Module 2: Introduction to general microbiology: Bacterial structure & morphology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
length: 2 um - 8 um
diameter: 0.2 - 2.0 um
size of bacteria
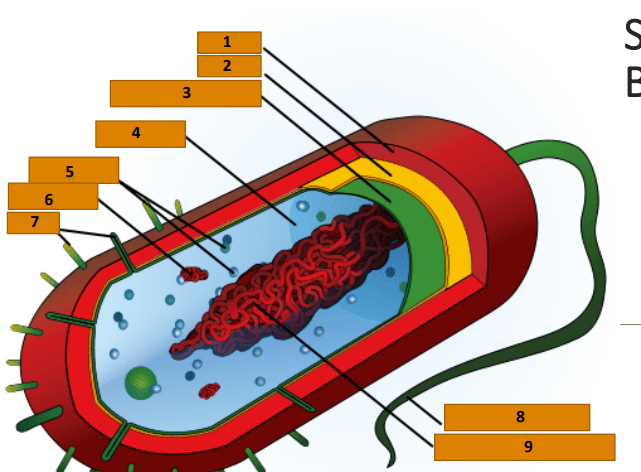
Capsule
1
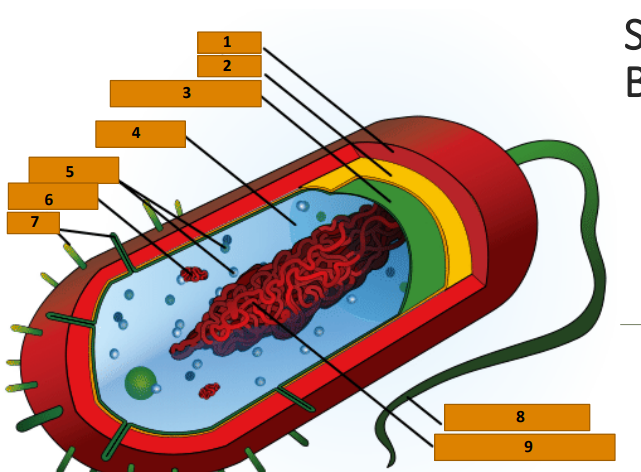
Cell wall
2
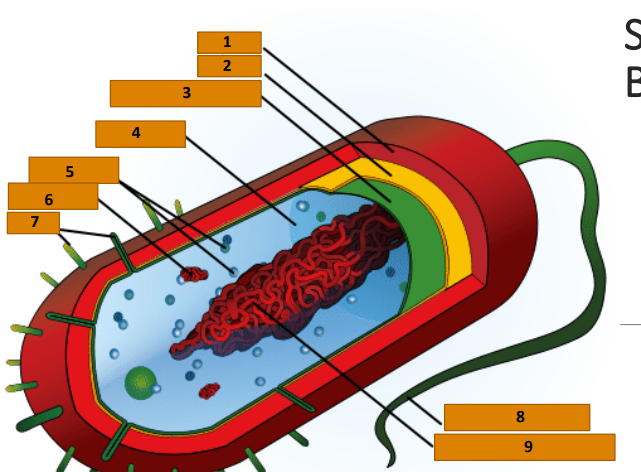
Plasma membrane
3
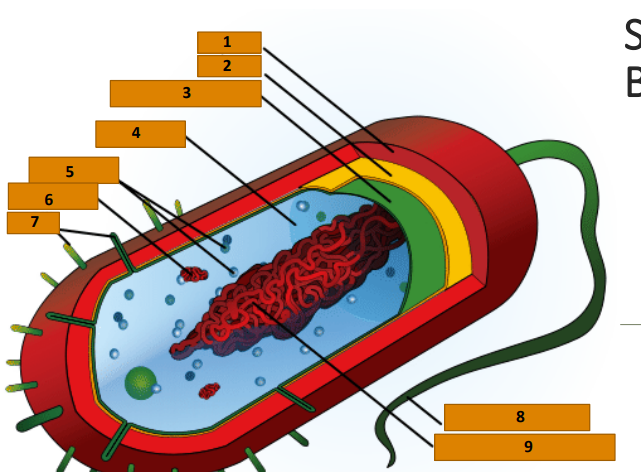
Cytoplasm
4
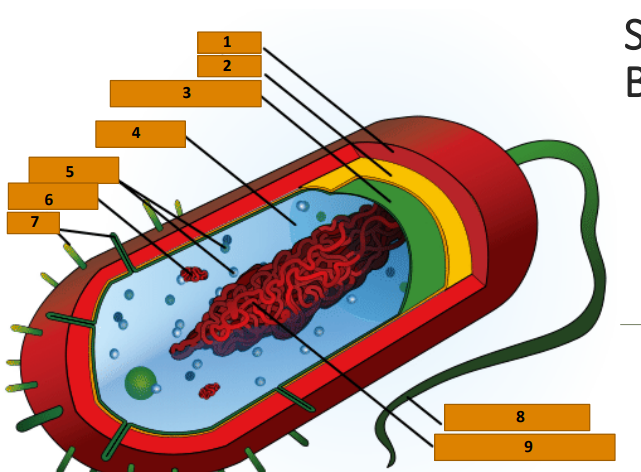
Ribosomes
5
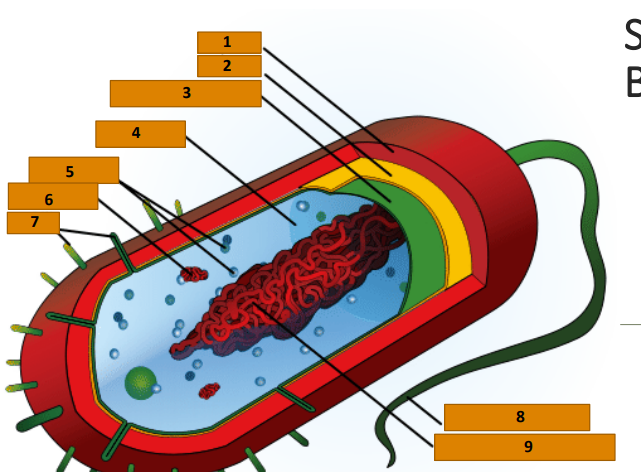
Plasmid
6
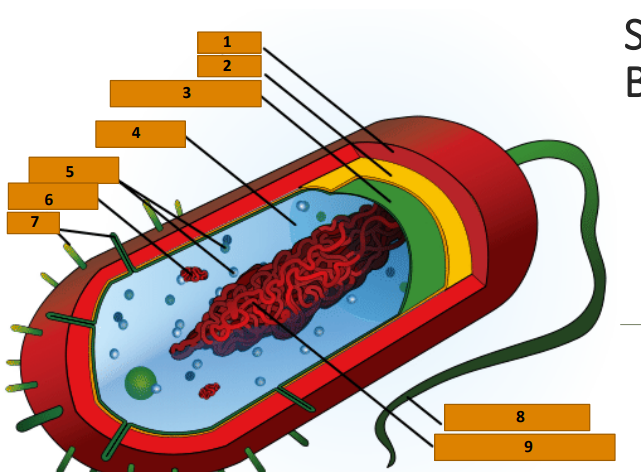
Pili
7
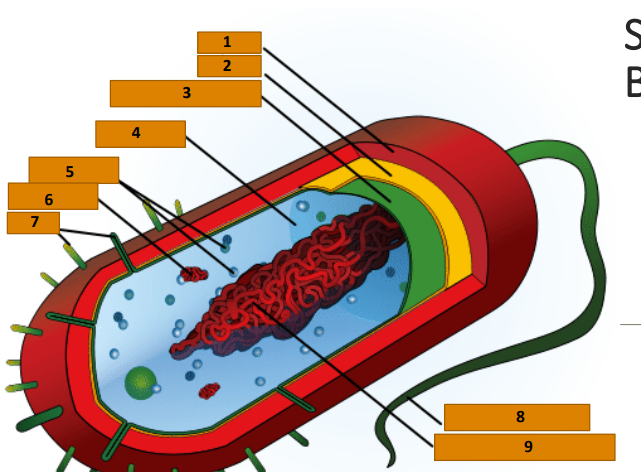
Bacterial Flagellum
8
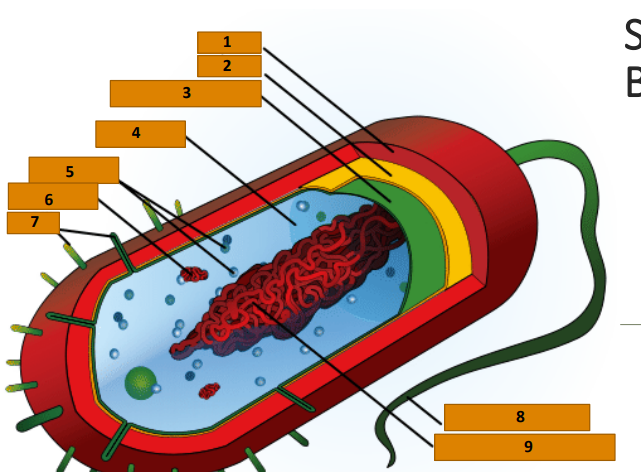
Nucleoid (circular DNA)
9
glycocalyx
General term used for substances that surround the cells
A coating that covers the outside of prokaryotic cells that provides a protective coat
It is viscous (sticky), gelatinous polymer external to the cell wall, composed of polysaccharide , polypeptide or both
Important component of Biofilms
Function:
Extracellular polymeric substance (EPS)
a glycocalyx that helps cells in a biofilm attach to their target environment and to each other
Protects cells within it and facilitates communication
Enables the cell to survive by attaching to various surfaces in natural environment
slime layer
if the substance is unorganized and only loosely attached to the cell wall, the glycocalyx
capsule
if the substance is organized and firmly attached to the cell wall
It is important in contributing to bacterial virulence.
often protect pathogenic bacteria from phagocytosis by the cells of the host
E.g. Bacillus anthracis - capsule of D-glutamic acid
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Klebsiella
cell wall
Prevent the bacterial cells from rupturing
Helps maintain the shape of the cell
Point of anchorage for flagella
Contributes to the ability of some species to cause disease
Site of action of some antibiotics (e.g. penicillin)
Chemical composition is used to differentiate major types of bacteria (Gram-positive, Gram-negative)
Composed of peptidoglycan (murein)
plasma membrane
Thin structure lying inside the cell wall and enclosing the cytoplasm of cell
Consists primary of phospholipids
Look like two-layered structures (lipid bilayer)
Serve as a selective barrier through which materials enter and exit the cell (selective permeability)
Breakdown of nutrients and the production of energy
flagella
long filamentous appendages that propel bacteria
Some bacteria have the capability to move in various patterns
atrichous
bacteria that lacks flagella
peritrichous
monotrichous and polar
lophotrichous and polar
amphitrichous and polar
arrangement of bacterial flagella
peritrichous
flagella are distributed over the entire cell
0.5 μm
monotrichous and polar
a flagellum at one pole
0.8 μm
Lophotrichous and polar
many flagella coming from one pole
turf of flagella
1.5 μm
Amphitrichous and polar
flagella at both poles of the cell
4 μm
amphi = 2
H antigen
flagellar protein; useful for distinguishing among serovars or variations
Example: there are at least 50 different ◦H antigens for E. coli. Those serovars identified as E. coli O157:H7 are associated with foodborne epidemics
spirochetes
group of bacteria that have unique structure and motility (spiral motion)
They move by means of axial filaments or endoflagella
E.g. Treponema pallidum – causative agent of syphilis
Borrelia burgdorferi – causative agent of Lyme disease
fimbriae and pili
Hair-like appendages that are shorter, straighter, and thinner than flagella
fimbriae
the bacterial cell or can be evenly distributed over the entire surface of the cell
pili
usually longer than fimbriae and number only one or two per cell
involved in motility and DNA transfer
Some are used to bring bacteria together, allowing the transfer of DNA from one cell to another (conjugation)
sex pilus
Pili that will transfer the DNA from one bacterium to another (conjugation)
cytoplasm
Refers to the substance of the cell inside the plasma membrane
nucleoid (containing DNA)
ribosomes
inclusions
plasmid
major structures in cytoplasm
nucleoid
Contains the bacterial chromosome
This is the cell’s genetic information
Bacterial chromosomes are not surrounded by a nuclear envelope and no histones
plasmid
Small, usually circular, double stranded DNA molecules
These are extrachromosomal genetic elements (not connected to main bacterial chromosome)
Replicate independently
ribosomes
Where protein synthesis takes place
Prokaryotic ribosomes are called 70S ribosomes (80S ribosomes in eukaryotes)
S = Svedberg unit = unit of size
Subdivided into 2 subunits that is targeted by some antibiotics:
30S
50S
inclusions
Several kinds of reserve deposits in the cytoplasm
endopores
Specialized “resting” cells formed by some gram-positive bacteria (genera Clostridium and Bacillus) when essential nutrients are depleted
Highly durable dehydrated cells with thick walls and additional layers
can survive extreme heat, lack of water, and exposure to many toxic chemicals and radiation
Cannot multiply
Can remain dormant for thousand of years
Not a means of reproduction (one vegetative cell forms a single endospore)
Importance in food industry because of resistance to processes that normally kill vegetative cells
Most vegetative cells can be killed with temp above 70 C
Endospores can survive in boiling water for several hours or more (thermophilic/heat-loving)
vegetative cells
State of bacteria wherein they can multiply through binary fission
sporulation / sporogenesis
From vegetative state to endospores
germination
endospores to vegetative cells
dipicolinic acid
a large amount of an organic acid contained in endospore; protects the endospore DNA against damage
a. cocci or spherical bacteria
diplococci
streptococci
staphylococci
sarcinae
tetrads
b. bacilli or rod-shape bacteria; may be cigar-like or straw=like
diplobacilli
streptobacilli
coccobacilli
bacilli with rounded ends
bacilli with square ends
filamentous bacilli
c. helical / spiral (one to two twist)
vibroid / comma-shape
spirilla
sprirochetes
other shape
genus stella
halophilic archaea
triangular shapes
shapes of bacteria
diplococci
round bacteria in pairs; remain in pairs after dividing
streptococci
cocci in chains
staphylococci
cocci in cluster resembling bunch of grapes
sarcinae
in groups of 8 in cubical pockets (octads)
tetrads
divide in 2 planes and remain in groups of 4
diplobacilli
in paired bacilli
streptobacilli
rods in chain
coccobacilli
short rods
filamentous bacili
usually do not separate and tend to form “long threads”
vibroid / comma-shape
(less than one complete twist); curved rods
spirilla
– loosely curved cells; have helical shape like a cork-screw and fairly rigid bodies with flagella
spirochetes
– tightly coiled form; flexible with axial filaments
genus stella
star-shaped
halophilic archaea
flat rectangular shape