Water properties, macro-molecules, polymers and monomers
1/90
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What is the bond between the elements of water?
covalent bonding
What is the bond between water molecules?
hydrogen-bond
Density
when water freezes it forms a crystal like structure creating space between the molecules. This results in ice being less dense than liquid water.
What an example of density in the lab?
The ice floating in water
Solvency
Water is excellent at being a solvent it can dissolve many polar and ionic substances
What’s an example of solvency in the lab?
the skittles dissolving in water
Latent heat of vaporization
water turning into a gas, when the hydrogen bonds are broken.
What does Latent heat of vaporization allow us to do?
It allows us to cool down without loosing too much water by utilizing the heat from our bodies to convert water into vapor.
What’s an example of the Latent heat of vaporization lab?
The blowing on the finger
Specific heat capacity
it takes a lot of heat energy to raise the temperature of water, which is why aquatic organisms can slowly adapt to the waters temperature without experiencing extreme temperature fluctuations.
What’s an example of the specific heat capacity lab?
The paprika and the water in the beakers
Polarity
the same electrons being pulled to the center of the atom making it partially negatively charged and the other side partially positively charged.
Hydrogen bonding
A hydrogen atom bonded with another molecule
What’s an example of the polarity lab?
the spritzing water on a plant
Cohesion
the attraction between the same type of molecules, water has a very strong cohesion due to it’s polarity
What does cohesion do for water?
it gives it a high surface tension
Adhesion
the different attraction between different types of molecules, water is attracted to other charged molecules
What’s an example of adhesion in the lab?
the water going up the xylem in the carnations
Capillary action
water climbing up the thin glass tubes
What does cohesion do for a plant?
allows the water to stick to each other
What does adhesion do for a plant?
allows the water to stick to the sides
Macromolecules
a larger molecule
Examples of macromolecules
proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleic acids
Polymer
a string of natural or synthetic substances made of macromolecules
Monomer
the small molecule of a polymer
What is a carbohydrate made of?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Examples of carbohydrates
sugars, starches, grains, pastas, breads, candy, cookies
Isomers
same number of atoms but different structure
Glucose is a..
monomer for carbs
Fructose and galactose are
another monomers
What are the polymers for carbohydrates?
polysaccarides
Lipids are ___ in water
insoluble
Where can lipids be found?
in fats, waxes, oils, hormones, steroids
Trigleceryde’s are stored for how long?
they’re stored long term
What do triglycerides do?
they’re used for insulation
What do phospholipids make up?
the cell membrane
Hydrophylic
water loving
Hydrophobic
Water hating
The fatty acids ___ water
hate
The phosphate group + glycerol ___ water
love
Cholesterol is a type of _____
steroid/lipid
Proteins are made of..
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen
Lipids are made of..
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What could be the other jobs of a protein?
structure, support, defense, and transport
Examples of proteins
nuts, meats, beans, and enzymes
Proteins are made from what kind of monomers?
amino acids
What are the monomers to lipids?
fatty acids
What are the polymers that make up lipids?
triglycerides and phospholipids
What elements are nucleic acids made of?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus
What are the monomers that make up nucleic acids?
nucleotides
What are the monomers for proteins?
amino acids
What are the polymers for nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
What are the polymers for proteins?
polypeptides
What do carbohydrates do?
they’re used for fast energy
What does a protein do?
preform functions
What do nucleic acids do?
code for proteins
What are the specific functions of proteins?
transport, enzymes, contractile, defense, hormones, structural, and storage
What are lipids used for?
longer term energy
What cells have cell membranes?
all cells
What’s the purpose of the cells membrane?
to assist the cell in maintaining homeostasis
Phospholids form the..
phospholid bilayer
Proteins are used for (cell membrane)..
transport in and out of the cell
Carbohydrates are used for (cell membrane)..
cell identification
Cholesterol is used for (cell membrane)..
regulating the fluidity of the membrane
Does a channel protein use ATP?
no
Does a carrier protein use ATP?
yes
What are the 4 functions of the cell membrane?
Transport, cell adhesion (cells sticking together, cell signaling (communication), cell recognition (ID)
Diffusion and osmosis are a movement from
high to low concentration
Osmosis can transport what kind of molecules?
water molecules
Diffusion can transport
solutes
Active transport only uses
carrier proteins
Diffusion is a process that can move
gases
Active transport
requires extra energy (ATP)
Diffusion and osmosis what type of process?
passive process
Active transport
movement from low to high concentration
Diffusion, osmosis, and active transport is the movement of
molecules
Osmosis and active transport require a
semi-permeable membrane
Diffusion sometimes uses
channel proteins
What is Osmosis?
the movement of water molecules from a high concentration of water to molecules to a low area
What is diffusion?
movement of gases from high to low concentration
What is active transport?
movement of molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration by using energy (ATP)
What is endocytosis?
cells from outside go in
What is exocytosis (HINT: think about exo-skeleton)
cells form inside go out
Hypotonic
A LOT of water goes into the cell
Hypertonic
water goes out of the cell
Isotonic
when the water and the fluids inside the cell remain the same even though they get exchanged
Water moves to a hy-
hypotonic area
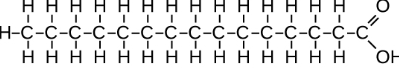
What macro molecule is this?
lipid
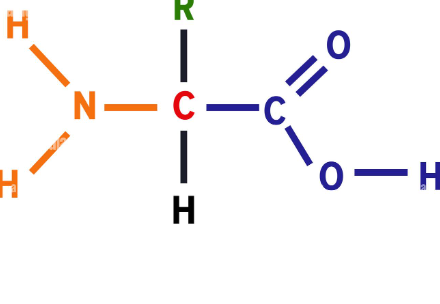
What macro molecule is this?
protein
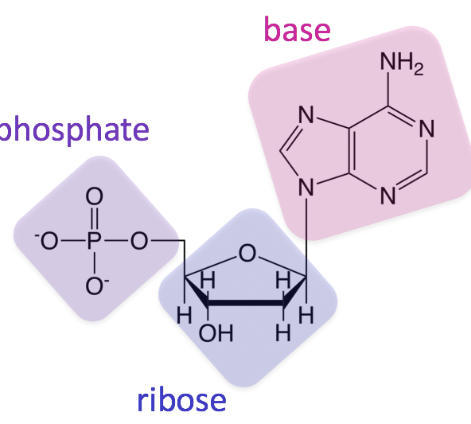
What macro molecule is this?
nucleic acids
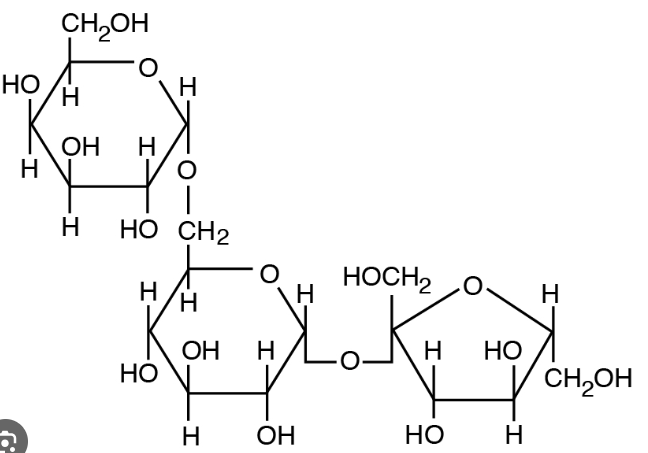
What macro molecule is this
carbohydrates