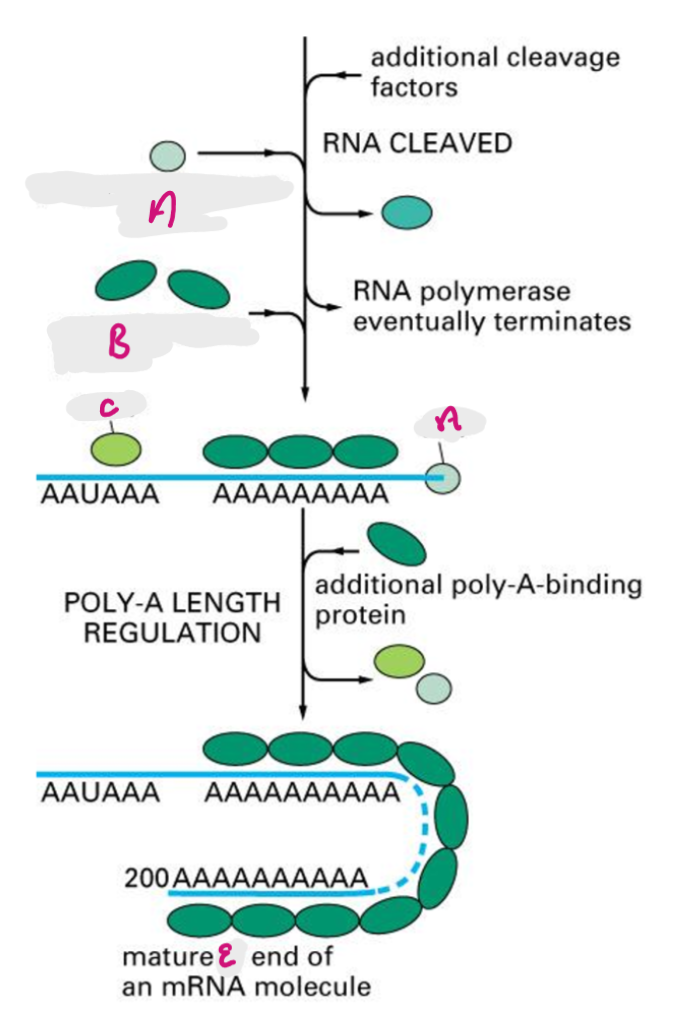
E
3’ end