Bootcamp.com - Developmental Biology (20)
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
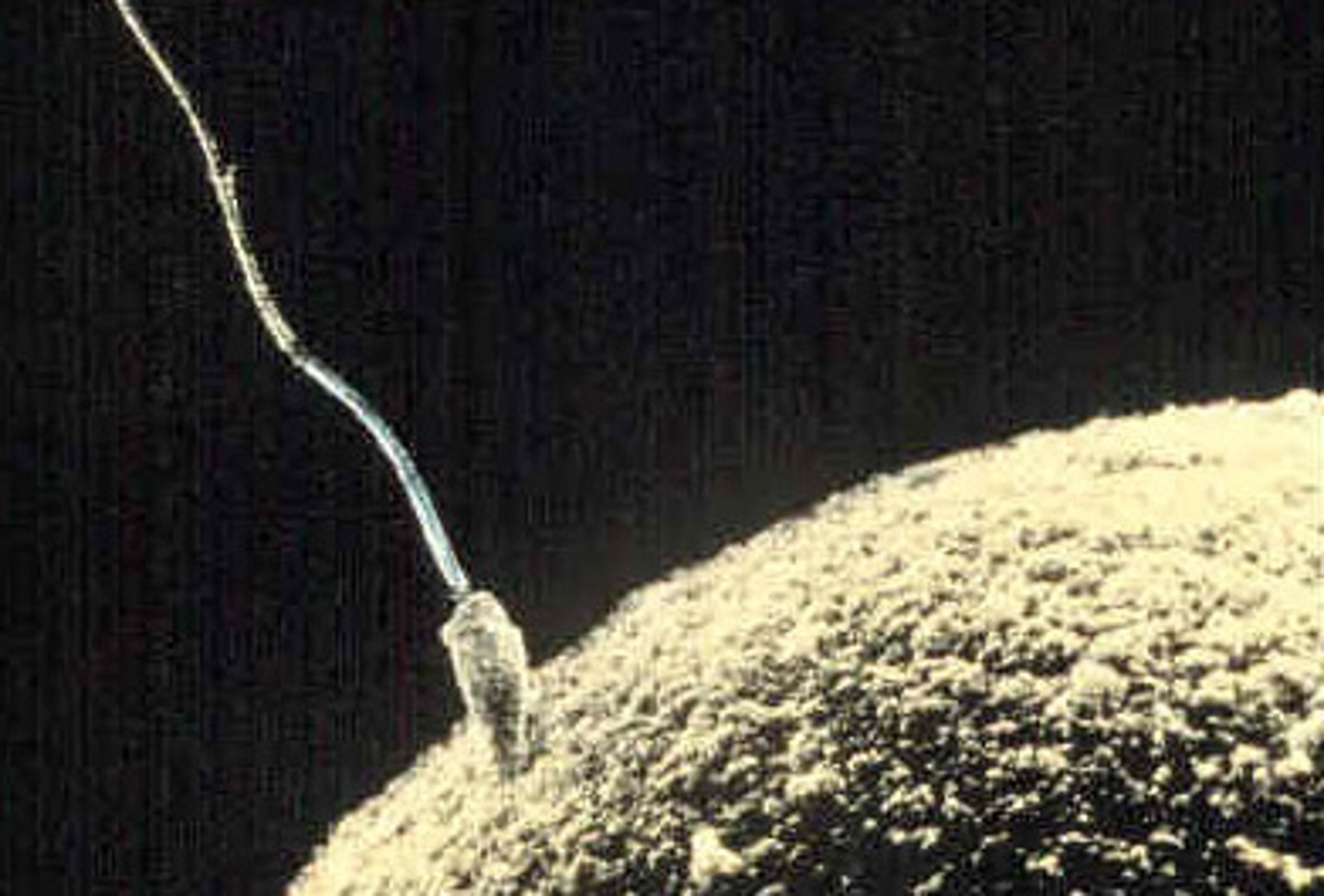
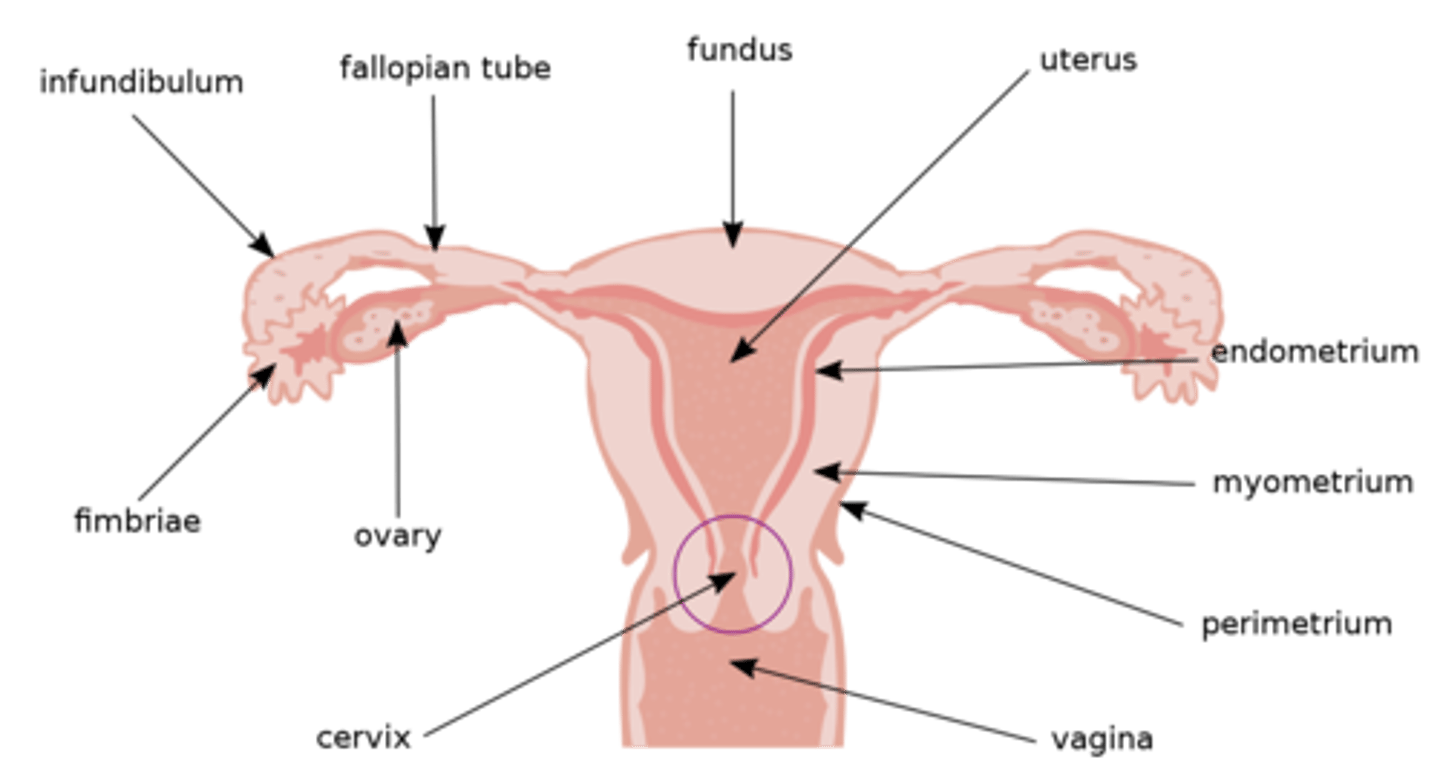
where does fertilization occur?
oviduct
_____ is the joining of a haploid sperm nucleus and a haploid egg nucleus to form a diploid zygote
fertilization
fertilization is the joining of a _____ sperm and a _____ egg to form a _____ zygote
haploid; haploid; diploid
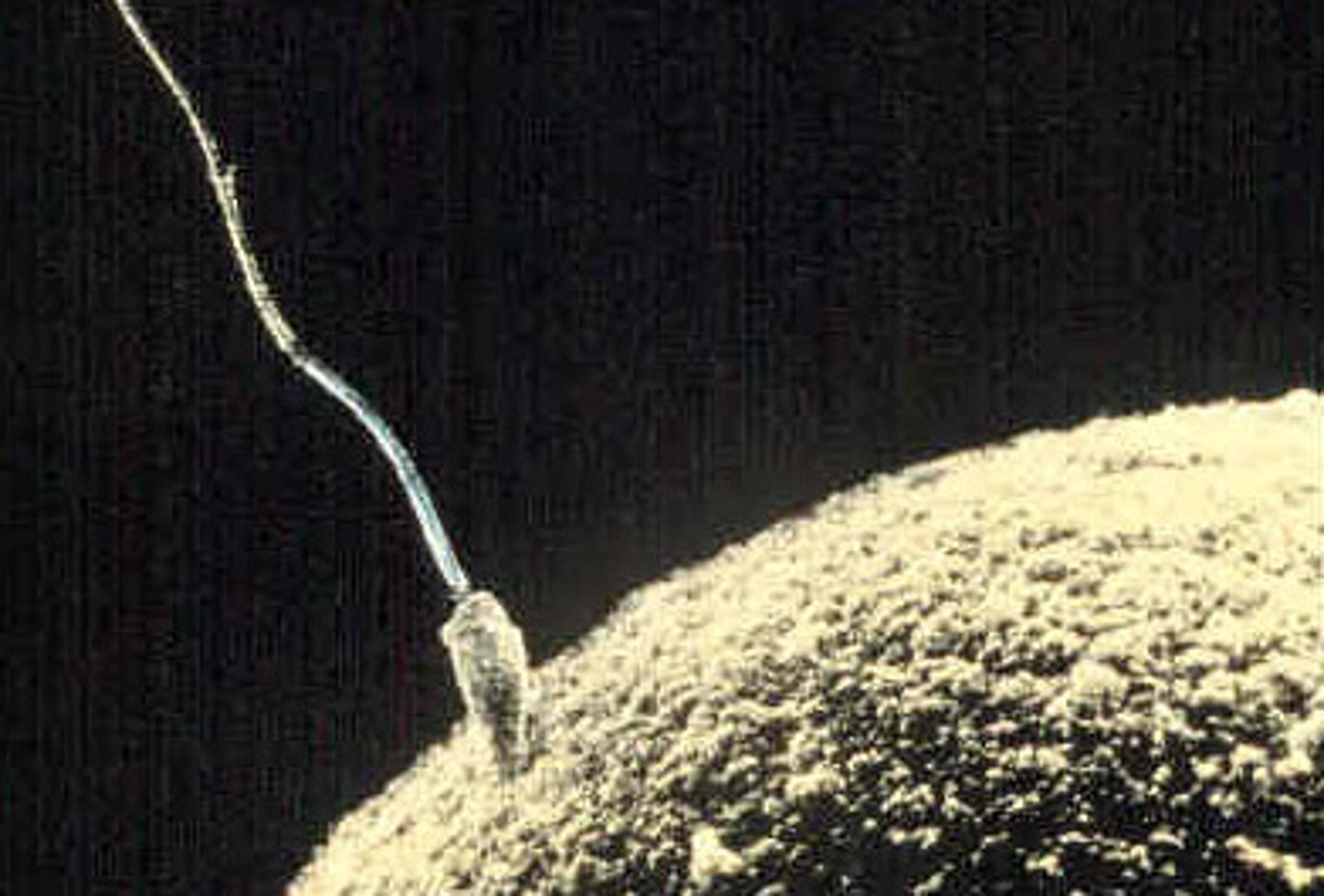
_____ is the final maturation step for the sperm prior to fertilization
capacitation
capacitation is triggered by secretions from the _____
uterine wall
capacitation _____ the sperm's plasma membrane and lipids
destabilizes
what are the two main results of capacitation?
acrosomal reaction preparation and increased Ca2+ permeability
what is significant about increased Ca2+ permeability for a sperm after capacitation?
it causes hyperactivity, making the flagellum beat harder
the _____ is the recognition process between the sperm and the egg before they fuse together in order to ensure _____
acrosomal reaction; same-species fertilization
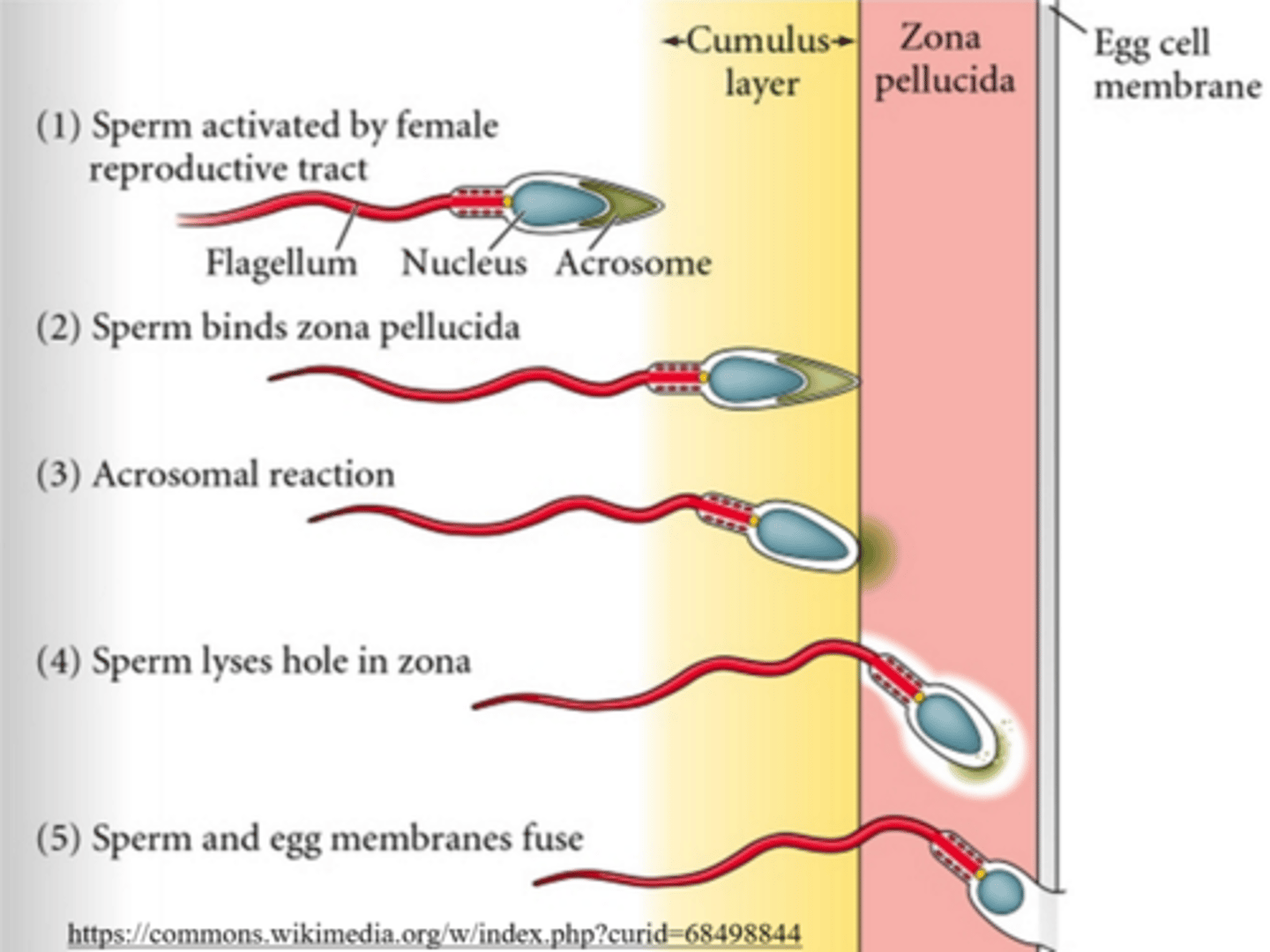
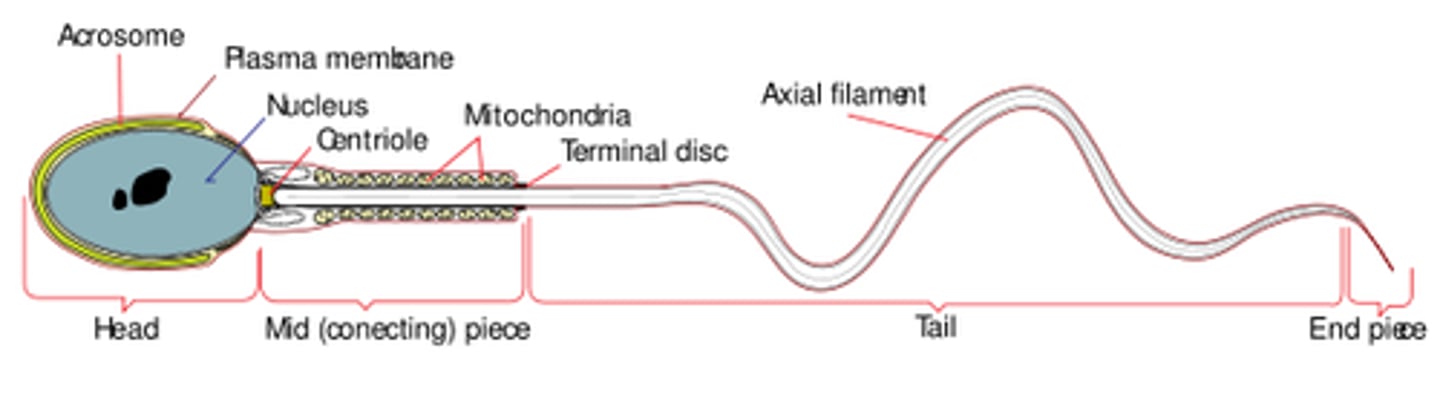
the _____ is found on the tip of the sperm head, and it contains hydrolytic enzymes for digestion of the outer egg layers
acrosome
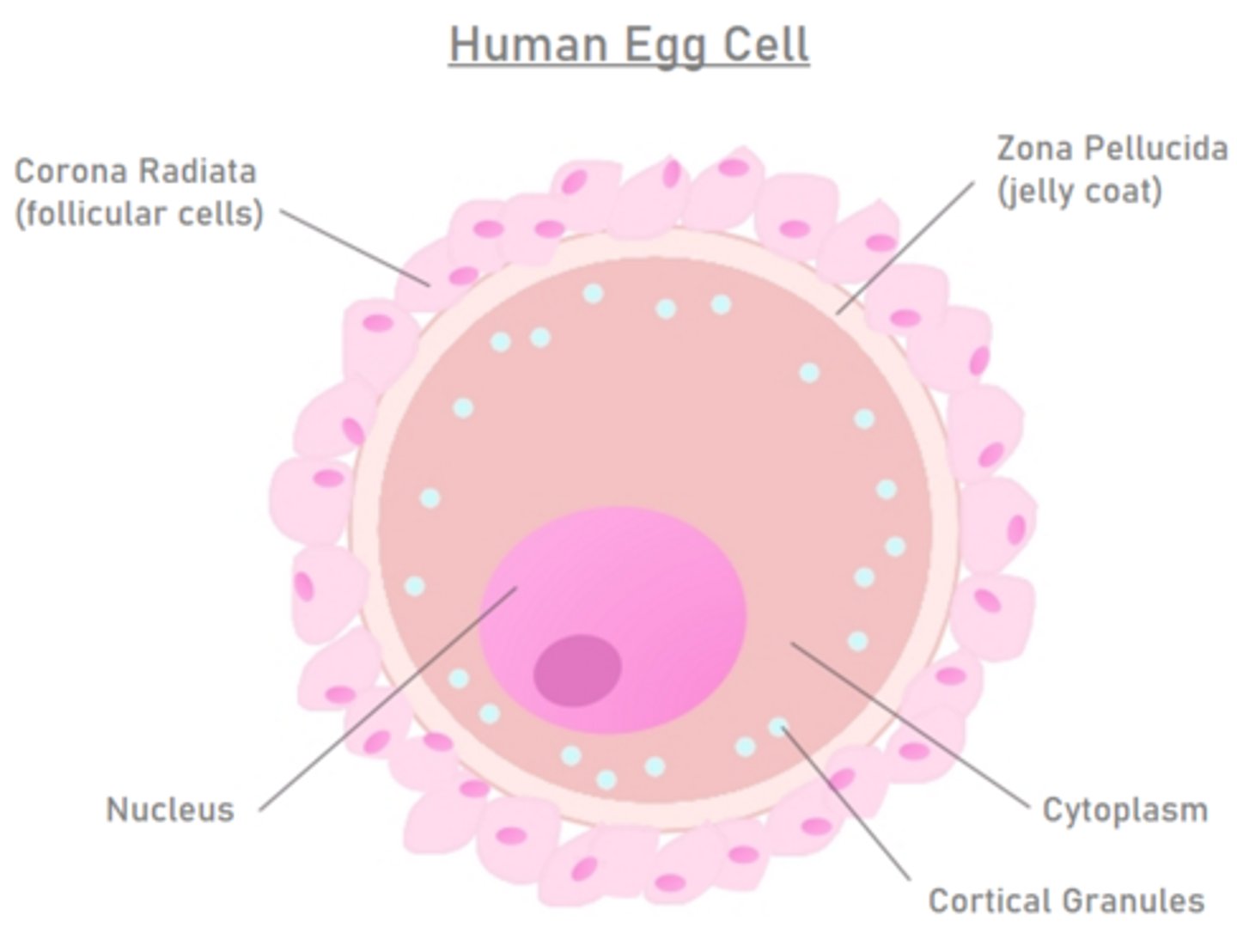
the corona radiata is the _____ layer of the egg
outermost
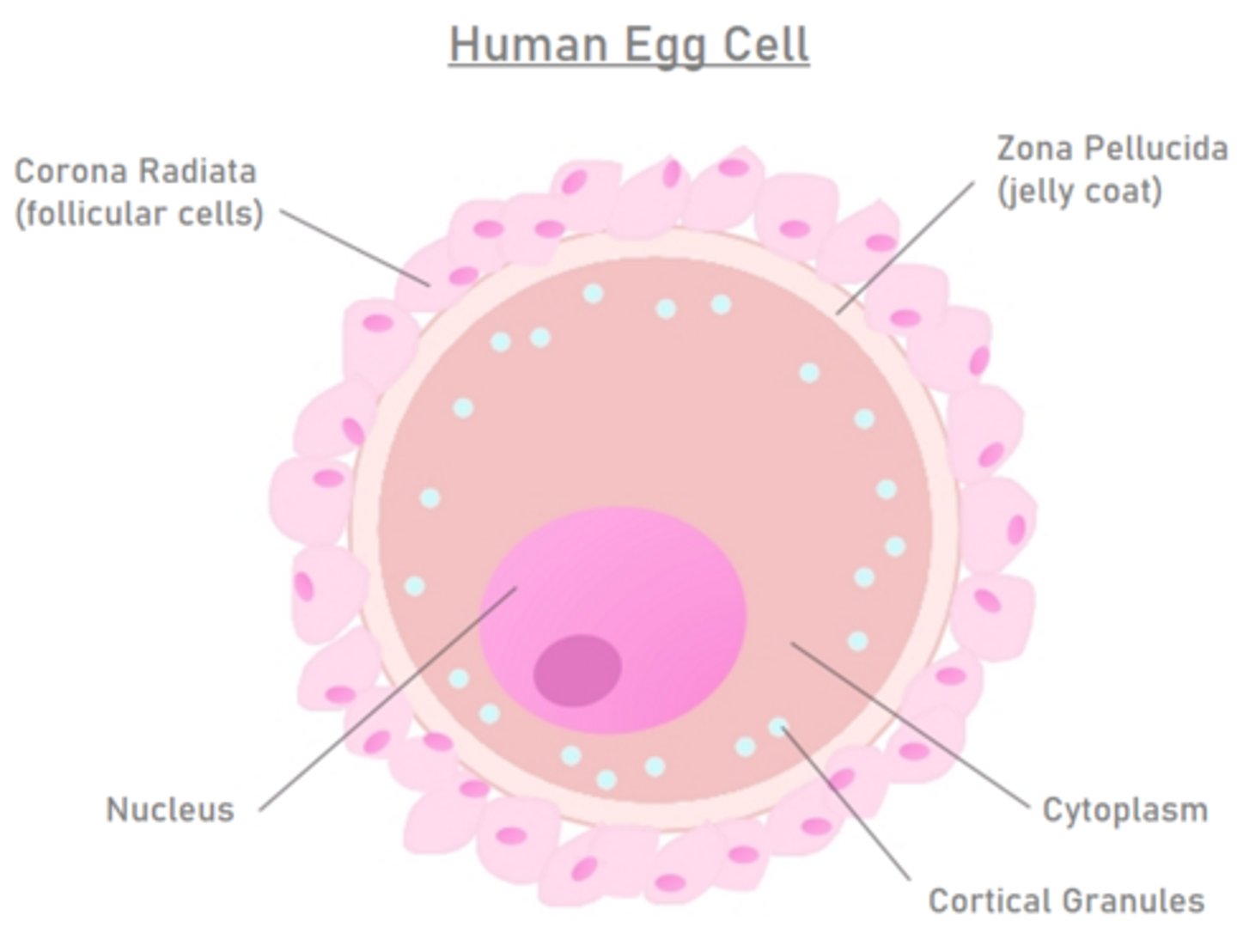
the _____ is a layer of glycoproteins underneath the corona radiata
vitelline layer
the vitelline layer is called the _____ in mammals
zona pellucida
what does the zona pellucida protein (ZP3) do?
binds to sperm and stimulates the acrosome reaction
an egg's plasma membrane is found underneath the _____
zona pellucida (vitelline layer)
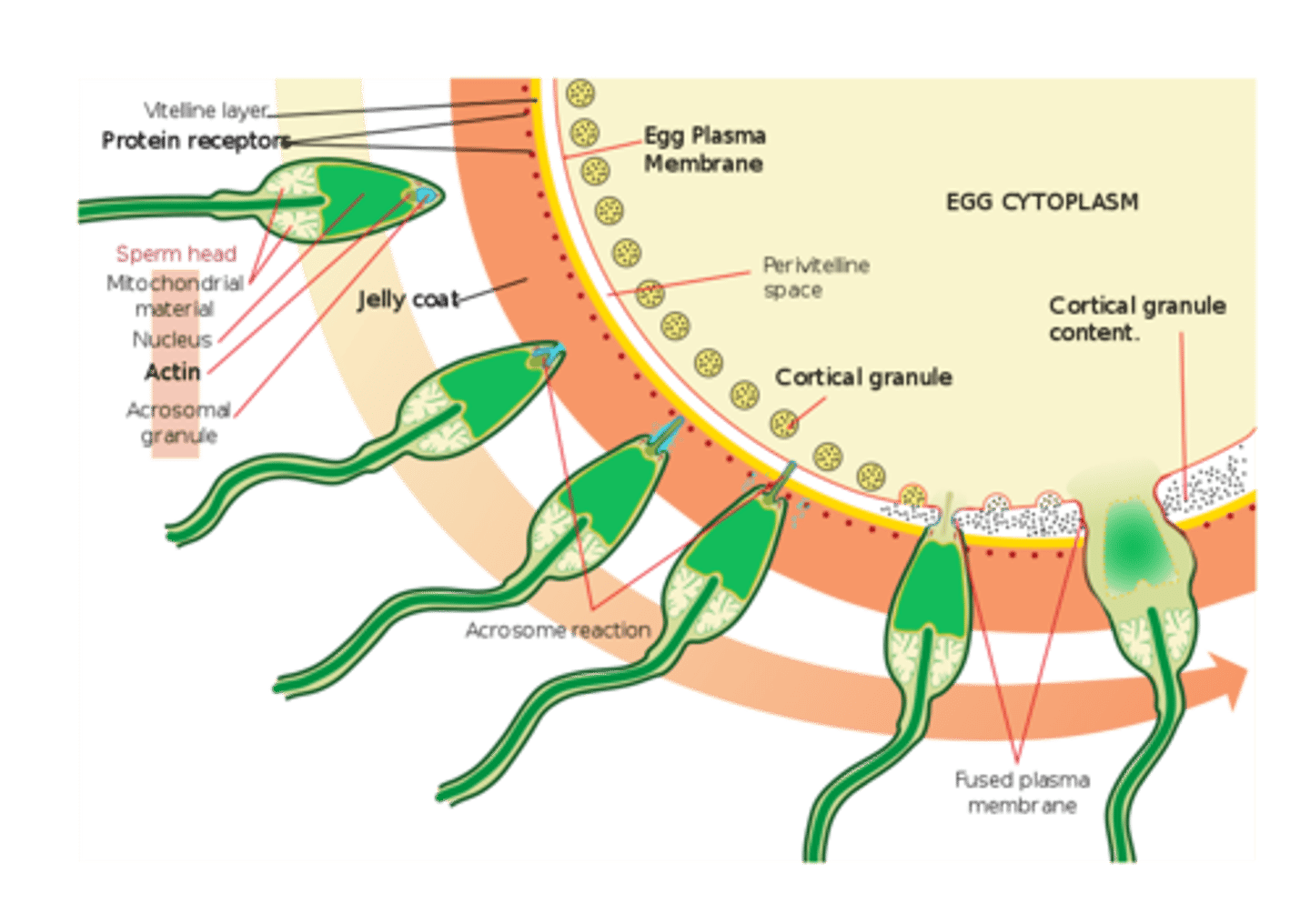
what is the general process of the acrosomal reaction?
sperm --> corona radiata --> zona pellucida --> sperm actin binds ZP3 --> acrosomal enzyme release --> membrane fusion between sperm and egg --> fertilization
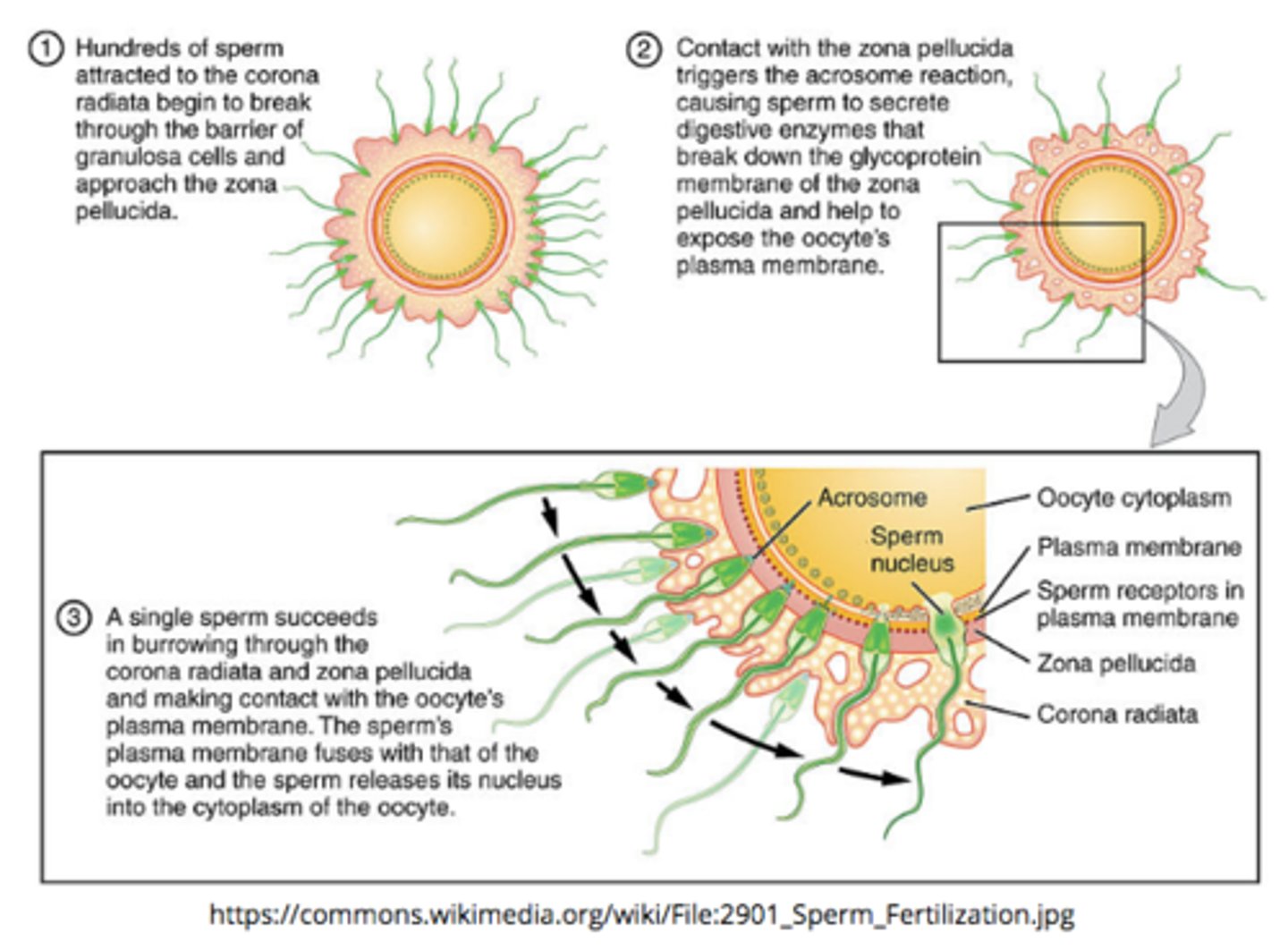
_____ describes the process where more than one sperm fertilizes an egg
polyspermy
what do polyspermy blocks do?
prevent more than one sperm from penetrating into the egg
what are the two types of polyspermy blocks?
fast and slow block
the _____ block to polyspermy happens first, immediately after the sperm's membrane has fused with the egg's membrane
fast
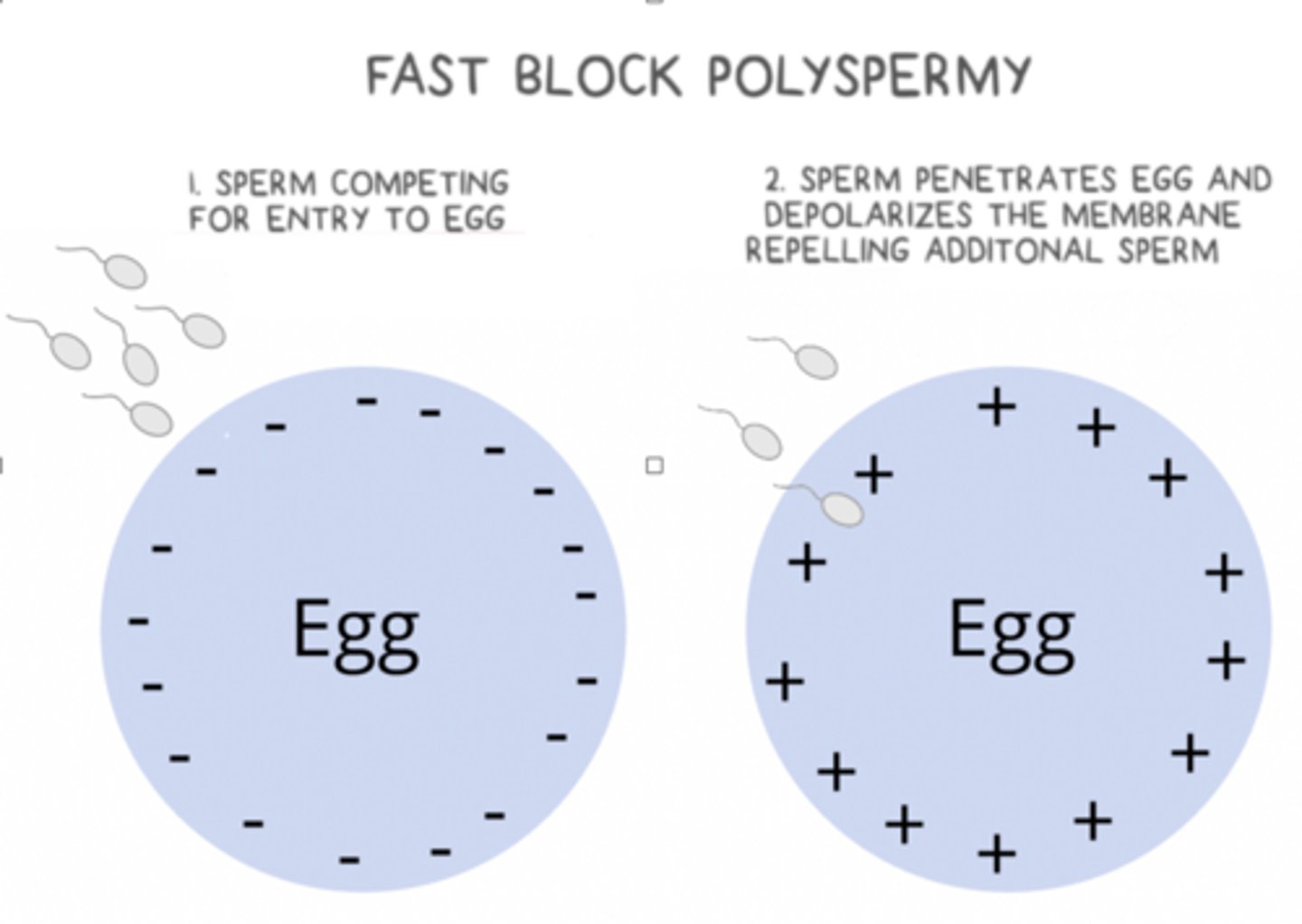
what is the general mechanism of the fast block to polyspermy?
egg penetration by sperm --> Na+ influx to egg --> membrane depolarization that repels additional sperm for a few seconds
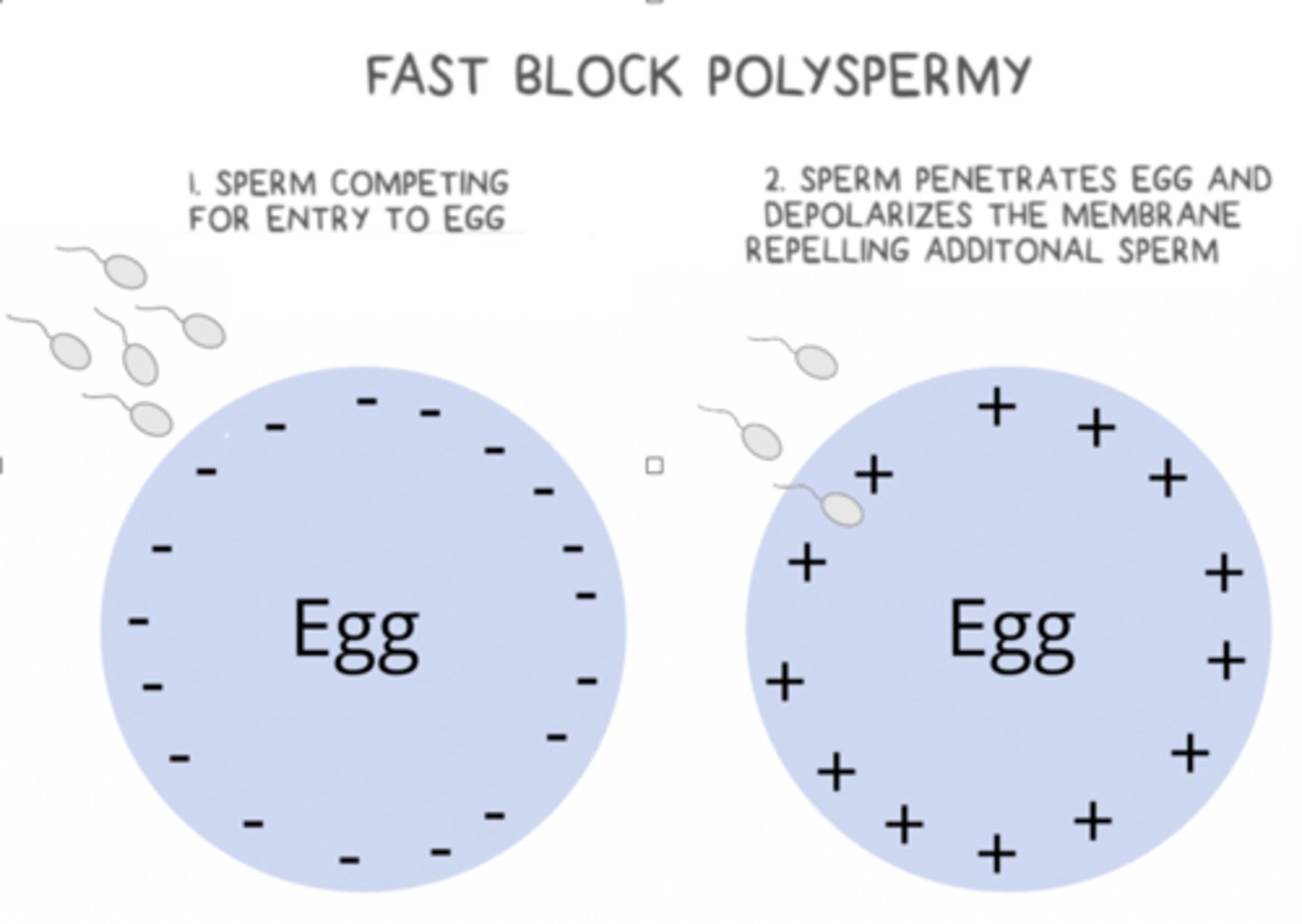
the _____ block to polyspermy happens second, gradually after the sperm has fused with the egg
slow
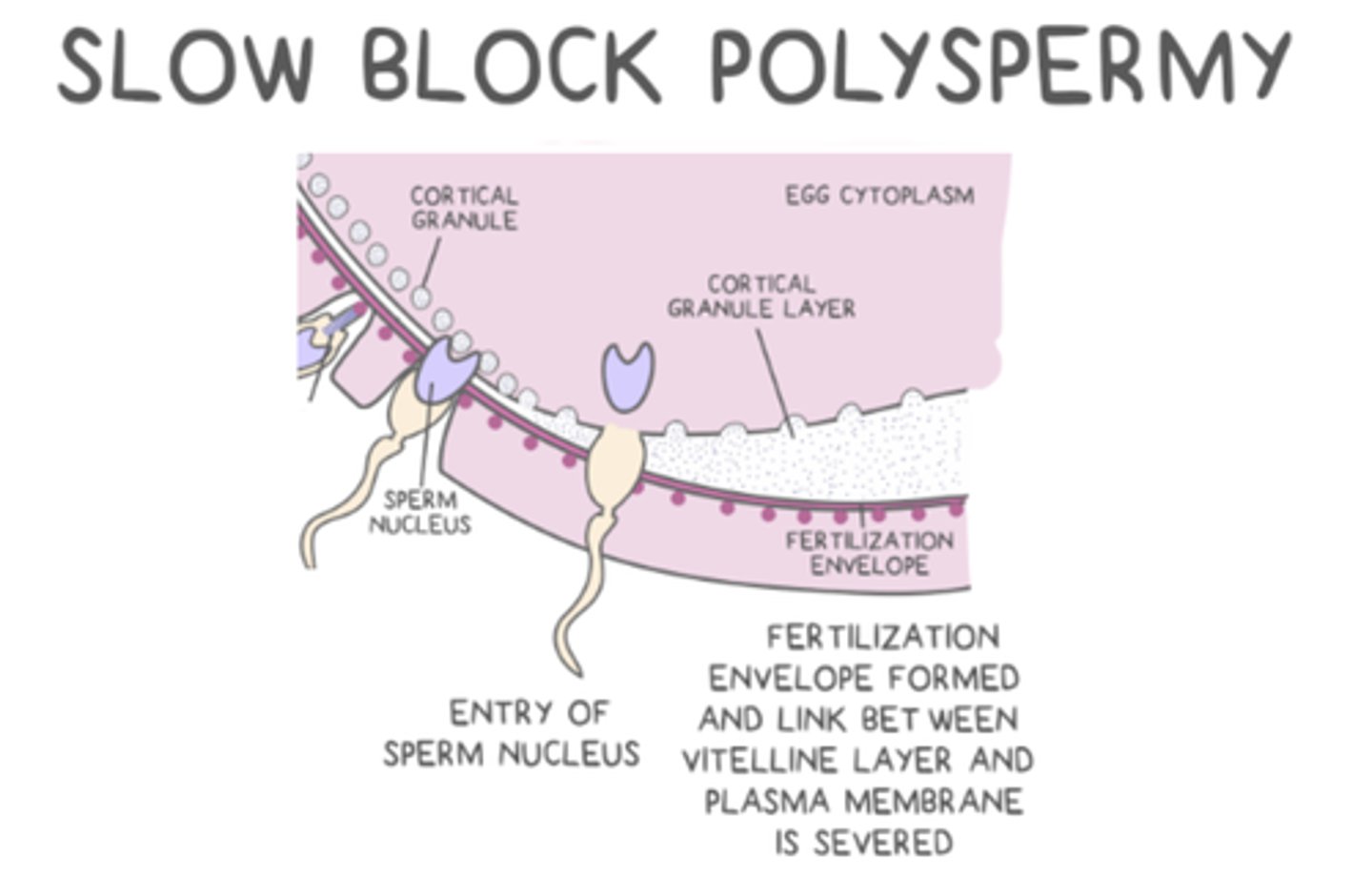
the slow block to polyspermy is a _____ solution than the fast block
longer lasting
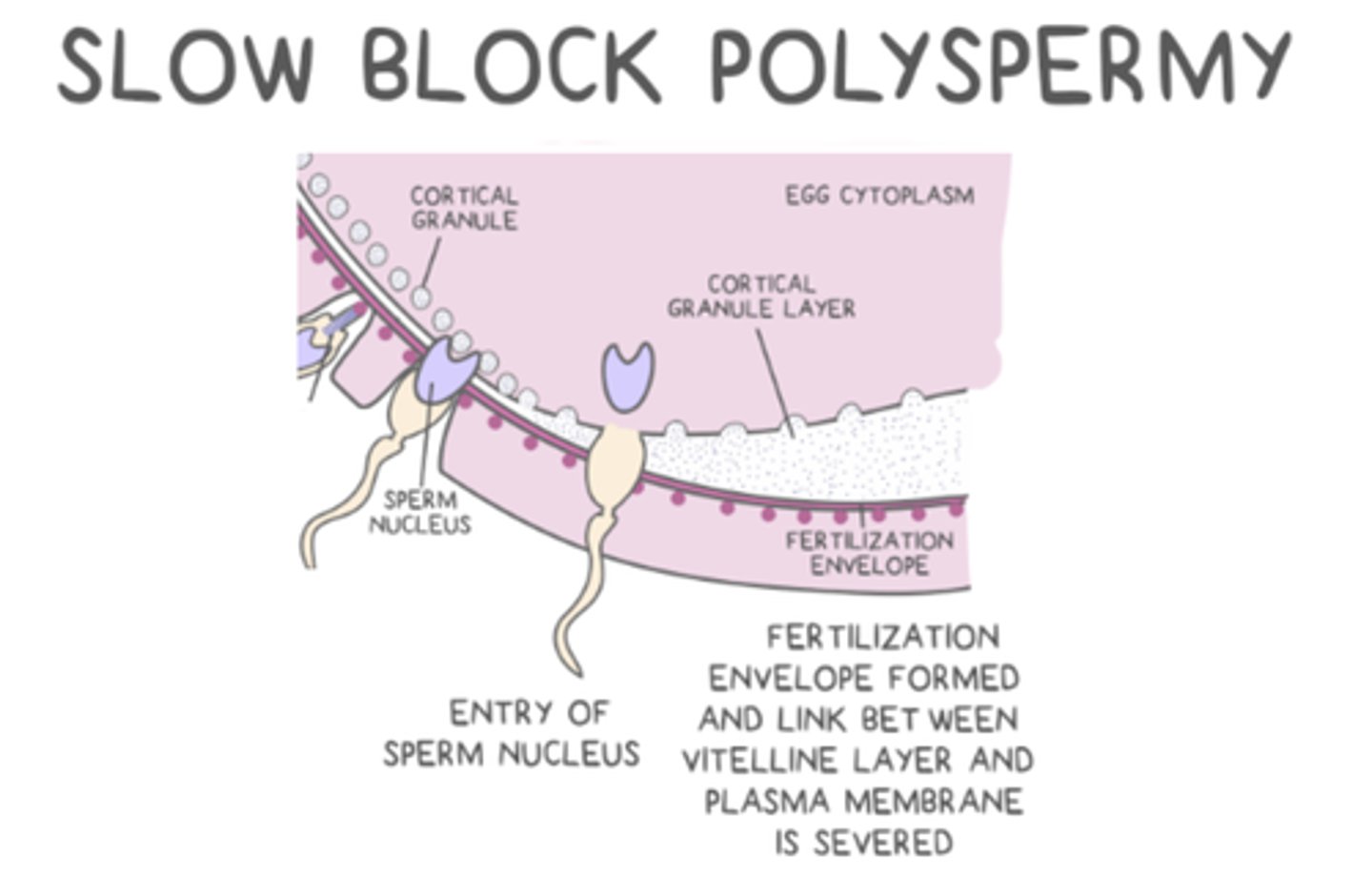
what is the general mechanism of the slow block?
sperm/egg membrane fusion --> fast block --> release of Ca2+ to egg membrane --> cortical reaction
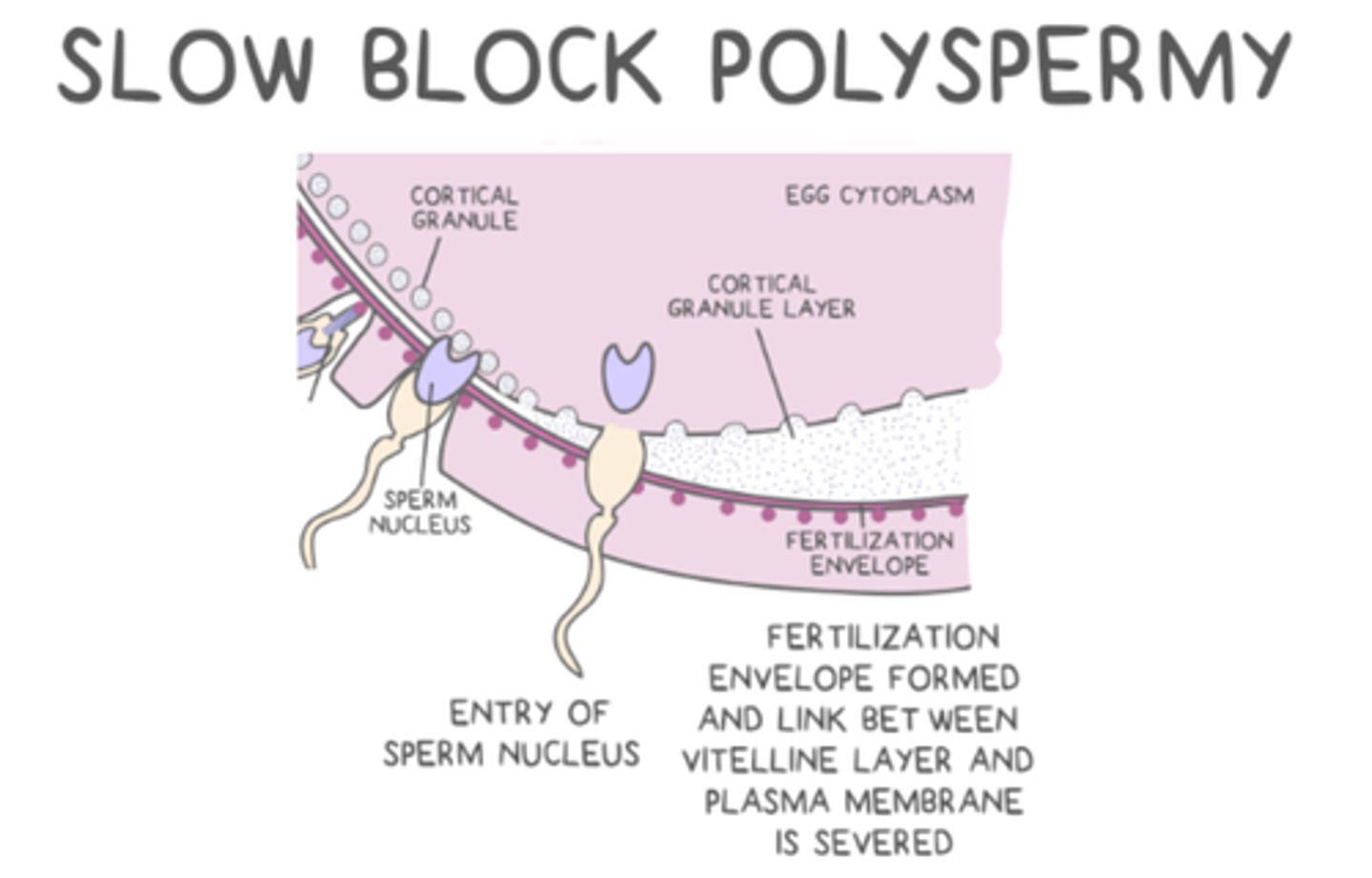
what happens during the cortical reaction?
there is an exocytosis of cortical granules from the egg cell
_____ (slow block) stimulate proteases to sever the link between the zona pellucida and the plasma membrane, creating an impenetrable fertilization envelope
cortical granules
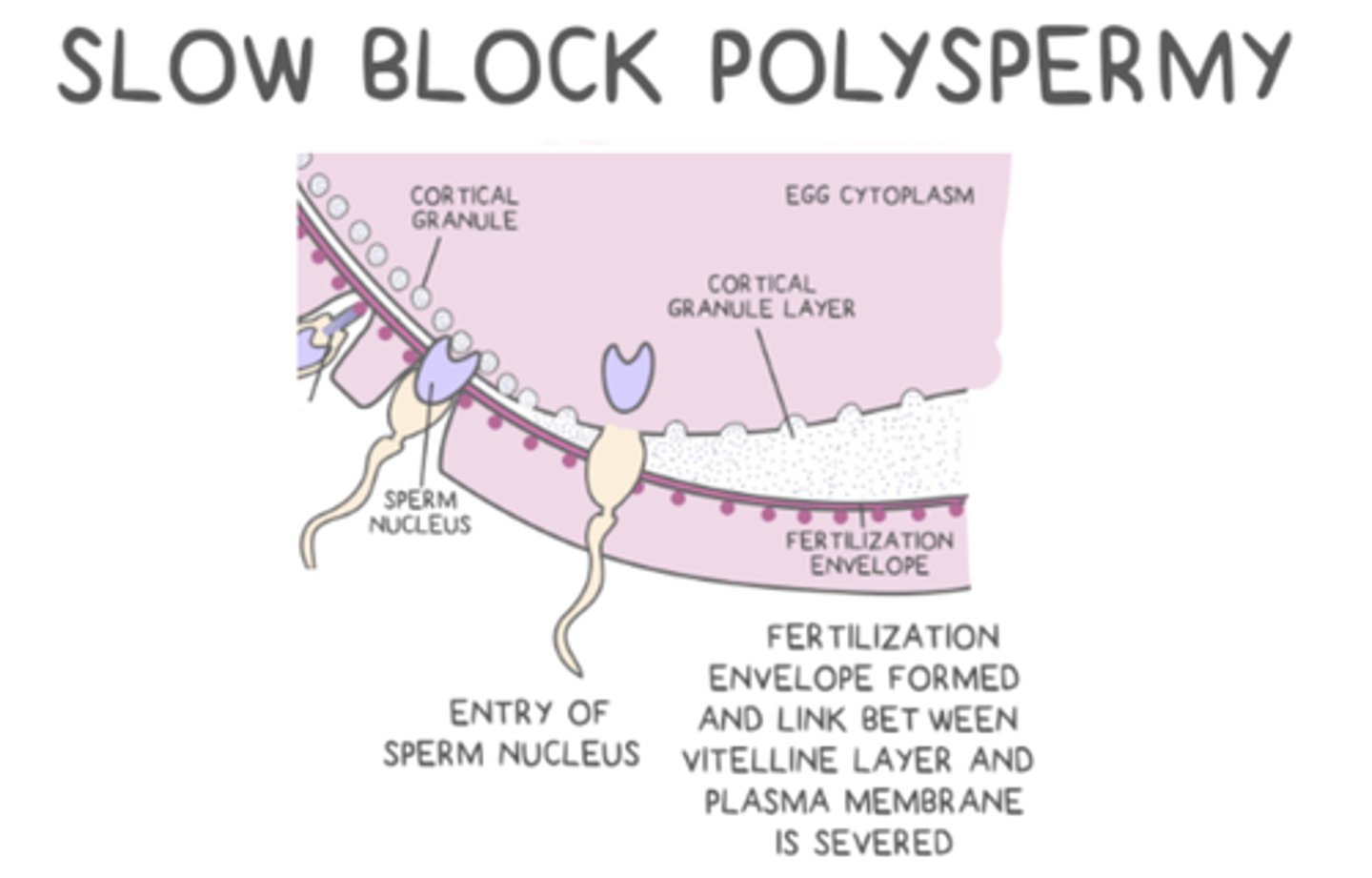
cortical granules (slow block) stimulate _____ to sever the link between the zona pellucida and the plasma membrane, creating an impenetrable _____
proteases; fertilization envelope
secondary oocytes complete _____ after successful sperm penetration
meiosis II
after penetration, meiosis in the secondary oocyte continues creating a _____ oocyte and producing a second _________
haploid; polar body
mitochondrial DNA is inherited exclusively from _____
the mother
nuclear DNA is passed down from _____
both the mother and father
_____ occur when one fertilization event gives rise to one zygote, which then divides to form two separate embryos
monozygotic twins
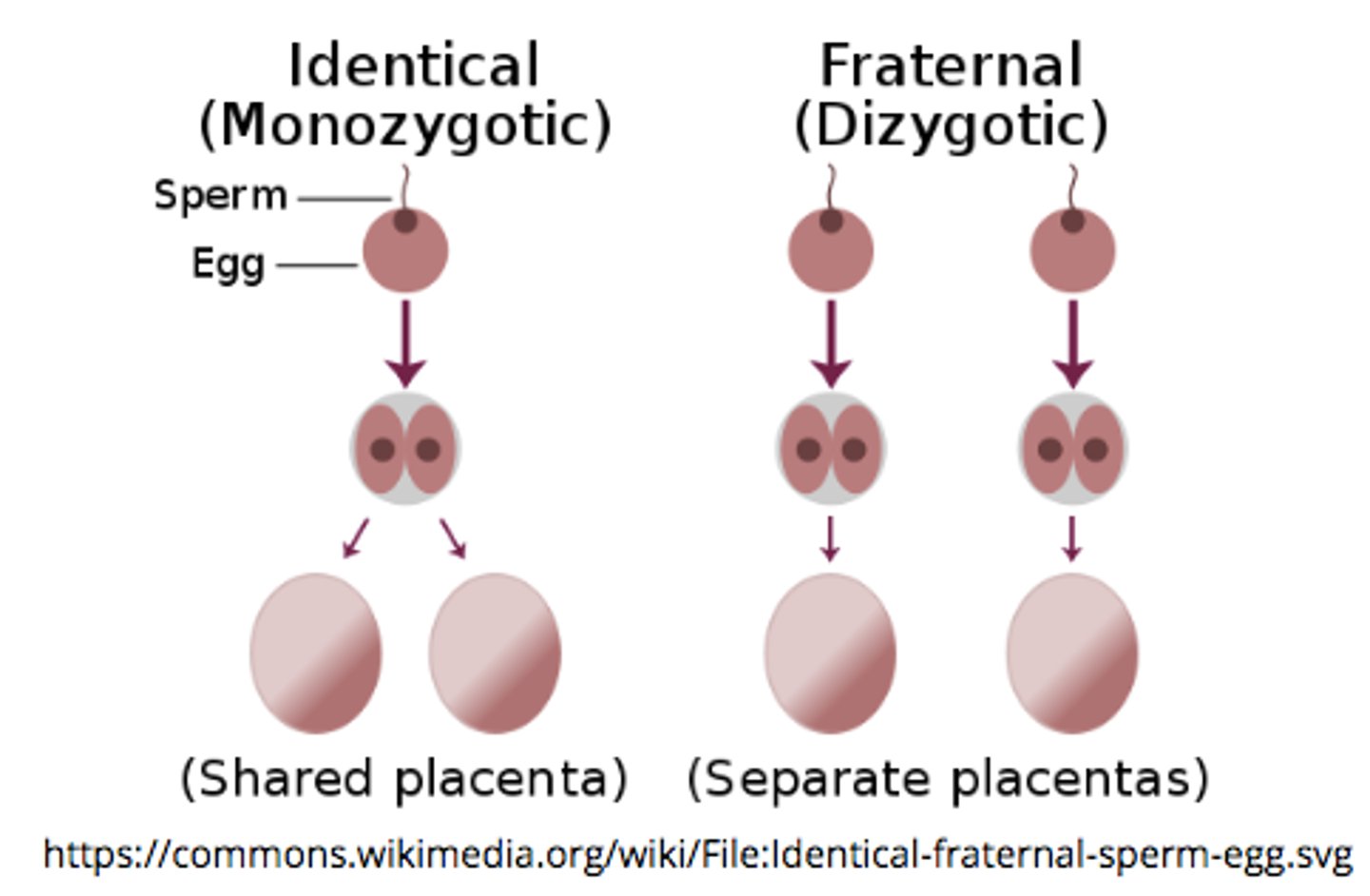
monozygotic twins have the exact same _____, so they are identical
genetic material
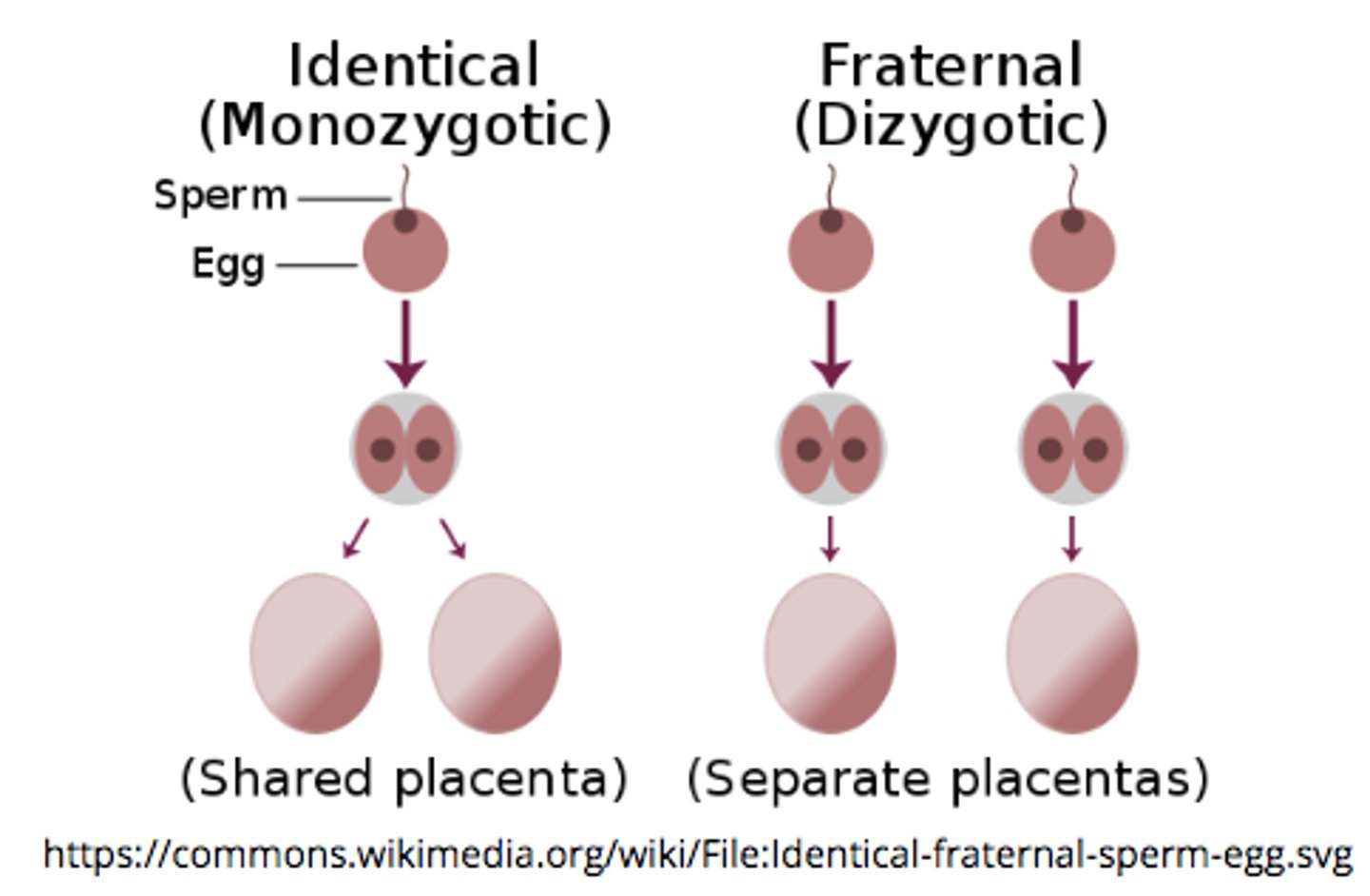
what is the general mechanism of dizygotic twin creation?
the mother ovulates 2 eggs --> both are individually fertilized by 2 different sperms --> 2 different zygotes with slightly different genetic material
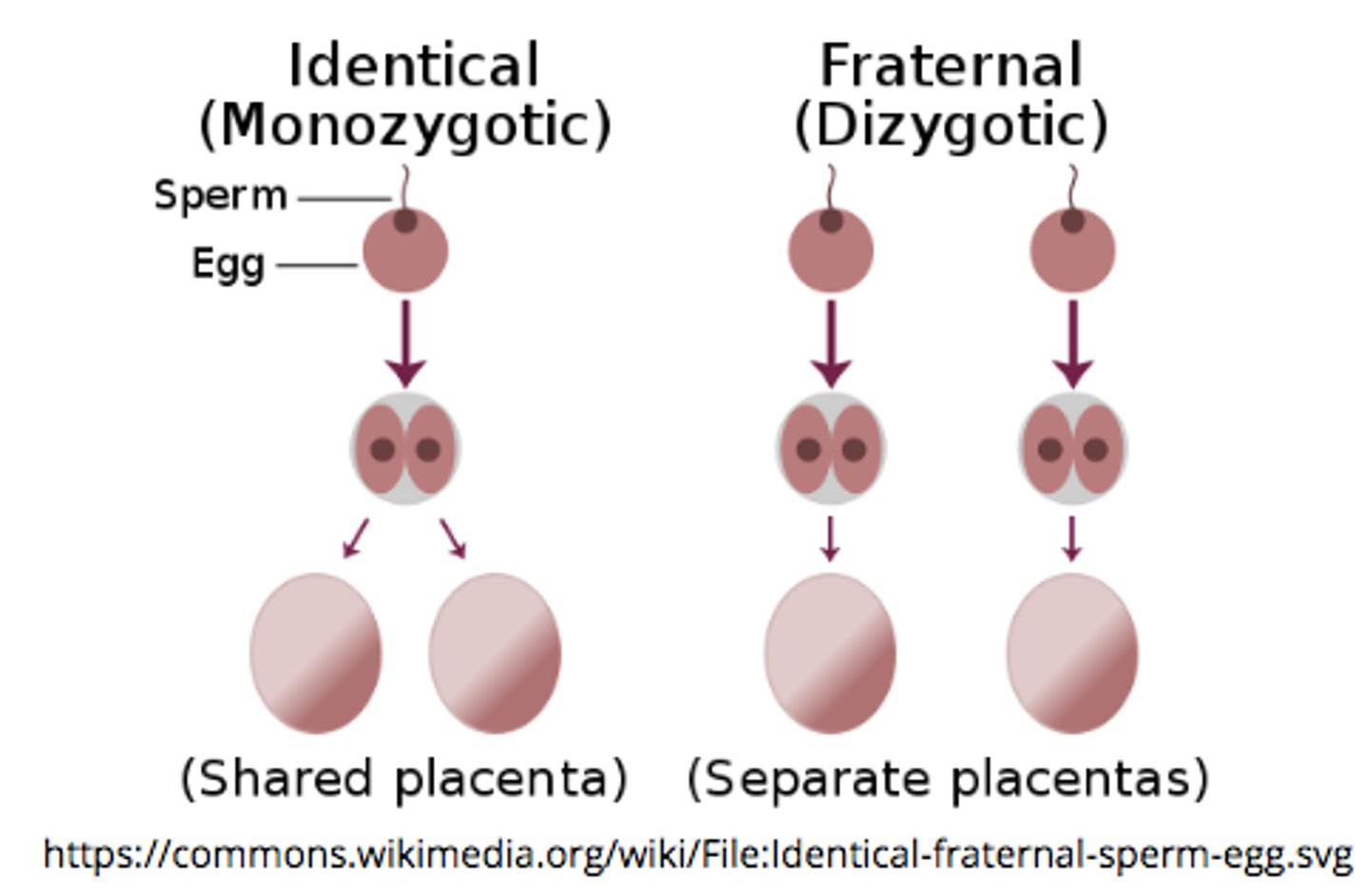
dizygotic twins are _____ twins
fraternal
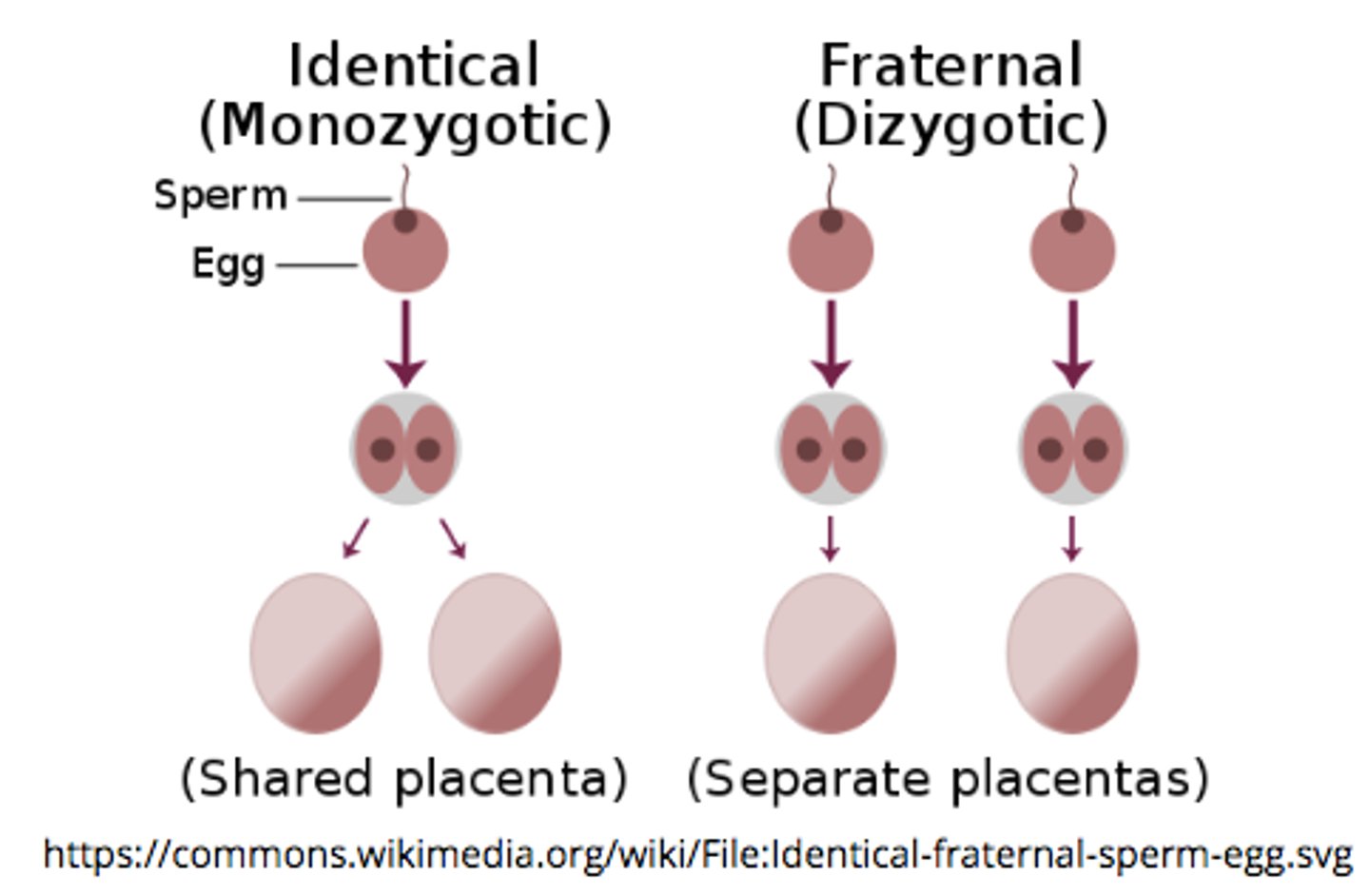
what is the first step of growth after the formation of the zygote?
cleavage
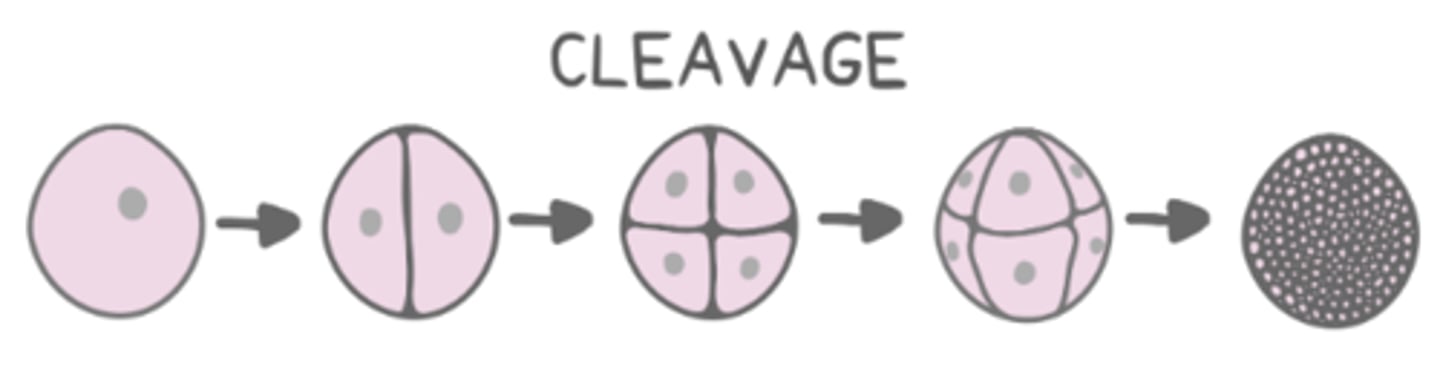
cleavage is rapid cell divisions that occur without changing the _____ of the embryo
total mass
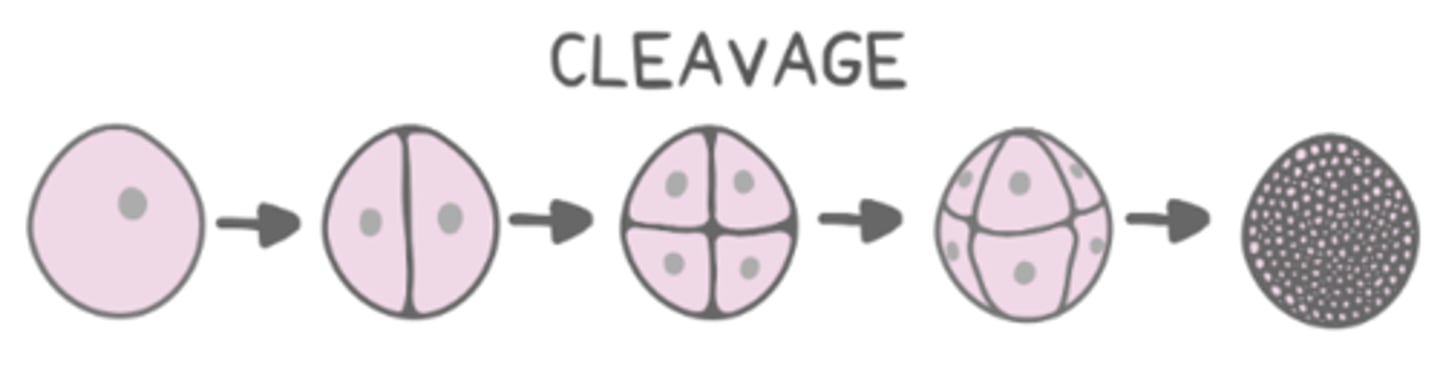
what is characteristic of daughter cells that result from cleavage?
they have less cytoplasm than the mother cell and are smaller
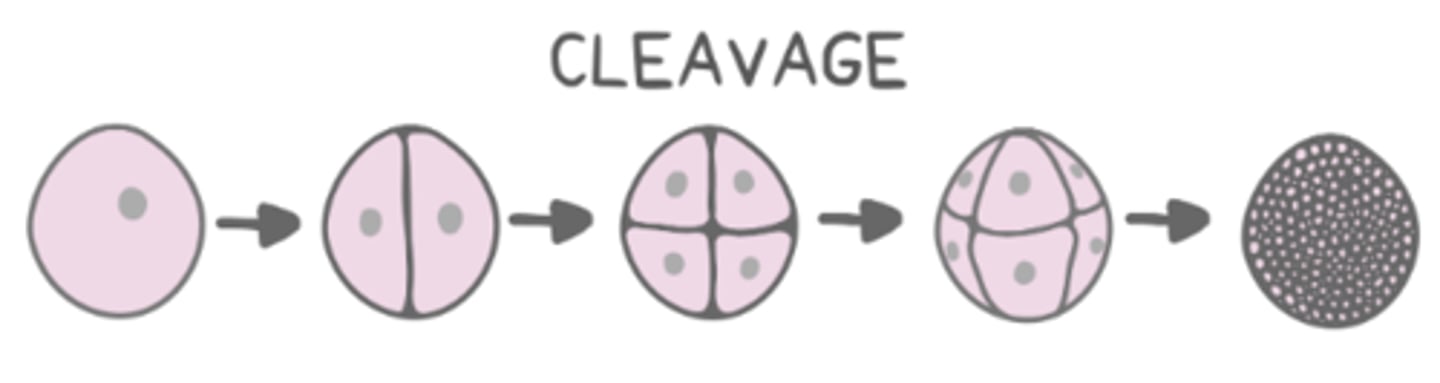
each small cell resulting from cleavage is called a _____
blastomere
what are the three main ways to classify cleavage?
axis; cell fate; evenness of embryo division
classifications of cleavage based on axis can be _____ or _____
radial; spiral
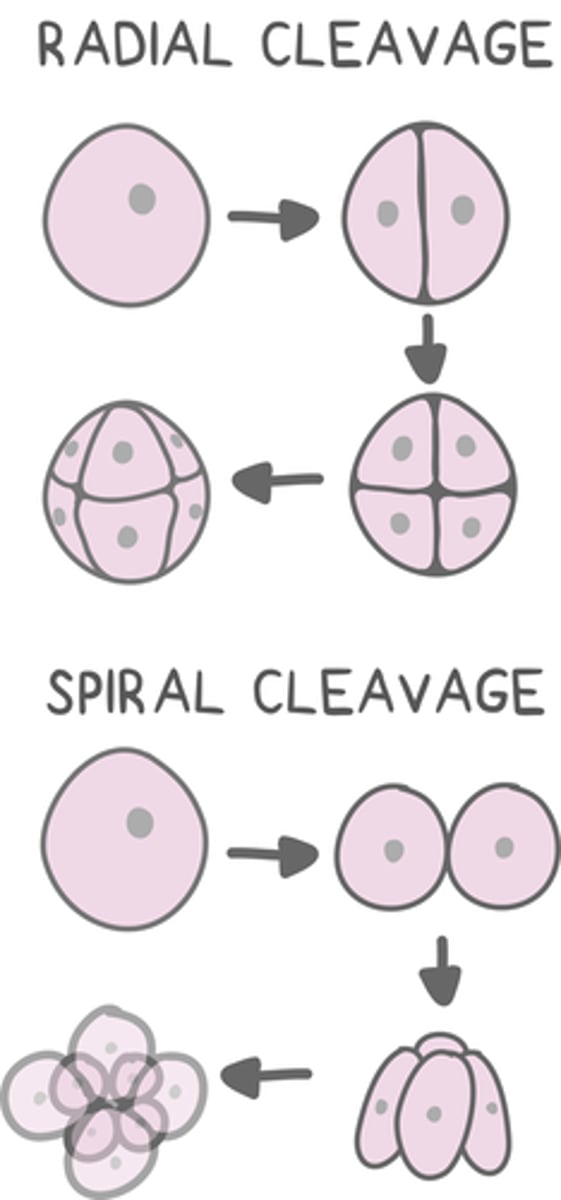
_____ cleavage results in cells aligned on the vertical axis with the top cells overlapping the bottom cells
radial
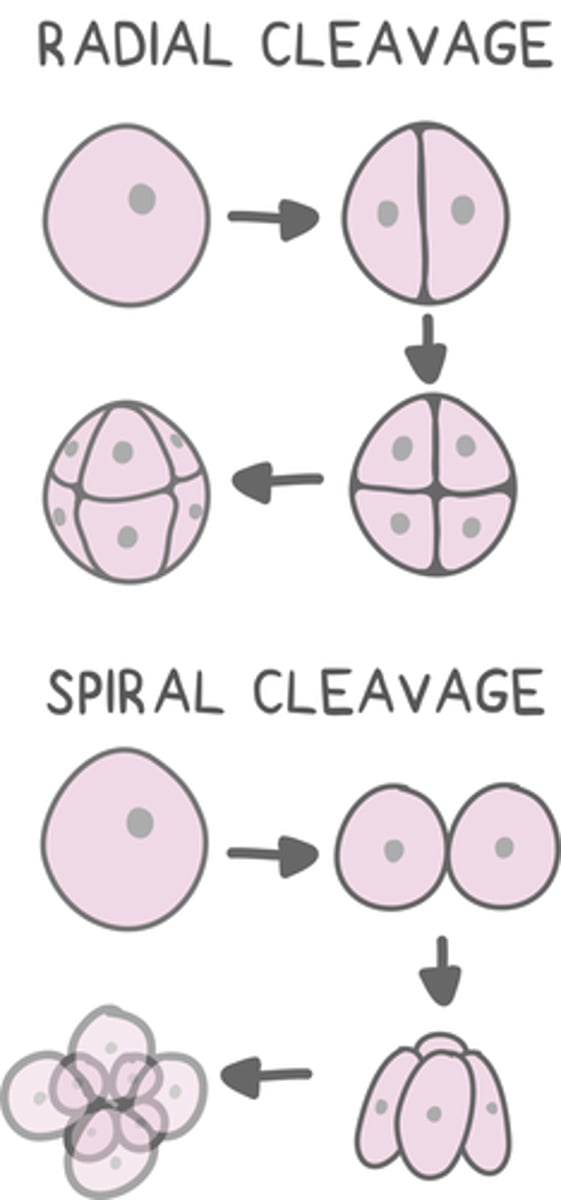
deuterostomes undergo _____ cleavage
radial
_____ cleavage results in misaligned cells that deviate away from the vertical axis
spiral
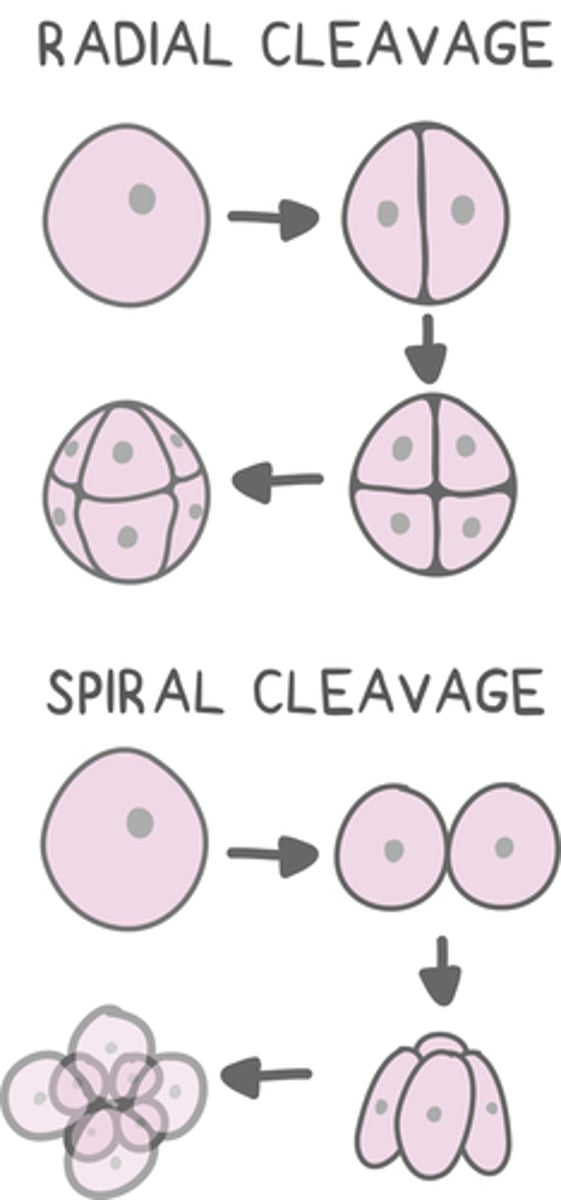
protostomes undergo _____ cleavage
spiral
classifications of cleavage based on cell fate can be _____ or _____
determinate; indeterminate
_____ cleavage refers to blastomeres that have a decided fate after they are made through cleavage
determinate (mosaic)
_____ cleavage refers to blastomeres that do not have a preset fate
indeterminate (regulative)
cells that result from indeterminate cleavage are ______
totipotent
classifications of cleavage based on evenness of embryo division can be _____ or _____
holoblastic; meroblastic
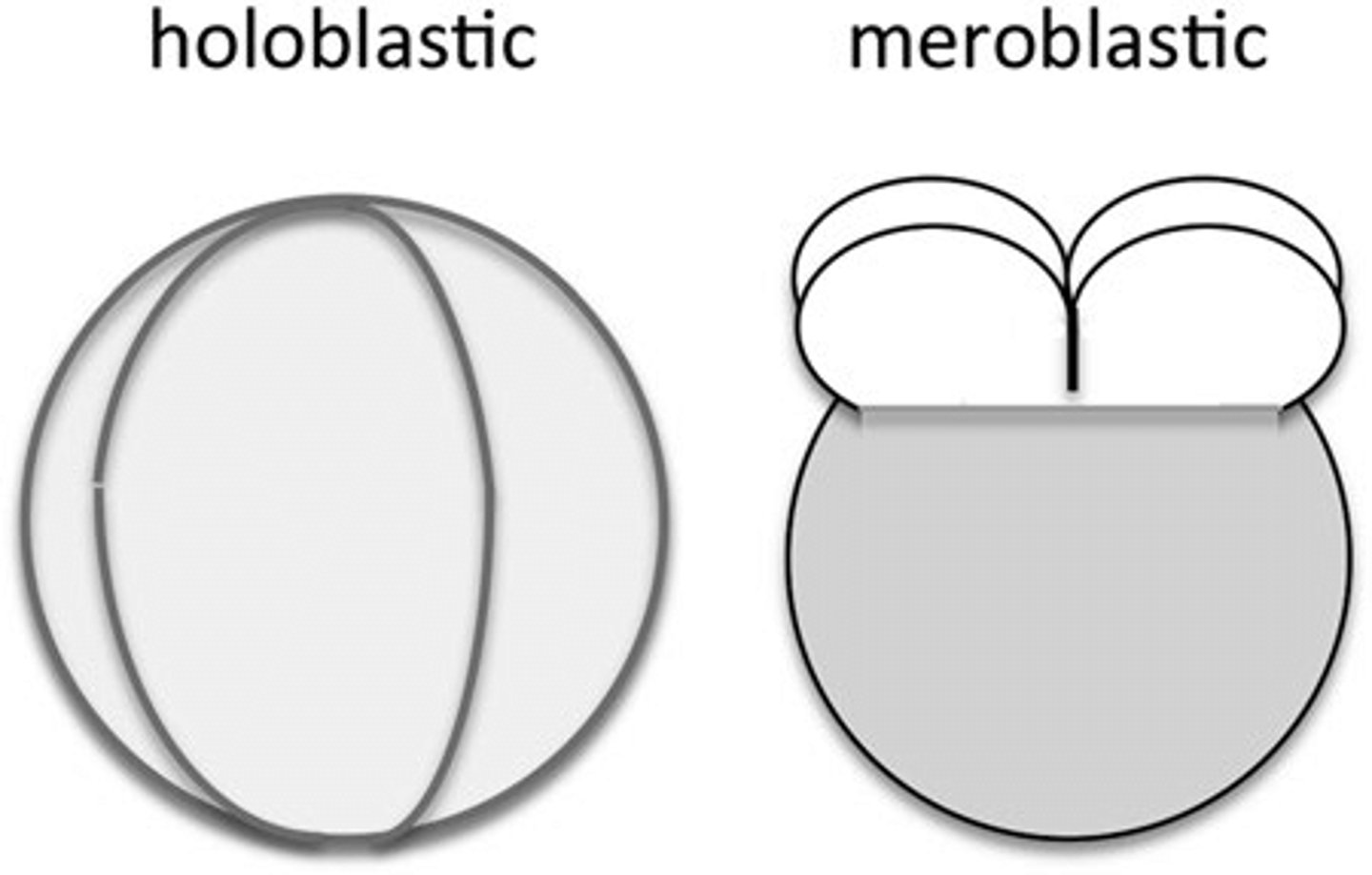
_____ cleavages happen through the entire embryo
holoblastic
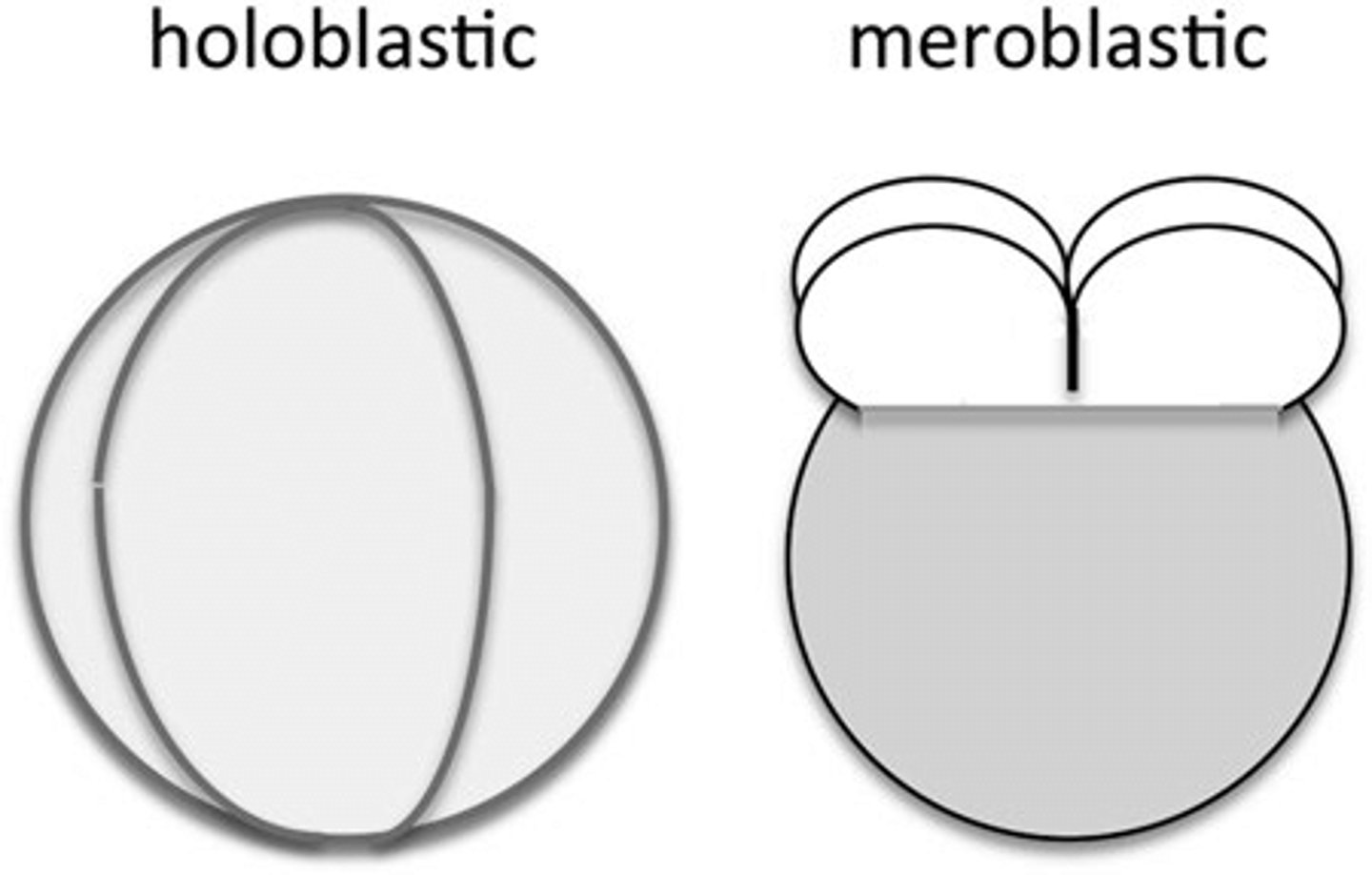
in which types of embryos does holoblastic cleavage typically occur?
embryos with minimal yolk
what are some examples of embryos that go through holoblastic cleavages?
humans, sea urchins, frogs (frogs have lots of yolk but are an exception)
_____ cleavages are partial (the entire embryo does not evenly divide)
meroblastic
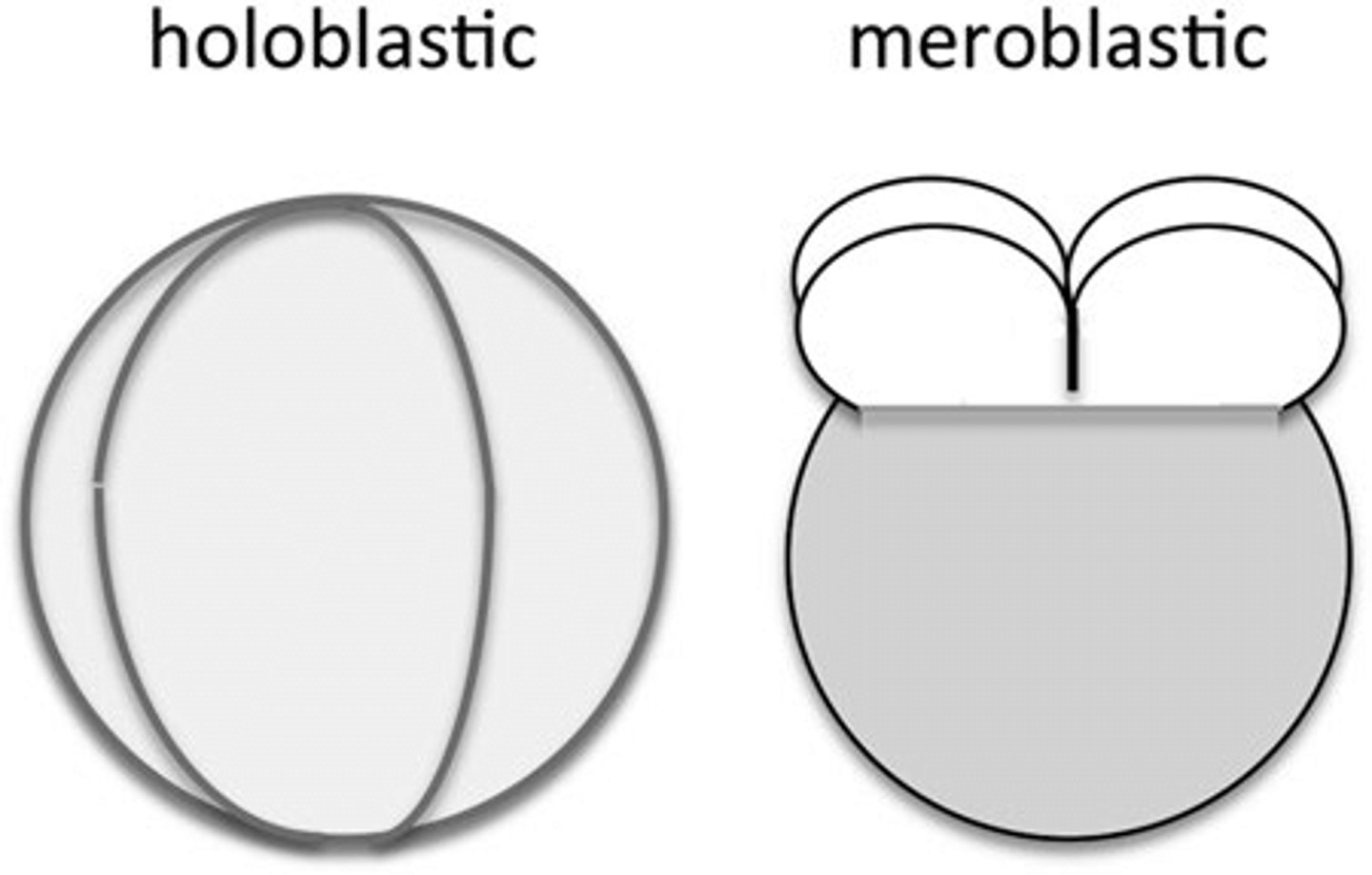
in which types of embryos does meroblastic cleavage typically occur?
embryos with substantial yolk
what are some examples of embryos that go through meroblastic cleavages?
birds, fish, reptiles
what does embryonic yolk do?
functions to provide nutrients to the growing embryo
embryos with _____ yolk exhibit polarity, containing an animal and vegetal pole
a lot of
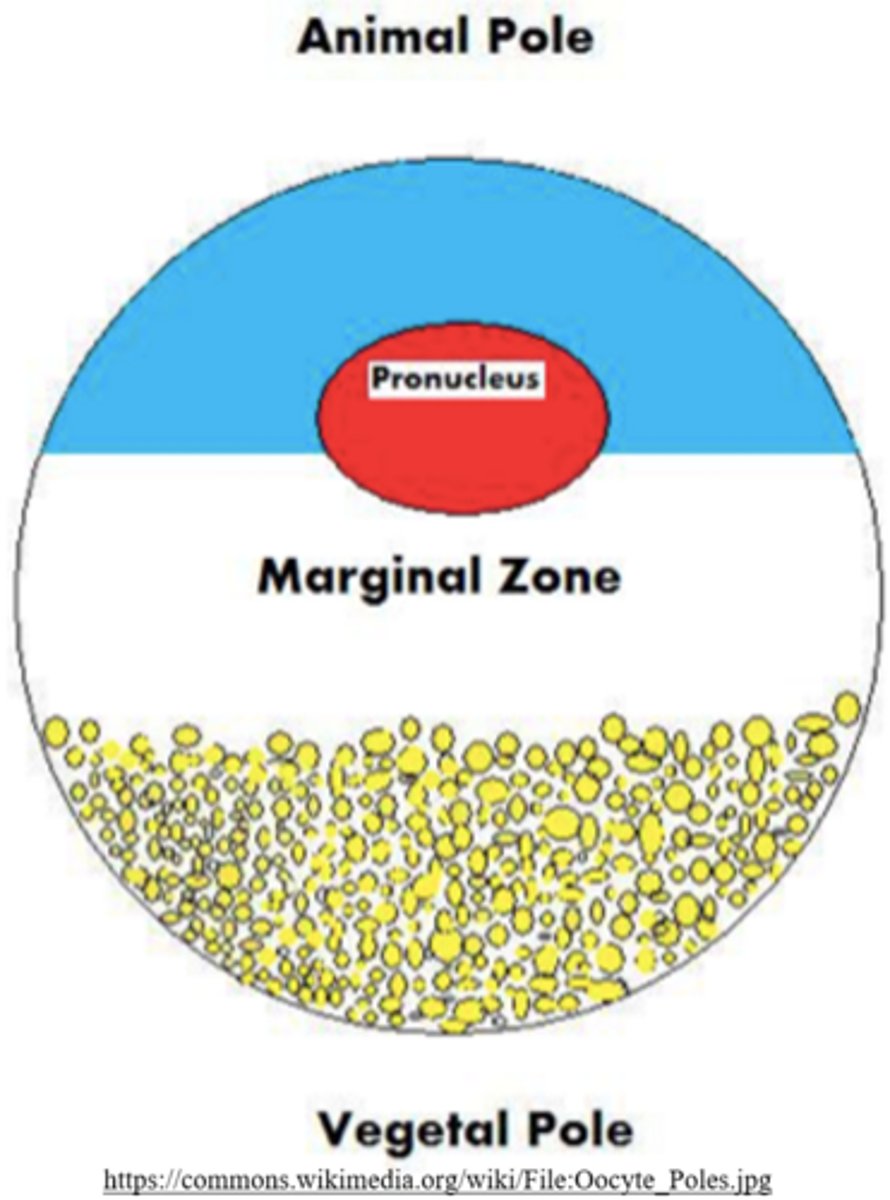
embryos with a lot of yolk exhibit polarity, containing an _____ and _____ pole
animal; vegetal
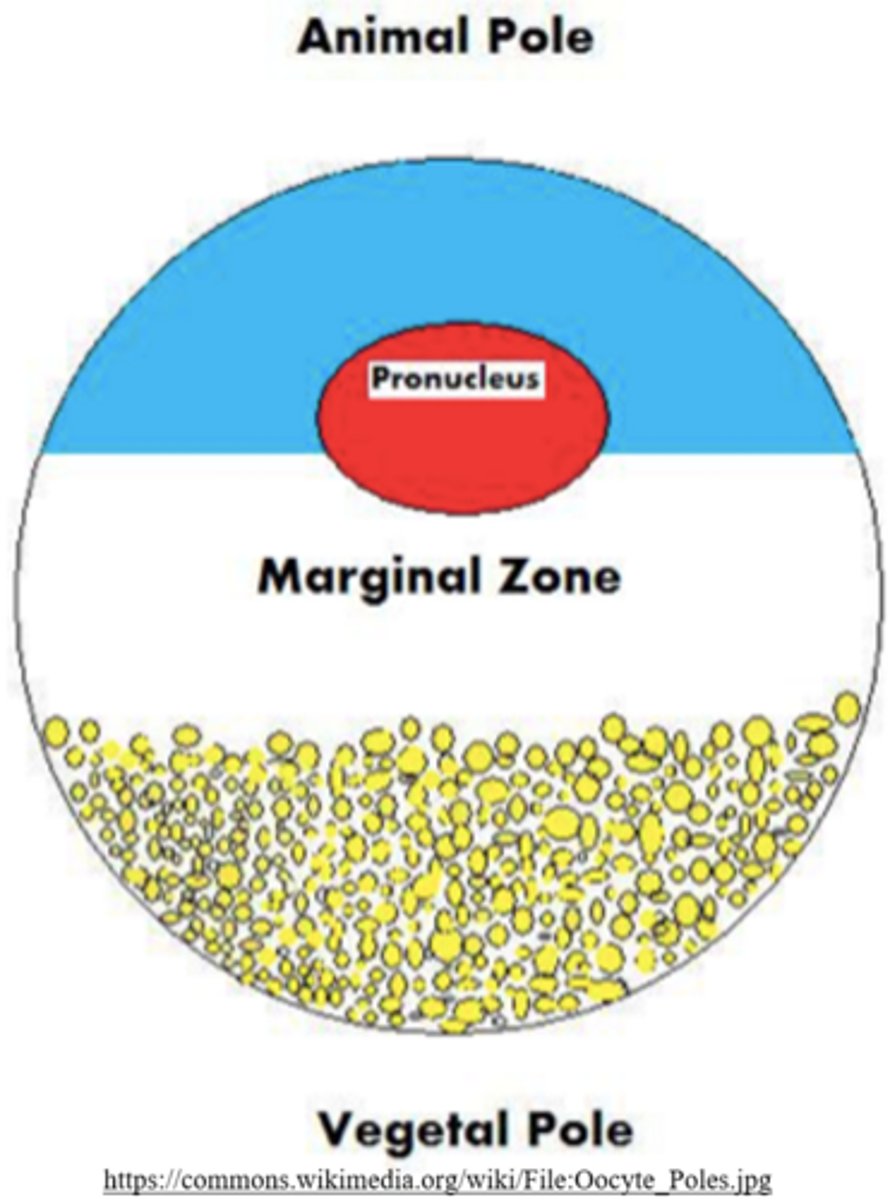
_____ poles exhibit active cleavage
animal
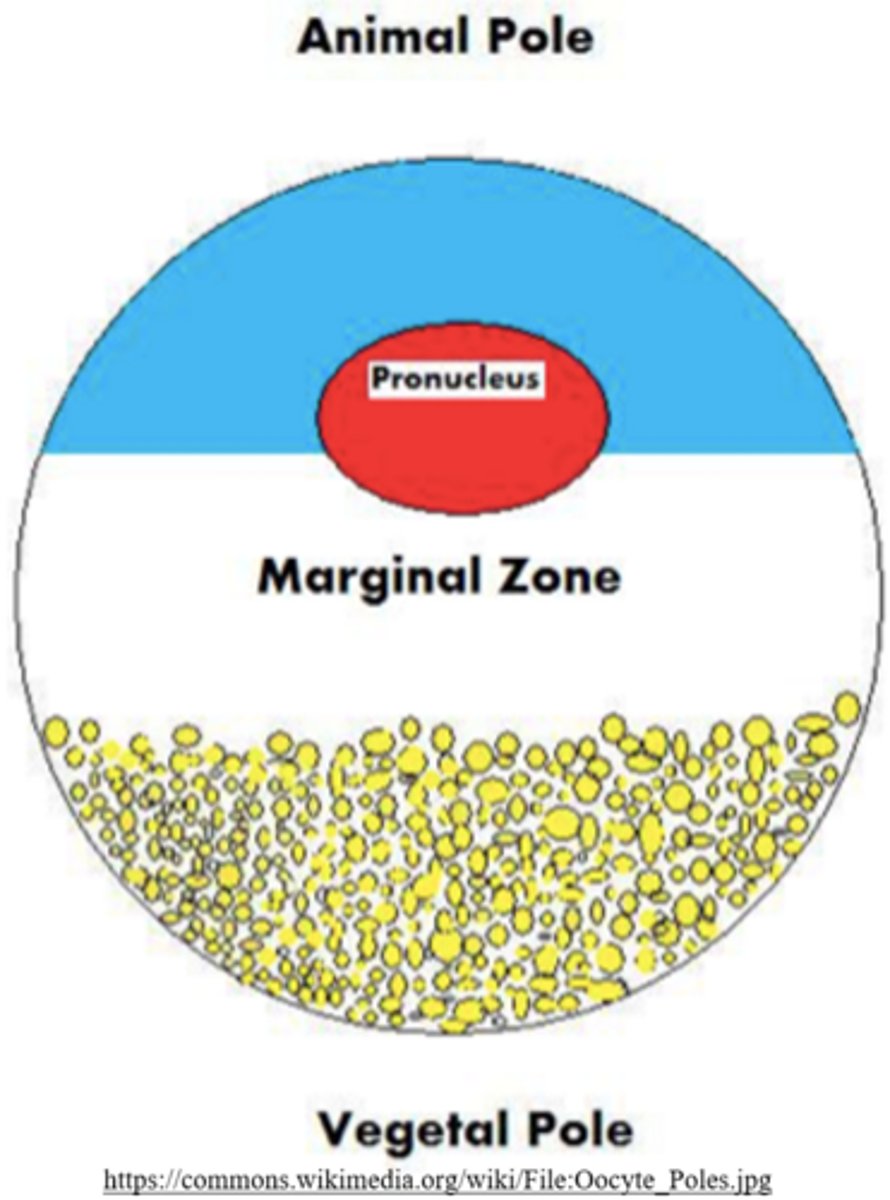
_____ poles exhibit slow/negligible cleavage because they contain a lot of yolk
vegetal
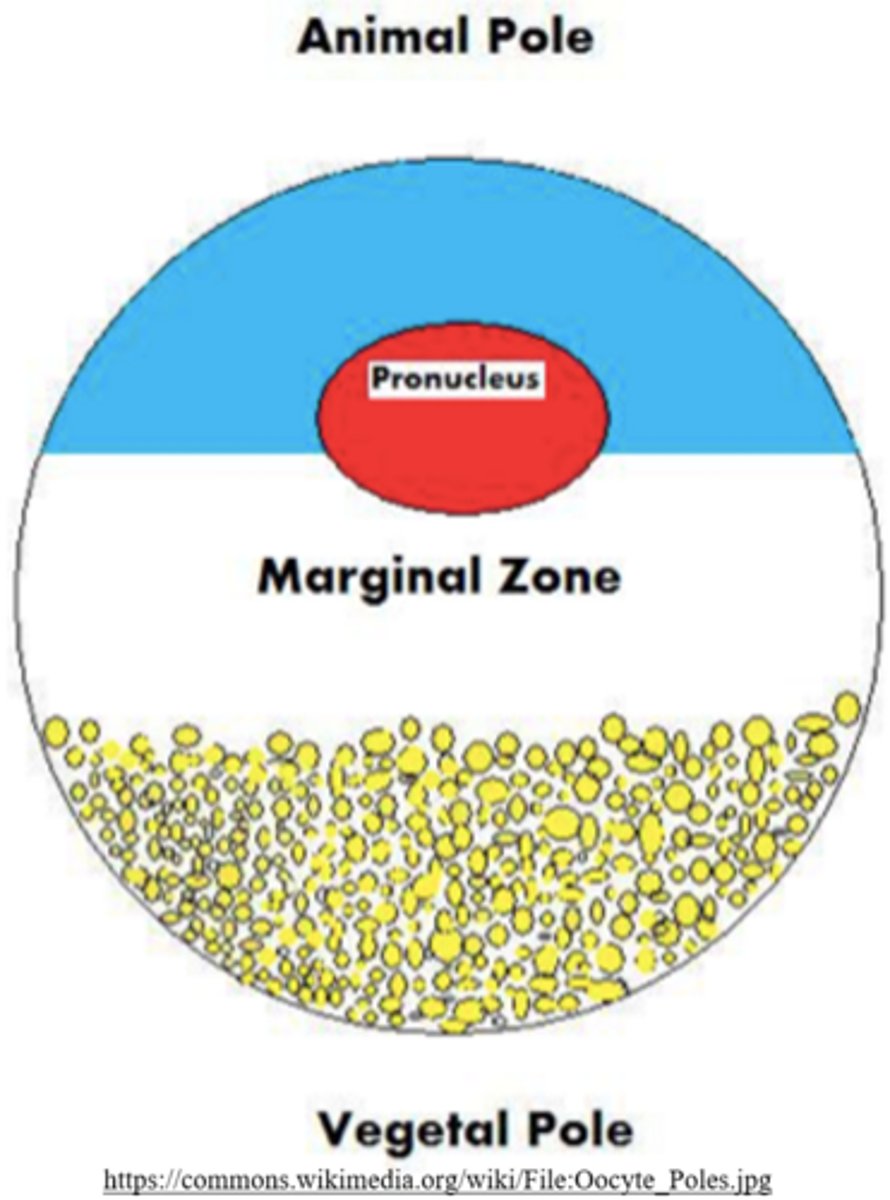
frog embryos contain a significant amount of yolk - they experience_____, yet_____ cleavages
uneven; holoblastic
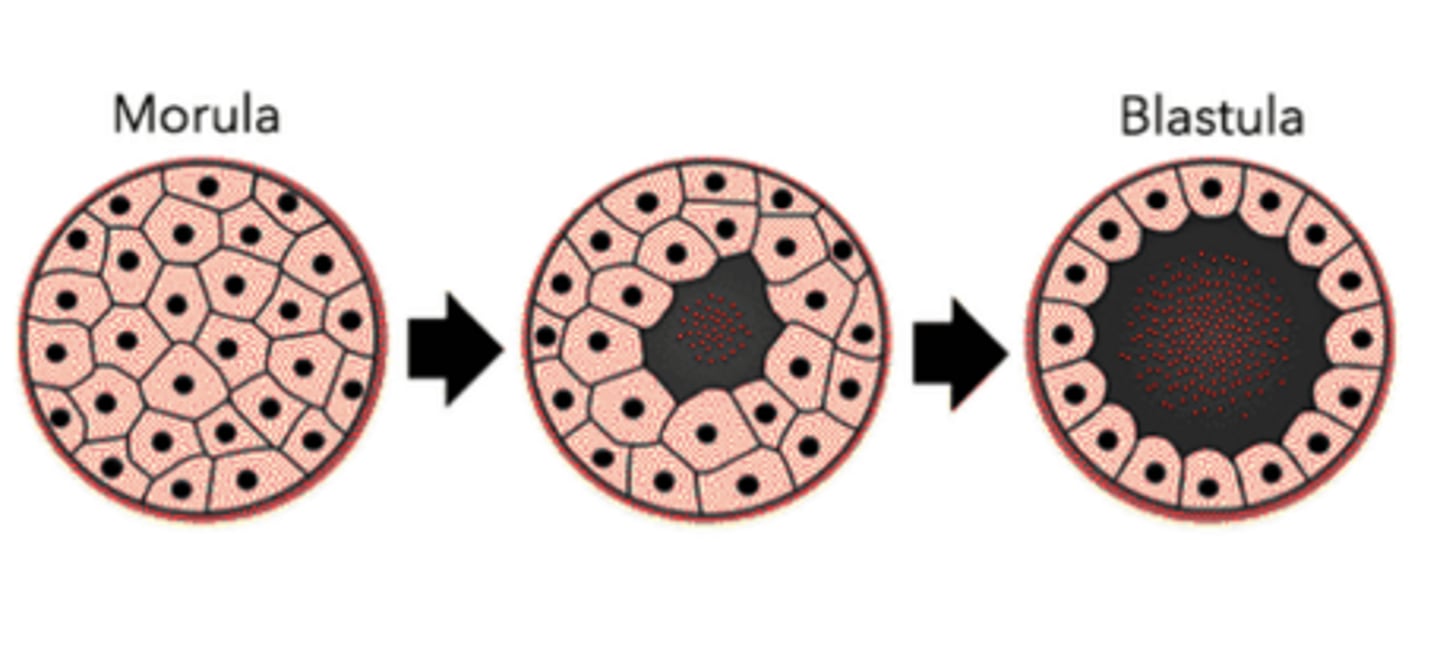
the solid ball of roughly 16-32 cells is called a _____
morula
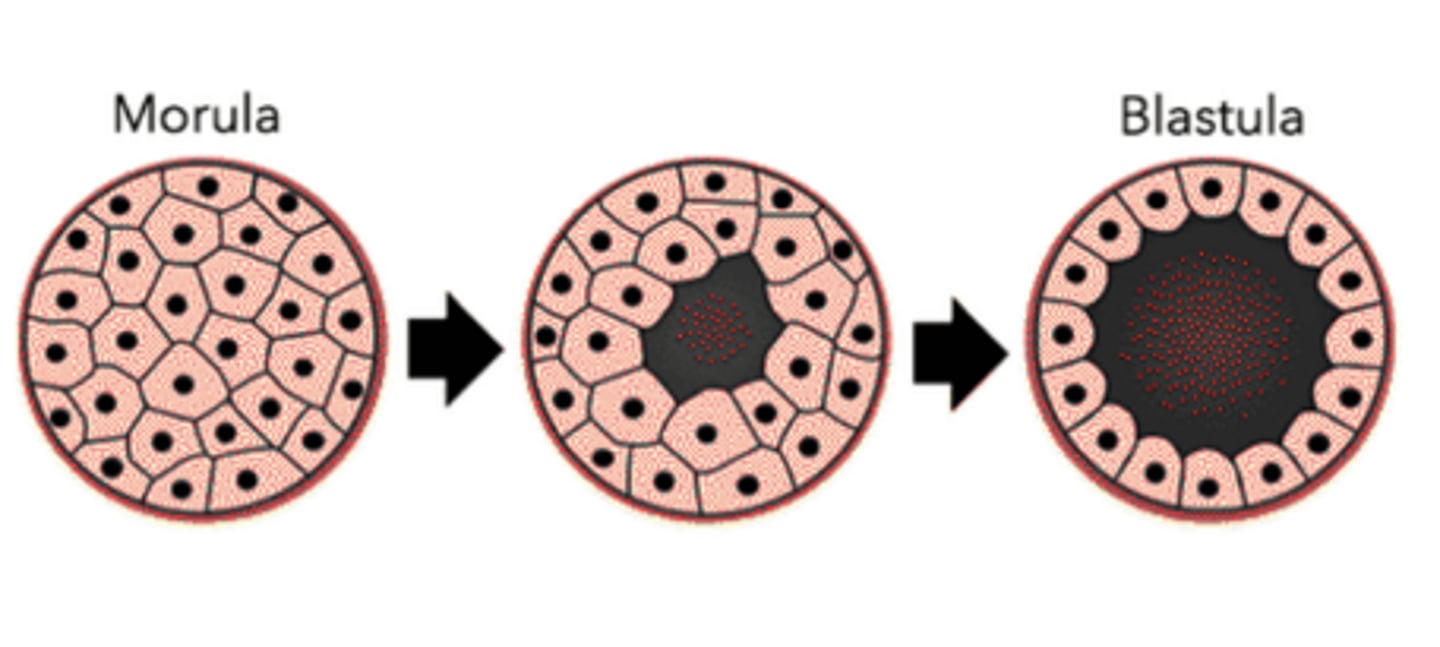
the _____ is a hollow cavity that begins to form around the 128 cell stage
blastocoel
when the hollow, fluid-filled blastocoel develops, the embryo is said to be a _____
blastula
where does cleavage happen?
when the fertilized egg travels toward the uterus (in the oviduct/fallopian tube)
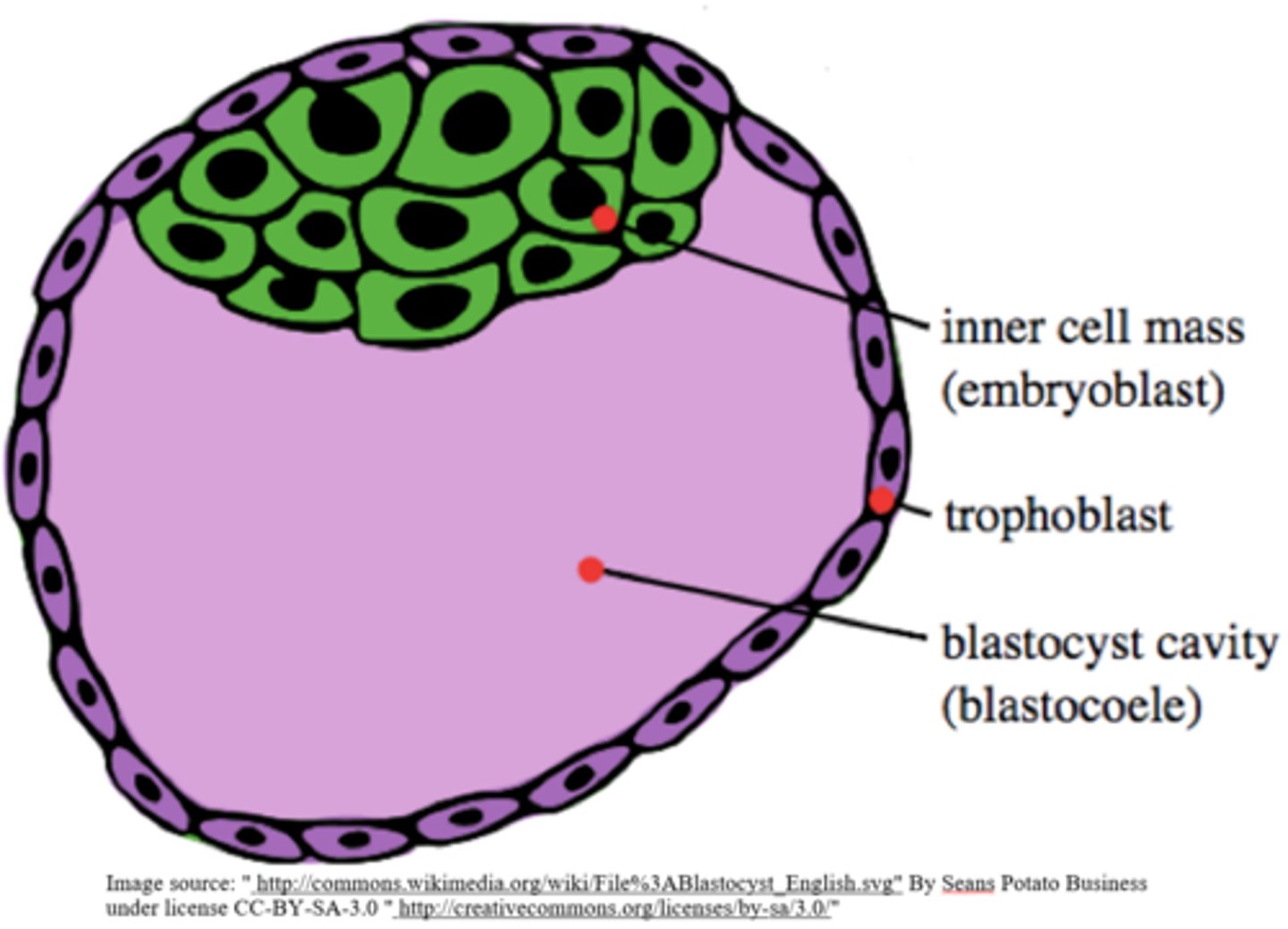
what stage of development is the embryo in when it implants into the uterine wall?
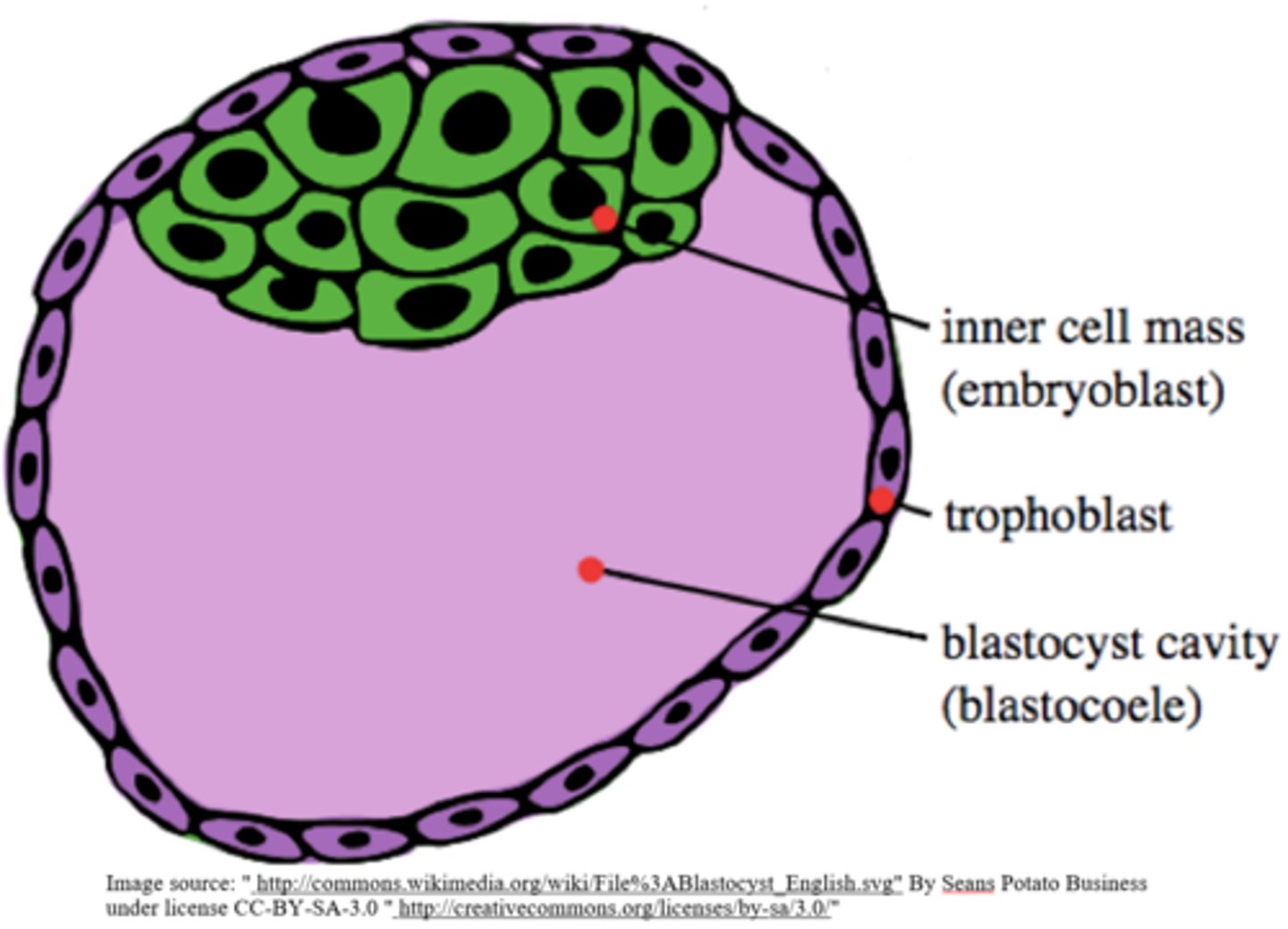
blastocyst
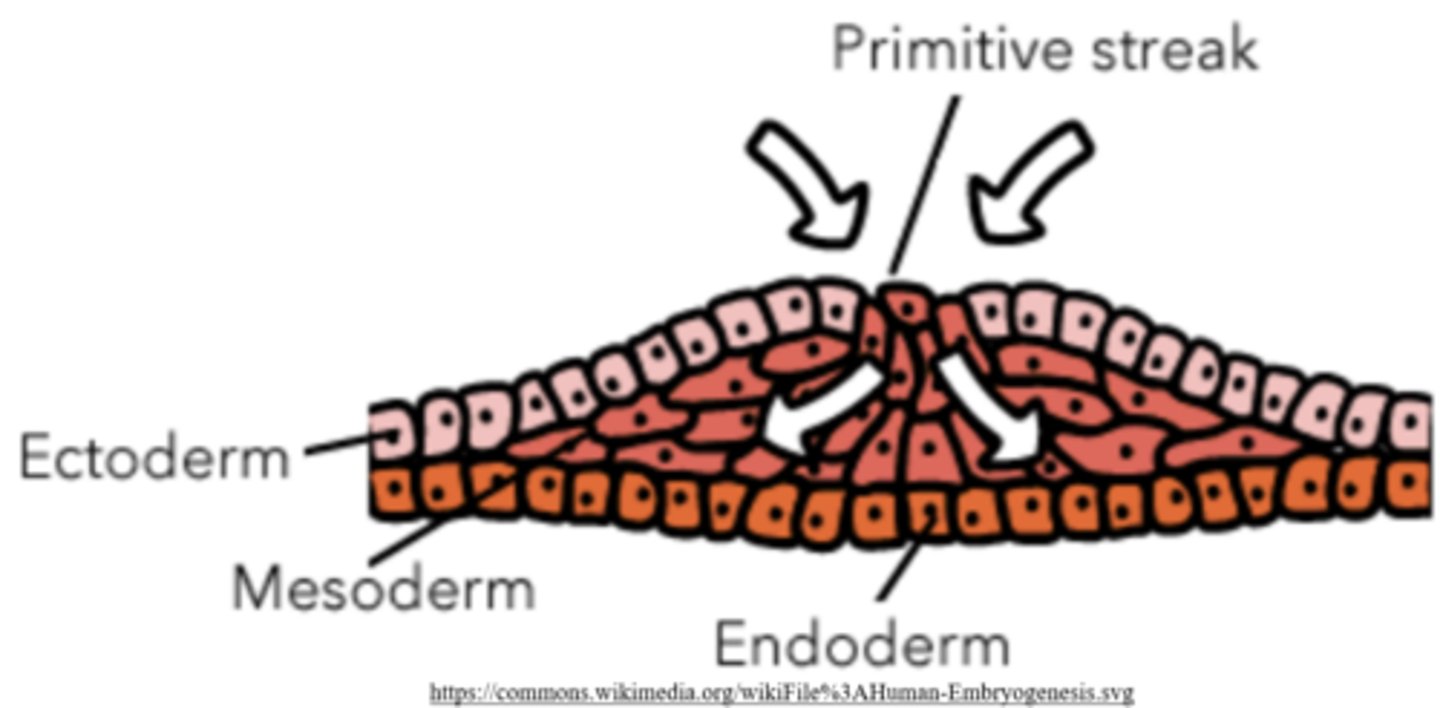
what is the formation of a trilaminar embryo called?
gastrulation
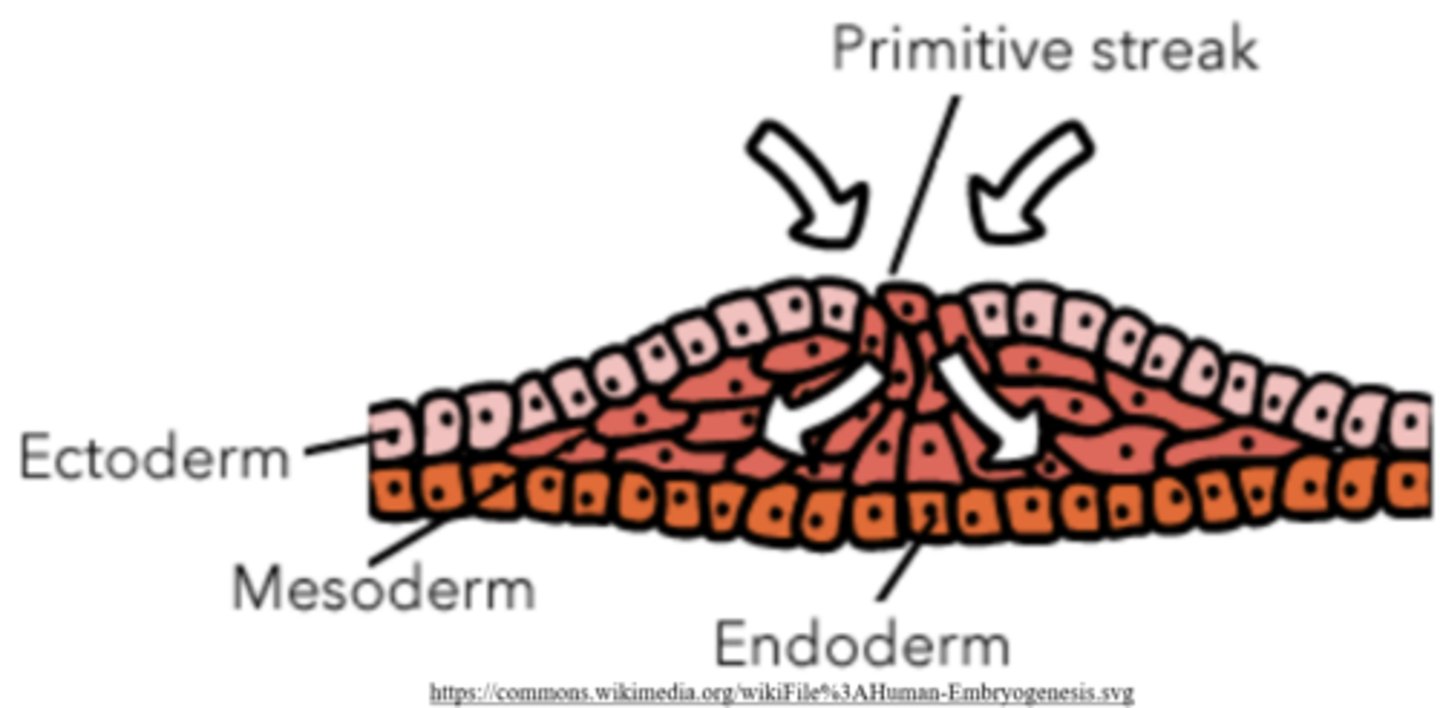
epiblast cells thicken and roll inward to form a structure called the _____
primitive streak
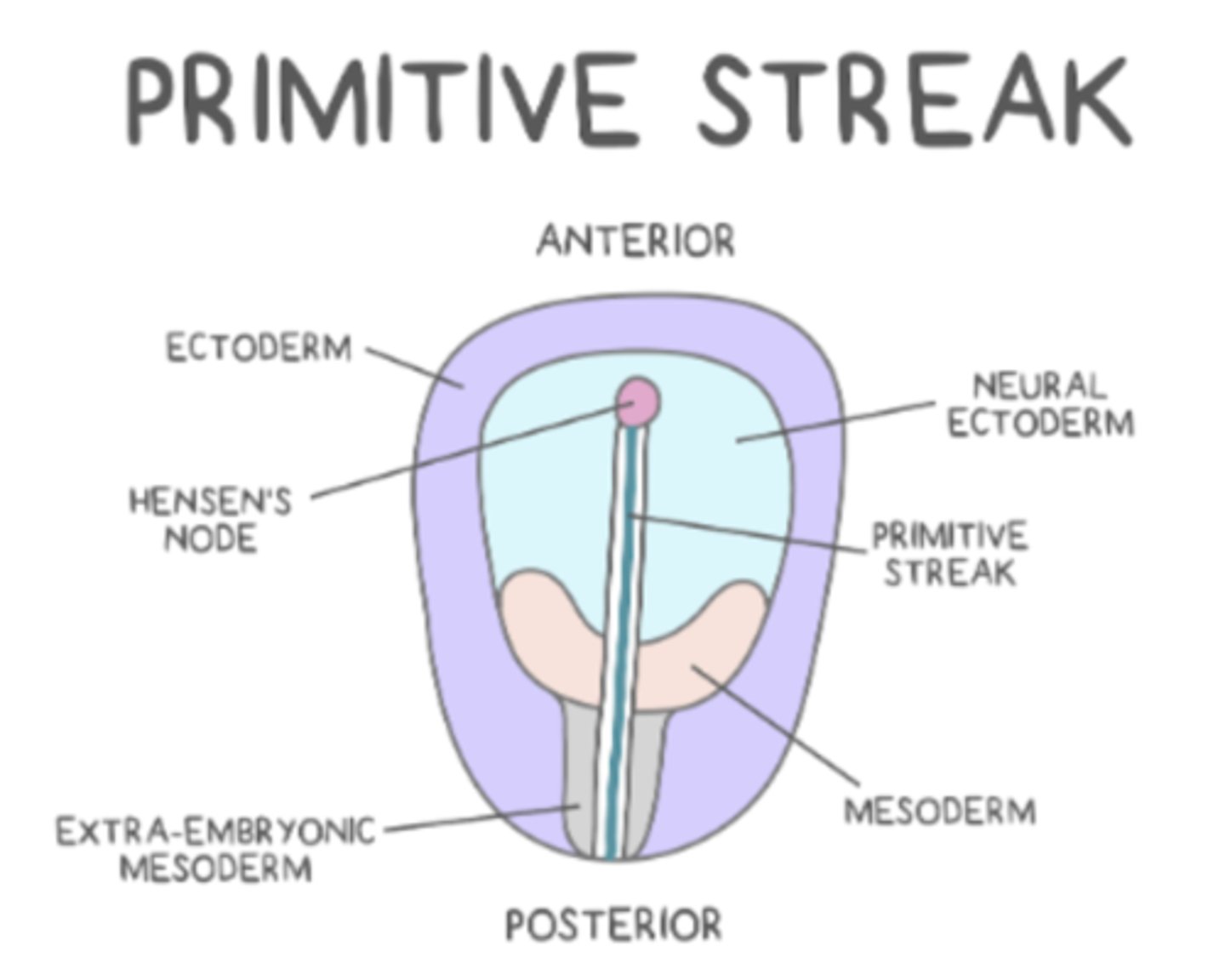
the _____ defines the left-right, top-bottom axis for the developing embryo
primitive streak
the primitive streak is a crucial structure to begin the process of _____
gastrulation
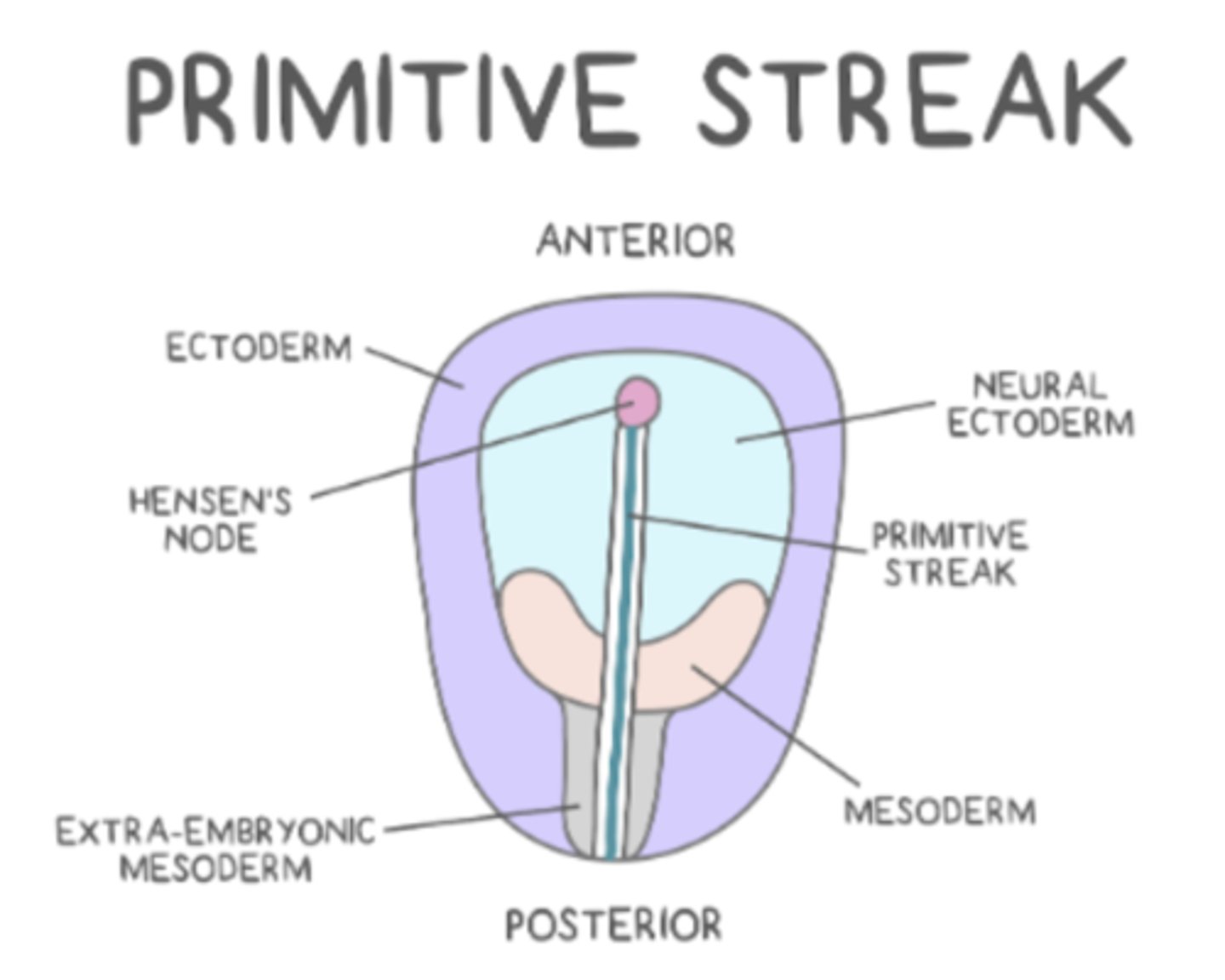
gastrulation makes a _____ embryo, which has _____ germ layers
trilaminar; three
what are the three germ layers of a trilaminar embryo from superficial to most deep?
ectoderm; mesoderm; endoderm
invagination along the primitive streak forms a _____, which initiates gastrulation
blastopore
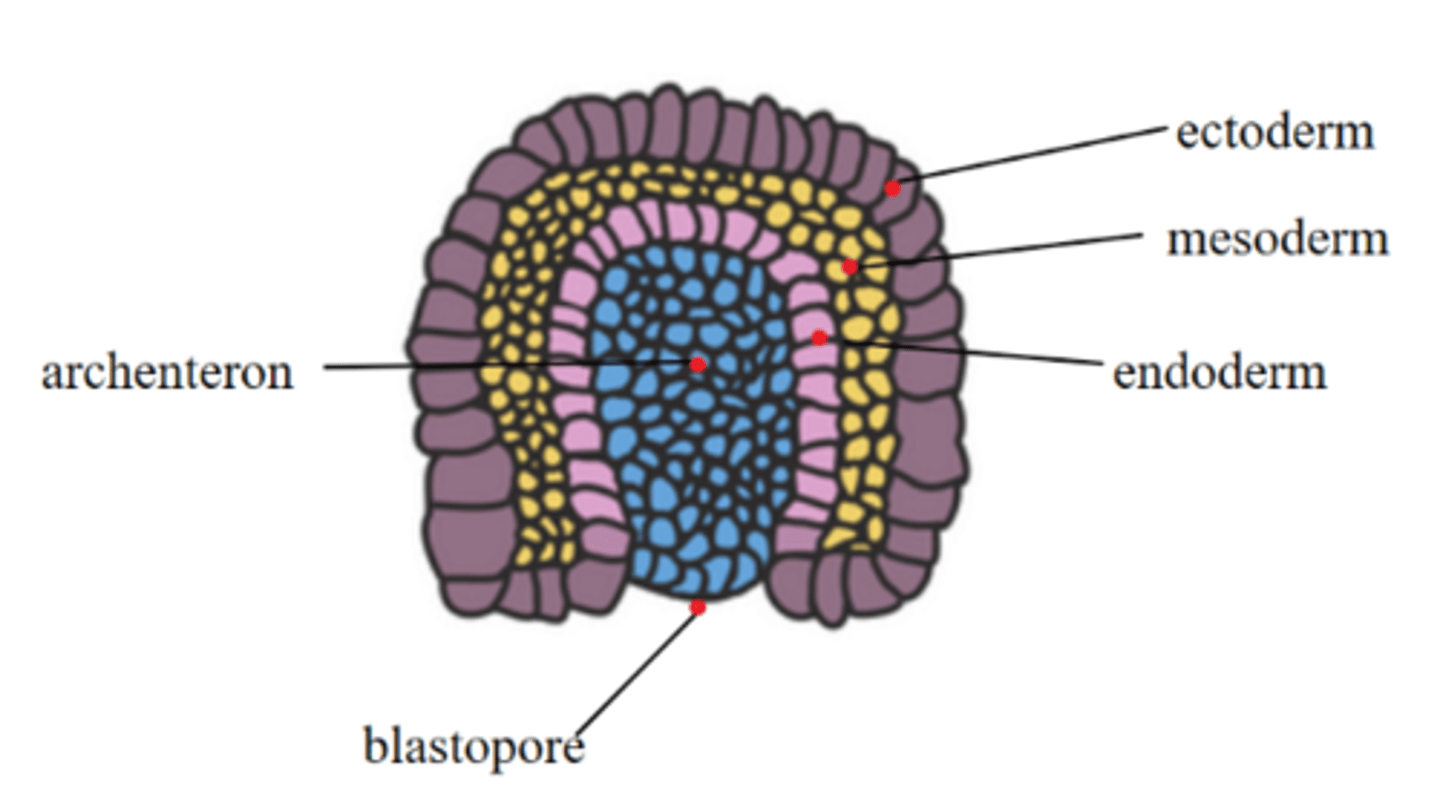
the _____ is a hollow cavity that forms as the blastopore deepens
archenteron
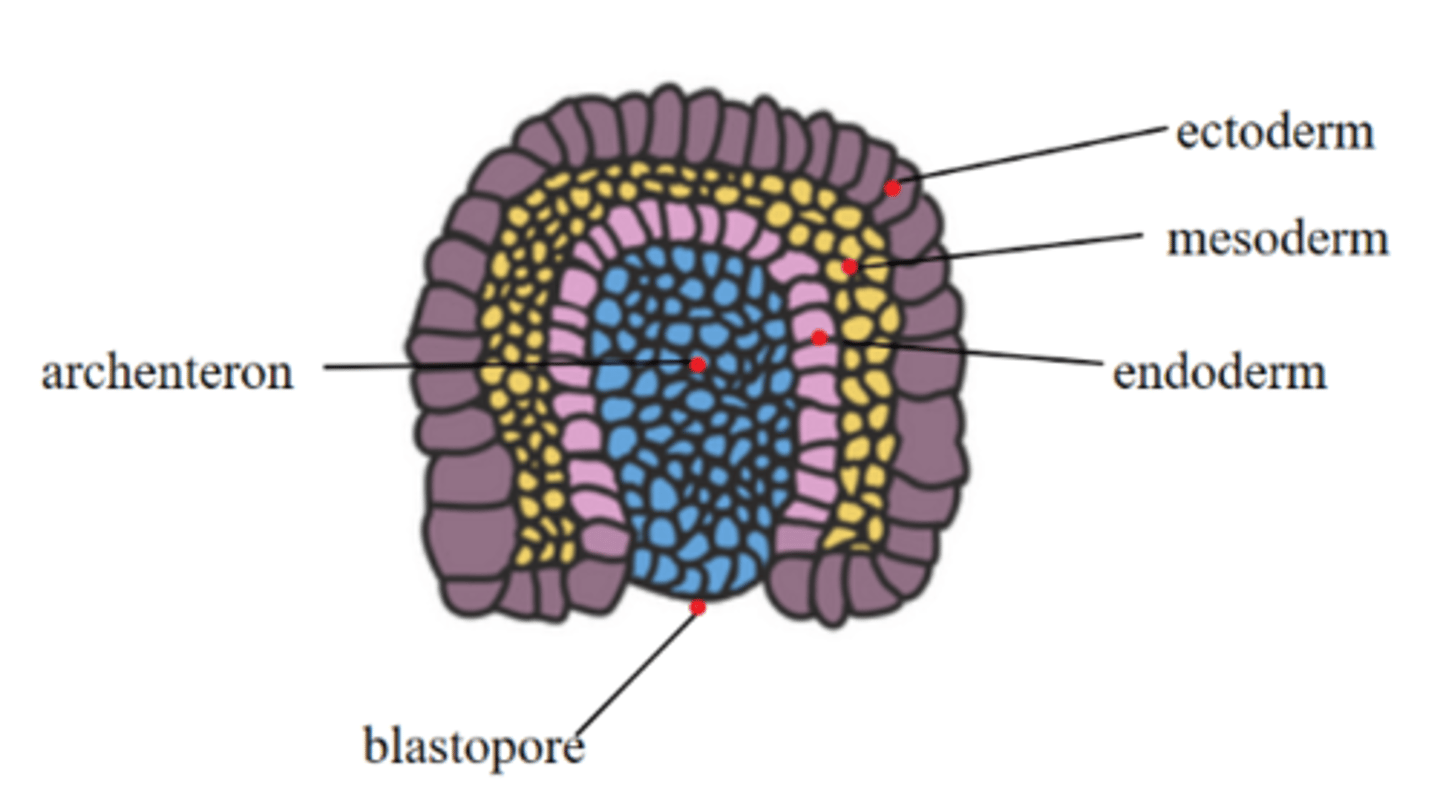
the archenteron eventually forms the _____
digestive tract (gut tube)
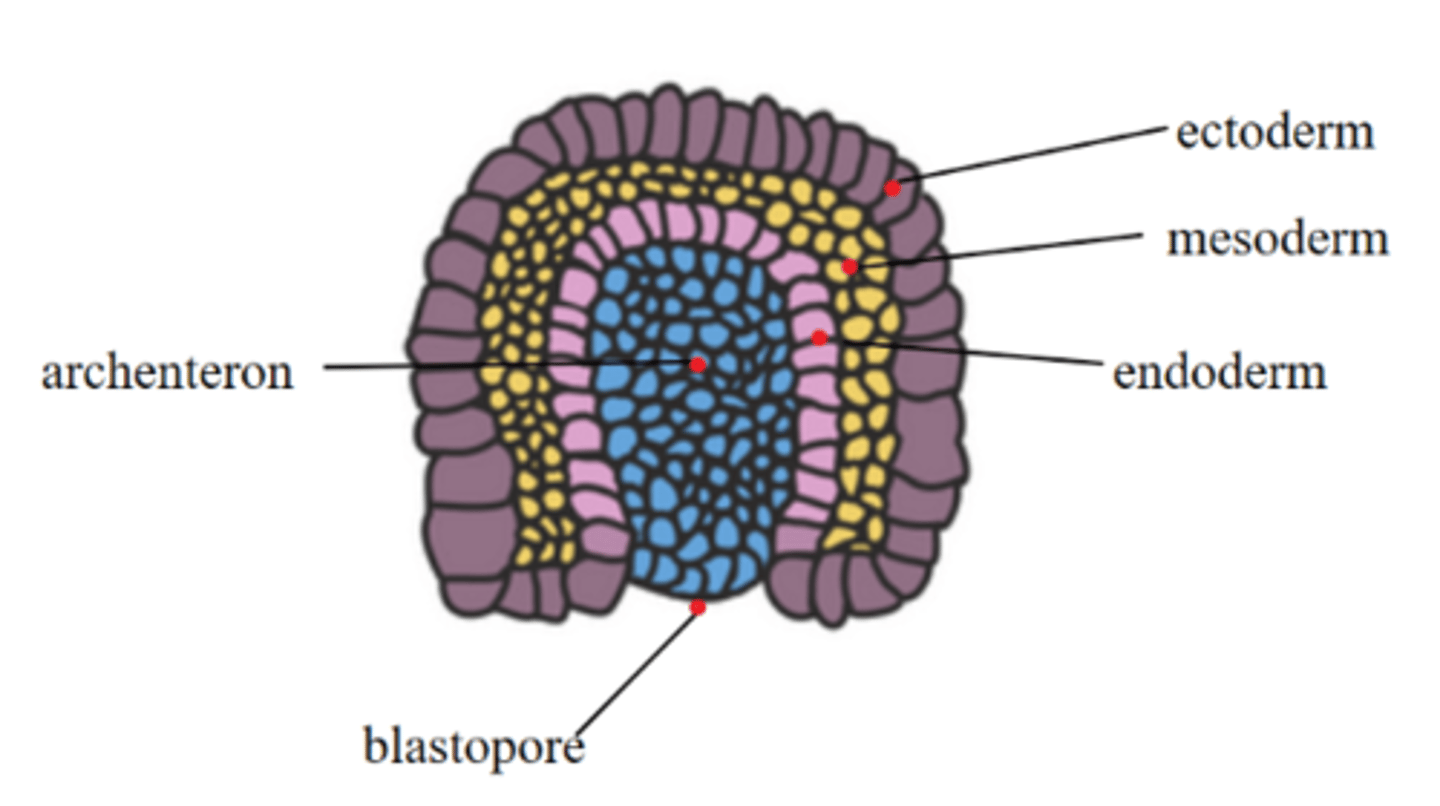
the blastopore is the opening to the _____
archenteron
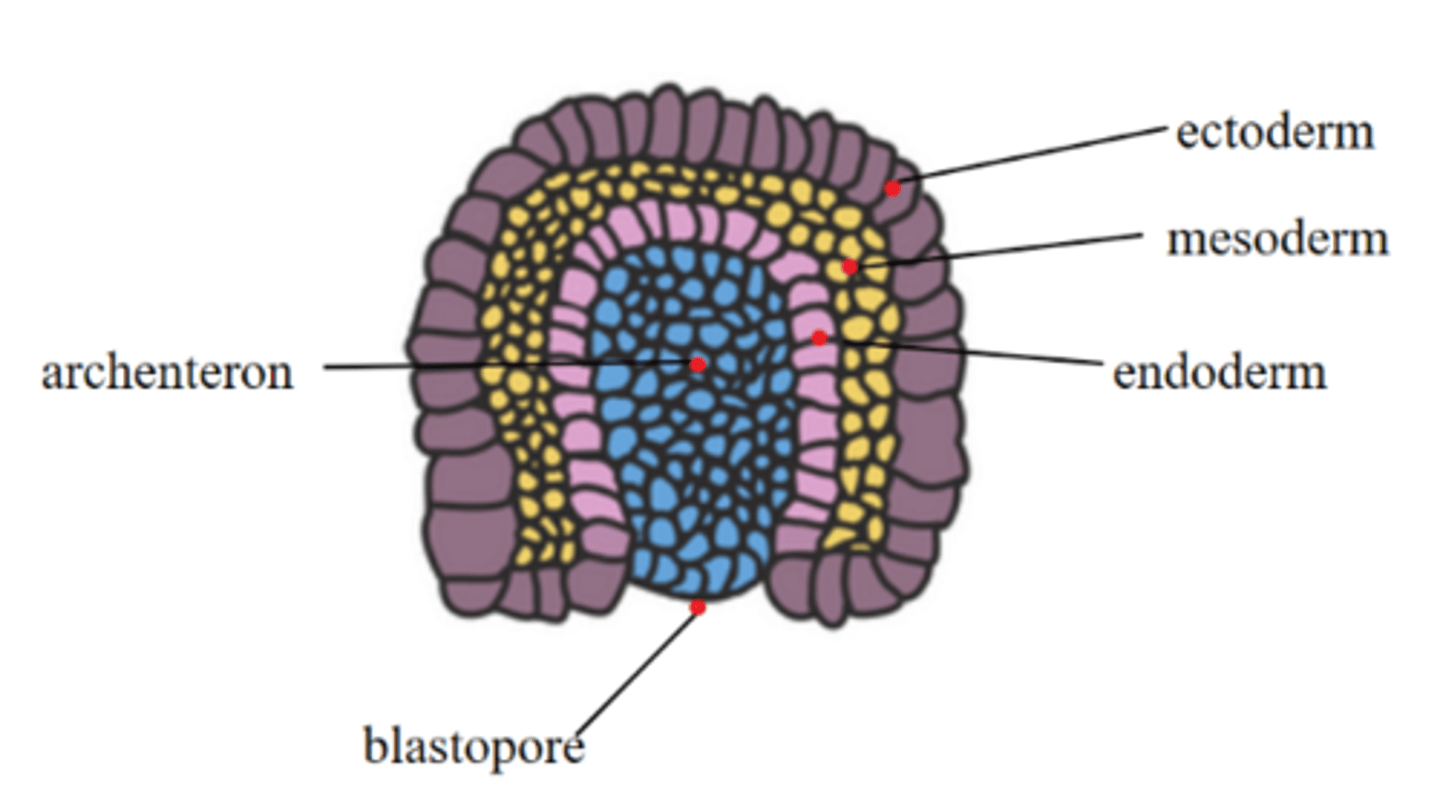
the _____ is the outermost germ layer
ectoderm
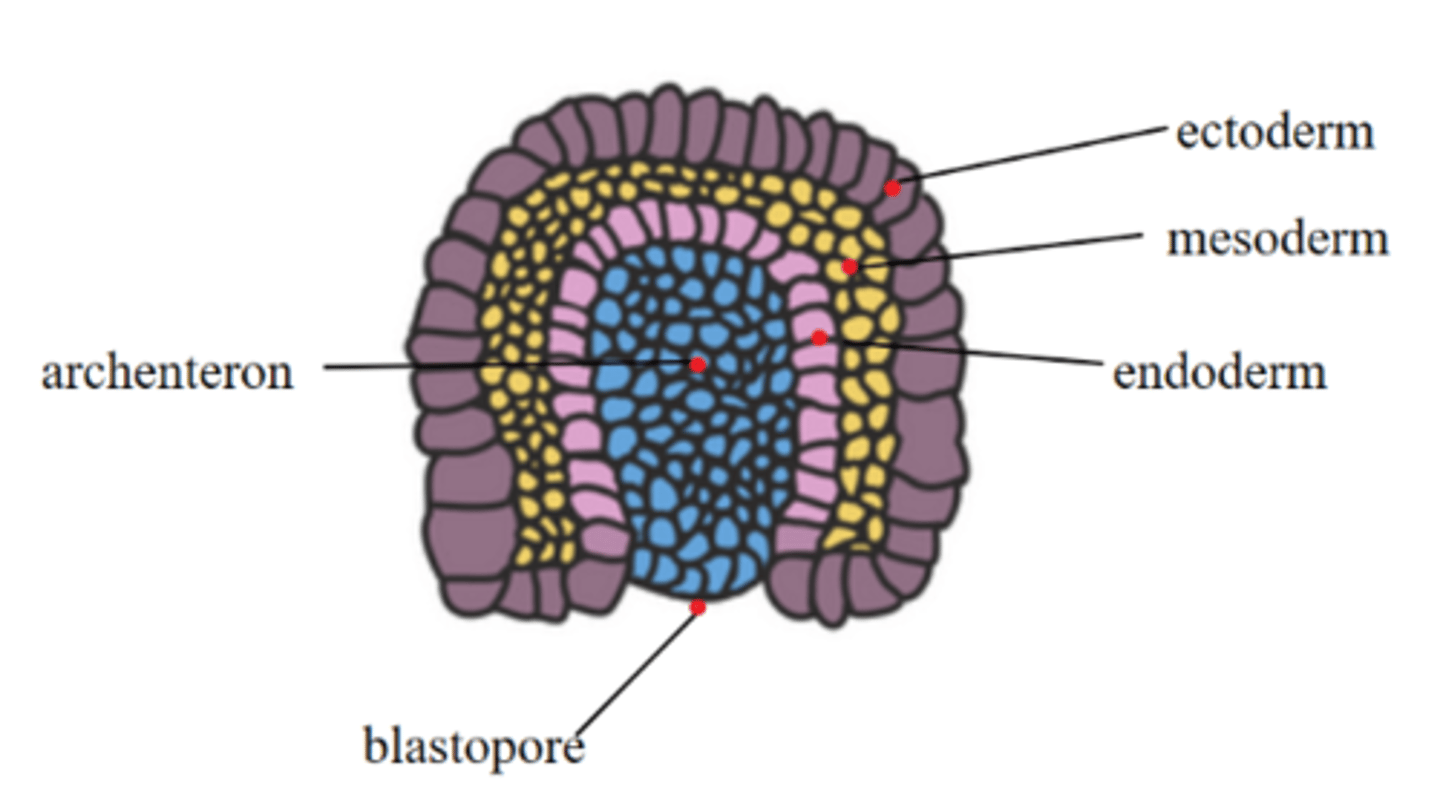
the CNS; PNS; sensory parts of the ear, eye, and nose; epidermis layer of the skin, nails, and hair; mammary and sweat glands; pigmentation cells; jaw and teeth; and adrenal medulla all arise from _____ tissue
ectoderm
the _____ is the middle germ layer
mesoderm
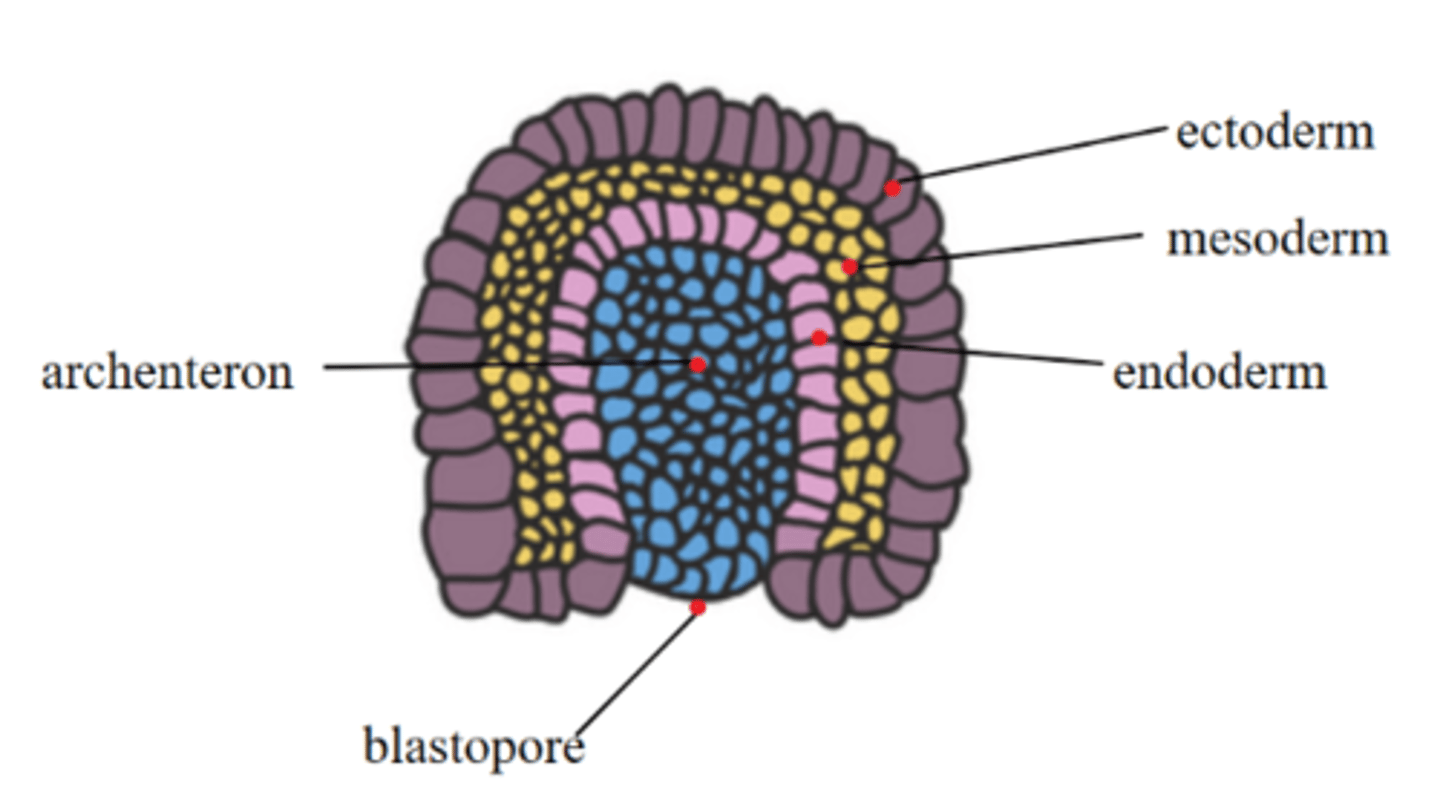
bone and skeleton; skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle; cardiovascular system; gonads; adrenal cortex; spleen; and notochord all arise from _____ tissue
mesoderm
the _____ is the innermost germ layer
endoderm
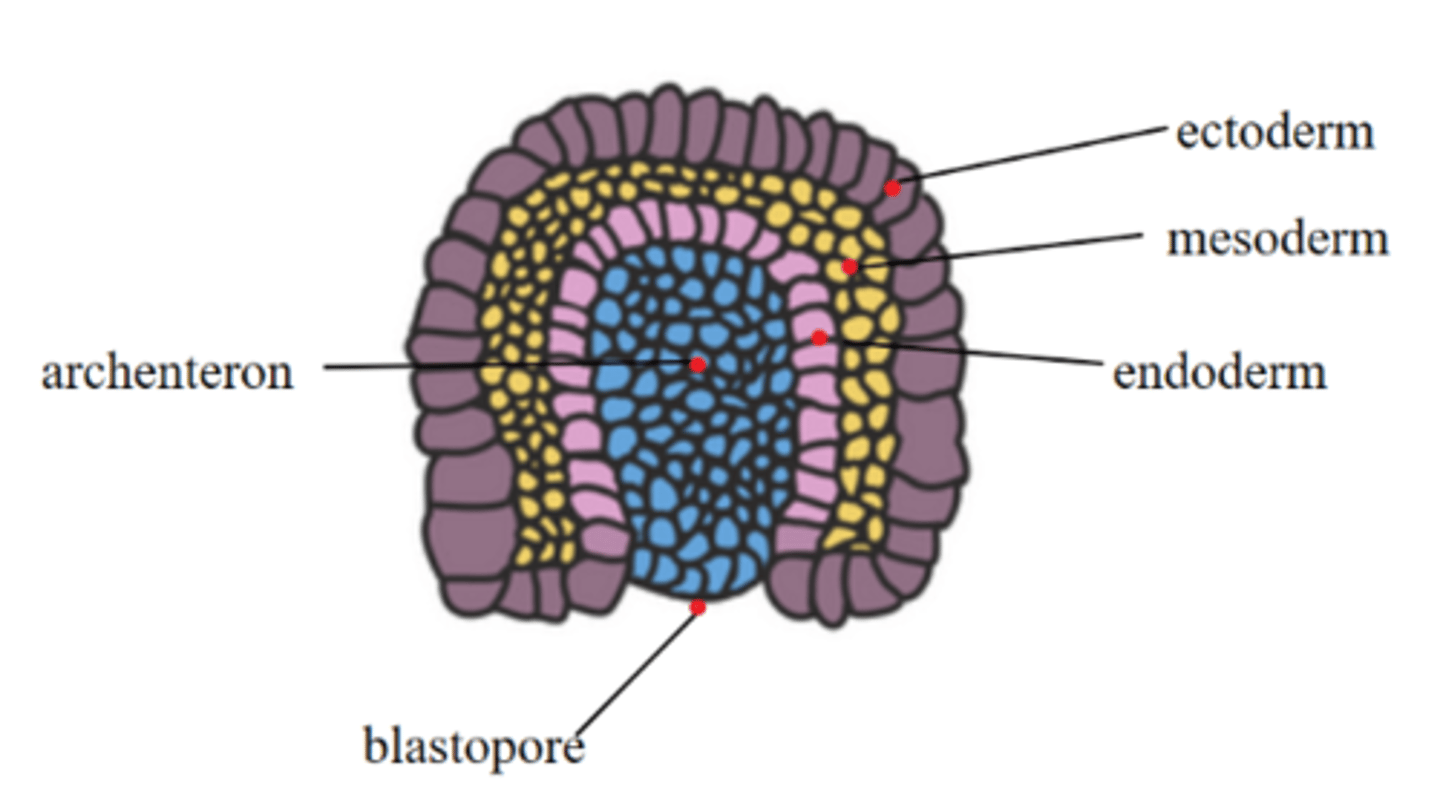
the epithelial lining of the digestive, respiratory, and excretory systems; PLTT (pancreas, liver, thyroid & parathyroid, thymus) all arise from _____ tissue
endoderm
what is organogenesis?
formation of new organs
the _____ is derived from the mesoderm germ layer
notochord
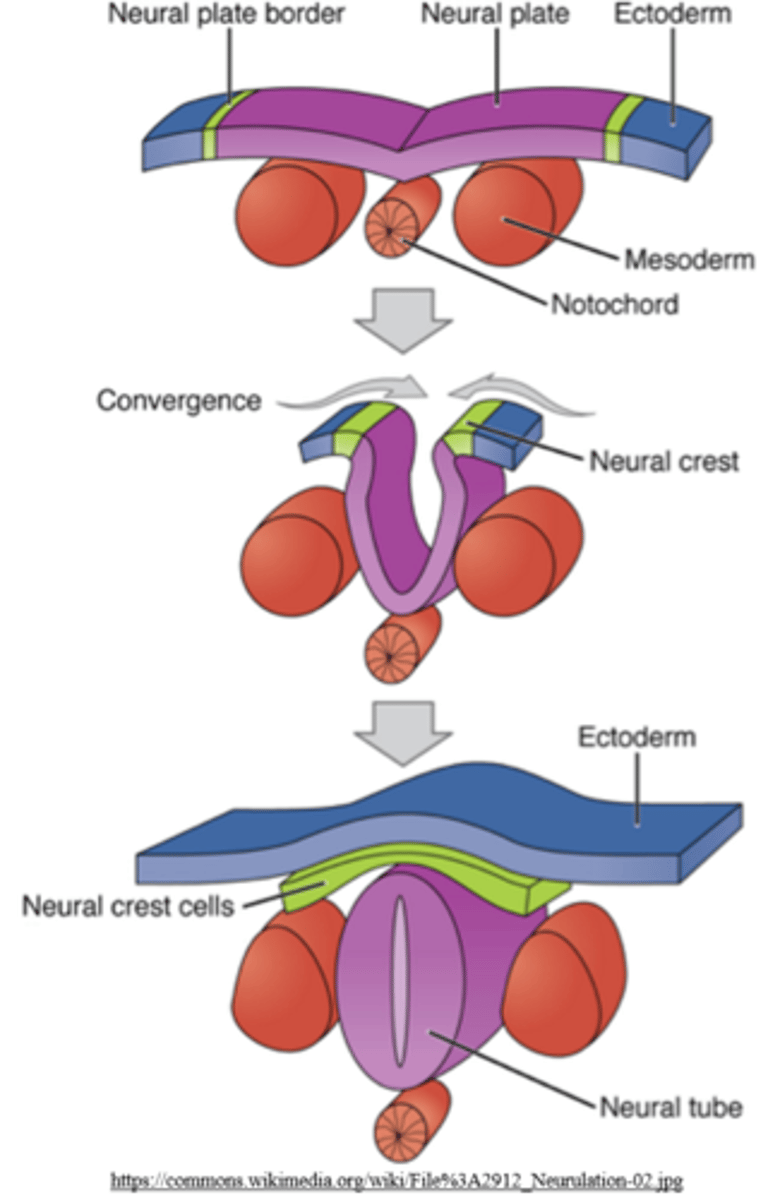
the notochord induces the formation of the neural tube from _____ cells
ectodermal
(the neural tube is made from ectoderm)
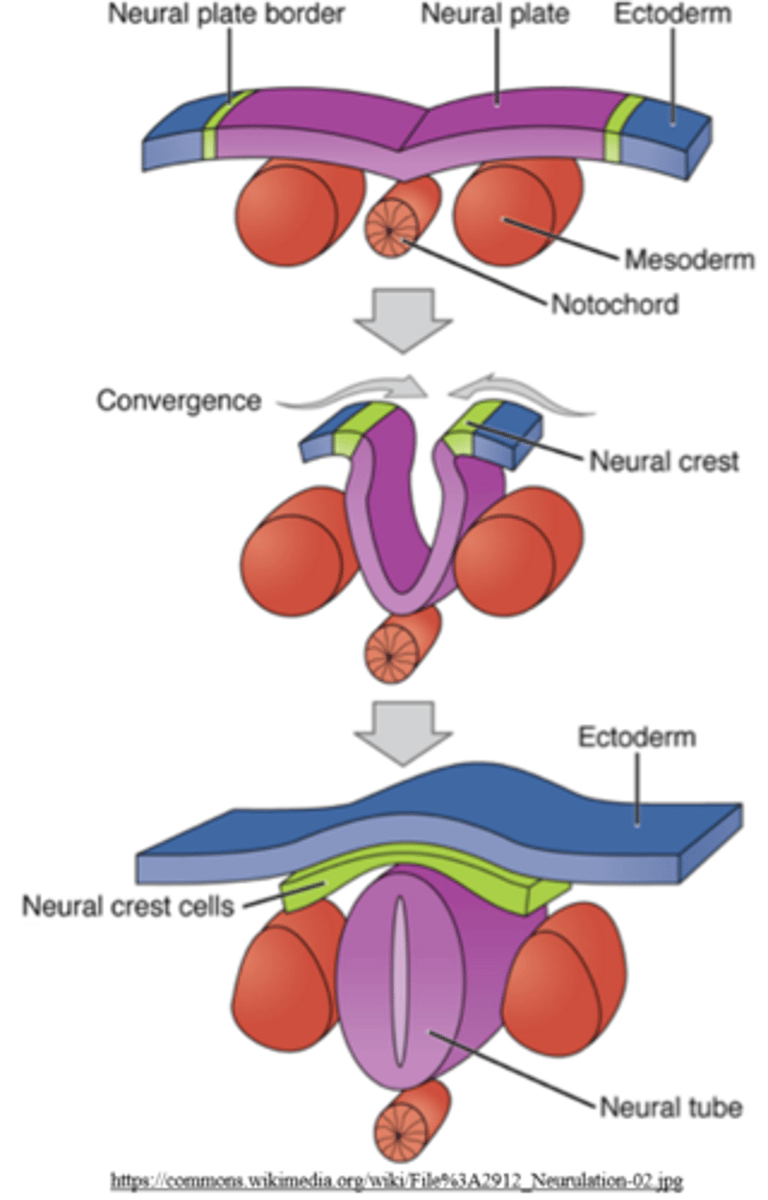
neural crest cells are derived from _____ cells that roll off during neural tube formation
ectoderm
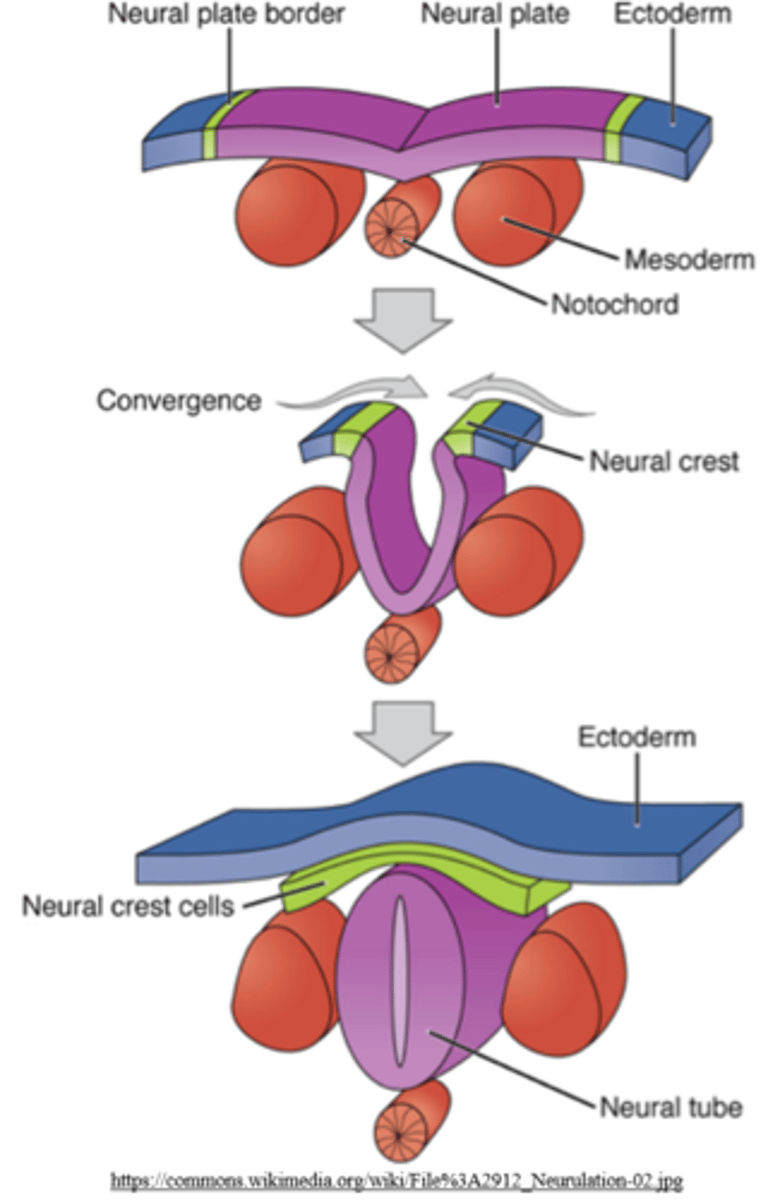
_____ migrate to different locations of the body, forming teeth, bones, skin pigmentation, etc.
neural crest cells
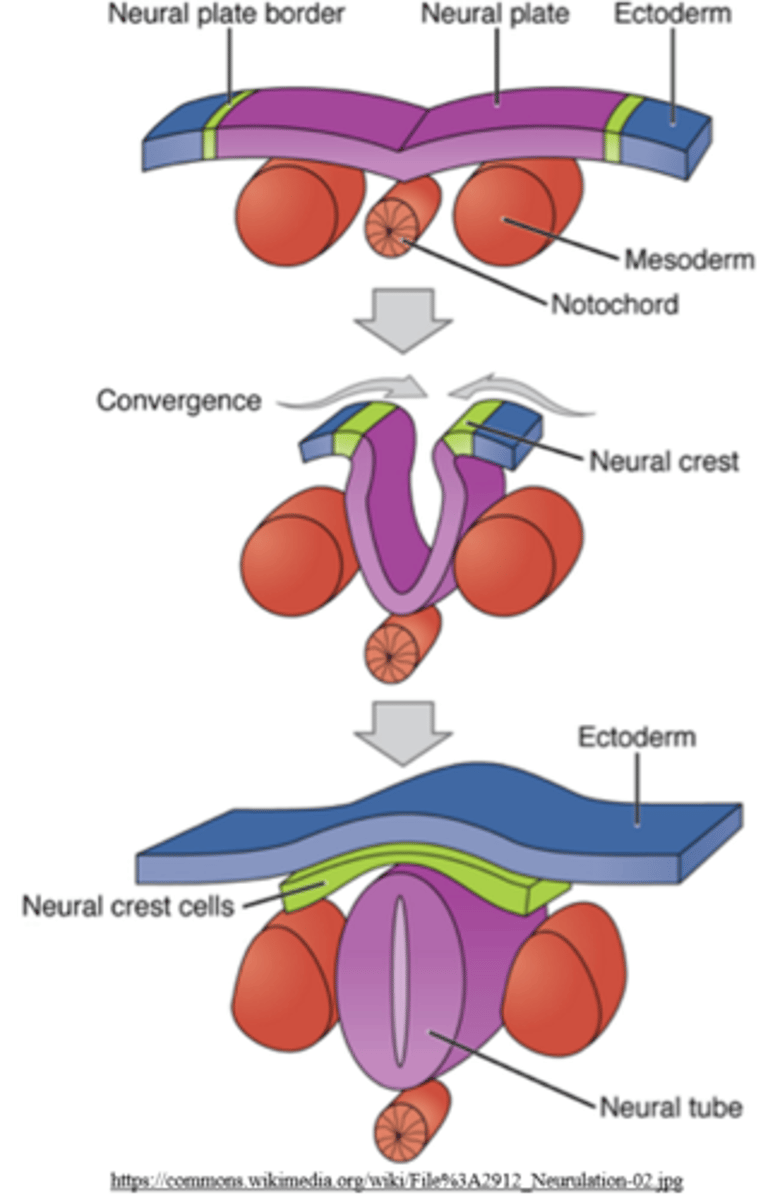
mesoderm cells contribute to two masses of cells on each side of the notochord, called _____
somites
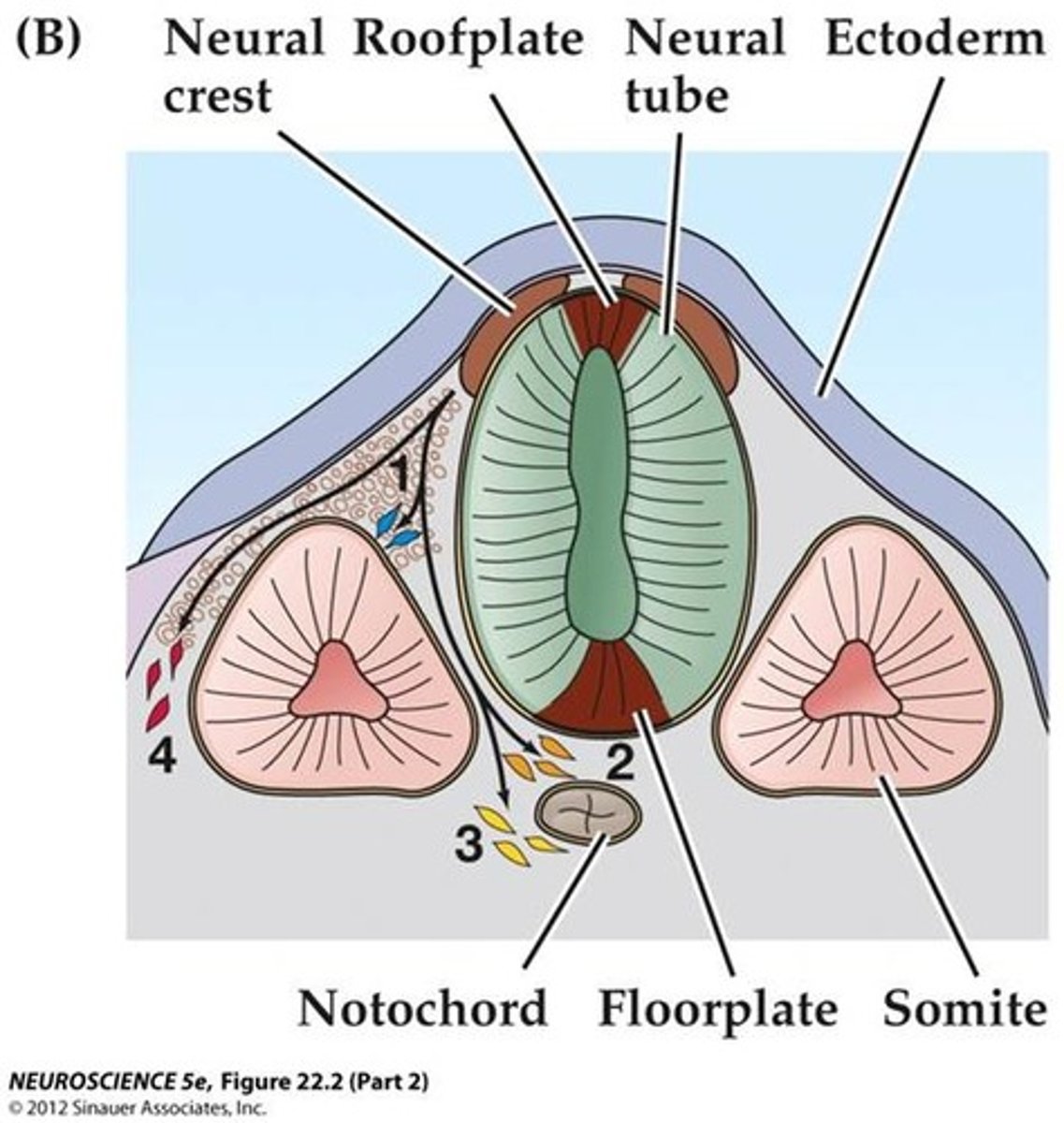
_____ cells contribute to two masses of cells on each side of the notochord, called somites
mesoderm
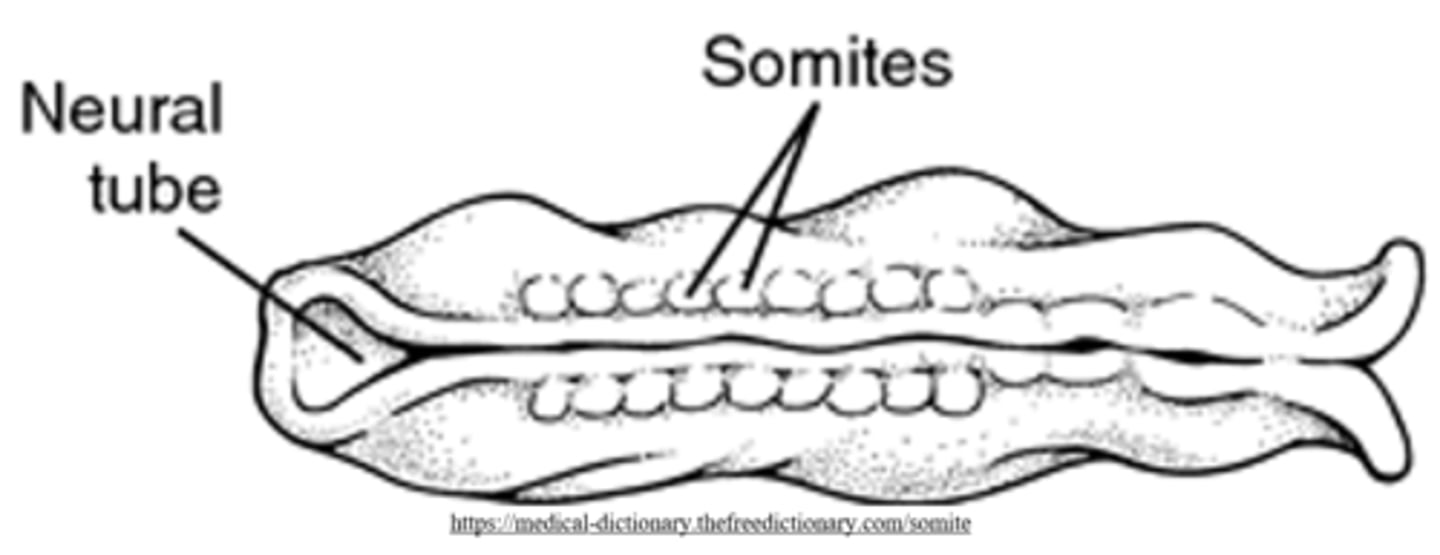
somites become the _____ and _____ associated with the axial skeleton
vertebrae; skeletal muscles
_____ are undifferentiated cells that have the potential to differentiate to different cell types
stem cells
what are the three types of stem cell potency?
totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent
_____ stem cells can become any cell in the body
totipotent
what are some examples of totipotent stem cells?
zygote, blastomeres of the morula
pluripotent stem cells can differentiate into any of the _____
three germ layers
(ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
what are some examples of pluripotent stem cells?
cells from the inner cell mass (embryonic stem cells)
_____ cells can only differentiate into a few cell types of a specific tissue type
multipotent
what are some examples of multipotent stem cells?
hematopoietic stem cells, which can divide into many blood cell types
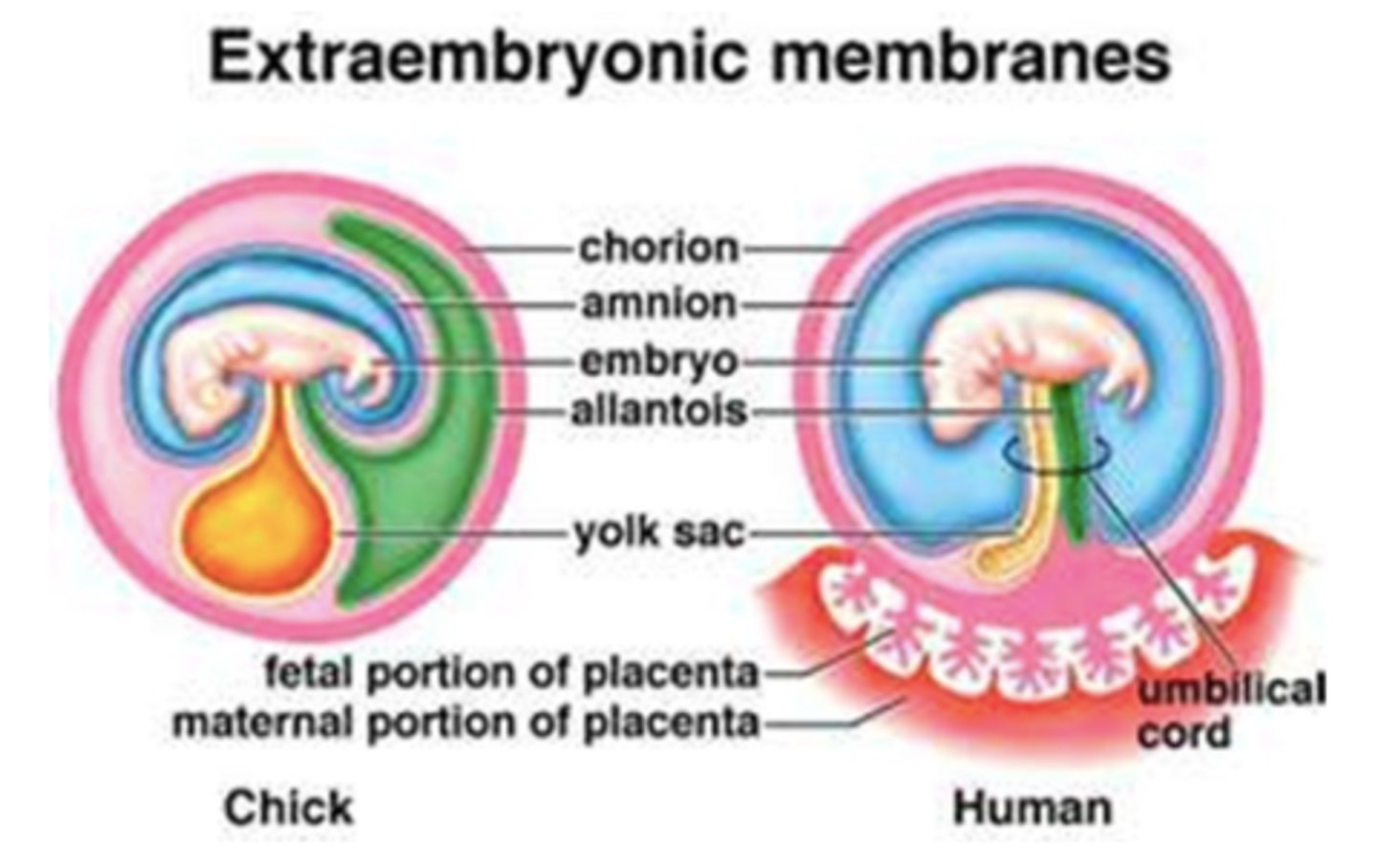
what are the four main extraembryonic membranes?
amnion; chorion; allantois; yolk sac