Plant structures
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the order of organisation in a plant cell
Cells→tissues→organs→organ systems→organisms
What are the main plant organs involved in transport
Roots, leaves, stems
Give an example of a plant organ
Leaf
What do leaves need for photosynthesis
Light energy, carbon dioxide and water
Where does water come from in plants
soil
What tissue transports water
Xylem
Direction of xylem transport
Roots→stem→leaves
How does carbon dioxide enter the leaf
Diffusion through the stomata
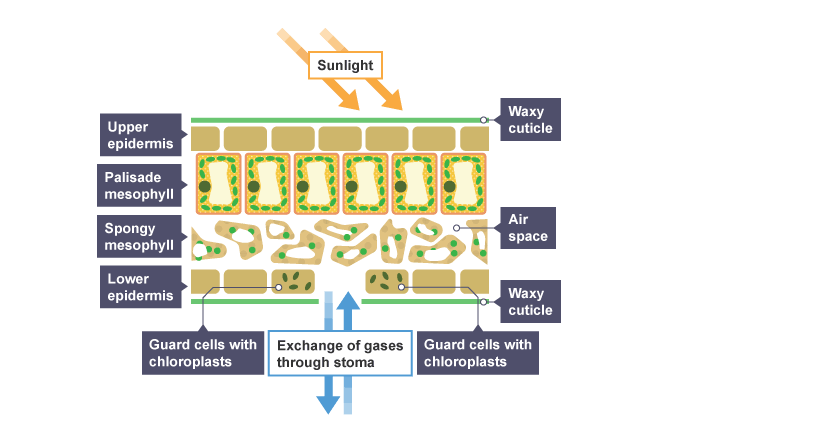
Where are most stomata found
Lower epidermis
Why are there many stomata
To allow gas exchange for photosynthesis
What is the function of the spongy mesophyll
Contains air spaces to help gasses diffuses
What is the function of the palisade mesophyll
Main site of photosynthesis, packed with chloroplasts
Why is the upper epidermis transparent
To allow light to reach palisade cells
What does the phloem transport
Sugars (product of photosynthesis)
Direction of Phloem transport?
Leaves→ rest of the plant
What is the main problem leaves face
Water loss due to evaporation
What is the waxy cuticle
Waterproof lipid layer that reduces water loss
What is a stoma
Gap between two guard cells
Why are stomata important
allows gas exchange
What happens when guard cells are turgid
Stomata opens→more Carbon dioxide enters
What happens when guard cells are flaccid
Stomata closes→less water loss
Why do guard cells become flaccid
Loss of water via osmosis
What happens to stomata at night
They close
Why are most stomata located on the underside of the leaf
Cooler and shader→less evaporation
Where is meristem tissue found
Tips of roots and shoots
What is the function of meristem tissue
Divide and differentiate to allow the plant to grow
Picture of the leaf diagram