Mitosis and Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction in Plants/Animals
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
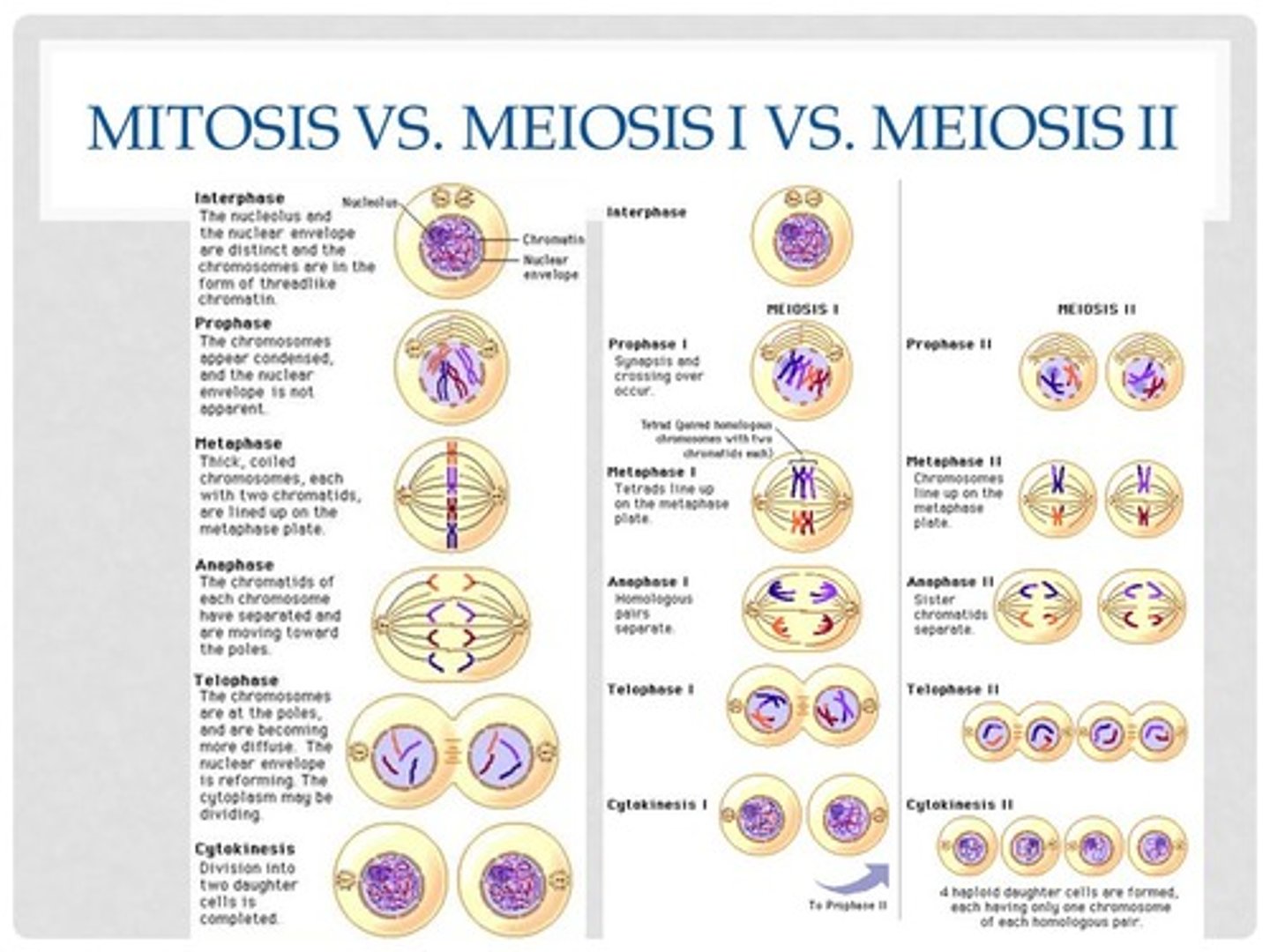
Meiosis I vs Meiosis II vs Mitosis
1.) Mitosis 2n to 2n
Meiosis I 2n to 1n
Meiosis II 1n to 1n
In meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate, resulting in two haploid daughter cells with replicated chromosomes. In meiosis II, sister chromatids separate, resulting in four haploid daughter cells with replicated chromosomes.
synapsis
the pairing of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
crossing over
Process in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
Cohesion, separase, and shugoshin in meiosis and mitosis
cohesion holds the sister chromatids together. In anaphase, one homologous chromosome is on one side and one on the other. To be able to pull them apart, separase comes and degrades cohesion proteins holding them together. They can be pulled apart. Shugoshin wraps around the cohesions between them to protect those.
Prophase I
The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. crossing-over occurs.

Metaphase I (Meiosis)
Tetrads are lined up at the metaphase plate; Spindle fibers attach
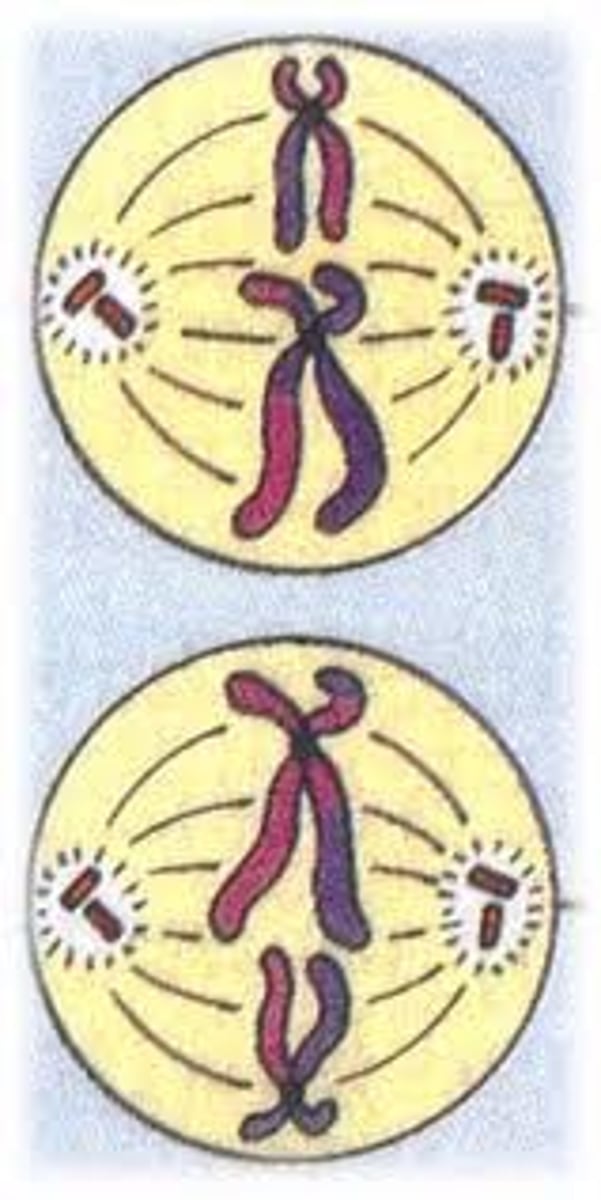
Anaphase I (Meiosis)
Homologous chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate on opposite sides so that they can be split by the spindle fibers.
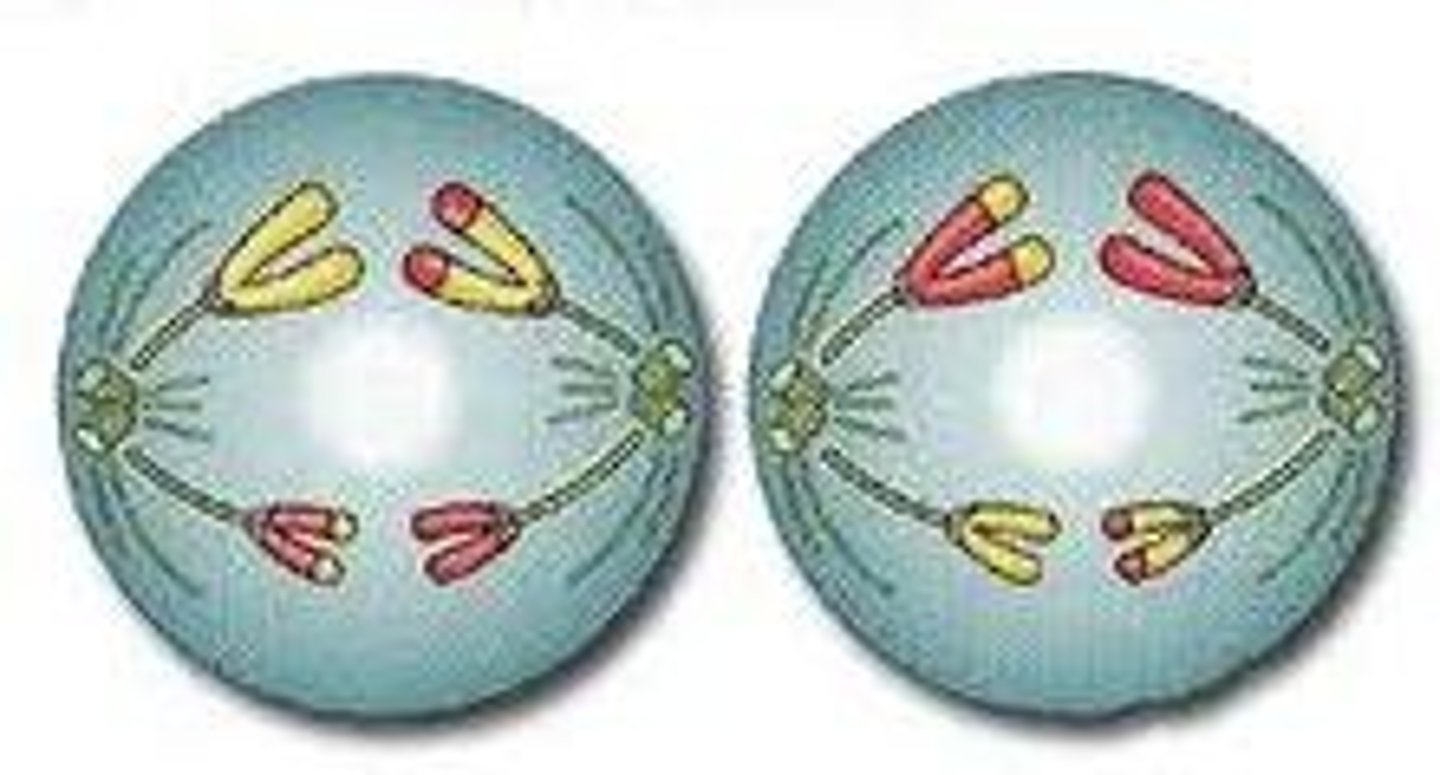

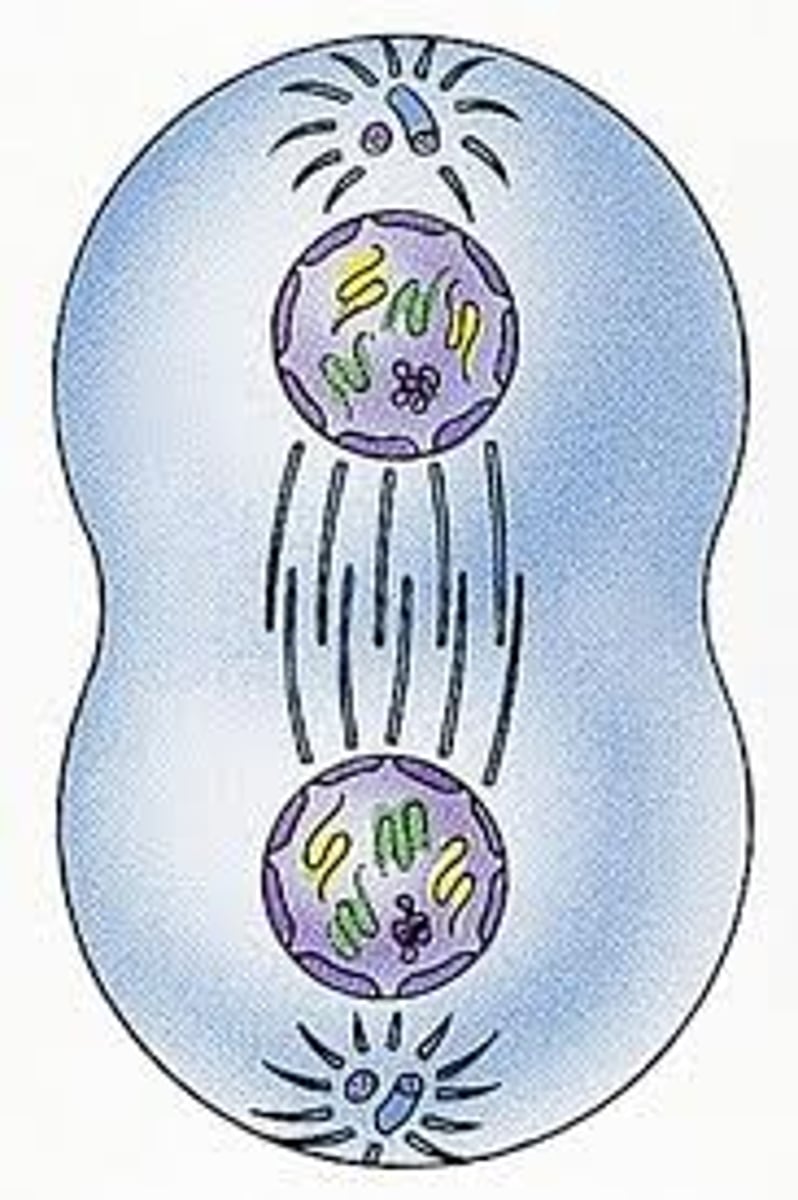
Telophase I
The cytoplasm divides in the cell, new membranes form to generate new cells.
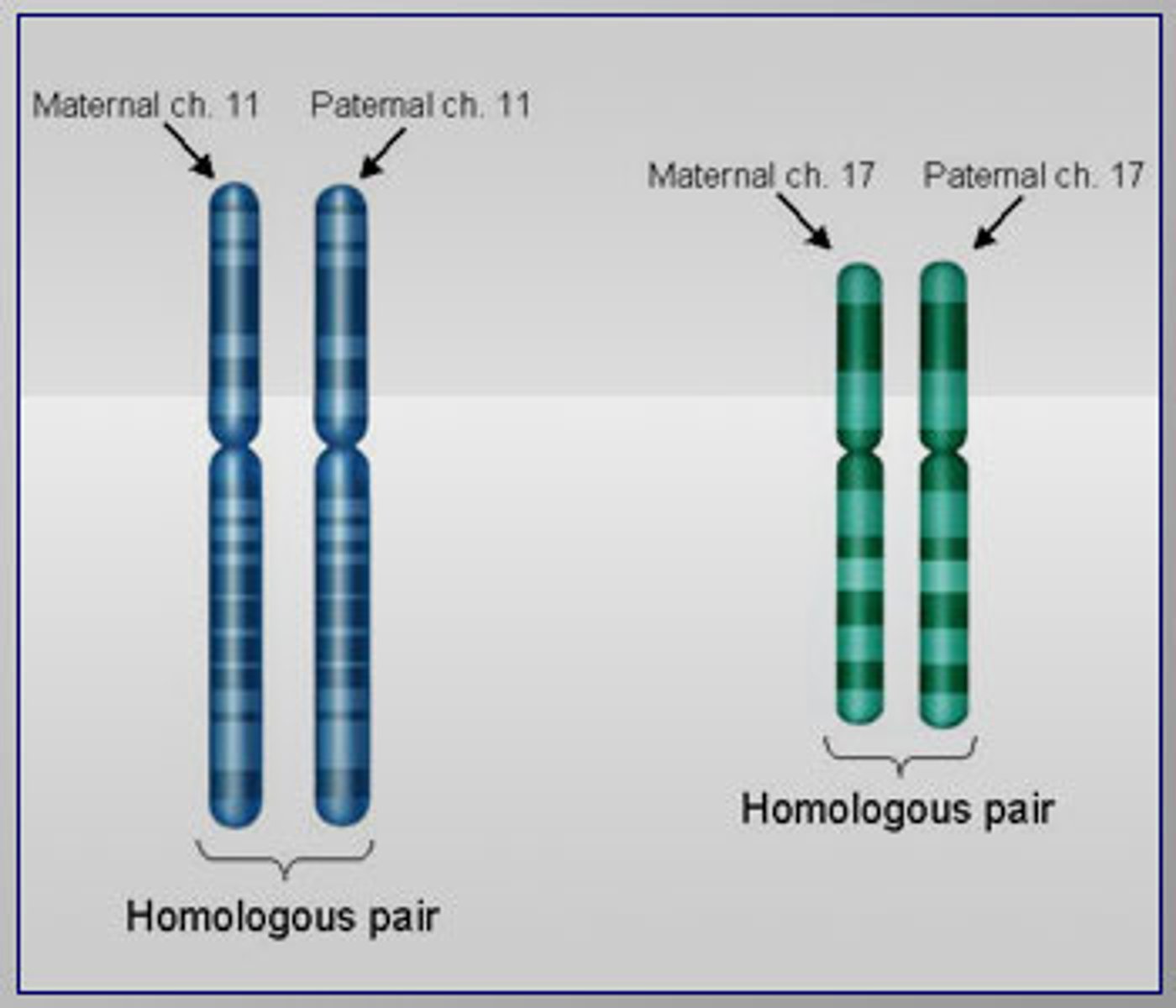
homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and same genes.
nonhomologous chromosomes
chromosomes that do not match because they have different sets of genes
isogamous
gametes that appear the same size
heterogamous
gametes unlike in size
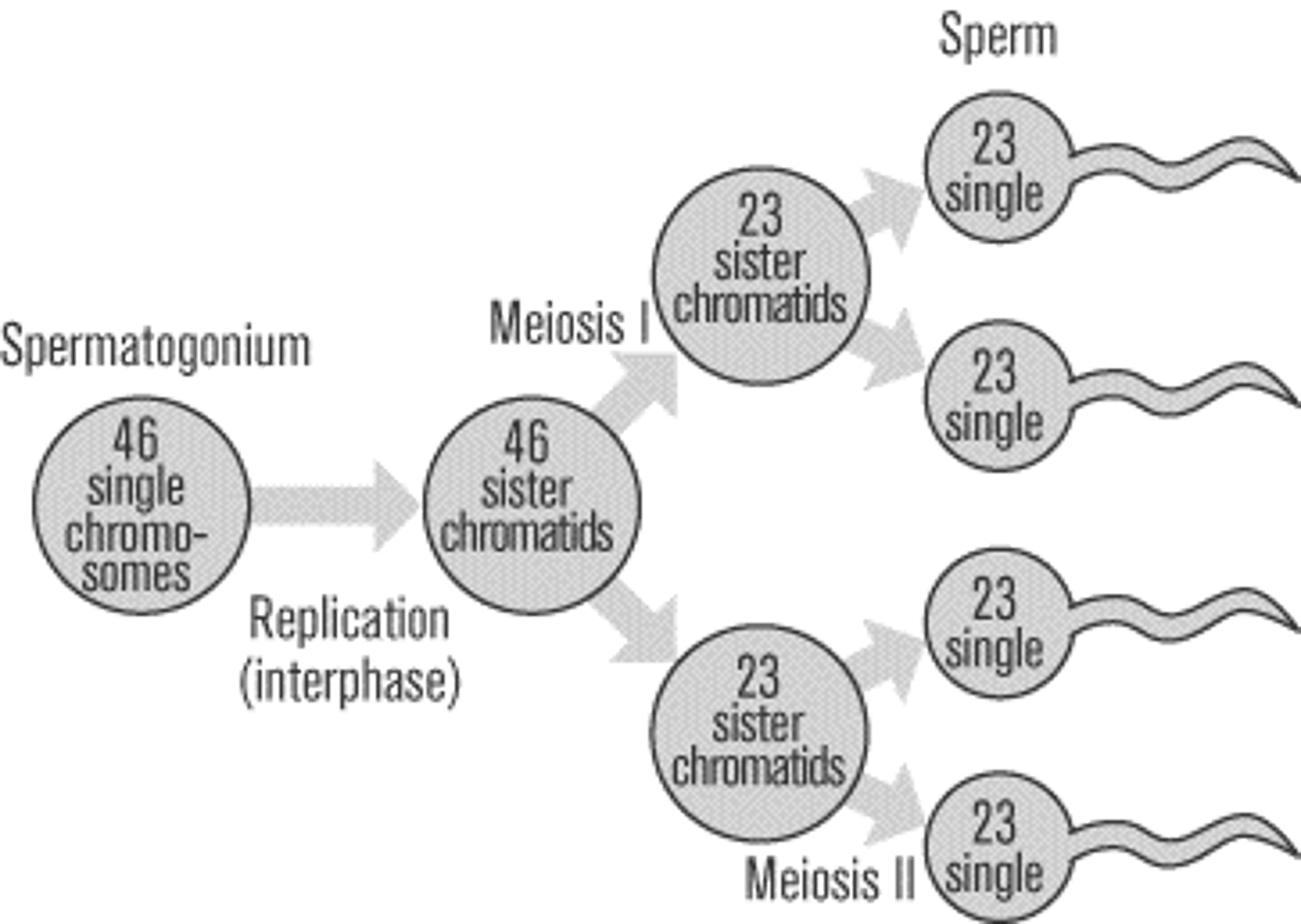
Spermatogenesis
Formation of sperm - genetically diverse haploid sperm, divided continually after puberty
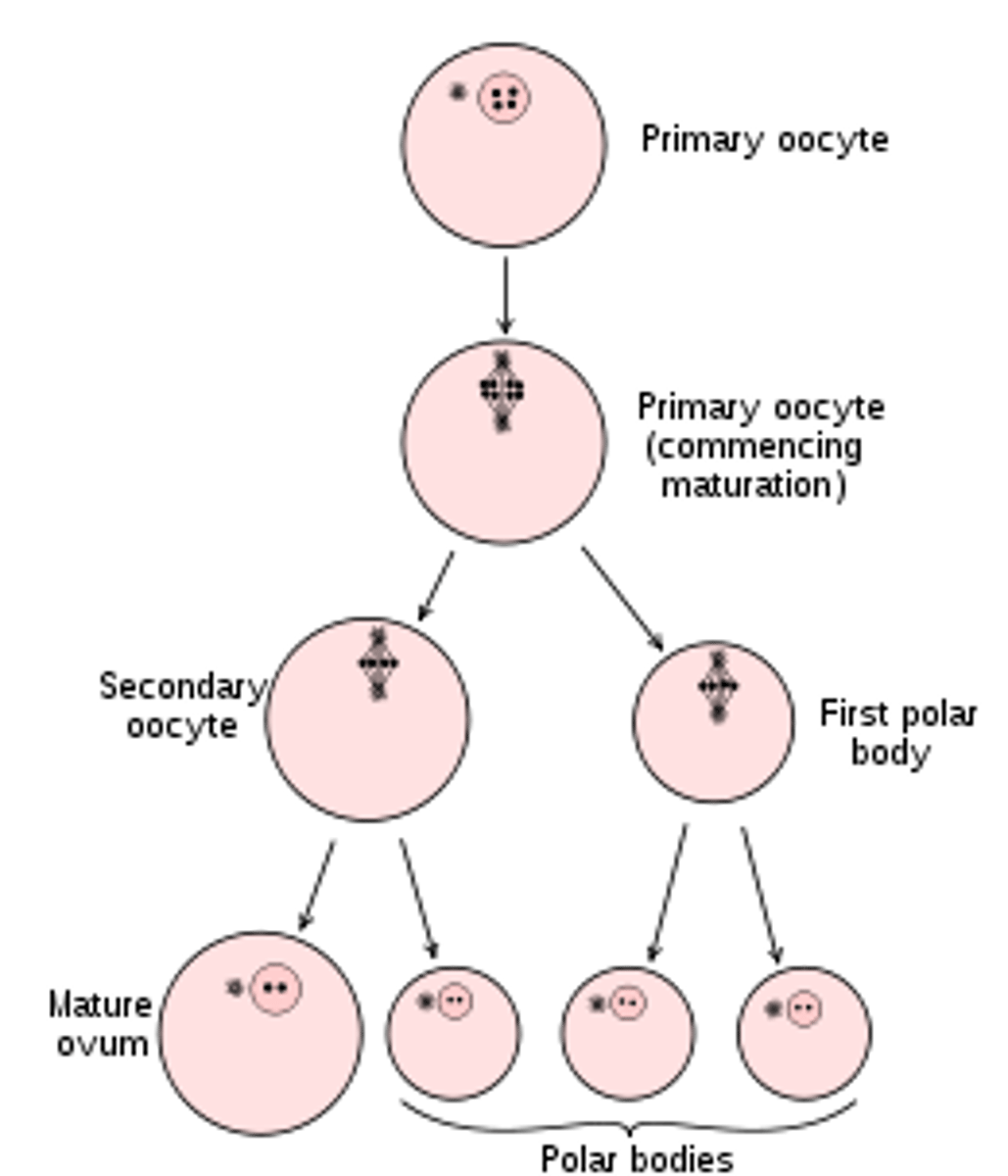
Oogenesis
the production, growth, and maturation of an egg, or ovum - all made at birth.
Microsporocyte vs Megasporocyte, what does it form
micro - male sperm, mega - female ovum, forms a zygote, and then through mitosis a plant
What do the three haploid nuclei from the microsporocyte do?
2 will fertilize, while one will join the megasporocyte egg to form. the 2n nucleus embryo.
double fertilization
The embryo with a haploid nuclei from mom and dad is the first, and then the second fertilization with 2 haploid nuclei from sperm and 1 haploid from egg = triploid nucleus