MKT100 - Final exam
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
What is a product
a product is anything that can be offered to a market for attention, acquisition use or consumption that might satisfy a need or a want
A good
a physical or tangible offering
A service
intangible offering that doesn’t involve ownership
Convenience good
A convenience good is inexpensive, highly available and required minimal effort to acquire
A shopping product
a shopping product is something that is purchased infrequently. buyer will want to compare alternatives before purchase
Specialty good
unique and requires special attention to obtain
Unsought good
a product that the consumer is unaware of needing until there is a sudden problem
5 product decisions
product attributes, branding, labelling and logos, product support services
Core product
the key benefit the consumer is wanting from a product
Actual product
the brand name, quality, design features, packaging and a blend of the form and function
Augmented product
the product support after sale services and warranties that are offered with a product
Examples of business to business trading
equipment, maintenance, specialised services, raw materials
product line
a set of closely related product items
Product mix
all product lines and items a company offers
Stretch down
new product is lower quality and price
Stretch high
new product is higher quality and more expensive
stretch both
new products are both high price high quality and low price and low quality
Stages of the product life cycle
development, intro, growth, maturity and decline
The introduction phase of the product lifecycle
the goal is to get first time customers to try the product
The growth stage of the product lifecycle
aim is to encourage repeat purchases
The maturity stage of the product life cycle
companies will try and sell at many outlets or on discount to reinforce brand loyalty
The decline stage of the product lifecycle
competitors tend to withdraw and there is less product variation released. Companies will try sell all remaining stock
Individual branding decision
each product in the product line is branded differently
Family branding decision
the same branding for multiple products
Manufacturing branding decision
owned by producers and identified with the product at the point of sale
Co-branding decision
two established named brands used together on a product
Licensed branding decision
names or symbols previously created by another company or manufacturer used on the branding of a product
brand value and equity
strong brands build an emotional connection with the customer
Why is new product development important
increases competition, due to the changes in technology and changing consumer lifestyles
What is a service
a result of the application of human efforts to people or objects that is intangible and doesn’t result in ownership of anything
The 4 service characteristics
intangibility, inseparability, perishability, variability
Intangibility
services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard or smelt before purchase
The challenge of intangibility
its harder to communicate the value of a service
Inseparability
Services cannot be separated from their providers
Challenges for inseparability
customers must be present at the time of consumption of the service and can’t take it home and services can’t be mass produced
Perishability
Services can’t be stored for later use
Challenges of perishability
hard to balance supply and demand so its difficult to maximise time as unused capicity is lost forever
Variability
the quality of services depends on who provides them when, where and how
Challenges of variability
picking the right people with the right skills and the quality if difficult to control
the 7 P’s - extended marketing mix
product, price, place, promotion, people, physical evidence, processes
Product - in services
core and supplementary services
Price - for services
variable to tasks, expertise and resources
Place - for services
direct channel where there is high contact
Promotion - for services
tangible cues that symbolise what service is offered
People - for services
the service and the provider are co-dependant
Processes - for services
how the customer is taken through the experience to ensure functional expectations and performance expectations are met
Physical evidence - for services
clues a customer may observe to validate the quality of services and positioning
Mapping the customer experience
checking where expectations aren’t met, unnecessary touch points, points of friction and moments of truth
What is price
the amount of money charged for a product/service that consumers exchange for the benefits of using a product or service
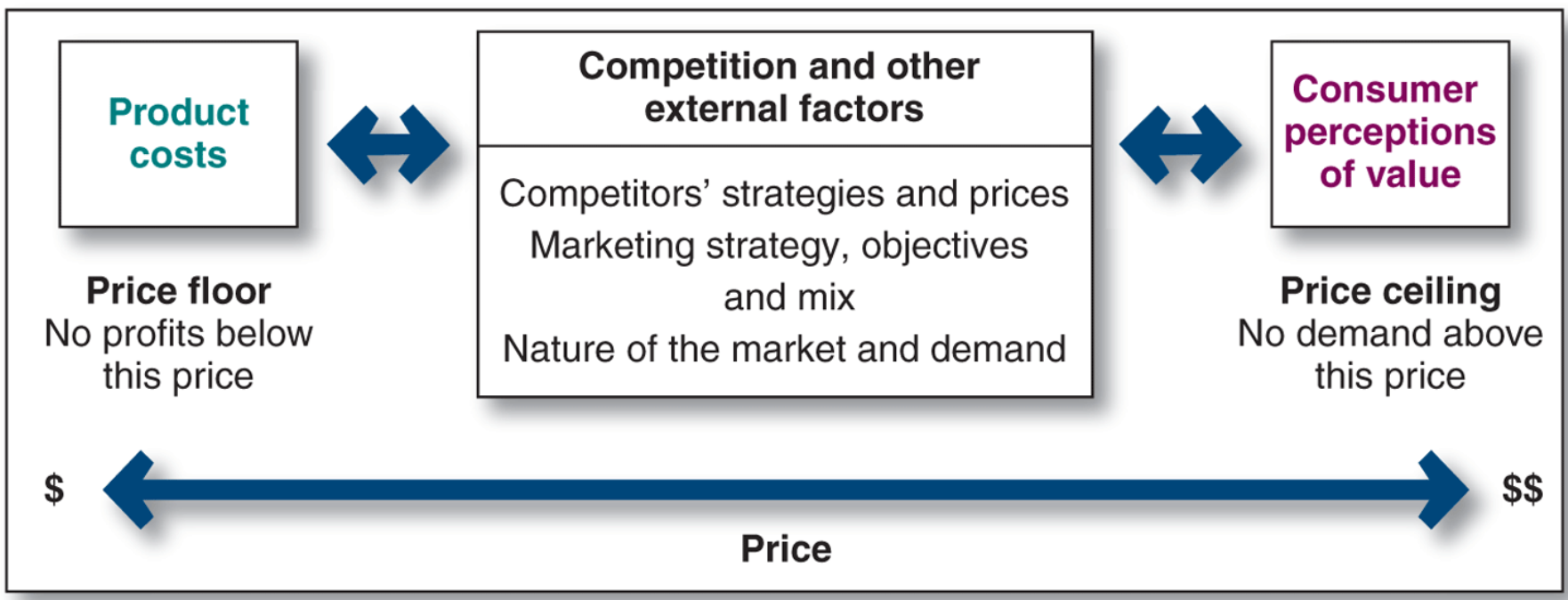
three main pricing strategies
(1) customer value-based pricing, (2) cost-based pricing and (3) competition-based pricing.
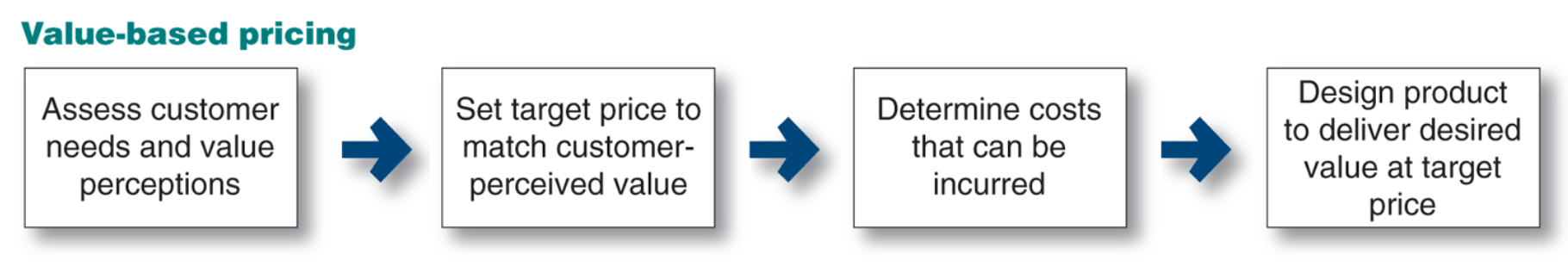
Customer value based pricing
uses buyers’ perceptions of value, not the seller’s cost, as the key to pricing.
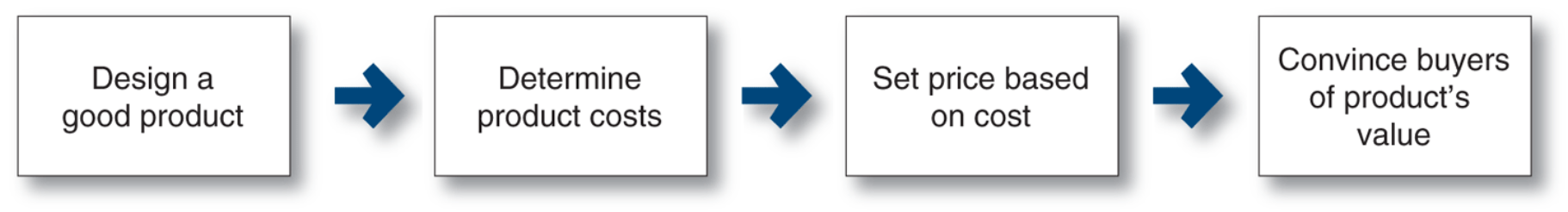
Cost based pricing
often product-driven. The company designs what it considers to be a good product, adds up the costs of making the product and sets a price that covers costs plus a target profit. Marketing must then convince buyers that the product’s value at that price justifies its purchase.
Competition based pricing
Setting prices based on competitors’ strategies, costs, prices and market offerings
Pure price competition marketing
marketing research, product development, pricing, advertising and sales promotion play little or no role. Thus, sellers in these markets do not spend much time on marketing strategy.
Monopolistic competition - marketing
many buyers and sellers who trade over a range of prices rather than a single market price. Sellers try to develop differentiated offers for different customer segments and, in addition to price, freely use branding, advertising and personal selling to set their offers apart
monopoly
In a regulated monopoly, the government permits the company to set rates that will yield a ‘fair return’. Non-regulated monopolies are free to price at what the market will bear
Price elasticity of demand
a measure of the sensitivity of the customer to the price of the products offered
New product pricing strategies
the price set for a new product depending on the market the product is trying to reach
Price skimming
Setting a high price for a new product to skim maximum revenue from the segments willing to pay the high price; the company makes fewer but more profitable sales.
Penetration pricing
Setting a low price for a new product in order to attract a large number of buyers and a large market share
Differential pricing strategy
different prices to different buyers for the same quality and quantity of product included negotiated and secondary pricing
Psychological pricing
an attempt to influence a customers perception of price to make a products price more attractive
examples of psychological pricing
reference, bundle, odd-even, prestige
6 steps for establishing prices
develop price objective, assess target market evaluation of price, evaluation of competitors prices, selection of basis for pricing, choose pricing strategy then determine on a price
What are the 5 C’s of pricing
company objectives, competition, costs, customers, channel members
Supply chain
A system of efficiently and effectively producing, making and getting products to end-users
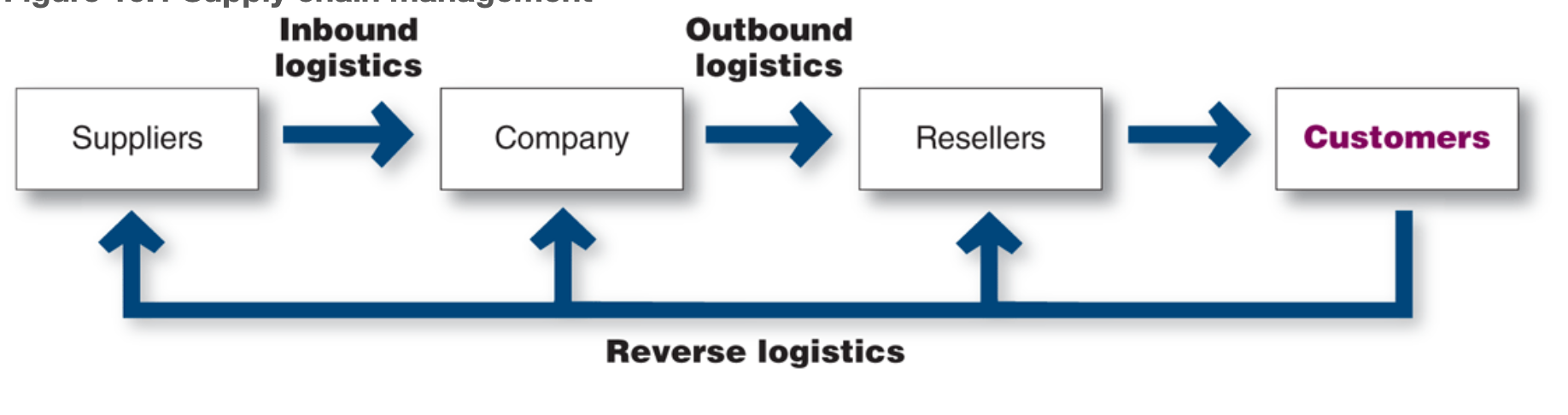
Supply chain management
Managing upstream and downstream value-added flows of materials, final goods and related information among suppliers, the marketing organisation, resellers and final consumers
Marketing logistics
The tasks involved in planning, implementing and controlling the physical flow of materials, final goods and related information from points of origin to points of consumption in order to meet customer requirements at a profit
Value delivery network
The network made up of the marketing organisation, suppliers, distributors and, ultimately, customers who partner with each other to improve the performance of the entire system.
Marketing channel
A set of interdependent organisations involved in the process of making a product or service available to users
Why use a intermediary
their contacts, experience, specialisation and scale of operation, intermediaries usually offer the firm more than it can achieve on its own
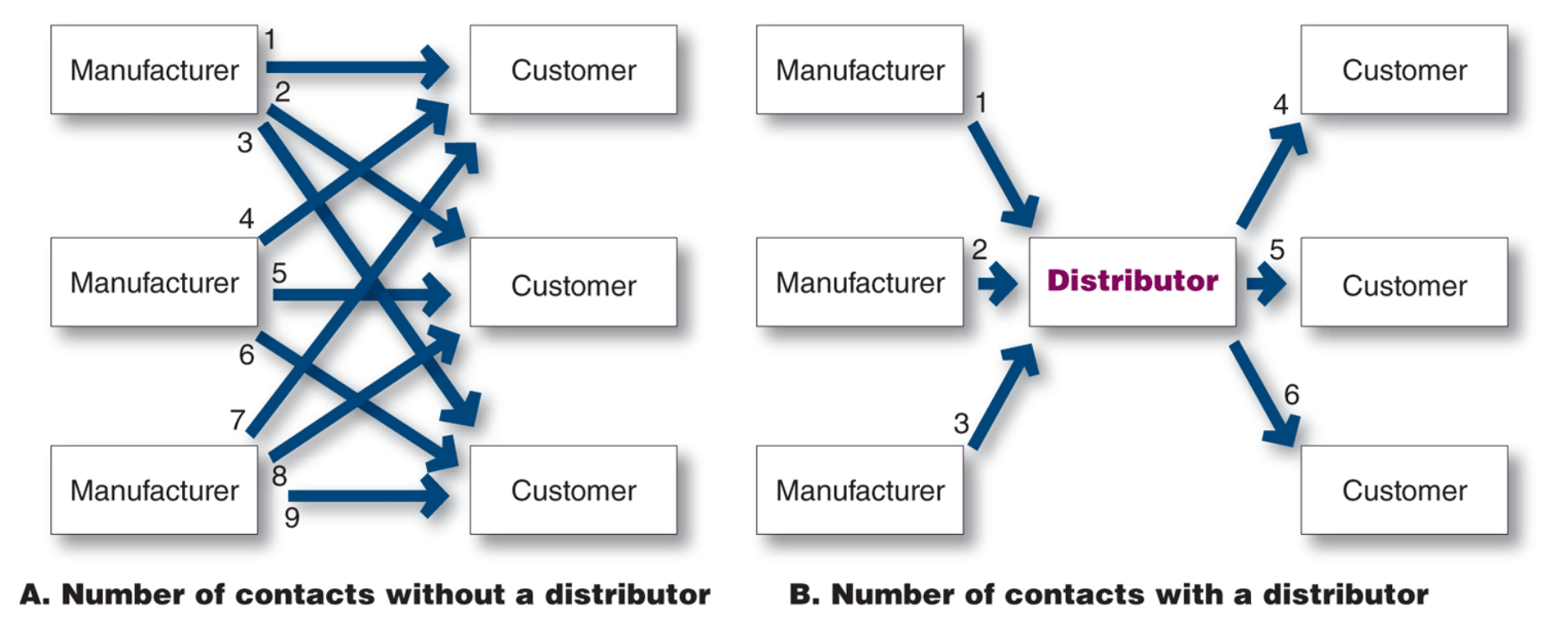
the role of a marketing intermediary
to transform the assortment of products made by producers into the assortments wanted by consumers
time utility
making products available at the time consumers want to purchase them
Place utility
making products available at the locations the consumers want them
Possession utility
making it easier for the consumers to acquire the product
Form utility
customising products to fit consumers needs
Exchanging efficancies
making transactions as cheap as possible by establishing and managing the exchange process
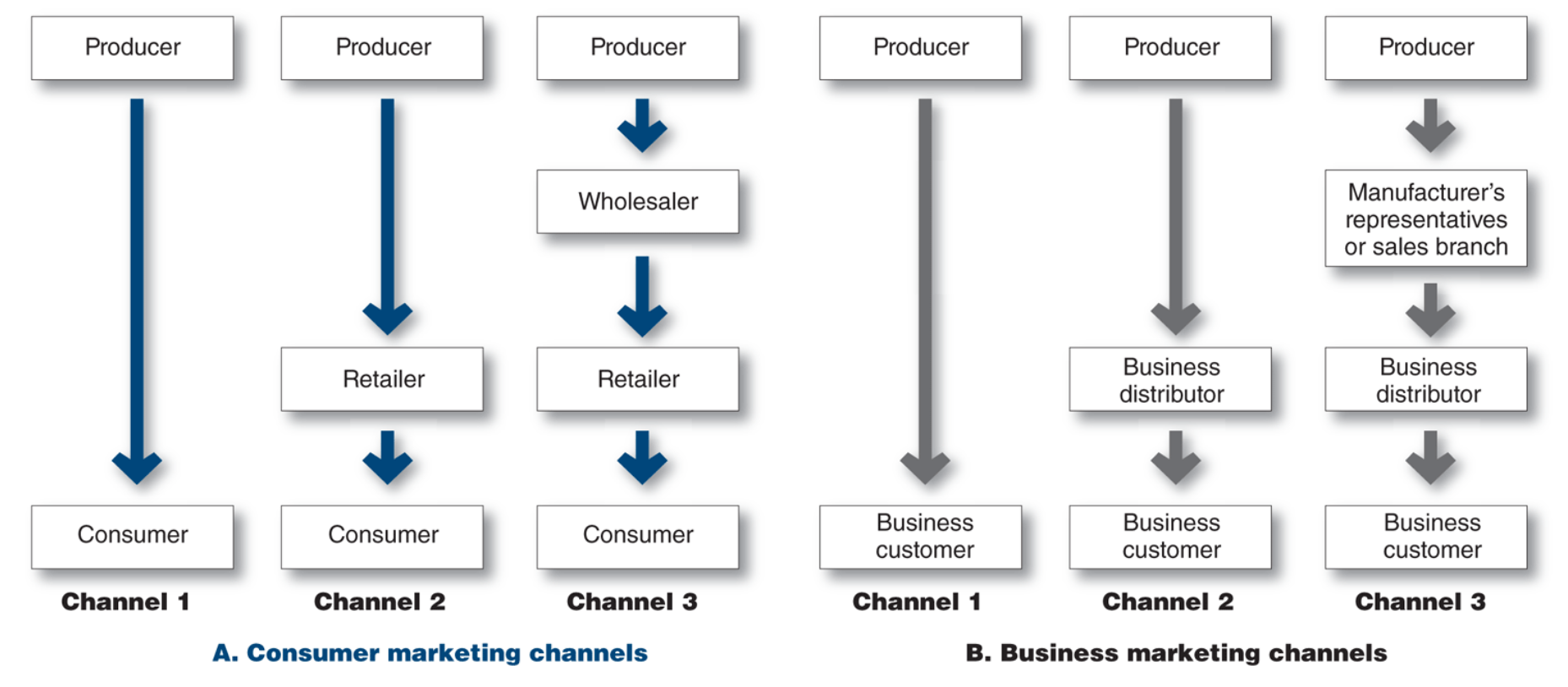
Channel levels
A layer of intermediaries who perform some work in bringing the product and its ownership closer to the final buyer.
Crucial functions marketing channel members perform
information, promotion, facilitating exchange, financing and risk taking
Channel conflict
Disagreements among marketing channel members on goals, roles and rewards – that is, on who should do what and for what rewards
Vertical marketing system
A distribution channel structure in which producers, wholesalers and retailers act as a unified network; one channel member owns the others, has contracts with them or wields so much power that all channel members cooperate.
Horizontal marketing system
A channel arrangement in which two or more companies at one level join together to follow a new marketing opportunity.
Conventional marketing system
A channel consisting of one or more independent producers, wholesalers and retailers, each a separate business seeking to maximise its own profits, perhaps even at the expense of profits for the system as a whole
Administered vertical marketing system
A vertical marketing system that coordinates successive stages of production and distribution, not through common ownership or contractual ties but through the size and power of one of the partie
Contractual vertical marketing system
A vertical marketing system in which independent firms at different levels of production and distribution join together through contracts
Multichannel distribution system
a single firm sets up two or more marketing channels to reach one or more marketing segments.
Disintermediation
The removal of marketing channel intermediaries by goods or service producers, or the displacement of traditional resellers by new and different types of intermediaries
Intensive distribution
A distribution strategy in which companies stock the product in as many outlets as possible
selective distribution
A distribution strategy in which a company uses more than one but fewer than all of the intermediaries that are willing to carry the company’s products.
Exclusive distribution
A distribution strategy in which a company gives only a limited number of dealers the exclusive right to distribute the company’s products in the dealers’ territories.
Retailing
All activities involved in selling goods or services directly to final consumers for their personal, non-business use
Shopper market
Using the entire marketing process, from product to logistics and promotion, to extend brand equity to ‘the last mile’ and encourage favourable point-of-purchase decisions.
Omni-channel buying
little distinction between in-store and online shopping and for whom the path to a retail purchase runs across multiple channels]
A retailer
A business whose sales come primarily from retailing
Category killer
A giant specialty store that carries a very deep assortment of a particular line.
Classifications of retail stores
amount of service offered, product line sold, relative prices charged and how they are organised
Specialty stores
carry a narrow product line with deep assortment
Department stores
carry several product lines each with a different department
Supermarkets
A relatively large low cost low volume high volume and self service operation designed to serve the consumers needs for grocery and household products
Convenience stores
small shops in residential areas open long hours that have a high prices for what they sell