A2 Unit 3.6 Human impact on the environment
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Extinction

What is a gene pool?
A gene pool is all the genes & alleles that exist in all members of that species.
Gene pool refers to the full genetic diversity that exists within a population.
A large gene pool acts as a buffer against disease and environmental change
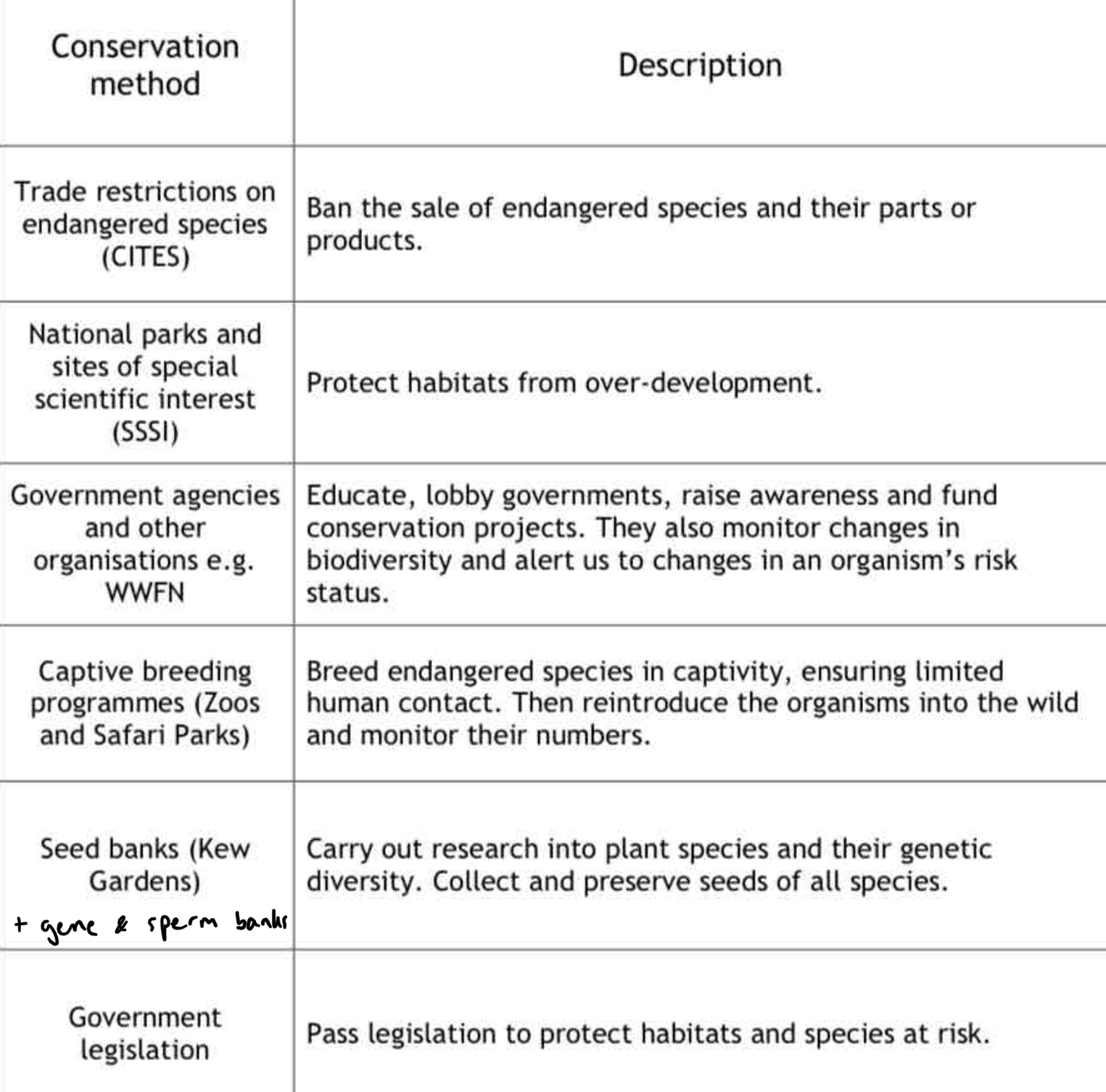
Conservation
Conservation is the protection, preservation, management and restoration of natural habitats and their ecological communities.
The aim is to maintain species and genetic biodiversity while allowing human activity to continue. Conservation can be achieved by:
On a graph, an increase in population size after a decrease may be due to conservation techniques.
Why is maintaining biodiversity important?
Maintaining biodiversity (both species and genetic) by conservation is essential for protecting potential sources of new crops for agriculture and new pharmaceuticals for medicine.
A diversity of alleles will be essential in combating climate change; some alleles may provide a selective advantage to some individuals, thus preventing extinction.
Conservation is also an ethical issue – each species, and their combination of genes, is unique and precious.
Agricultural Exploitation - Intensive Farming
Intensive farming has seen an increase in the use of chemical fertilisers, pesticides and herbicides.
Mechanisation requires larger fields to accommodate large machinery; this has led to a reduction in the number of hedgerows. Hedgerows are an important habitat and their loss reduces biodiversity.
These larger fields are used to grow monocultures, in which a single crop, e.g. wheat or barley, is grown on a massive scale.
Monocultures provide only one type of habitat, which reduces biodiversity. Monocultures reduce soil fertility as roots grow to the same length and extract minerals from the same depth – this increases the need for chemical fertilisers.
Plants of the same species, grown so close together, are also susceptible to the same pests and diseases, which are able to pass from plant to plant rapidly. To combat this farmer uses more pesticides.

Overgrazing
Overgrazing land can cause soil compaction, reducing air spaces (so less oxygen and water) and inhibiting nitrogen fixing and nitrifying bacteria – leading to a loss of soil fertility (look back at Unit 3.5 on pages 39-43).
Water is also unable to penetrate compacted soil and grass growth is inhibited. There is also less space for root growth.
Farming in the future - Solutions for reduction in biodiversity

Deforestation
Timber is used for building, fuel, paper and packaging.

Forest Management

Overfishing
