Bladder, Urethral, and Penile Disorder - MedPath
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What does this refer to
Storage and voiding phases
Detrusor muscle and sphincter coordination
Normal Bladder Function
What does this refer to
Chronic syndrome of detrusor overactivity
Symptom syndrome of urgency, with or without urge incontinence; usually associated with urgency, frequency and nocturia
Urodynamic evaluation: To confirm diagnosis
Detrusor overactivity on urodynamics
Overactive bladder syndrome (OAB)
What does this refer to
Lifestyle modifications
Behavioral therapy, neuromodulation
Pharmacotherapy (antimuscarinic agents); botulinum toxin therapy; surgery
Treatment for Overactive Bladder Syndrome
What does this refer to
Weak detrusor contraction or outlet obstruction
Bladder contraction of reduced strength and/or duration
Prolonged bladder emptying or incomplete bladder emptying, or both
Caused by spinal cord injury, stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson disease, diabetic neuropathy, aging
Symptoms of weak stream, intermittency, hesitancy, straining
Treatment includes sacral neuromodulation, drugs.
Underactive bladder syndrome (UAB)
What does this refer to
Bladder dysfunction caused by neurologic disorders (CNS or PNS); problems with urine storage or voiding
Affects detrusor contractility and sphincter tone
Upper motor neurons
Dyssynergia: Overactive or hyperreflexive bladder function
Detrusor hyperreflexia: Uninhibited or reflex bladder
Detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia
Detrusor hyperreflexia with vesicosphincter (detrusor sphincter) dyssynergia: Both the bladder and the sphincter are contracting at the same time, causing a functional obstruction of the bladder outlet
Spastic bladder, small capacity, frequent voids
Neurogenic bladder
What does this refer to
Lower motor neurons
Detrusor areflexia: Underactive, hypotonic, or atonic bladder
Flaccid detrusor
Large capacity, urinary retention, overflow incontinence
Neurogenic Bladder
What does this refer to
Frequent daytime voiding: More often than every 2 hours while awake
Nocturia: Night-time voiding
Urgency: Often combined with hesitancy
Dysuria
Poor force of stream; intermittency of urinary stream
Feelings of incomplete bladder emptying, despite micturition
Clinical manifestations of Neurogenic Bladder
What does this refer to
Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia
α-adrenergic blocking (antimuscarinic) medications or botulinum toxin
Intermittent catheterization in combination with higher dose antimuscarinic drugs
Condom catheter containment, supplemented by an α-adrenergic blocking drug or transurethral sphincterotomy (surgical incision of the striated sphincter)
Obstruction
Medication
Bladder neck incision
Low bladder wall compliance
Antimuscarinic drugs and intermittent catheterization
Severe cases: Augmentation enterocystoplasty (enlargement of bladder wall using a detubularized piece of small bowel), urinary diversion, or long-term indwelling catheterization
Treatment of Neurogenic Bladder
What does this refer to
Acute or chronic
Causes: obstruction, meds, neurogenic
Urinary retention
What does this refer to
Stress, urge, overflow, functional
Mixed patterns common
Urinary Incontinence Types
What does this refer to
Pessary: Rubber or silicone device designed to compensate for vaginal wall prolapse
Intravaginal hormone replacement therapy and regular follow-up
Surgery
Pelvic organ prolapse
What does this refer to
Prostatic enlargement, strictures
Impaired flow, incomplete emptying
Bladder Outlet Obstruction
What does this refer to
Chronic pain syndrome
Bladder hypersensitivity, urgency
Exact etiology unknown, probably multifactorial including inflammation, hypersensitivity, pelvic floor tension
Symptoms of cystitis for longer than 6 weeks’ duration, but with negative urine cultures and no other known cause
Treatment
Oral and intravesical therapies, sacral nerve stimulation, onabotulinumtoxinA; surgery
Painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis
What does this refer to
Inflammation of the bladder
Acute or chronic
Clinical manifestations
Asymptomatic
Frequency, dysuria, urgency, and low back and/or suprapubic pain
Evaluation
Urine culture of specific microorganisms with counts of 10,000/mL or more
Treatment
Antimicrobial therapy
Cystitis
What does this refer to
Most common pathogens
Escherichia coli
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Virulence of uropathogens
Ability to evade or overwhelm the host defense mechanisms and cause disease in a host
Adherence to the uroepithelium
Have pili or fimbriae or both
Ability to resist the host’s defense mechanisms
Biofilms
Urinary Tract Infection
What does this refer to
Sulfamethoxazole/Trimethoprim (Bactrim) DS po BID
Nitrofurantoin (Macrobid) 100mg po BID
Fosfomycin (Monurol) 3 gram as a single dose
First line for UTI
What does this refer to
Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) 250mg po BID
Levofloxacin (Levaquin) 250mg po daily
Second line Fluoroquinolones for UTI
What does this refer to
Amoxicillin/Clavulanate (Augmentin) 500/125mg po BID
Cefdinir (Omnicef) 300mg po BID
Second Line– Beta-lactams for UTI
What does this refer to
Form in setting of urinary stasis
May cause hematuria, infection
Bladder Stones
What does this refer to
Urothelial (transitional cell) carcinoma: Most common
Risk factors
Smoking
Aromatic amines, e.g. aniline dyes
Arsenic in drinking water
Phenacetin
Cyclophosphamide
Pioglitazone
Oncogenes of the ras gene family and tumor-suppressor genes including TP53 mutations
Inactivation of retinoblastoma gene (pRb)
Loss of heterozygosity at Chromosome 9
Bladder tumors
What does this refer to
Painless microscopic hematuria
Papillary vs. flat lesions
Clinical manifestations of bladder tumors
What does this refer to
Transurethral resection or laser ablation, combined with intravesical chemotherapy or immunotherapy
Radical cystectomy with urinary diversion
Adjuvant chemotherapy
Radiation therapy
Cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy
Treatment of bladder tumors
What does this refer to
Male vs. female length and segments
Important for infection/spread
Urethral Anatomy
What does this refer to
Inflammation of the urethra usually but not always caused by a STD
Nonsexual origins can be due to urologic procedures, anatomic abnormalities, or trauma
Pain, discharge, dysuria
Urethritis Pathophysiology
What does this refer to
GC: abrupt, purulent
NGU: chlamydia, mycoplasma
Gonococcal vs. Nongonococcal Urethritis
What does this refer to
Fibrotic narrowing of urethra caused by scarring
Commonly due to
Trauma
Untreated or severe urethral infections
Urinary catheters
Urethral strictures
What does this refer to
Collagen deposition, fibrosis
Reduced urinary flow, retention
Stricture Pathophysiology
What does this refer to
Rare, often squamous
Risk: chronic inflammation, STIs
Urethral Carcinoma
What does this refer to
Female dysuria-frequency syndrome
No proven infection, linked to irritation
Urethral Syndrome
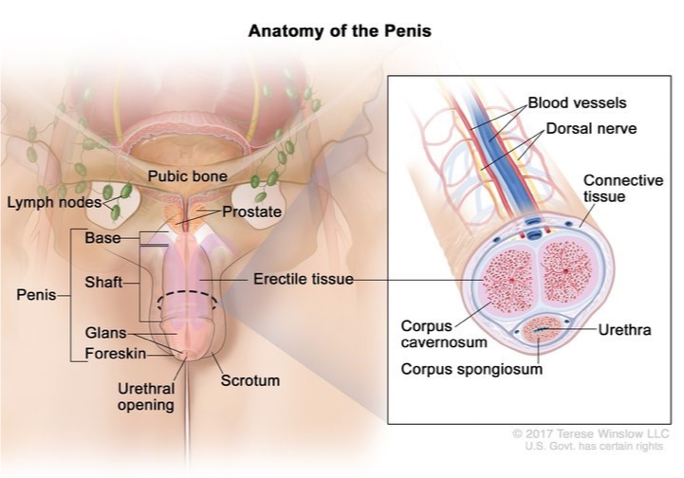
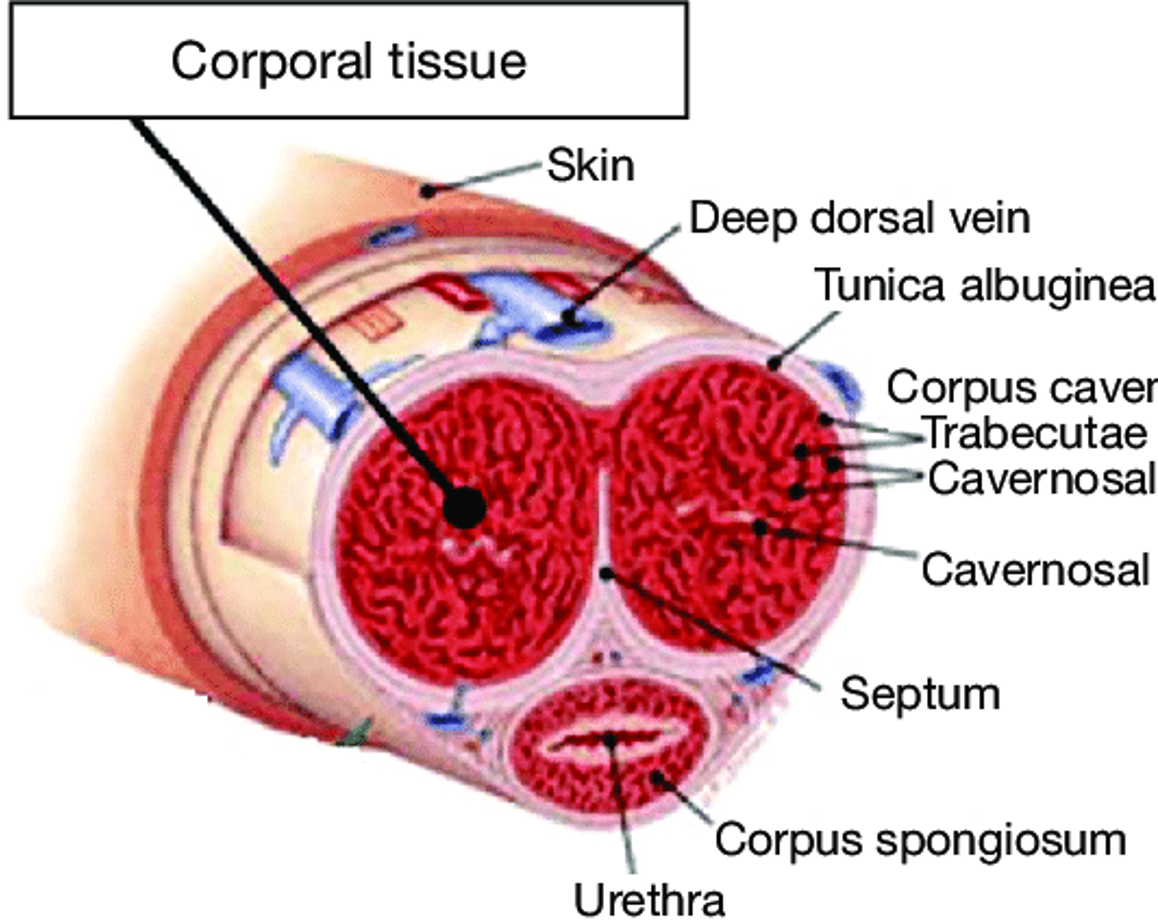
What does this refer to
Corpora cavernosa, corpus spongiosum
Tunica albuginea, glans, urethra
Penile Anatomy Overview
What does this refer to
Penile foreskin (prepuce) is “too tight”
Phimosis
Inability to retract foreskin from the glans of the penis (distal to proximal)
Paraphimosis
Inability to replace or cover the glans with the foreskin (proximal to distal)
Frequently caused by poor hygiene or chronic infections
Disorders of the penis
What does this refer to

Balanitis
What does this refer to
Prolonged erection (>4h)
Ischemic vs. non-ischemic types
Priapism Pathophysiology
What does this refer to
Low flow, painful, emergency
Risk: sickle cell, medications
Ischemic Priapism
What does this refer to
High flow, less painful
Often post-trauma
Non-Ischemic Priapism
What does this refer to
Tearing of tunica during trauma
Audible pop, swelling, detumescence
Penile Fracture
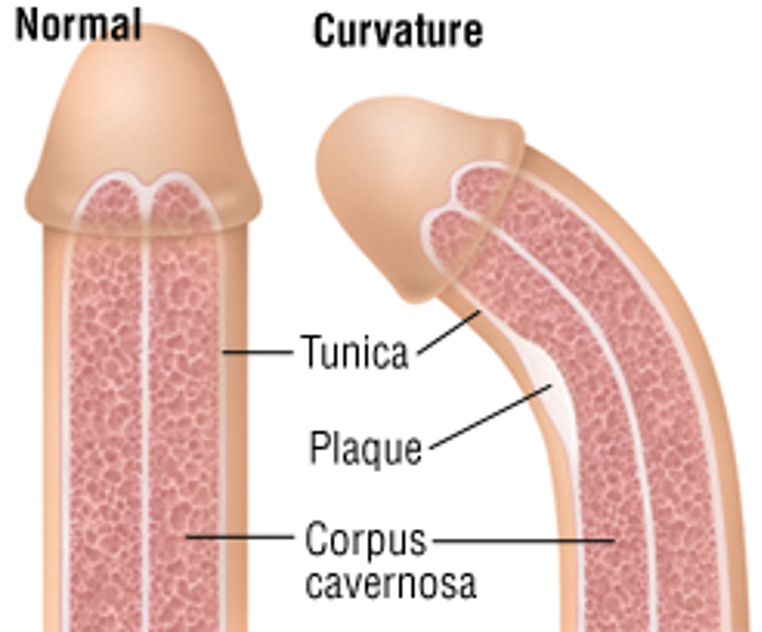
What does this refer to
Slow development of fibrous plaques (thickening) in the tunica albuginea, causing lateral curvature of penis during erection
Occurs in middle-aged men and causes painful erections and intercourse
Peyronie disease
What does this refer to
STI-related (HSV, syphilis) vs. non-infectious
Evaluate based on pain and appearance
Penile Ulcers
What does this refer to
Carcinoma of the penis is rare
Mostly squamous cell carcinomas
HPV, smoking
Often diagnosed in men older than age 55
Penile cancer (Malignancy)
What does this refer to
HPV 16/18, chronic inflammation
Commonly begins as lesion on glans
Penile Cancer Pathophysiology
What does this refer to
Neurogenic, vascular, psychogenic causes
May signal cardiovascular disease
Penile Disorders: Erectile Dysfunction Overview
What does this refer to
Nitric oxide-cGMP pathway impaired
Vascular insufficiency, nerve damage
Penile Disorders: Erectile Dysfunction Pathophysiology