IB Biology Cells Unit Flashcards
1/127
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Organelle
specialized structure that performs important specific cellular functions within a cell
cell fractionation
technique in which cells are broken into pieces and the different cell parts are separated
ultracentrifugation
The second stage of cell fractionation when the fragments in filtered homogenate are separated in a machine called a centrifuge.
Plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells
homogenization
when trying to separate cell organelles, a tissue containing cells is blended in a cold buffered solution isotonic to the cell cytoplasm
nucleus
double membrane organelle where transcription and production of mRNA takes place
cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Transcription
(genetics) the organic process whereby the DNA sequence in a gene is copied into mRNA. occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
translation
(genetics) the process whereby genetic information coded in messenger RNA directs the formation of a specific protein at a ribosome in the cytoplasm
metabolites
chemical products of metabolism
enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions
Lysosomes
single membrane bound cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
phagocytosis
process in which extensions of cytoplasm surround and engulf large particles and take them into the cell
phagocytic vacuole
forms when microbe is engulfed and will fuse with a lysosome
mitochondria
a double membrane bound organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of respiration and energy production occur.
Cytoskeleton
network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in many forms of cell movement. Not considered an organelle
Chloroplast
a double membrane bound organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
ribosome
organelle not bound by a membrane that is the site of protein synthesis
cell wall
not considered an organelle - outside of a plant cell. rigid structure made of cellulose that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell
flagella
membrane bound organelle that allows for movement of cells
Organelles with no membrane
Ribosomes
Free DNA in prokaryotes
Microtubules
Organelles with single membrane
Rough and smooth eR
Vacuole and Vesicles
Lysossomes
Golgi Apparatus
Organelles with double membrane
Chloroplasts
Mitochondria
Nucleus
Amyloplasts
Chromoplasts
SA:Volume ratio
Impacts the function of exchange surfaces in different organisms by determining the efficiency of exchange.
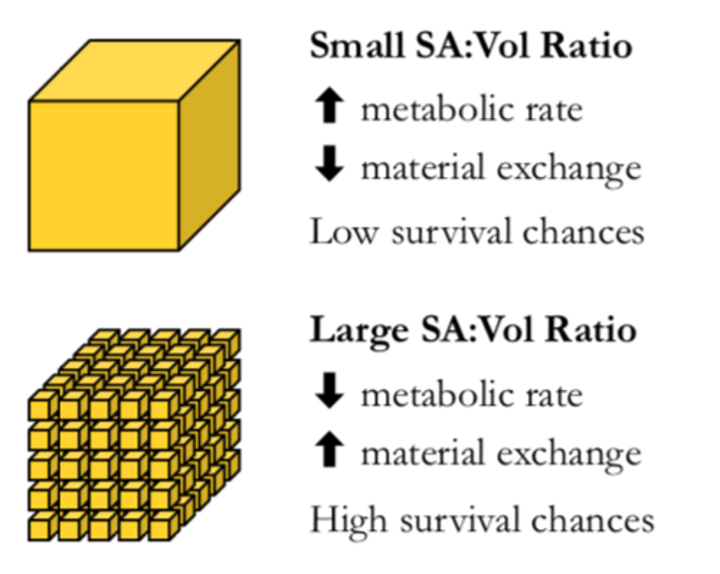
Multicellularity
Organisms composed of many cells - developed by cellular specialisation and division of labour.
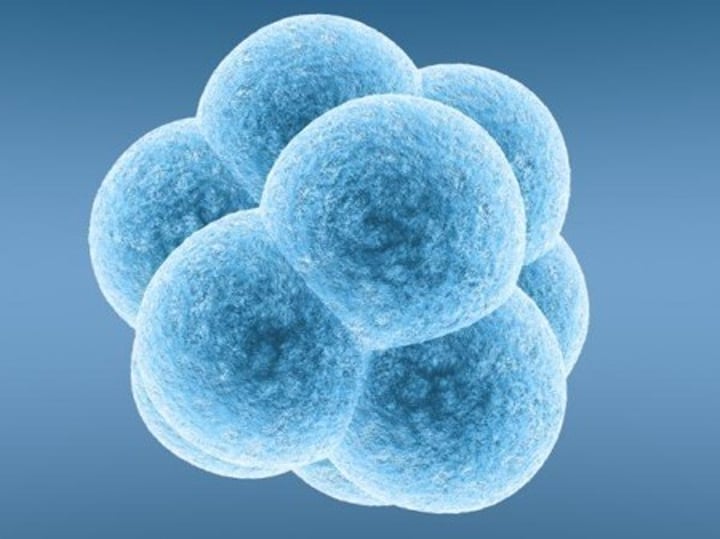
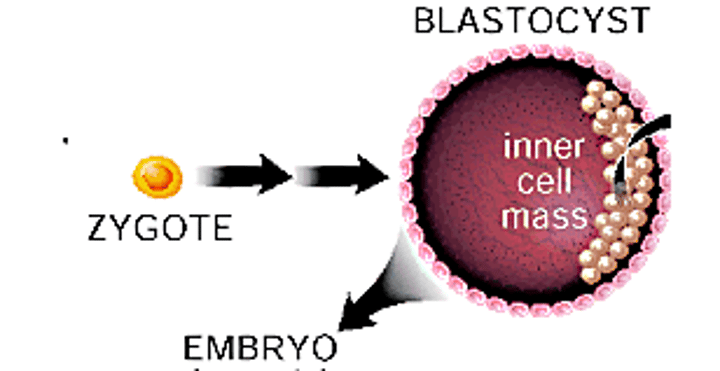
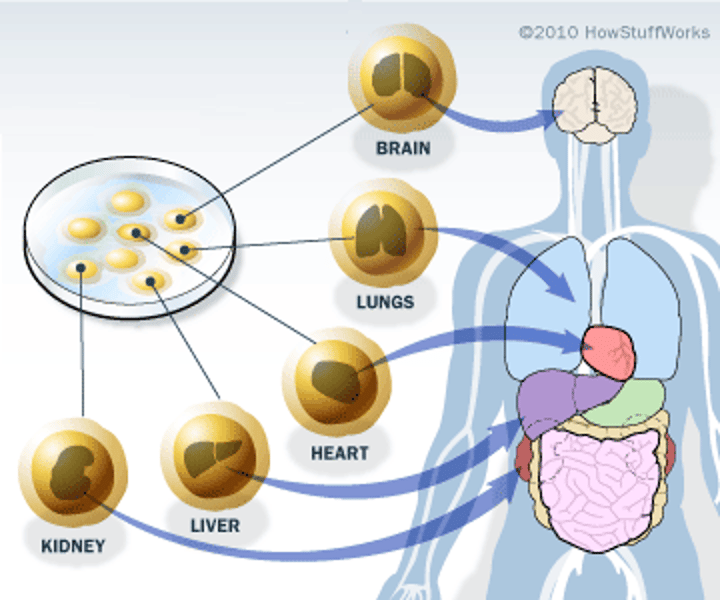
Embryonic Stem Cells
Pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-implantation embryo (4/5 days)
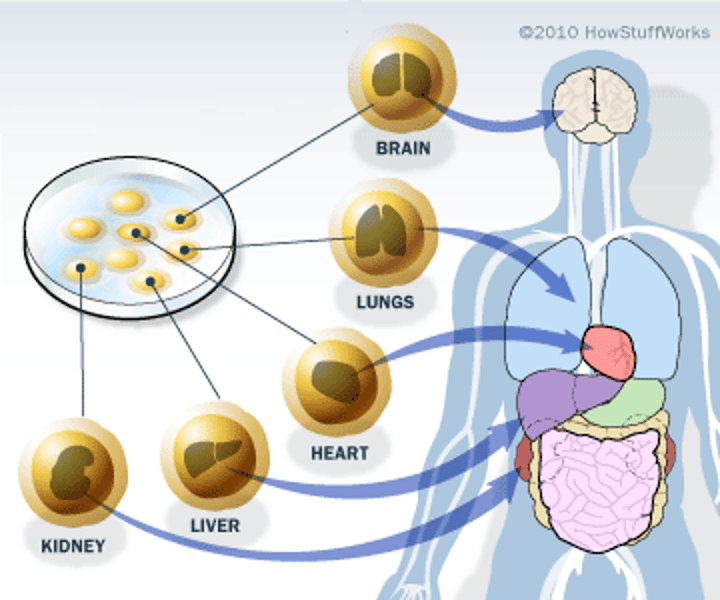
Adult Stem Cells
Undifferentiated cells, found throughout the body after development, multiply by cell division to replace dying cells and regenerate damaged tissues. AKA somatic stem cells.
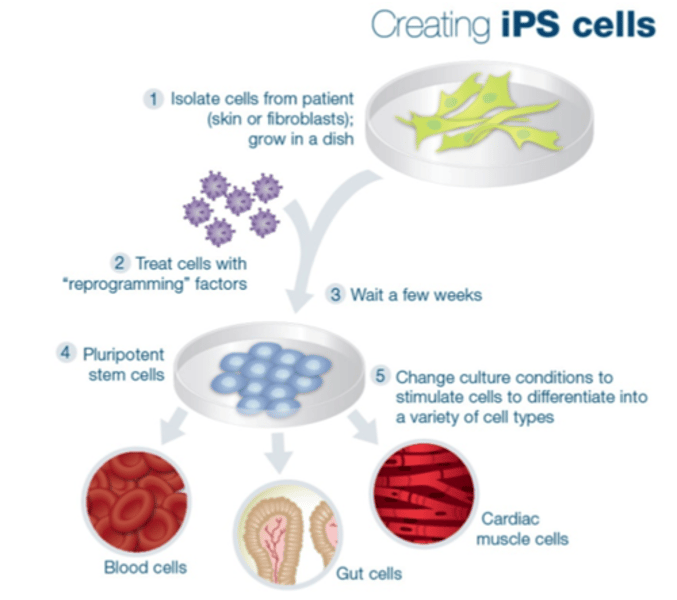
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Stem cells derived from adult somatic cells. Reprogrammed to be pluripotent, they are similar to embryonic stem cells.
Totipotent
Cells with the greatest differentiation potential. Can divide to form any embryonic cell, as well as any extraembryonic cell.
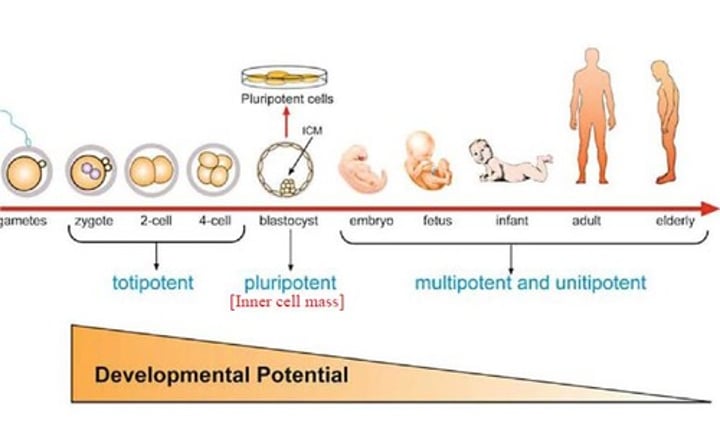
Pluripotent
Can self-renew by dividing and can develop into the three primary germ cell layers of the early embryo and all body cells (but not extra-embryonic tissues such as the placenta).
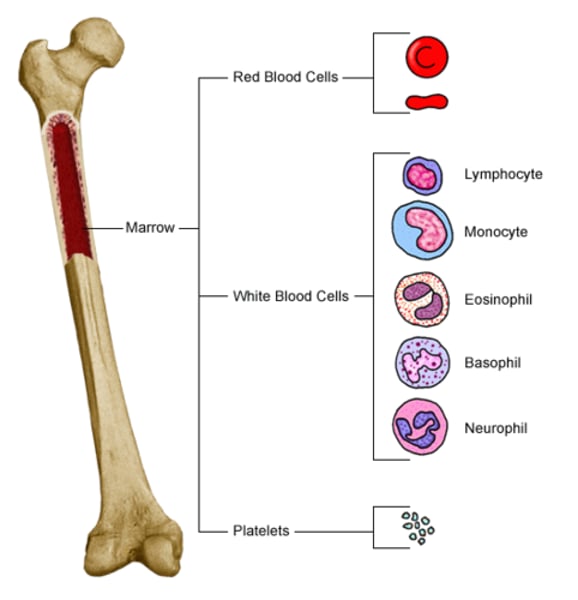
Multipotent
Can develop into more than one cell type, but within the same lineage, e.g., stem cells in the bone marrow only make blood cells.
Unipotent
A cell that can differentiate into one specific cell type.
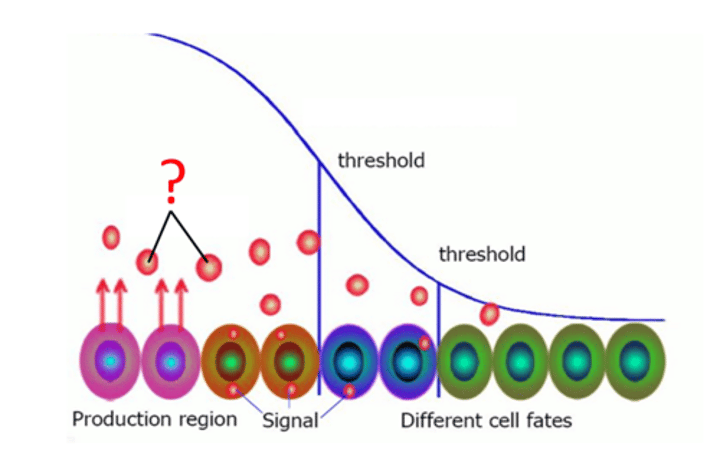
Morphogen
Signalling molecules that cause a change in cells during their development. Changes in concentration give rise to different effects, and therefore different cell types.
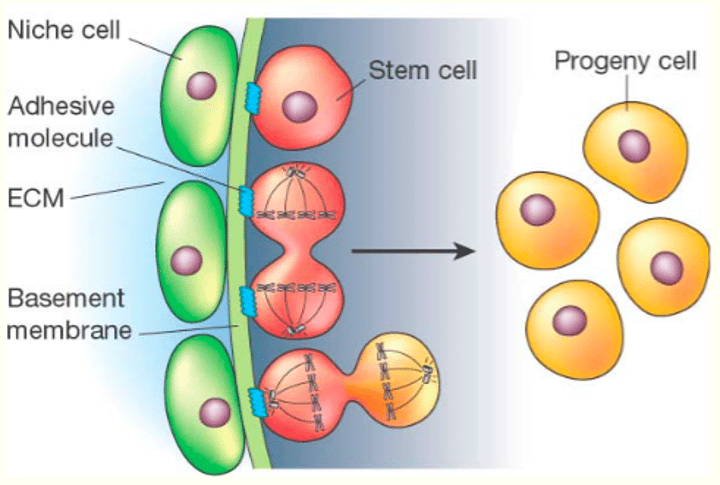
Stem Cell Niche
The microenvironment where stem cells are found and receive stimuli that determine their fate.
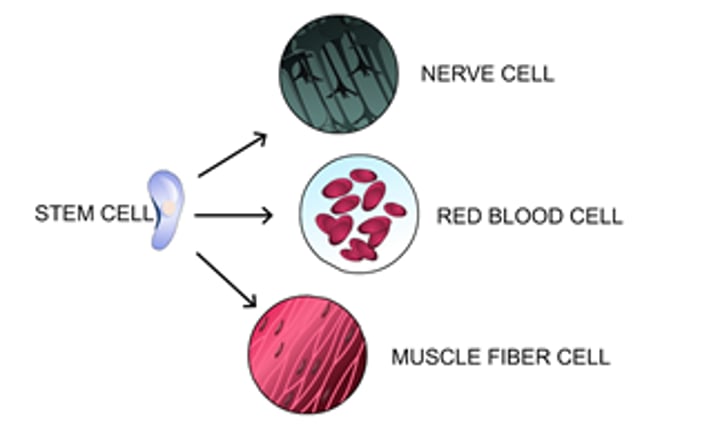
Differentiation
The process of changing from an undifferentiated stem cell into a specialised cell with a particular function.
Specialisation
The development of specific functions and structures within a cell, after it has differentiated.
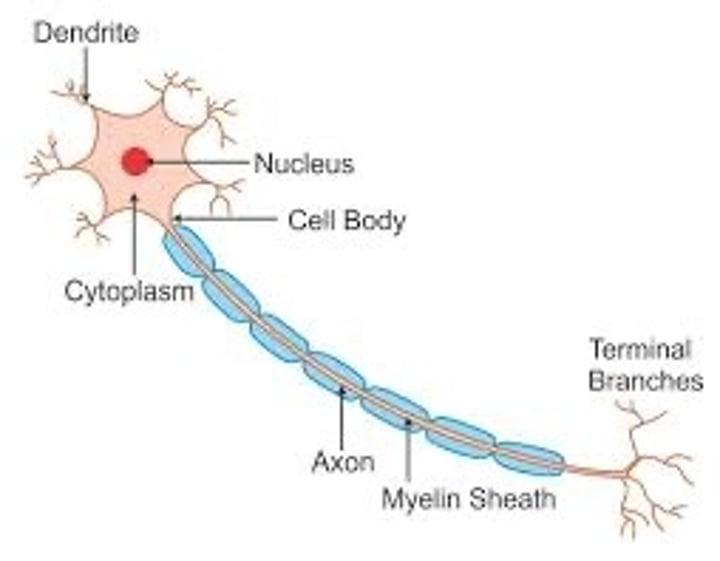
Proliferation
Stem cells divide to form one daughter cell that remains a stem cell and a second that differentiates.
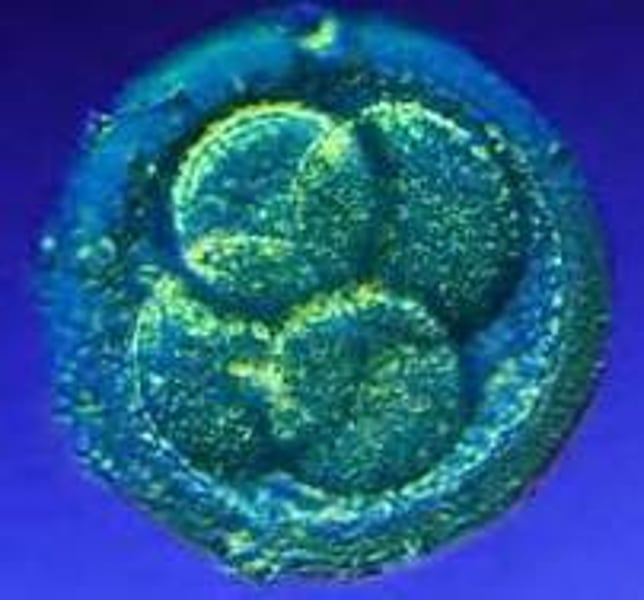
Progenitor Cell
Can produce only one cell type but unlike other body cells are able to self-renew.
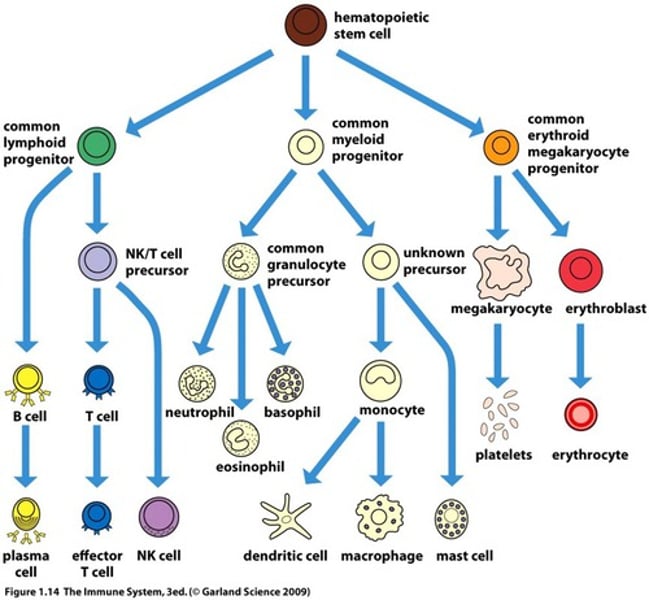
Gene Expression
Changes in gene expression result in differentiation - some genes are turned on and others off.
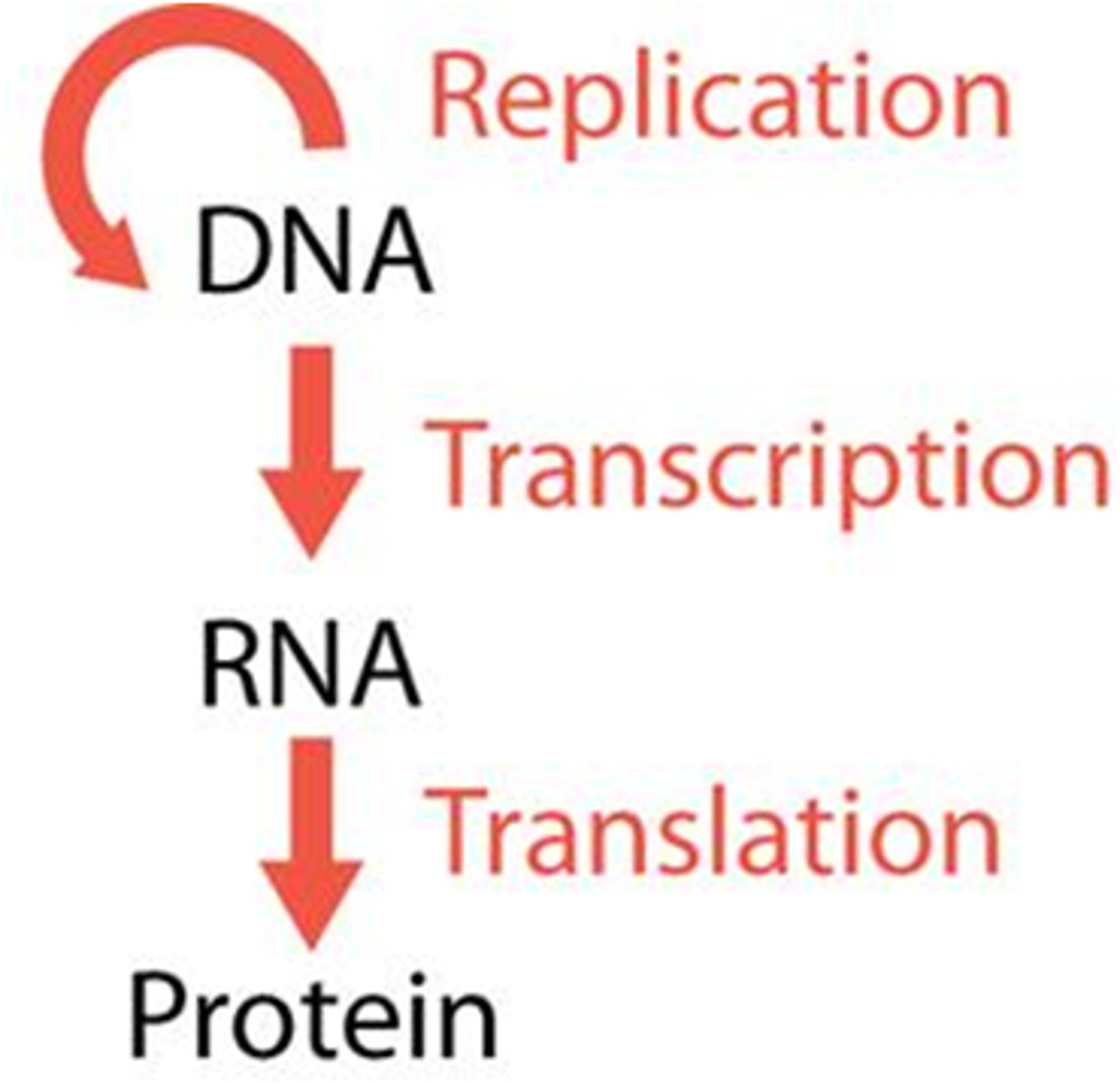
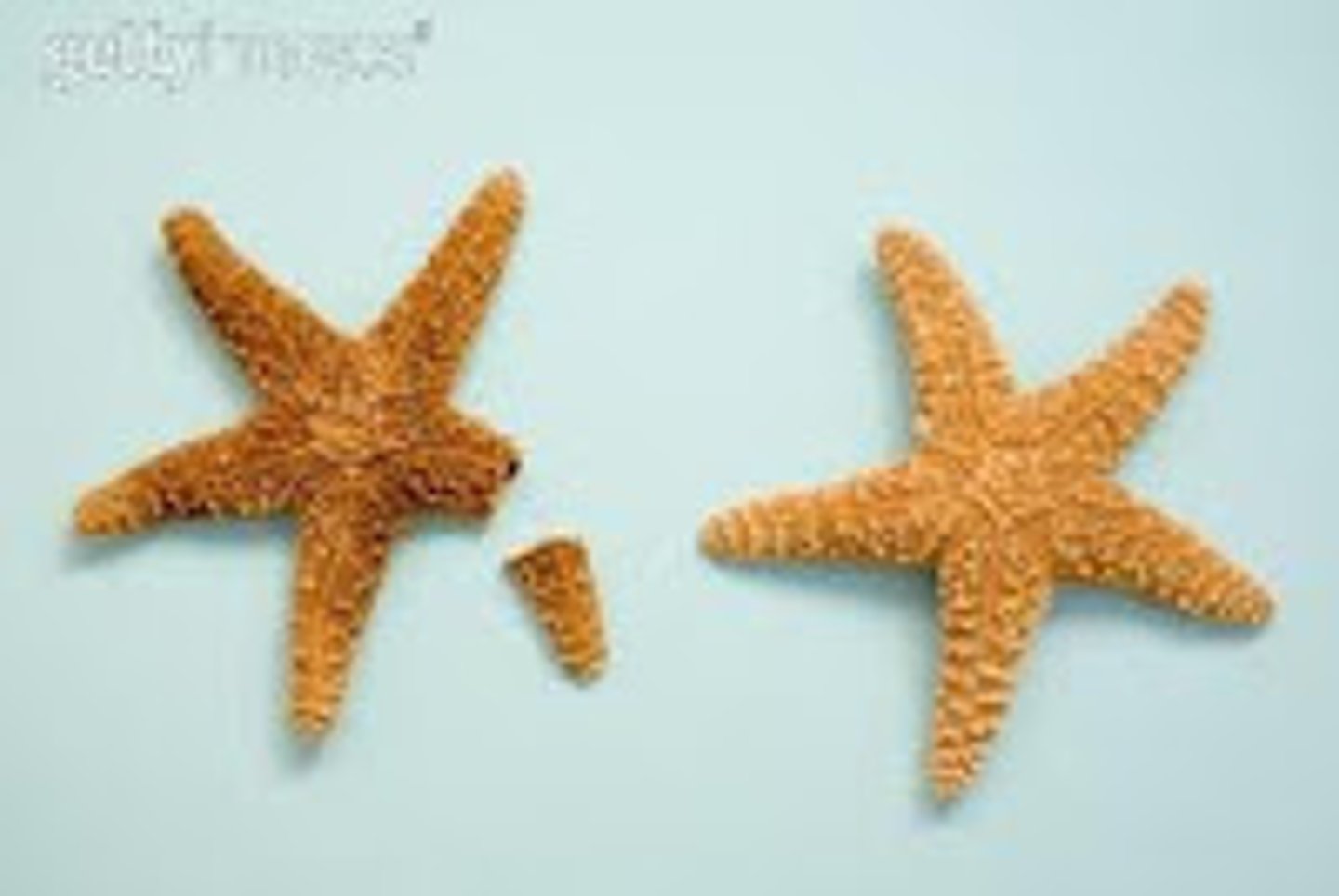
Regeneration
The process of replacing or restoring damaged or missing cells, tissues, organs, and even entire body parts - stem cells are responsible for this.

What is the plasma membrane?
A selectively permeable membrane which is made up by a phospholipid bi-layer which includes polar heads and non-polar fatty acid tails. It is able to regulate what goes in and out of the cell.
Six functions of membrane proteins...
Transport things in and out of cell
Enzymatic activities
Attachment to cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
Communication with other cells (identification)
Adhesion to other cells
Receptor proteins
Why is the plasma membrane described as a fluid mosaic model?
Has many parts that come together to make a whole and those parts constantly move.
What are glycoproteins? What is their function?
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins. Serve as "chemical ID" for the cell.
What are glycolipids? What is their function?
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to lipids. Serve as "chemical ID" for the cell.
What is cholesterol? What is its function?
Cholesterol is a steroid and is mostly hydrophobic. It makes sure the plasma membrane is not too fluid, but fluid enough. It also prevents crystallization and restricts cellular motion.
Function of channel/carrier proteins
Passive transport across the membrane
Function of protein pumps
Active transport across the membrane
Function of enzymes
Used in cell surface reactions
Function of Adhesion proteins
Binding cells together
Function of receptor proteins
Hormone binding and recognition
How do the hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties of the phospholipid bilayer allow the membrane to maintain its structure?
Since the cell membranes are phospholipid bilayers, a double layer of molecules exist as a stable boundary between two aqueous compartments because the molecular arrangement shelters the hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids from water while exposing the hydrophilic heads to water.
What does selectively permeable (in the context of the plasma membrane) mean?
Some substances can cross the membrane, while others can't.
What is diffusion?
The spreading out of particles in liquids and gases that happens because the particles are in continuous random motion.
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
Distinguish between solute, solvent, and solution.
solute-
solvent-
solution-
Simple diffusion
1. Does it go with the concentration gradient?
2. Does it use a selectively permeable membrane?
3. Does it use membrane proteins?
4. Does it need ATP?
1. Yes
2. No/Yes
3. Yes
4. No
Osmosis
1. Does it go with the concentration gradient?
2. Does it use a selectively permeable membrane?
3. Does it use membrane proteins?
4. Does it need ATP?
1. Yes
2. Yes
3. Yes
4. No
Facilitated Diffusion
1. Does it go with the concentration gradient?
2. Does it use a selectively permeable membrane?
3. Does it use membrane proteins?
4. Does it need ATP?
1. Yes
2. Yes
3. Yes
4. No
Active Transport
1. Does it go with or against the concentration gradient?
2. Does it use a selectively permeable membrane?
3. Does it use membrane proteins?
4. Does it need ATP?
1. Against
2. Yes
3. Yes
4. Yes
What are the four types of membrane transport?
Simple diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, active transport
What method of membrane transport is used by water?
Osmosis through aquaporins
What method of membrane transport is used by non-polar molecules?
diffusion
What method of membrane transport is used by polar molecules?
facilitated diffusion
What method of membrane transport is used by any molecule against the concentration gradient?
active transport
What method of membrane transport is used by macromolecules?
endocytosis or exotycosis
What is a vesicle?
Vesicles are tiny sacs made of membranes, which are used to transport items around the cell.
What is the process of vesicle transport of a protein molecule through a eukaryote cell? Begin with protein synthesis in the Rough ER and finish with exocytosis through the plasma membrane.
Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes on the Rough ER. The protein then gets transported to the golgi apparatus, where it will get further modified and packaged for secretion. When it gets packaged, phospholipids from the golgi membrane will pinch off to form a vesicle around the protein. The vesicle will move to the plasma membrane, fuse with it, and then the protein will get released from the cell.
Exocytosis vs. Endocytosis...
In endocytosis, the cell takes IN biological membranes and particulate matter by forming new vesicles from the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane temporarily shrinks in size.
In exocytosis, the cell SECRETES certain biological molecules by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane. Plasma membrane temporarily increases in size.
Compare and contrast facilitated diffusion and active transport.
Compare: Both types of transport use integral membranes to move molecules.
Contrast: Facilitated diffusion is a form of passive transport: no energy required because molecules are moving with their concentration gradient. Active transport requires energy because molecules are being moves against their concentration gradient.
Since carbs are big, the cell uses facilitated diffusion to help move them into the cell. What factors will increase the rate of carbohydrate uptake by the cell? Can the rate of carbohydrate uptake continually increase or will the rate eventually level out? Explain your reasoning.
The rate of carb uptake by the cell will be increased as the concentration of carbs on the outside of the cell increases. It adds to the concentration gradient and more carbs will be moved into the cell. However, the rate of uptake will NOT continually increase because there are only so many integral proteins that can facilitate the movement into the cell before they're all occupied. The rate will level out.
A property of the phospholipid bilayer that makes it both hydro phobic and philic
Amphipathic
Indirect Active Transport
When the movement of one molecule down its concentration gradient allows another molecule to be actively pumped against the concentration gradient. Eg: The sodium poassium pump.
During photosynthesis, where do the reactions that produce oxygen gas (O2) occur?
Photosystem II
During the light reactions, electrons within the pigments of the light-harvesting complex are moved to an excited state and then return to a ground state, releasing ___________. Eventually, chlorophyll A molecules in the reaction center get excited and lose _____________.
energy, electrons
During the reduction step of the Calvin cycle, an unstable six-carbon intermediate is formed and then split in half. What molecule is eventually formed that is used to make glucose?
G3P
The light reactions occur in the _____________ and the Calvin cycle occurs in the _____________.
thylakoid membrane, stroma
True or False: The electrons lost in photosystem I are replaced by the splitting of carbon dioxide and the electrons lost in photosystem II are replaced by the splitting of water.
False
What molecule attaches to RuBP in the Calvin cycle?
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
What process does the following equation describe?
Photosynthesis
Where does the process of photosynthesis occur within a leaf?
Mesophyll
Which of the following is produced during cyclic electron flow?
ATP
During the light reactions, ______ is produced in photosystem II and ______ is produced in photosystem I.
ATP and NADPH
calculation for magnification
measured length/scale bar label
calculation for actual size
measured length/magnification
three parts of cell theory
- the cell is the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms.
- all organisms are made up of one or more cells.
- cells arise from other cells through cell division.
resolution
the ability to clearly distinguish between two separate points in a field of vision (smallest interval distinguishable)
light vs. electron microscope
electron microscopy is able to produce images of a higher resolution.
compound light microscopes
use multiple lenses to bend light and magnify images
electron microscope
a microscope that focuses a beam of electrons (by electromagnets) to magnify objects
structures common to ALL cells
plasma membrane, cytoplasm, DNA, ribosomes
what types of cells are prokaryotes?
archaea (unicellular), bacteria
prokaryotic cell structures
cell (plasma) membrane, cytoplasm, 70s ribosomes, cell wall, pili, capsule, flagellum, DNA
cell (plasma) membrane
responsible for regulating what materials move in and out of the cell - SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE
cytoplasm
gel-like fluid substance (mostly water with many dissolved molecules), site of METABOLIC REACTIONS
ribosome
builds proteins during TRANSLATION
cell wall
ONLY FOUND IN PLANTS - provides shape and allows the cell to withstand turgor pressure without bursting
nucleoid
prokaryotic cell DNA is "naked", which means that the DNA is not associated with proteins
difference in RIBOSOMES in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
prokaryotes - smaller 70s ribosomes
eukaryotes - larger 80s ribosomes
plasmid
ONLY IN PROKARYOTES - small, circular pieces of DNA that can be transferred from one prokaryotic cell to another.