Anxiety and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
anxiety
a feeling of apprehension, uneasiness, uncertainty, or dread resulting from a real or perceived threat
fear
reaction to specific danger
known as "helpful anxiety"
mild anxiety
3 multiple choice options
mild anxiety
occurs in the normal experience of everyday living and allows an individual to perceive reality in sharp focus
symptoms of mild anxiety
restlessness, increased motivation, irritability
moderate anxiety
second level of anxiety results in selective inattention and some diminished thinking, although learning and problem solving can still occur
symptoms of moderate anxiety
- selective inattention
- diminished thinking
- beginning of sympathetic nervous system symptoms (tension, pounding heart, increased pulse and respiration rate, perspiration, gastric discomfort, headache, urinary urgency, voice tremors, and shaking)
severe anxiety
an increased level of anxiety when more primitive survival skills take over, defensive responses ensue, and cognitive skills decrease significantly
symptoms of severe anxiety
- inability to function, ritualistic behavior, unresponsive
- perceptual field greatly reduced
- difficulty concentrating on environment, inability to focus
- hyperventilation
- somatic symptoms increase (nausea, headache, dizziness)
panic level of anxiety
the most extreme level of anxiety and results in markedly dysregulated behavior
symptoms of panic level of anxiety
- distorted perception, loss of rational thought, immobility
- running, shouting, screaming, pacing
- unable to process reality
- impulsivity
defense mechanisms
automatic coping styles that protect people from anxiety and enable them to maintain their self-image by blocking feelings, conflicts, and memories
compensation
used to counterbalance perceived deficiencies by emphasizing strengths
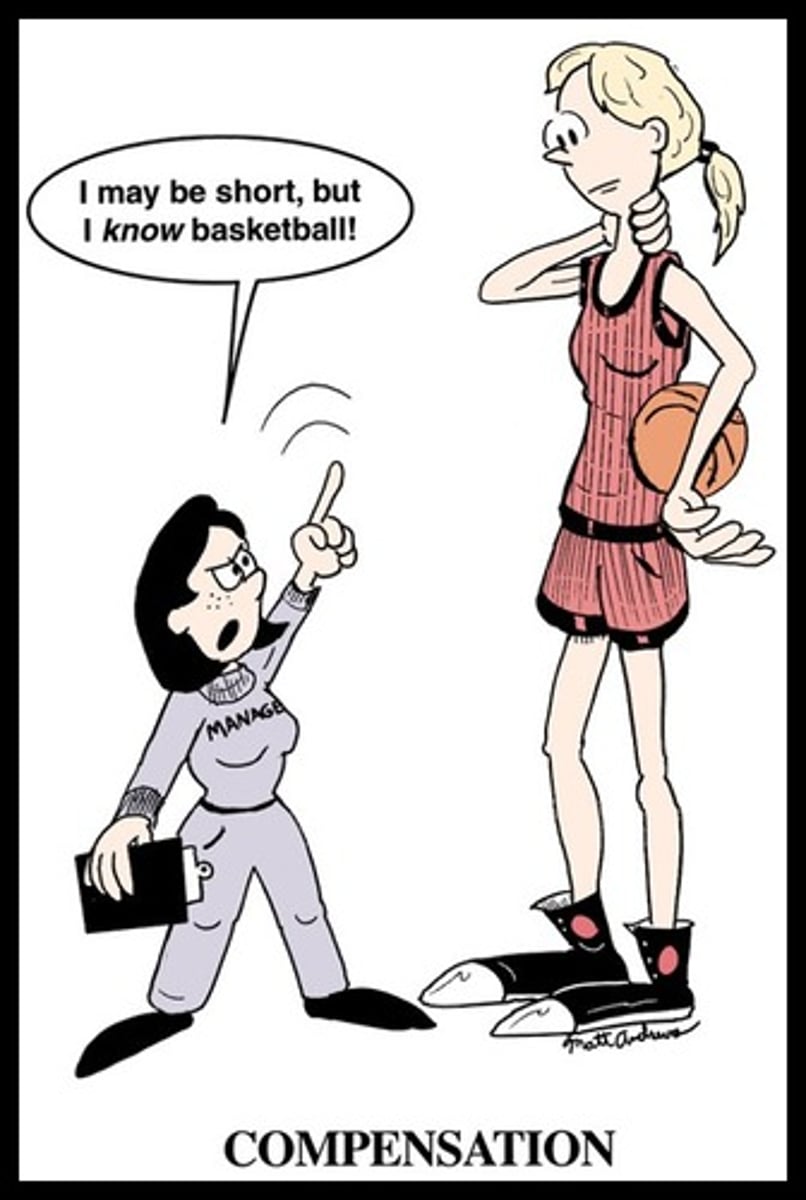

adaptive example of compensation
a shorter-than-average man becomes assertively verbal and excels in business.
maladaptive example of compensation
a woman drinks alcohol when her self-esteem is low to temporarily ease her discomfort.
denial
escaping unpleasant, anxiety-causing thoughts, feelings, wishes, or needs by ignoring their existence.

adaptive example of denial
a man reacts to the death of a loved one by saying, "No, I don't believe you," to initially protect himself from the overwhelming news.
projection
the unconscious rejection of emotionally unacceptable features and attributing them to others.
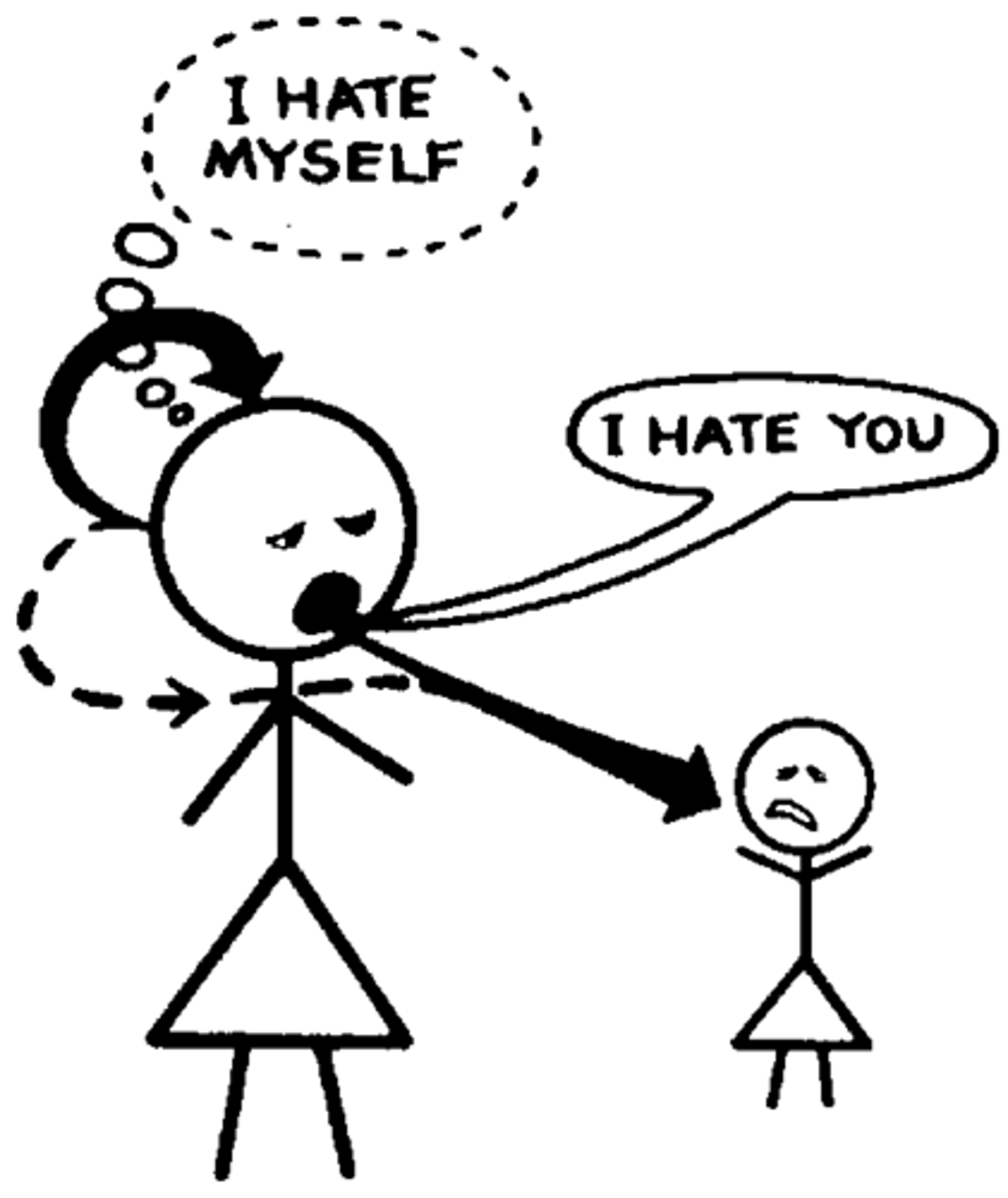
maladaptive example of denial
a woman whose husband died 3 years earlier still keeps his clothes in the closet and talks about him in the present tense.
adaptive example of projection
no example; this is considered an immature defense mechanism.
maladaptive example of projection
a woman who has repressed an attraction toward other women refuses to socialize. she fears that another woman will come on to her.
repression
an unconscious exclusion of unpleasant or unwanted experiences, emotions, or ideas from conscious awareness.
adaptive example of repression
after a marital fight, a man forgets his spouse's birthday.
undoing
when a person makes up for a regrettable act or communication

maladaptive example of repression
a woman is unable to enjoy sex after having pushed out of awareness a traumatic sexual incident from childhood.
adaptive example of undoing
after flirting with her male secretary, a woman brings her husband tickets to a concert he wants to see.
reaction formation
when unacceptable feelings or behaviors are controlled and kept out of awareness by developing the opposite emotion or behavior

maladaptive example of undoing
a man with rigid, moralistic beliefs and repressed sexuality is driven to wash his hands to gain composure when he is around attractive women.
adaptive example of reaction formation
a recovering alcoholic constantly talks about the evils of drinking
adaptive mechanisms
healthy strategies for coping with anxiety
maladaptive example of reaction formation
a woman who has an unconscious hostility toward her daughter is overprotective and hovers over her to protect her from harm, interfering with her normal growth and development
maladaptive mechanisms
immature strategies that hinder coping with anxiety
anxiety becomes a disorder when it affects
- ability to cope
- ability to go through normal activities of daily living
- ability to interact with the world in an appropriate way
- well-being/happiness
generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
an anxiety reaction characterized by persistent apprehension and worry greater than 6 months
generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) affects which sex more
female
1 multiple choice option
generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) leads to
avoidance that may result in lateness of absence from school or work and overall social isolation
symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD)
- restlessness
- muscle tension
- avoidance of stressful activities or events
- increased time and effort required to prepare for stressful activities or events
- procrastination in decision making
- sleep disturbance
separation anxiety
excessive fear or anxiety when separated from an individual to which the client is emotionally attached
age range for children with separation anxiety
8-24 months; peak = 18 months
symptoms of separation anxiety in children
- sleep disruption
- nightmares
- GI issues
- headaches
separation anxiety in adults is a
common comorbidity of other disorders
symptoms of separation anxiety in adults
- worry
- shyness
- uncertainty
- fatigability
- lack of self-direction
selective mutism
a condition where children do not speak owing to fears of negative responses or evaluations
substance-induced anxiety
characterized by symptoms of anxiety, panic attacks, obsessions, and compulsions that develop with the use of a substance (e.g., alcohol, cocaine, heroin, hallucinogens)
anxiety due to a medical condition
symptoms of anxiety are a direct physiological result of a medical condition
panic attack
an intense, sudden, and overwhelming fear or feeling of anxiety that produces terror and immediate physiologic changes that result in paralyzed immobility or senseless, hysteric behavior
panic disorder
psychological disorder that is characterized by recurrent attacks of anxiety or terror and usually results in the development of one or more phobias
"fear the fear" leading to avoidance characterizes which anxiety disorder
panic disorder
3 multiple choice options
symptoms of panic disorder
- palpitations
- shortness of breath, hyperventilation (respiratory alkalosis)
- choking or smothering sensation
- chest pain
- nausea
- feelings of depersonalization
- fear of dying or insanity
- chills or hot flashes
comorbid conditions of panic disorder
- depression
- OCD
- phobias
- hyperthyroidism
- dizziness
- cardiac arrhythmias
- asthma
- COPD
phobias
irrational fear causing avoidance of specific situations
agoraphobia
intense excessive anxiety or fear about being in places or situations from which escape might be difficult or embarrassing or where help might not be available
agoraphobia affects which sex more
females
1 multiple choice option
obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
an anxiety disorder characterized by recurrent and persistent thoughts, ideas, and feelings or repetitive acts sufficiently severe to cause marked distress, consume considerable time, or significantly interfere with the patient's occupational, social, or interpersonal functioning

obsessions
thoughts, impulses, or images that persist and recur so that they cannot be dismissed from the mind even though the individual attempts to do so
compulsions
ritualistic behaviors individuals feel driven to perform in an attempt to reduce anxiety or prevent an imagined calamity
daily symptoms of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) may involve
issues of contamination, illness, etc
defense mechanism associated with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
undoing
3 multiple choice options
body dysmorphic disorder
an obsessive-compulsive disorder that involves preoccupation with an imagined defective body part, resulting in obsessional thinking and compulsive behavior.

hoarding
an obsessive accumulation of belongings that may have little or no value and that prevents people from leading normal lives

trichotillomania
compulsive hair pulling often leading to hair loss.
excoriation disorder
compulsive skin picking leading to skin damage.
risk factors for anxiety disorders
- genetics
- neurobiological (too little of GABA)
- traumatic events
- learned behaviors
- distortion of thoughts
assessment for anxiety disorders
- interview room should be safe, quiet, non-stimulating, structured, and simple
- full physical and neurological exam (nonverbal and body posture)
- determine source of anxiety
- determine current level of anxiety
- assess for potential self-harm (ask patient about causes they can identify [triggers])
- self-assessment (severity measures for GAD, Yale-Brown OCD scale, hoarding scale)
outcome identification: risk for injury d/t anxiety
- self-monitors
- uses reduction techniques
- maintains role performance
- recognizes triggers for anxiety
outcome identification: ineffective coping
- identifies effective and ineffective patterns
- asks for assistance and information
- modifies as needed
outcome identification: chronic low-self esteem
- verbalizes acceptance
- increased confidence
outcome identification: self-mutilation
- identified predictive feelings
- practices self-restraint
planning care for patients with anxiety disorders
- usually doesn't require inpatient admission
- encourage active participation to increase positive outcomes
- patient experiencing severe levels of anxiety may not be able to participate
guidelines for basic nursing interventions
- keep the patient safe
- use simple language and calm manner when speaking or providing instructions
- slow, deep breathing exercises with progressive muscle relaxation
- identify community resources and support groups
priority nursing interventions for acute anxiety or panic attacks
- assist with reduction of anxiety
- calm
- brief, direct communication
- eye contact (focus)
- breathing
- explaining you are there to help
self-care activities for clients with anxiety
- nutrition and fluid intake
- personal hygiene and grooming
- elimination
- sleep
first line of treatment for anxiety and obsessive-compulsive disorders
SSRIs
3 multiple choice options
onset of long-term anxiolytic
2-4 weeks
Paxil, Prozac, Lexapro, Zoloft
SSRIs
3 multiple choice options

Effexor, Cymbalta
SNRIs
3 multiple choice options
short-term, PRN medications for anxiety
benzodiazepines
3 multiple choice options
Ativan, Valium, Xanax, Klonopin
benzodiazepines
3 multiple choice options
benzodiazepines work on which neurotransmitter
GABA
3 multiple choice options
benzodiazepines have a potential for
dependence
benzodiazepines should be cautiously used in
elderly patients
3 multiple choice options
what should be avoided while taking SSRIs, SNRIs, benzodiazepines
alcohol
3 multiple choice options
long-term anti-anxiety medication that has no dependence
buspirone/Buspar
cognitive restructuring
process of changing an individual's perceptions of stress by reassessing a situation and replacing irrational beliefs
components of cognitive restructuring
- identification
- exploration
- realistic evaluation
- replacement of negative self-talk
behavioral therapy
psychotherapy that attempts to modify observable maladjusted patterns of behavior by substituting a new response or set of responses to a given stimulus
relaxation training
a therapeutic technique in which a person acquires the ability to relax the muscles of the body in almost any circumstance
modeling
therapist or significant other acts as a role model to demonstrate appropriate behavior in a feared situation, and then the patient imitates it
systematic desensitization
patient is gradually introduced to a feared object or experience through a series of steps, from the least frightening to the most frightening (graduated exposure); the patient is taught to use a relaxation technique at each step when the anxiety becomes overwhelming
flooding
involves exposing the client to a great deal of an undesirable stimulus in an attempt to turn off the anxiety response
effective behavioral therapies for patients with phobias
systematic desensitization and flooding
response prevention
focuses on preventing the client from performing a compulsive behavior with the intent that anxiety will diminish
thought stopping
teaches a client to say "stop" when negative thoughts or compulsive behaviors arise, and substitute a positive thought
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
evidence-based therapeutic modality for children, adolescents, and adults that seeks to identify negative and irrational patterns of thought and challenge them based on rational evidence and thoughts
evaluation of effective in clients with anxiety
- is the patient experiencing a reduced level of anxiety?
- does the patient recognize symptoms as anxiety-related?
- does the patient continue to display signs and symptoms such as obsessions, compulsions, phobias, worrying, or other symptoms of anxiety disorders? (if still present, are they more or less frequent? more or less intense?)
- is the patient able to use newly learned behaviors to manage anxiety?
- does the patient adequately perform self-care activities?
- can the patient maintain satisfying interpersonal relations?
- is the patient able to assume usual roles?
what do we hope your level of anxiety is on the day of a nursing exam?
mild
3 multiple choice options