Causes & consequences of urban trends in the UK
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is suburbanisation?
The outward spread of urban areas to suburbs & rural areas
What are the causes of suburbanisation?
- Growing populations create a demand for more housing, meaning that cities must expand
- Public transport & private car ownership allows people to live outside cities while still remaining connected to central urban areas
- Land outside of cities is ideal to build on as it is cheaper & has more space for larger houses & gardens, making it a more attractive place for people to live
What are the social consequences of suburbanisation?
- Houses outside of cities become a popular place to live as they as often bigger & cheaper
- If too many people start moving out of cities, the area as well as the houses could become derelict & vulnerable to vandalism
What are the economic consequences of suburbanisation?
- The development of services such as shopping centres in suburban areas creates job opportunities for locals
- If cities look empty & derelict, it could prevent future inward investment
What are the environmental consequences of suburbanisation?
- More parks & recreational spaces are built outside of cities
- Expands the congestion & pollution from cities into suburban & rural areas
What is counter-urbanisation?
The movement of people from urban areas into rural areas
What are the causes of counter-urbanisation?
- Many people want to escape the congestion, pollution & higher cost of living often found in cities
- Rural areas are quieter, greener & safer, making it an attractive place to live, especially for families raising children
- Public transport allows easy commuting so people can live in rural areas while still being connected to urban areas
- Working in rural areas is now more manageable due to more office buildings locating in outside of cities & high-speed broadband allowing people to work from home
What are the social consequences of counter-urbanisation?
- Cities can become abandoned & derelict if too many people start living in rural areas
What are the economic consequences of counter-urbanisation?
- Rural economy benefits due to more people using rural services
- House prices in rural areas increase as they become more in demand
What are the environmental consequences of counter-urbanisation?
- With more people attracted to living outside of cities, rural areas can become less rural & more congested
What is re-urbanisation?
The movement of people back into an area that has been previously abandoned
What are the causes of re-urbanisation?
- Government incentives
- Cities have a wider variety of shops, services & entertainment
- Urban areas are well connected & have good public transport
- There is often a wide range of job opportunities available in cities
What are the social consequences of re-urbanisation?
- Increasing population in cities means that the businesses & services in the area can benefit, grow & improve
- Redeveloped cities attract more visitors & tourists
What are the economic consequences of re-urbanisation?
- As the area starts to regrow, the local economy will benefit as more taxes are being paid
What are the environmental consequences of re-urbanisation?
- Increases congestion & pollution in that area
- Previous parks & green spaces could be replaced with office buildings & housing to accommodate for the people moving in
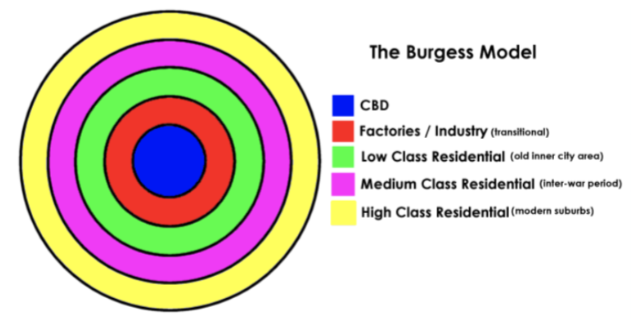
What is the Burgess model?
A land use model that divides urban areas into 5 zones:
- Central business district (CBD)
- Manufacturing zone
- Lower class residential zone
- Middle class residential zone
- Upper class residential zone
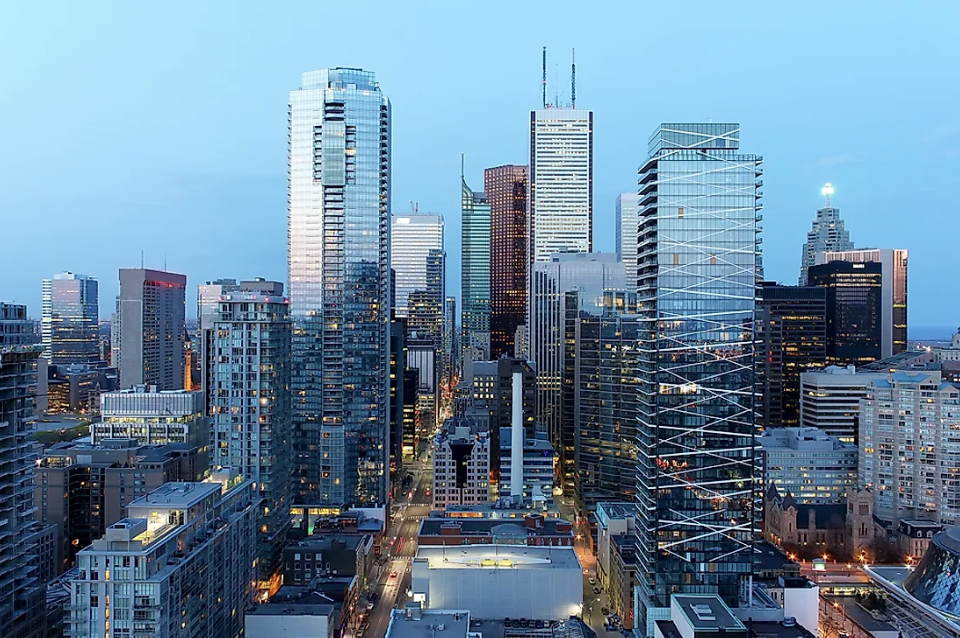
What are the key features & characteristics of the central business district?
- City centre
- Office buildings
- Busy
- Skyscrapers

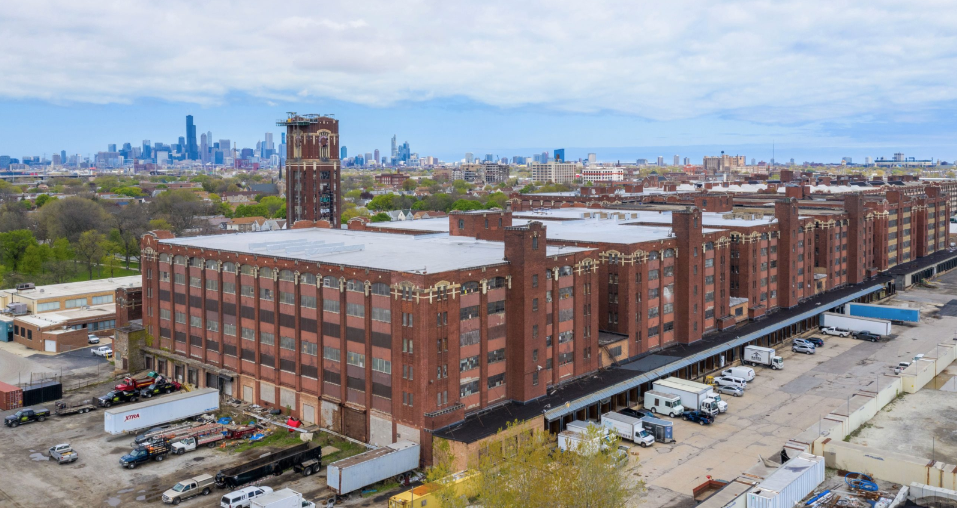
What are the key features & characteristics of the manufacturing zone?
- Factories
- Industrial housing

What are the key features & characteristics of the lower class residential zone?
- Small housing
- Terrace houses
- Attached
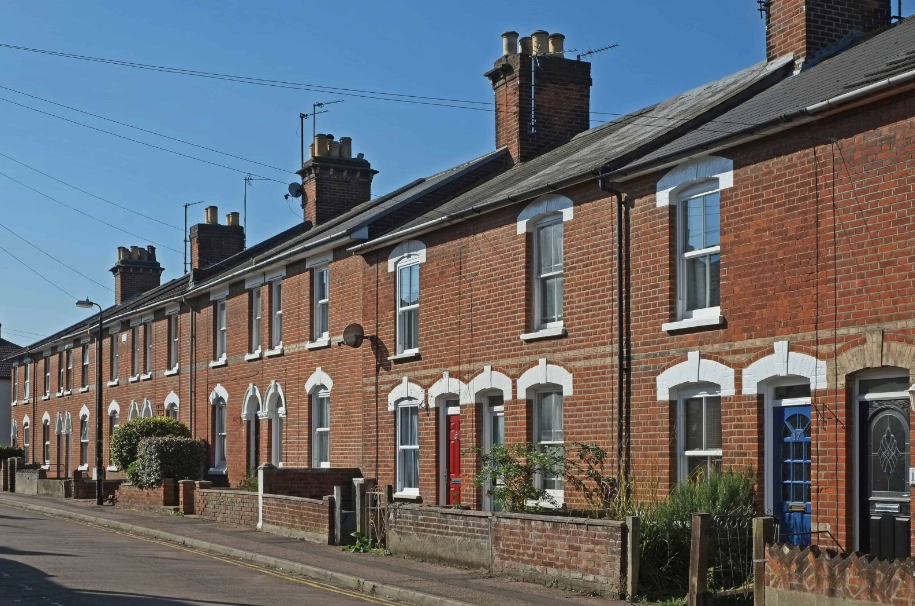

What are the key features & characteristics of the middle class residential zone?
- Bigger housing
- Semi-detached
- Gardens
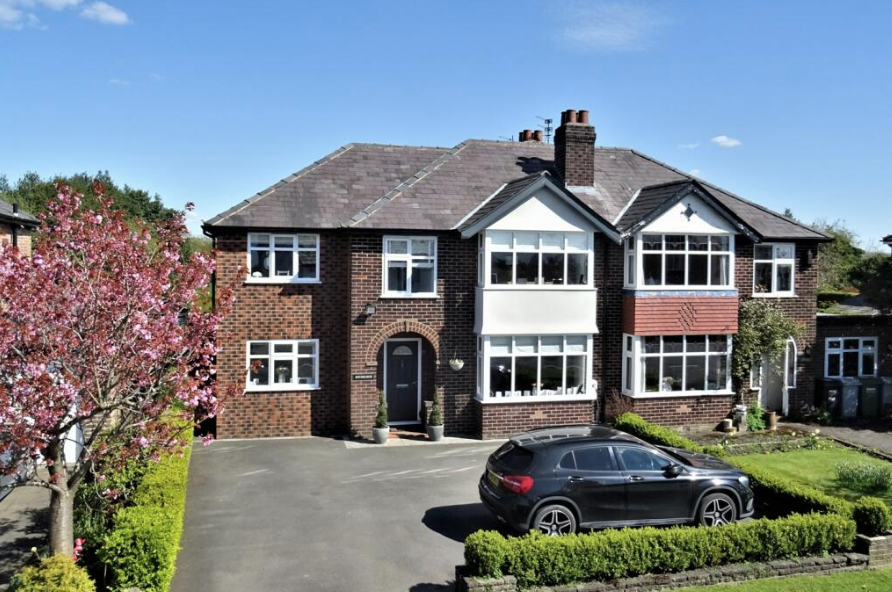

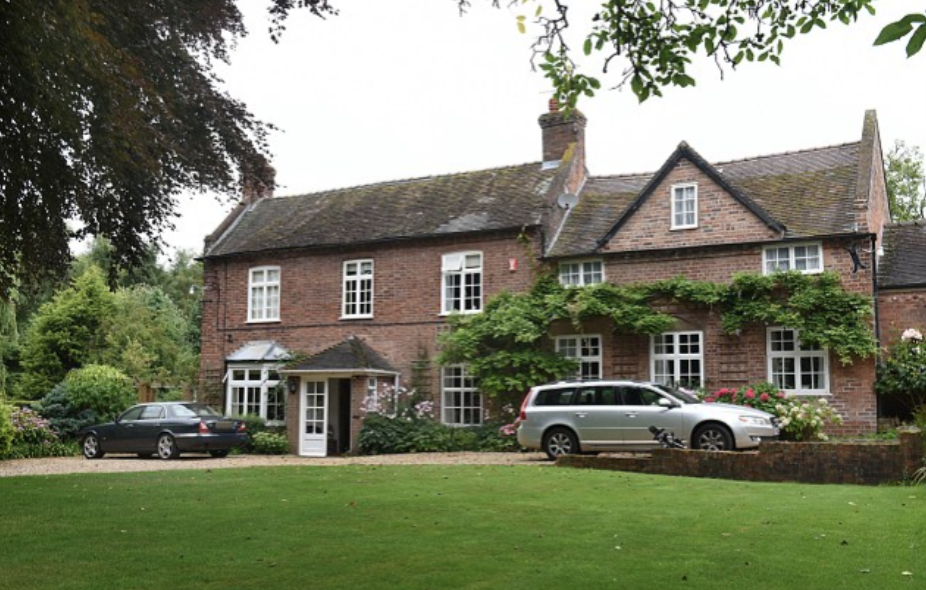
What are the key features & characteristics of the upper class residential zone?
- Large housing
- Big gardens
- Detached
