Unit 2 AP Calc AB Derivatives
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
How to find derivative on calculator (make sure it is in radians): 1. MATH -> 2. 8:nDeriv( -> 3. input function, variable, and value of x (if you're using TI-84 plus w/o color, input nDeriv(function, variable,
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Derivative (instantaneous rate of change) at x=a as h approaches 0
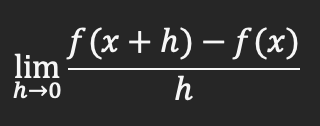
Derivative (instantaneous rate of change) at x=a as x approaches a number
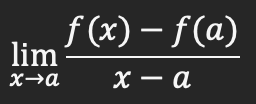
Equation of a tangent line formula
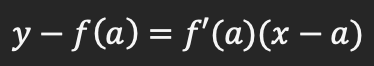
Average rate of change of a function over an interval without h
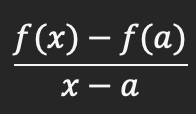
Average rate of change of a function over an interval with h
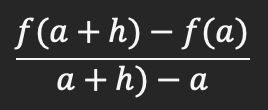
The derivative fails to exist where the function has a:
Hole or Jump
Vertical Asymptote
Corner or Cusp
Differentiability implies continuity
True
Continuity implies differentiability
False; a counter example would include a corner or a cusp
Power rule
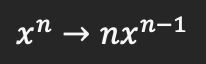
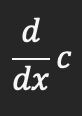
Derivative for a constant

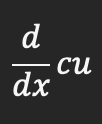
Derivative for a constant multiple
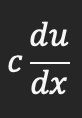
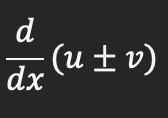
Derivative for a sum/difference
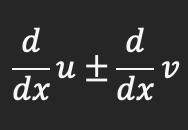
Steps for finding the equation of a derivative
Point (a,b)
Slope (find derivative, then plug x-value into derivative)
Equation ( y - f(a) = f ’(a) ( x - a ) )
Normal line
Goes through same point as tangent line does but is perpendicular to tangent line. Slope is reciprocal of tangent’s slope
Steps to find if x=? is differentiable when given a piecewise function
Determine continuity: Find limits as x approaches ? from both sides by plugging in x → equal = continuous
Determine differentiability: Find derivatives of limits as x approaches from both sides and plug in x → equal = differentiable
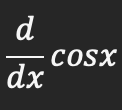
Derivative of cosx
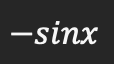
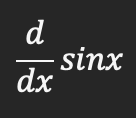
Derivative of sinx
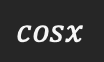
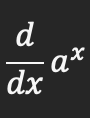

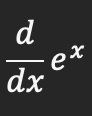
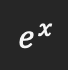
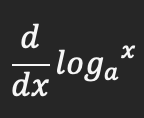
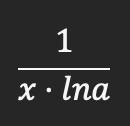
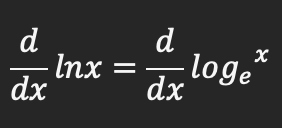

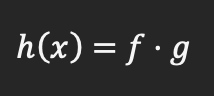
Product rule
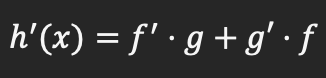

Quotient rule
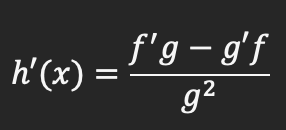
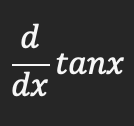
Derivative of tanx

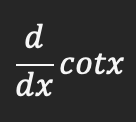
Derivative of cotx

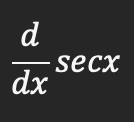
Derivative of secx
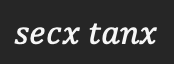
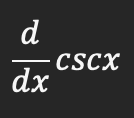
Derivative of cscx
