Unit 2: Soil Vocabulary
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

23 Terms
Soil
provides nutrients for plants: made of
rock, humus, clay, silt, and sand
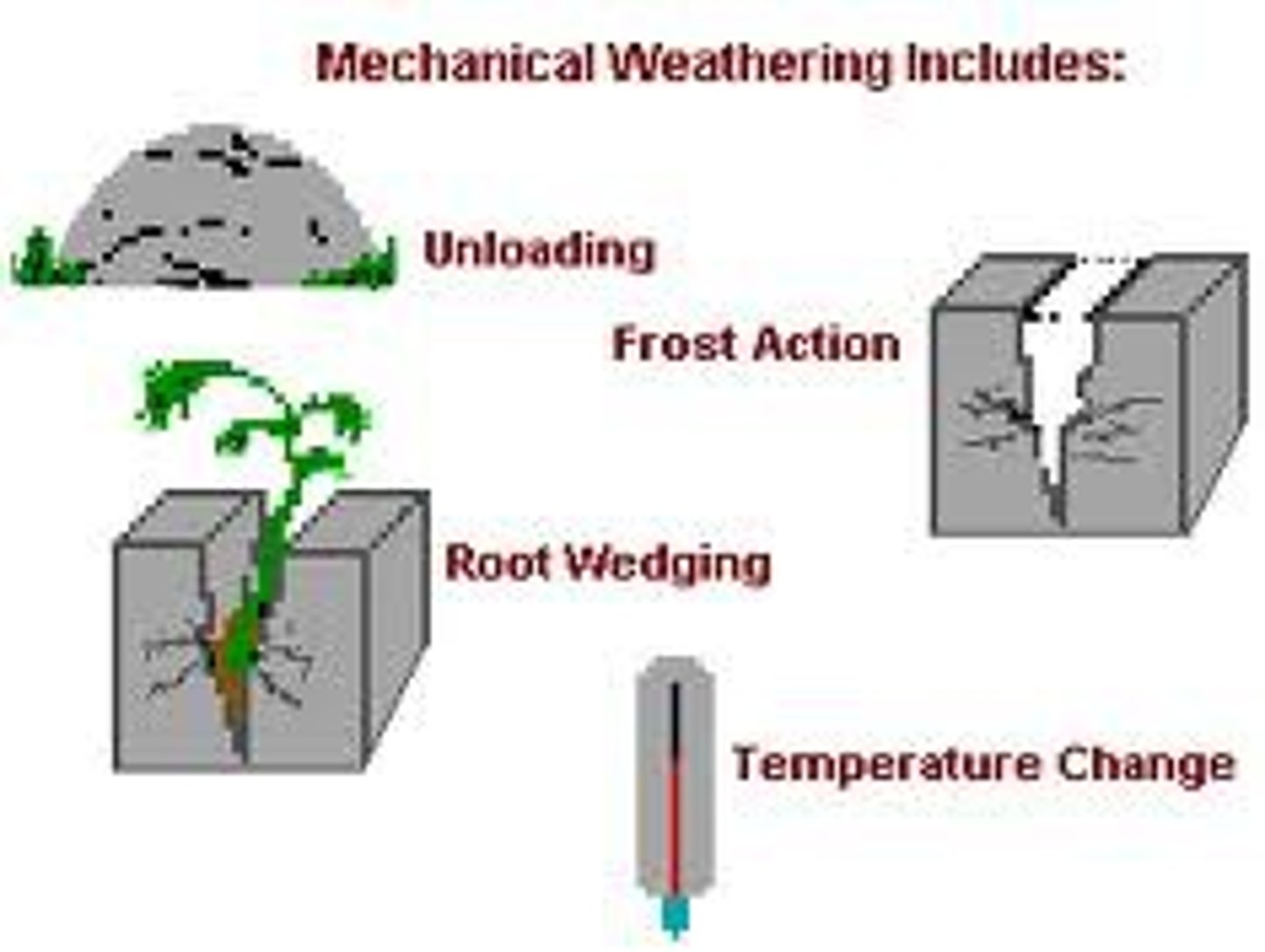
Weathering
break down of rocks: creates soil
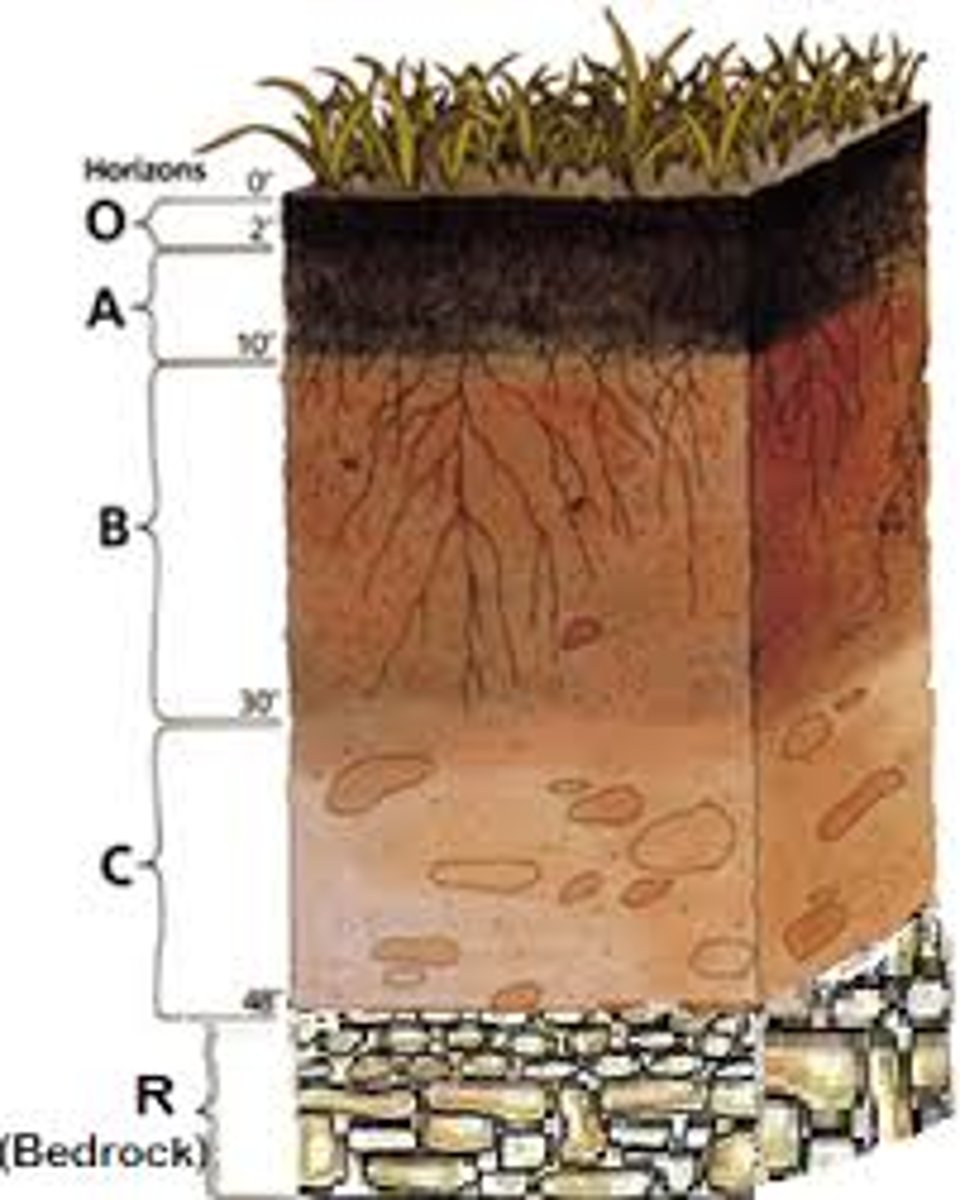
Topsoil
upper soil- natural product of subsoil and
bedrock and it is the best for plants

Subsoil
made up mostly of clay and under the
topsoil

Bedrock
The bottom layer of soil and the worst for plants to
grow

Humus
decayed matter found in top soil and does
not hold water well

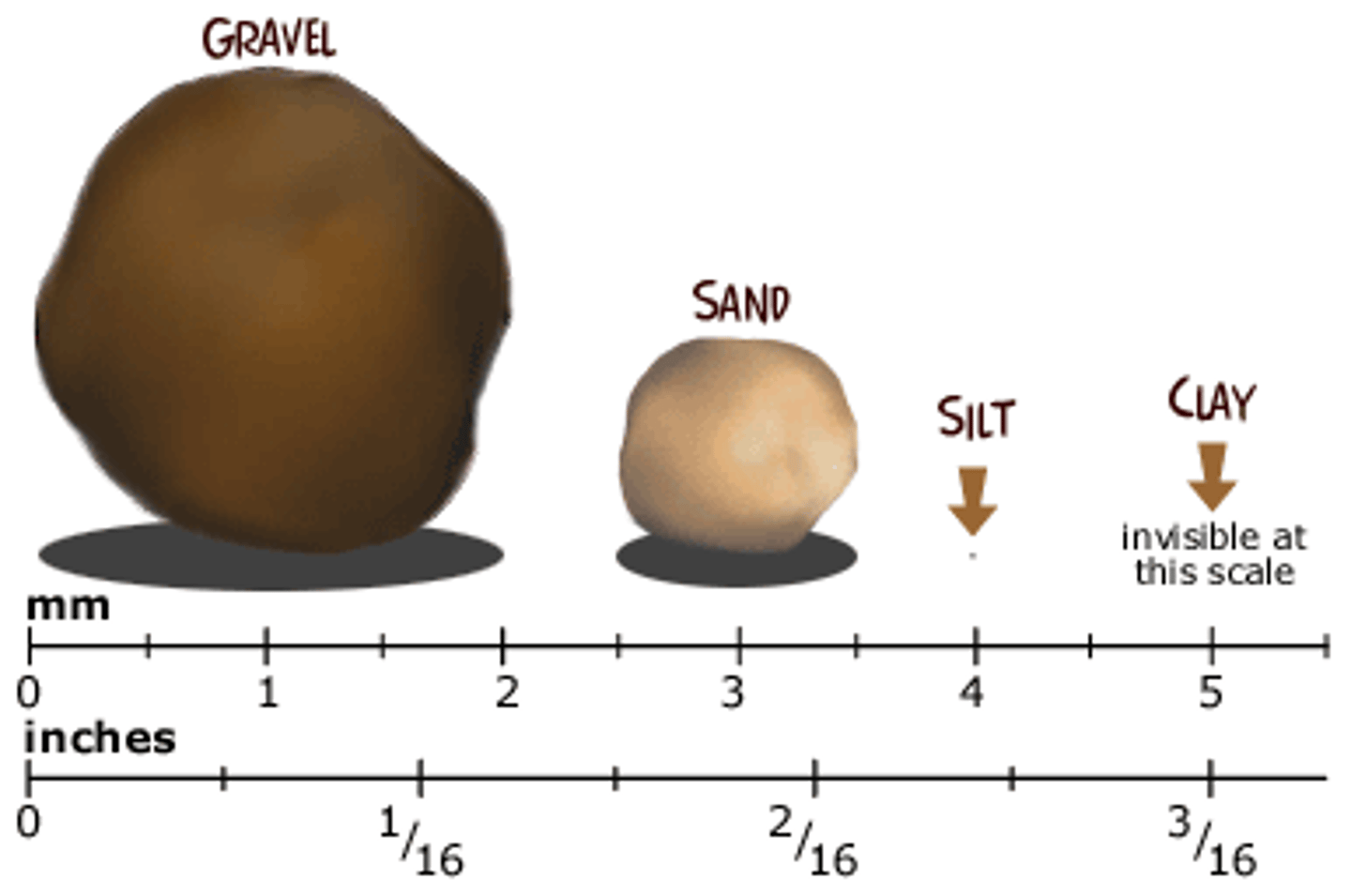
Sand
Grains of worn down rock, larger than silt-
has few nutrients and does not hold water
well
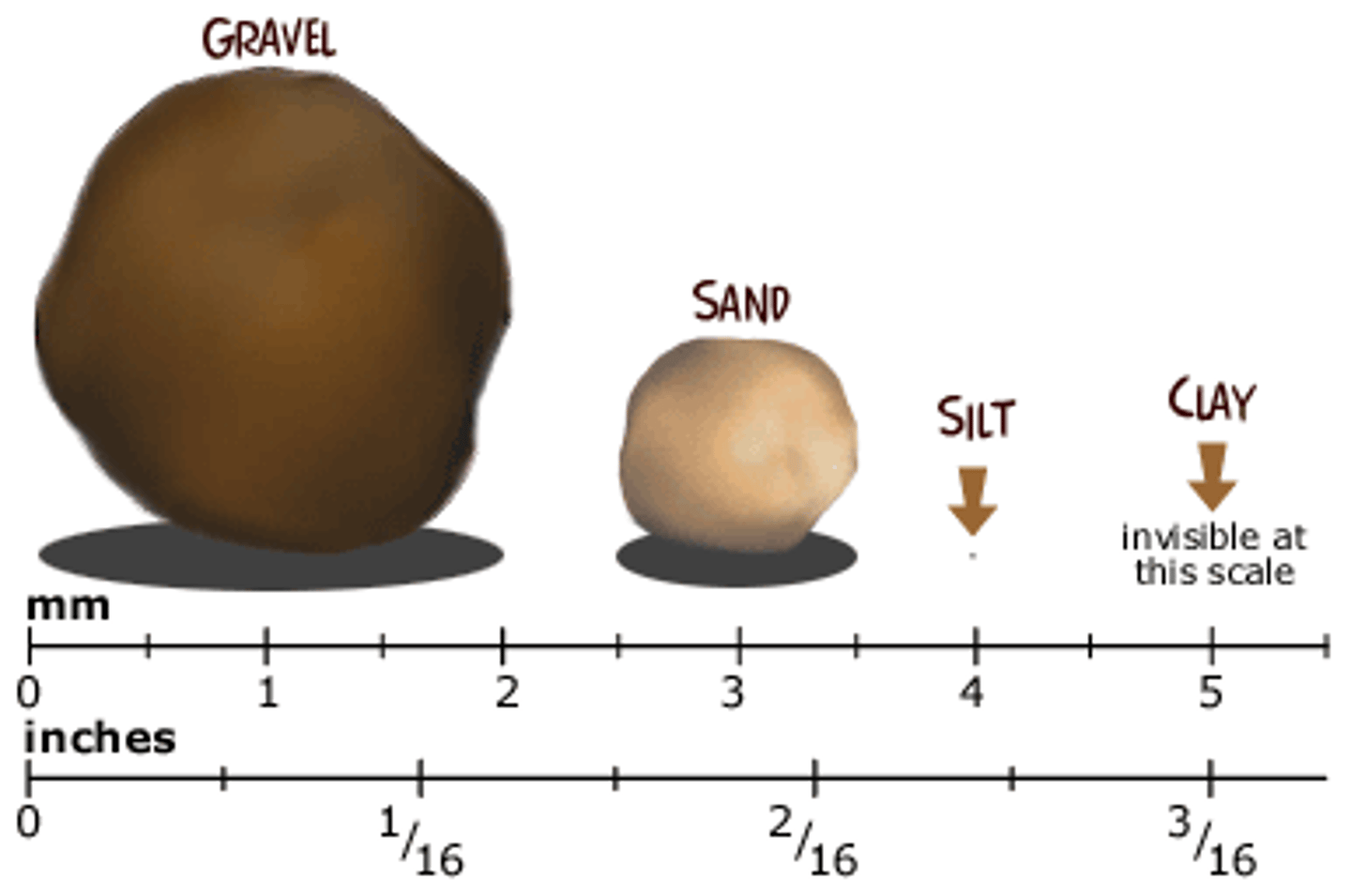
Silt
Very small broken pieces of rock, smaller
than sand and larger than clay
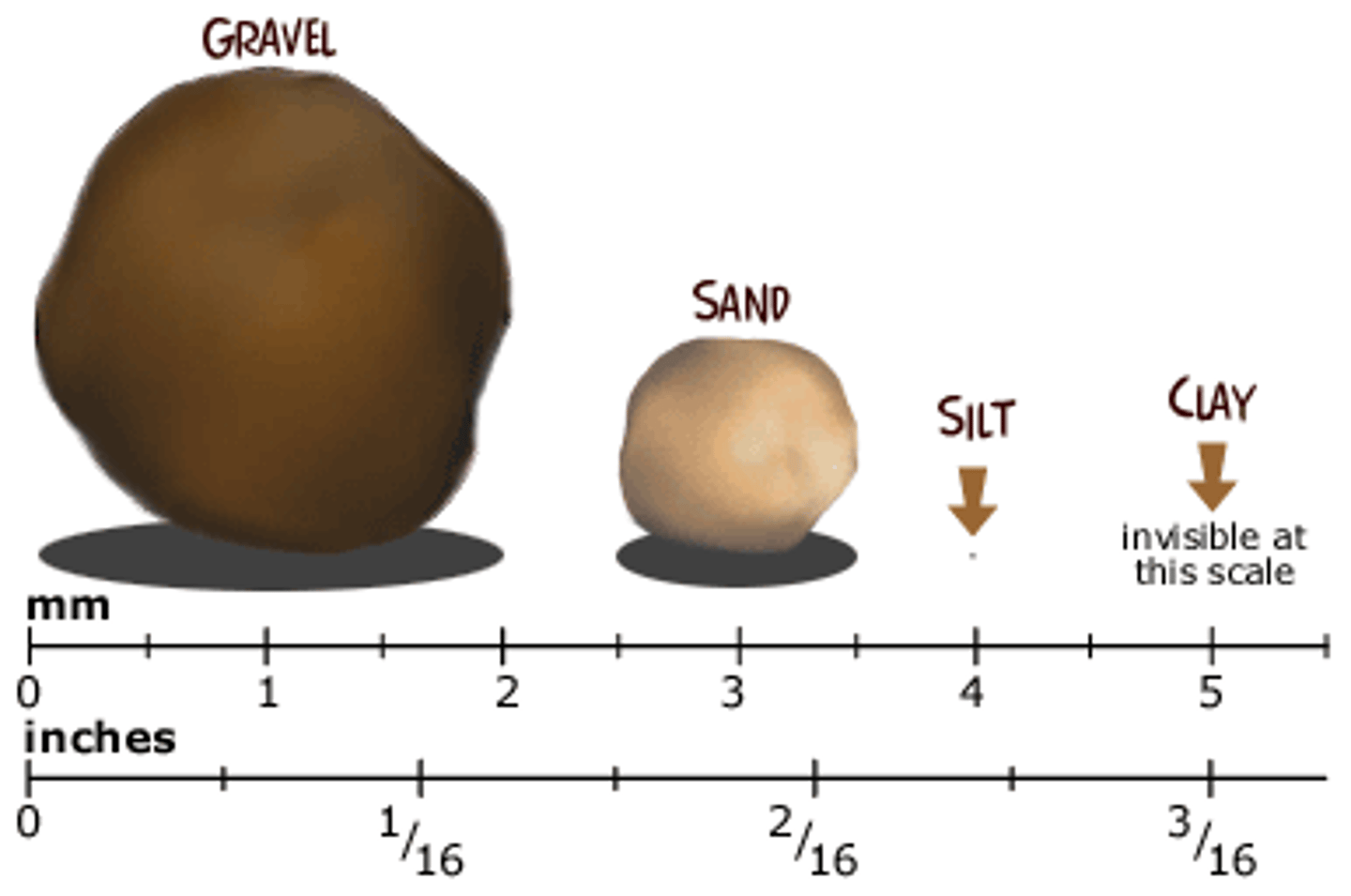
Clay
Contains nutrients and holds water well-
can be red or yellow, smallest grain size
Conserve
To save

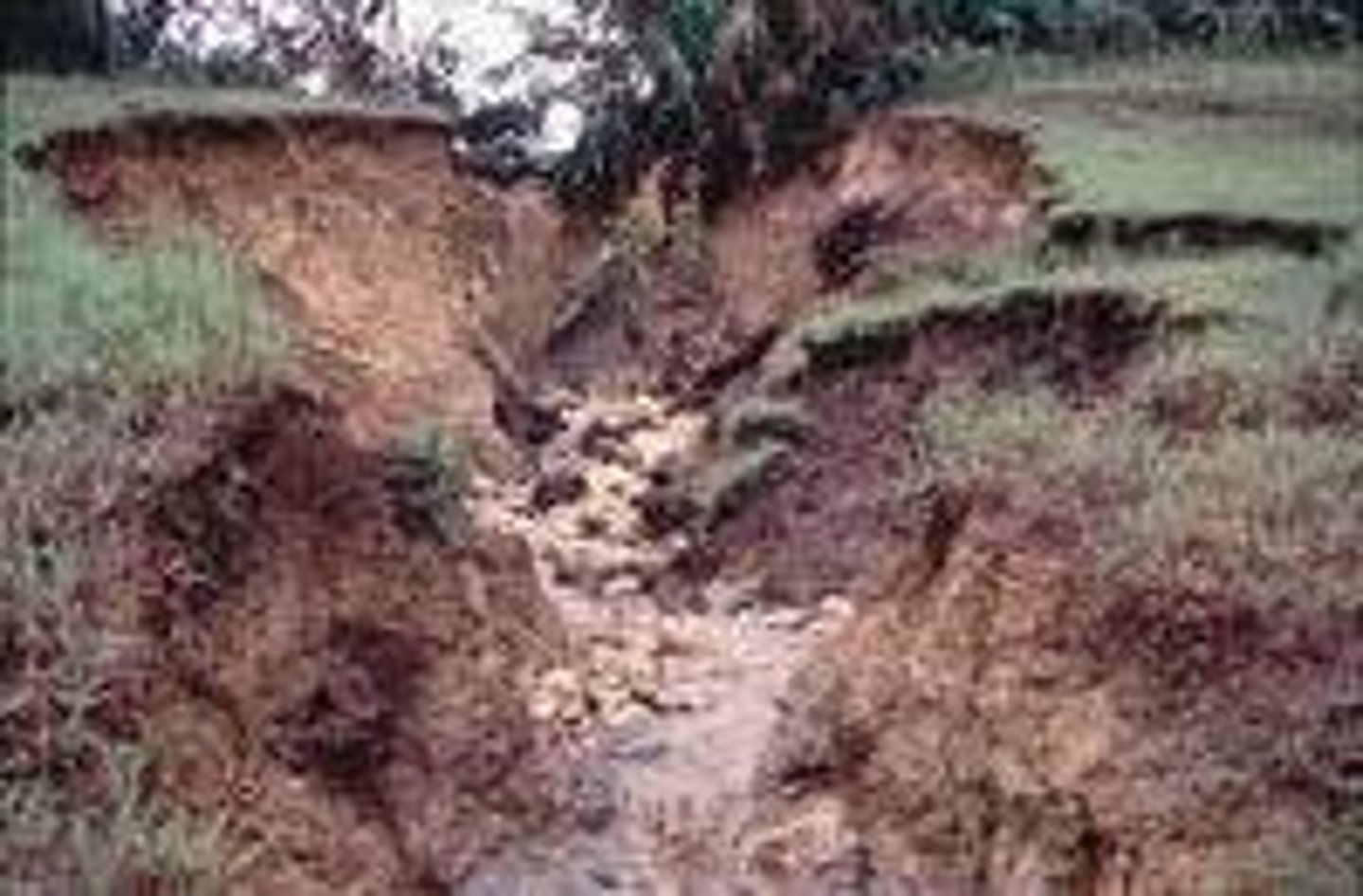
Erosion
Processes by which rock, sand, and soil are broken down and carried away (i.e. weathering, glaciation)

Creep
Type of Wind Erosion, Small soil particles roll or slide while maintaining contact with the ground.

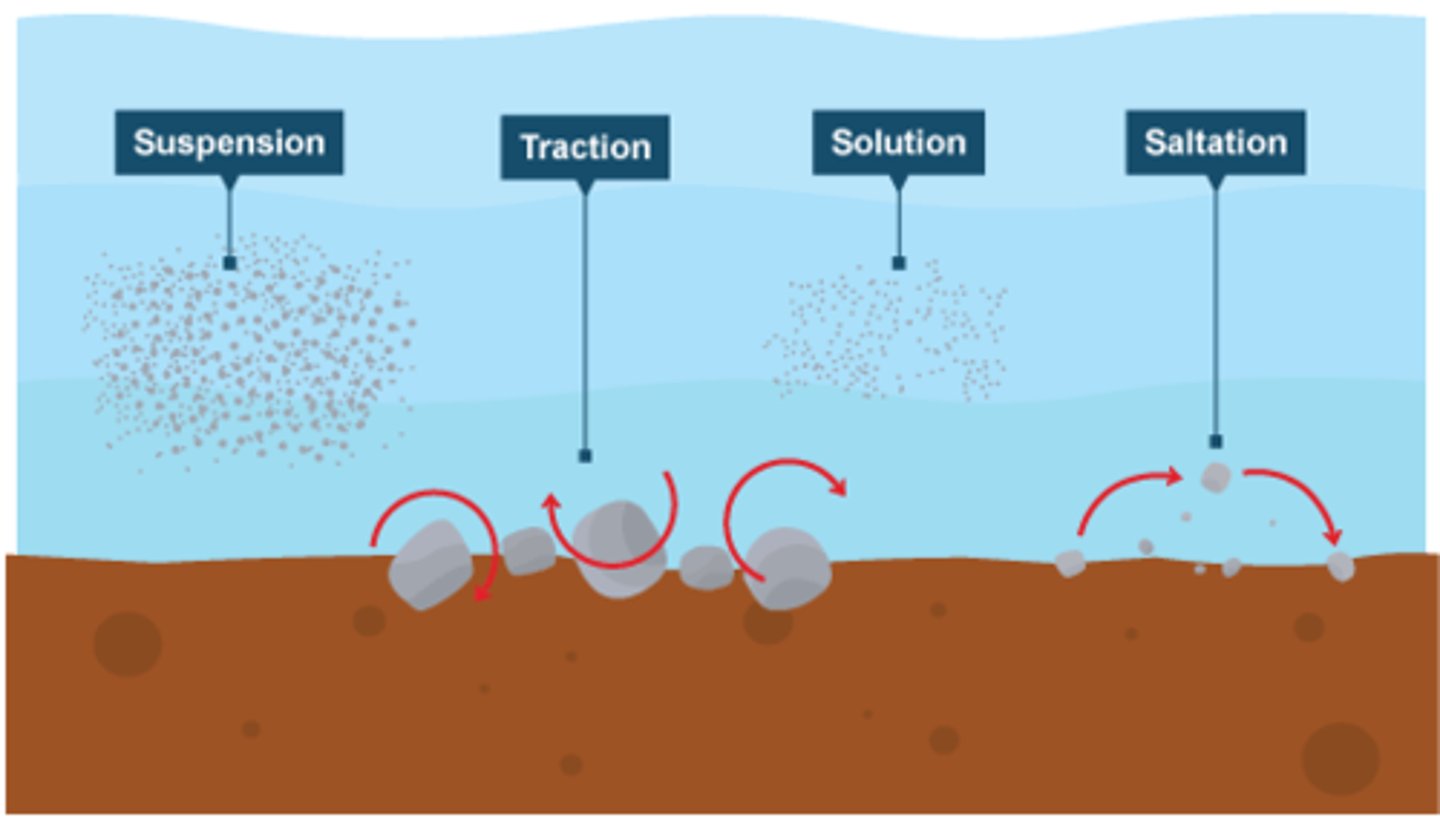
Saltation
Type of Wind Erosion, Grains of soil bounce across the ground.
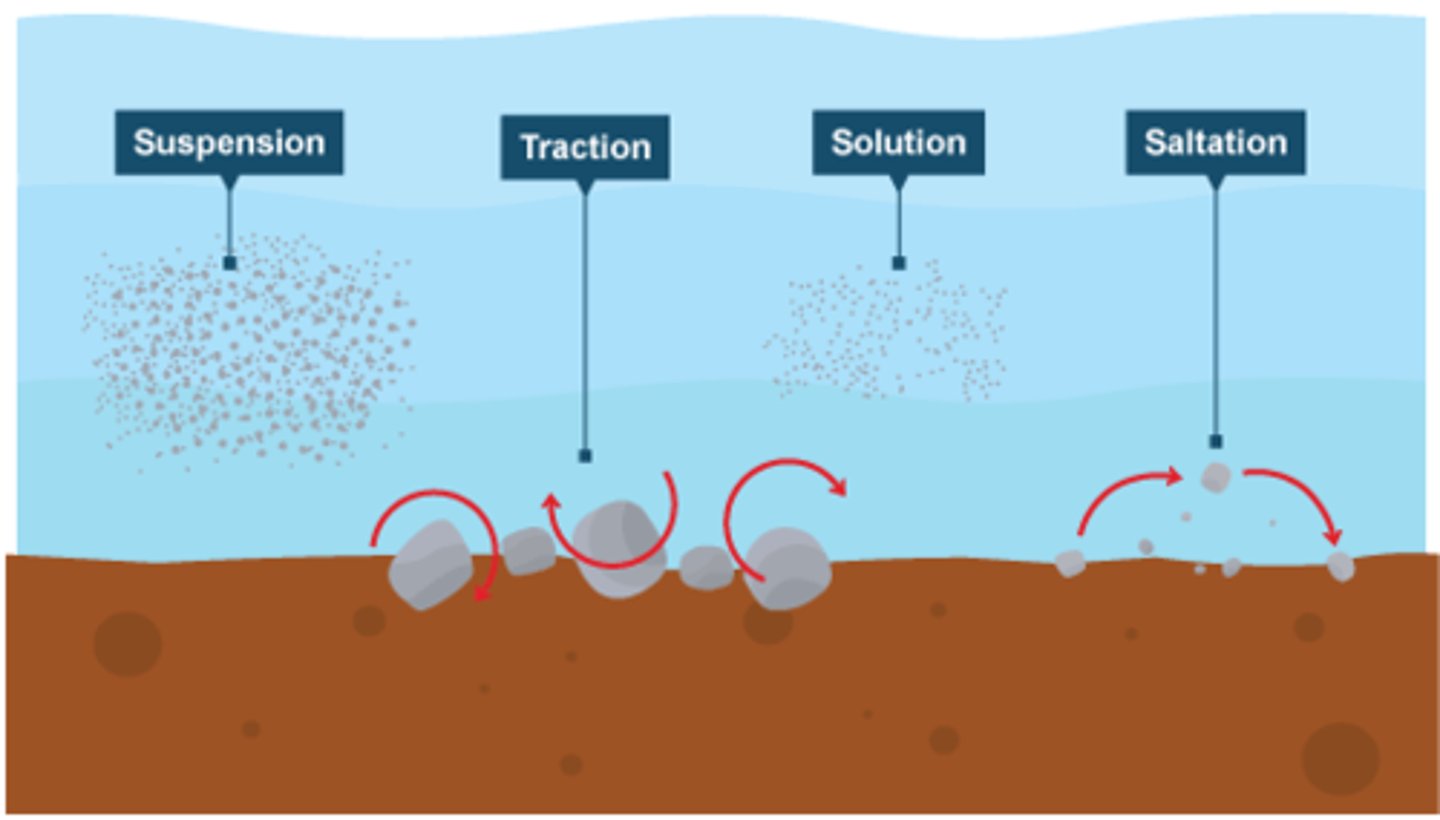
Suspension
Type of Wind Erosion, Soil moves through the air like in a dust storm
Sheet
Type of water erosion, loss of thin uniform layers of soil over a full field
Rill
Type of water erosion, channels or rills forming runoff, randomly located

Ephemeral
Type of water erosion, channels / depressions that form in the same place each year
Gully
Type of water erosion, large channels not able to be repaired by tilling of fields
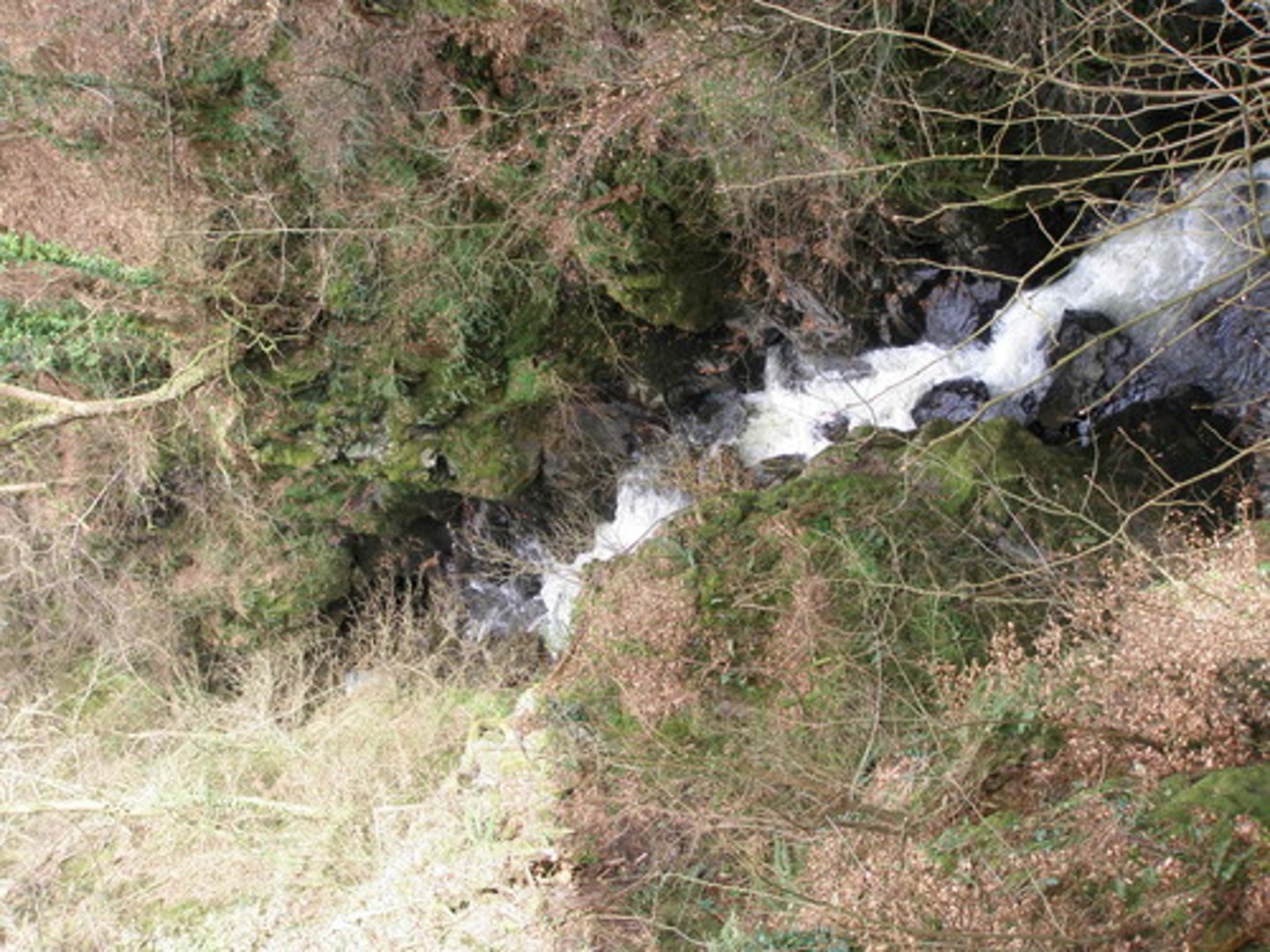

Streambank
Type of water erosion, erosion of the sides of a stream over time
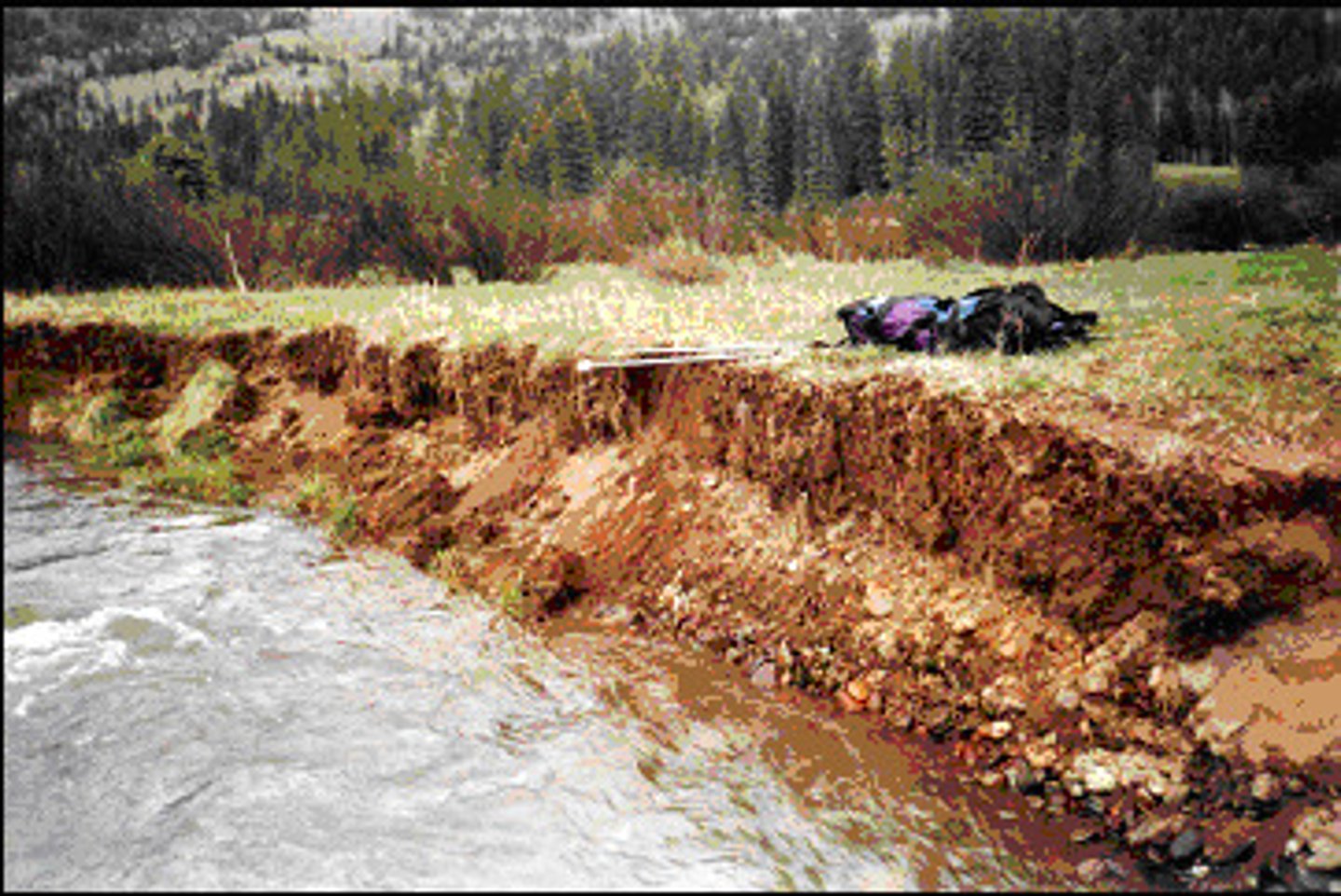

Identify the layers of soil

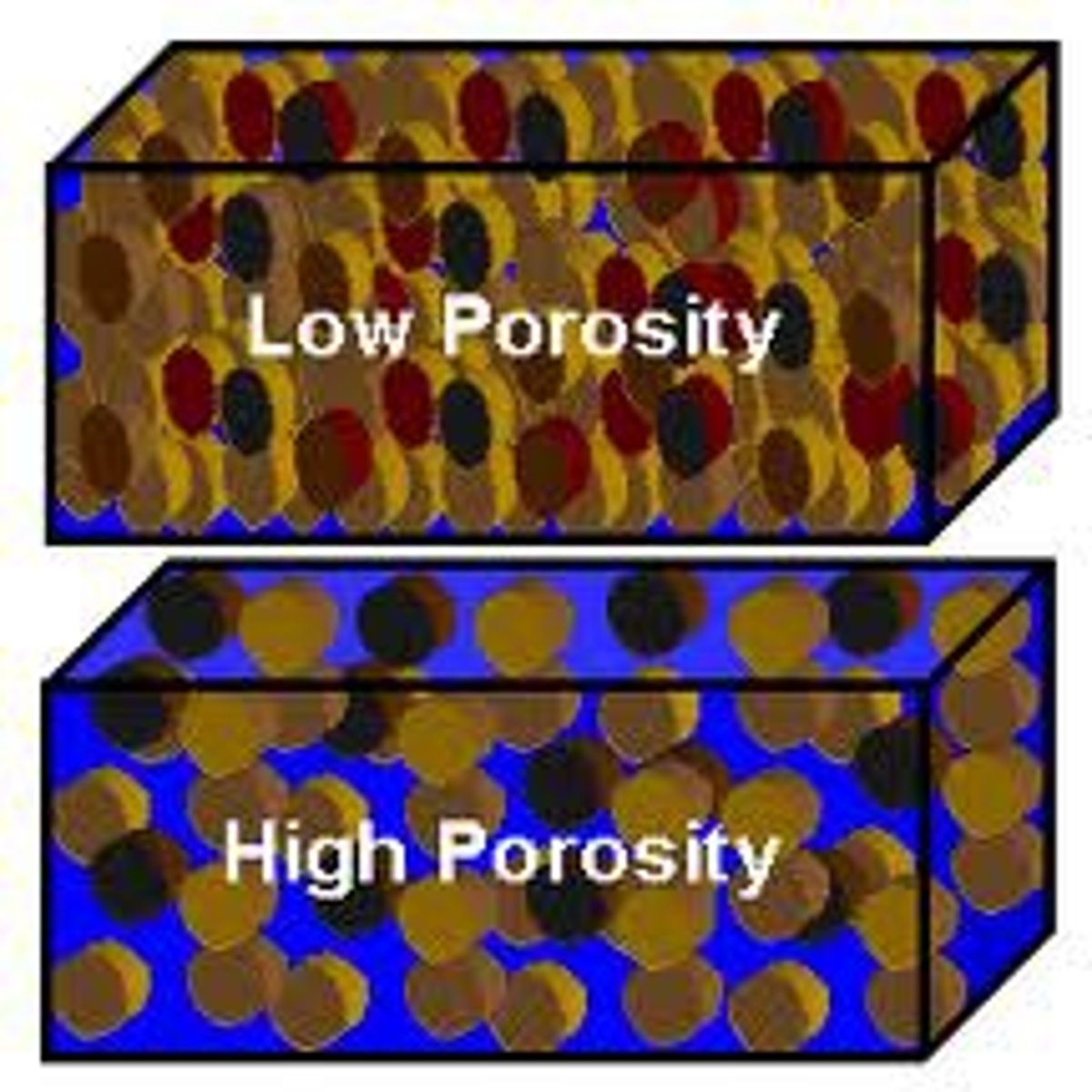
Porosity
Percentage of open spaces between grains in a rock. Ability to hold water
Permeability
Ability of rock or soil to allow water to flow through it. Sand has highest permeability.

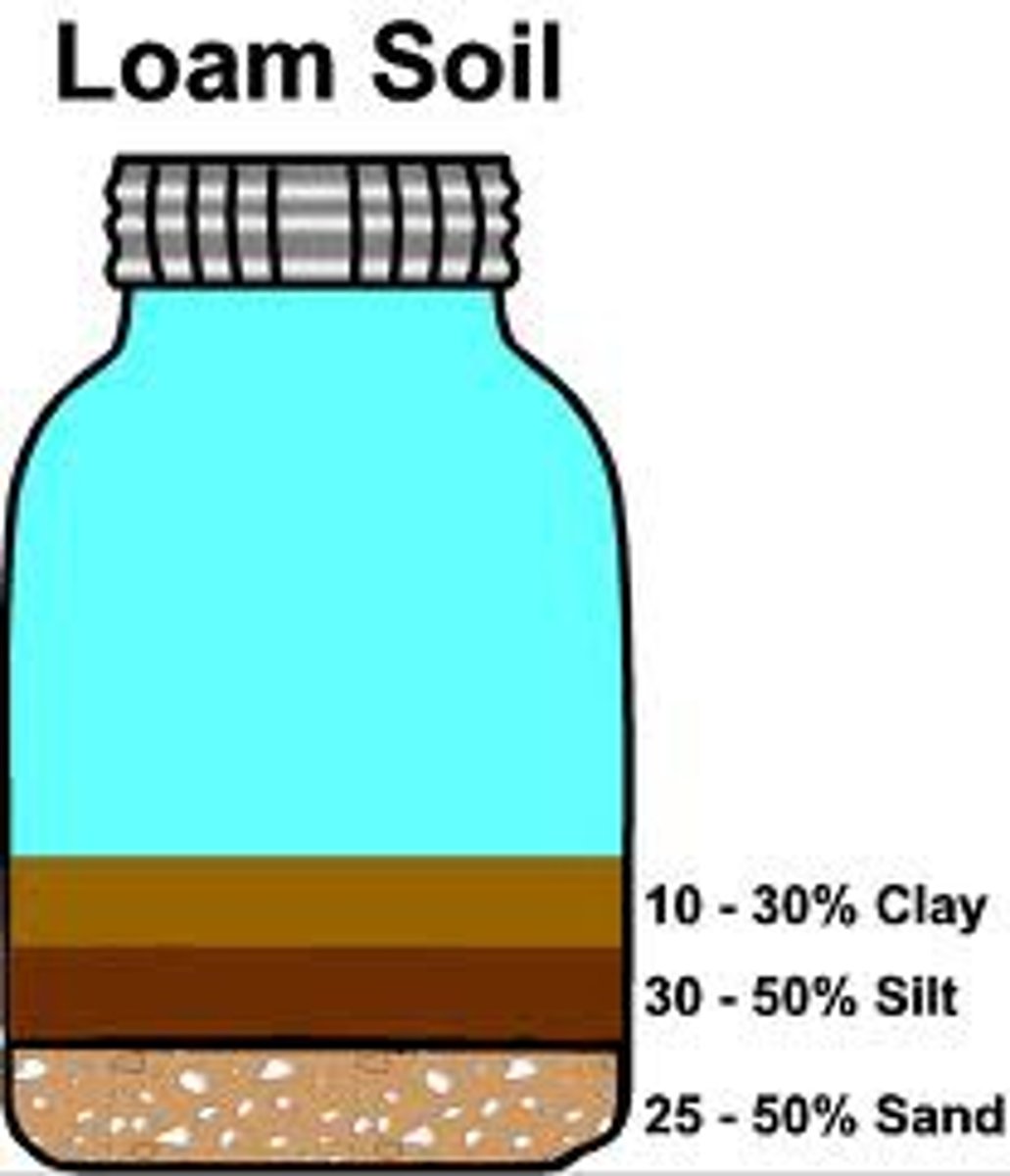
Loam
A mixture of gravel, sand, silt, clay, and organic matter