Biochemistry Unit Exam
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
metabolism
is a reaction of all enzyme-catalysed reaction in a cell
anabolic reaction
is the make up of simpler molecules to complex molecules that undergo condensation reactions
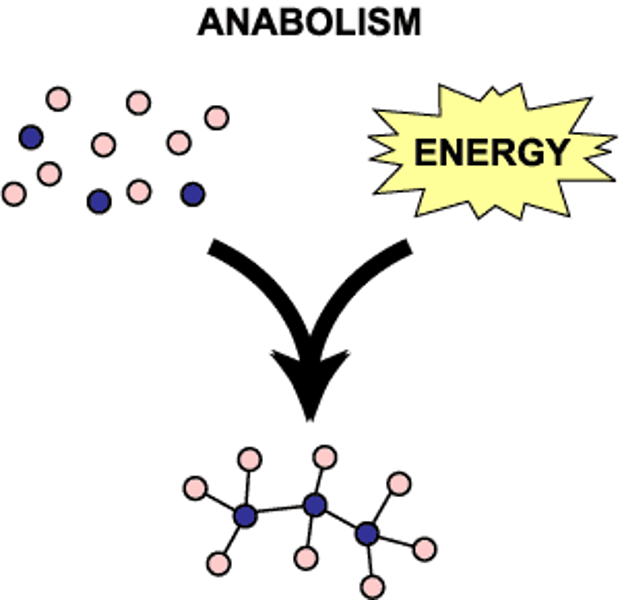
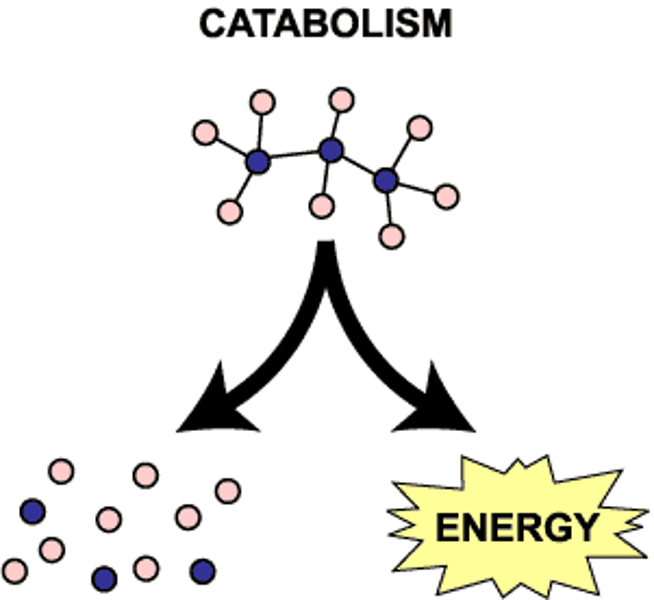
canabolic reaction
is the breakdown of complex molecules to simpler molecules that undergo hydrolysis
condensation reaction
a chemical reaction in which two or more molecules combine to produce water and form a larger molecule
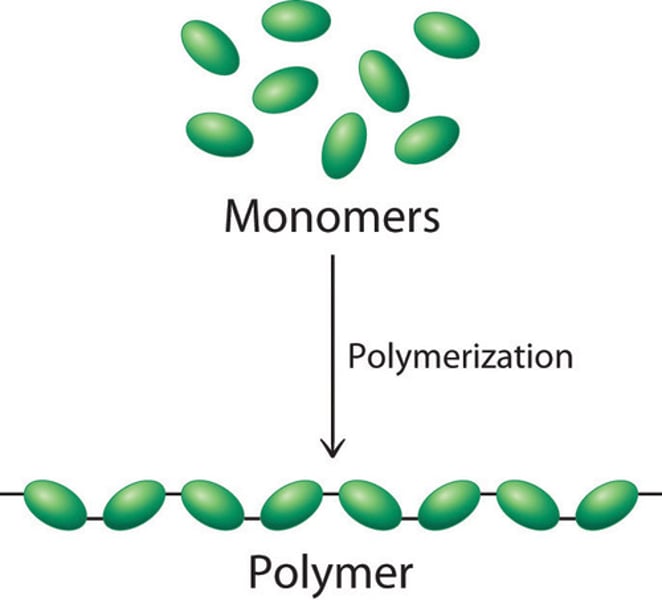
polymer
A long molecule consisting of many monomers
polypeptide
a link of multiple amino acids that occur because of a condensation reaction; this is called a peptide bond
3 monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
- they are made up of a 1:2:1 ratio
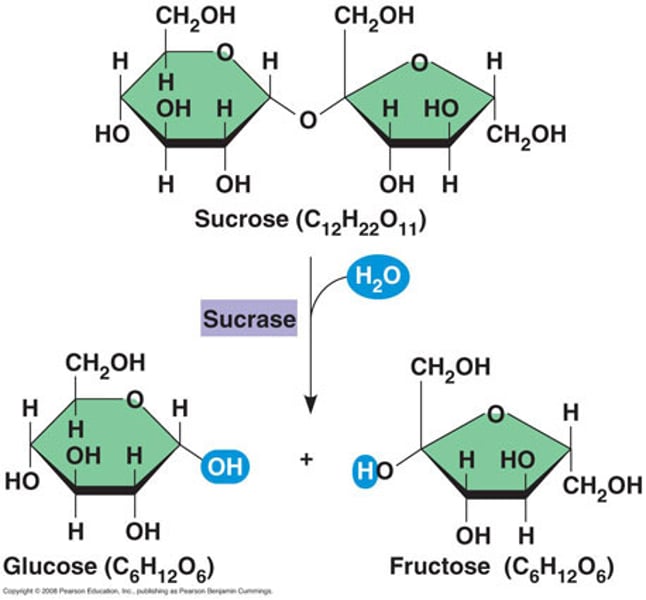
3 disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
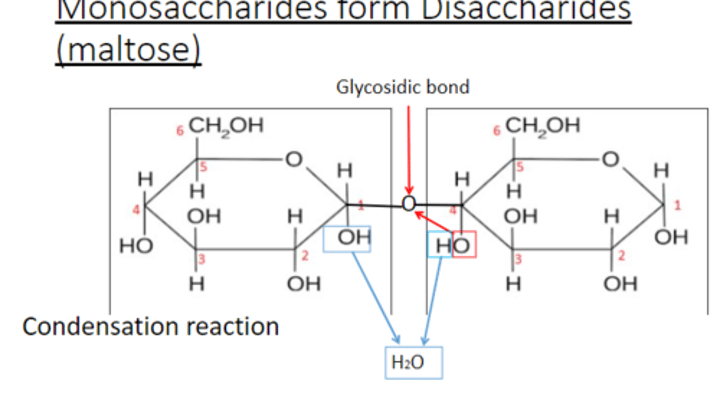
how disaccharides form
from two monosaccharides that undergo a condensation reaction and form a glycosidic linkage
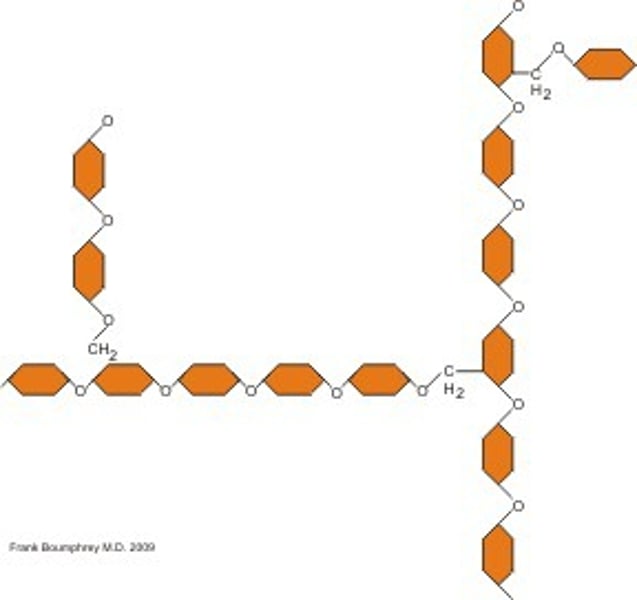
how glycerides form
fatty acids are linked to a glycerol by condensation reactions to produce lipids
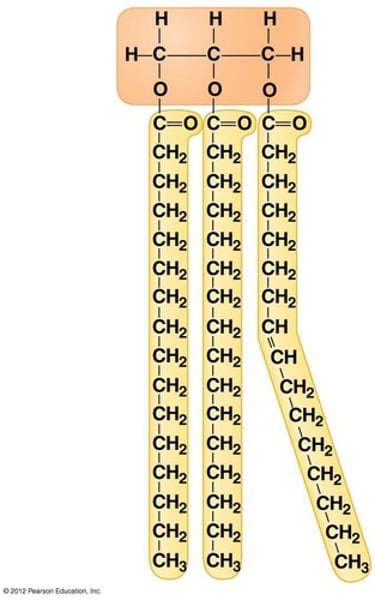
Triglycerides
3 fatty acids attached to glycerol & H2O
hydrolysis
- a reaction of a large molecule broken down into a smaller molecule; water is used up; lysis=splitting
- catabolic reactions are hydrolysis reactions
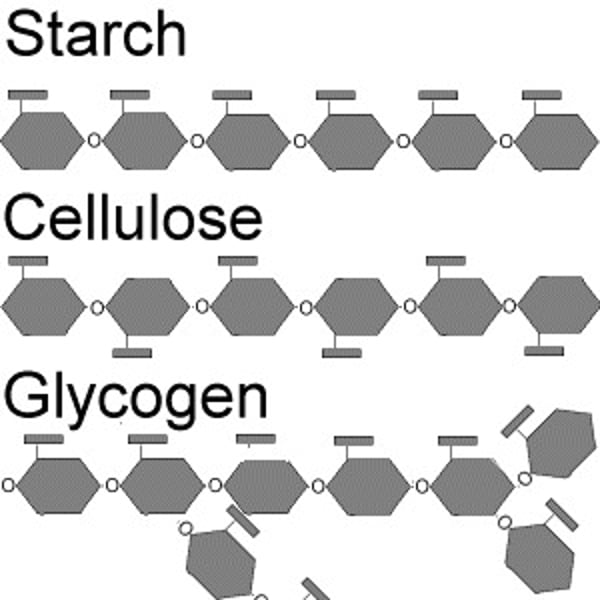
3 types of polysaccharides
cellulose, glycogen, and starch
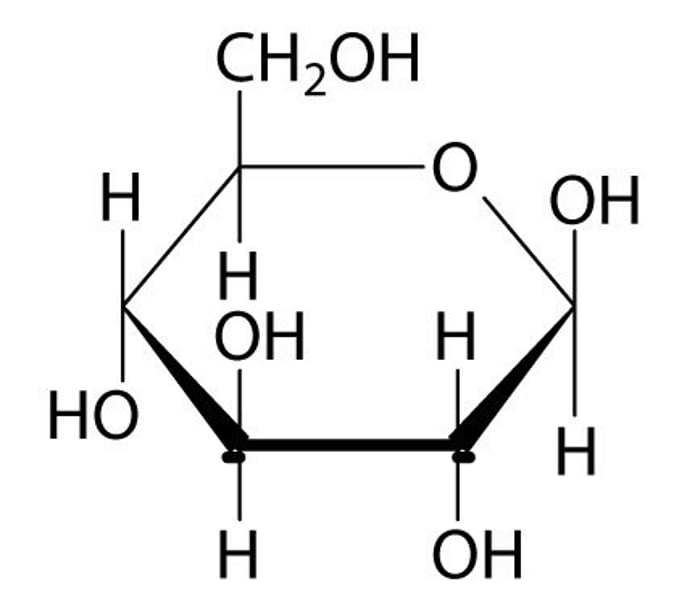
glucose molecule
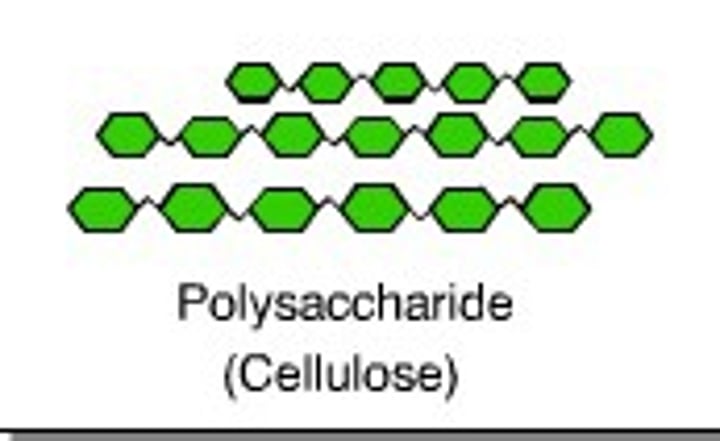
cellulose
linear beta glucose polymer consisting of glucose monomers that reinforces plant-cell walls
starch (amylose & amylopectin)
is an alpha polymer with a branched helical shape; is used by plants to store glucose
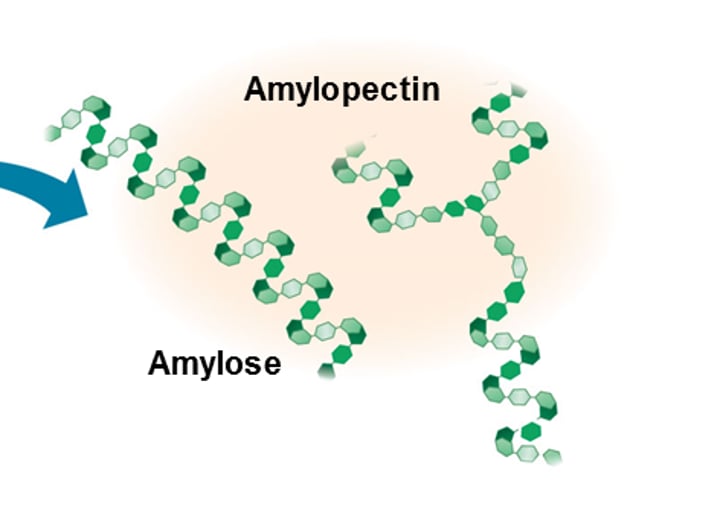
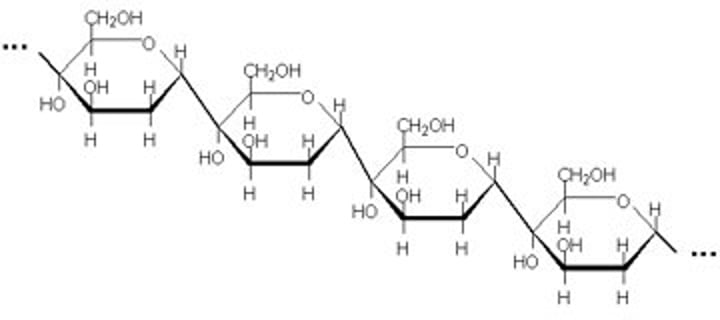
amylose
a α-polysaccharide found in plants that is a helical chain; has only 1-4 linkages
amylopectin
has α-1,6-linkages that cause branching; stores energy in plants
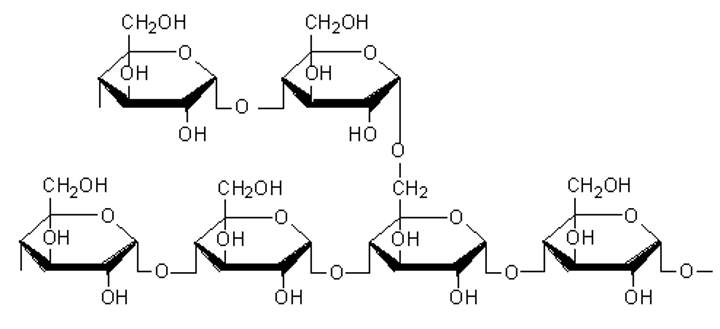
glycogen
- a branched polymer of α-glucose and has more than 1-6 linkages
- is used by mammals to store glucose in liver and muscle cells
types of fatty acids
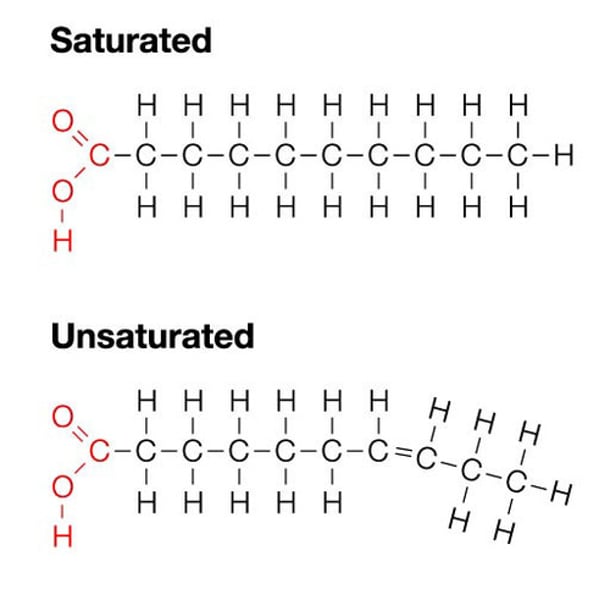
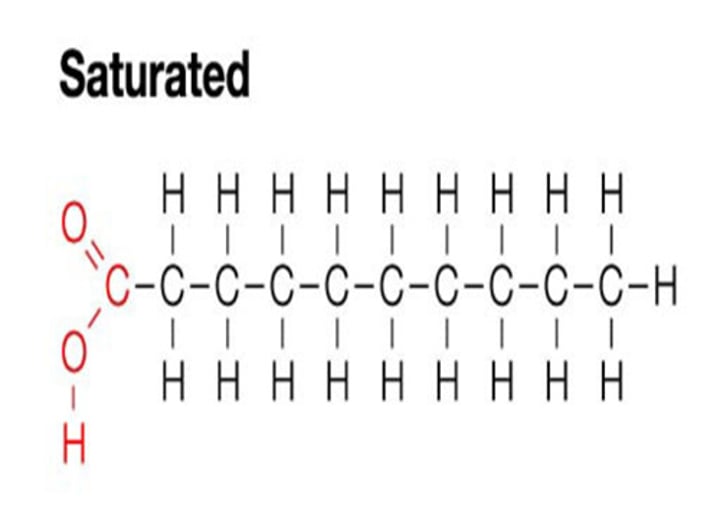
saturated fatty acids
all carbon atoms are connected by single covalent bonds
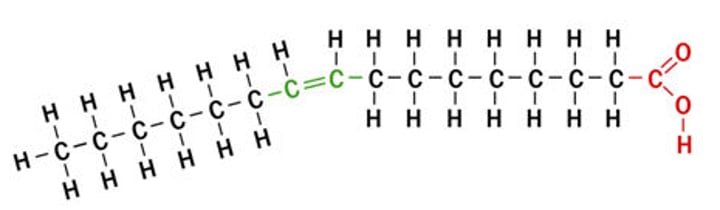
unsaturated fatty acids
contain one or more double bonds between the carbon atoms
monounsaturated
only one covalent bond
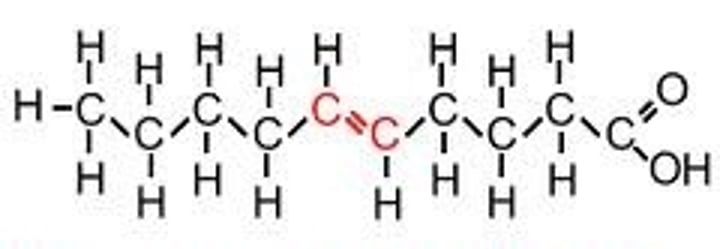
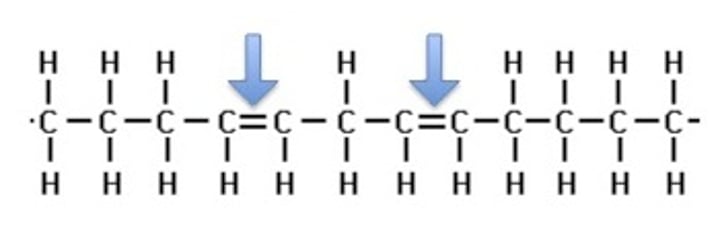
polyunsaturated
two or more double bonds
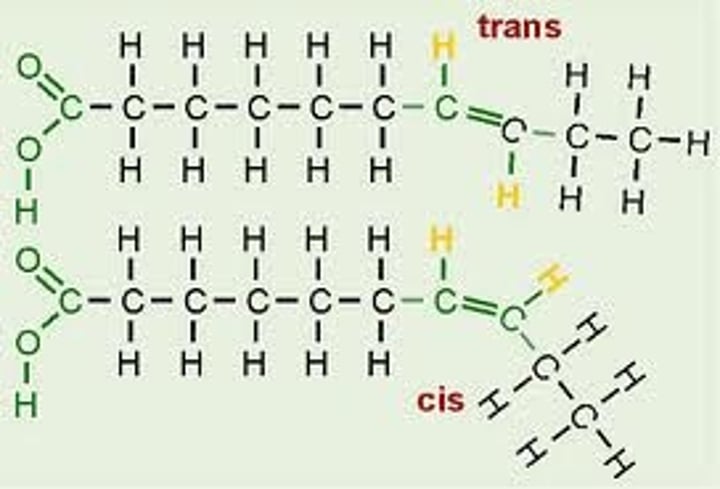
cis unsaturated fatty acid
hydrogen atoms are bonded to carbon atoms on the SAME SIDE of a double bond in a fatty acid carbon chain; they have a bent shape
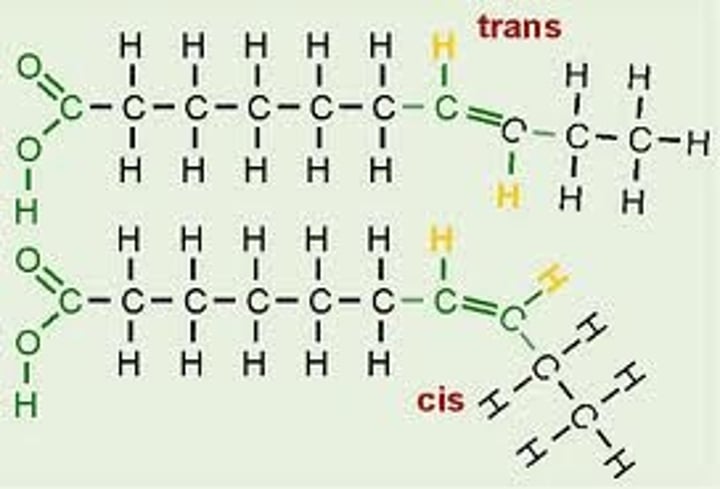
trans unsaturated fatty acids
hydrogen atoms are bonded to carbon atoms on opposite sides of a double bond; they have a linear shape
how to find BMI
weight (kg) / height (m^2)
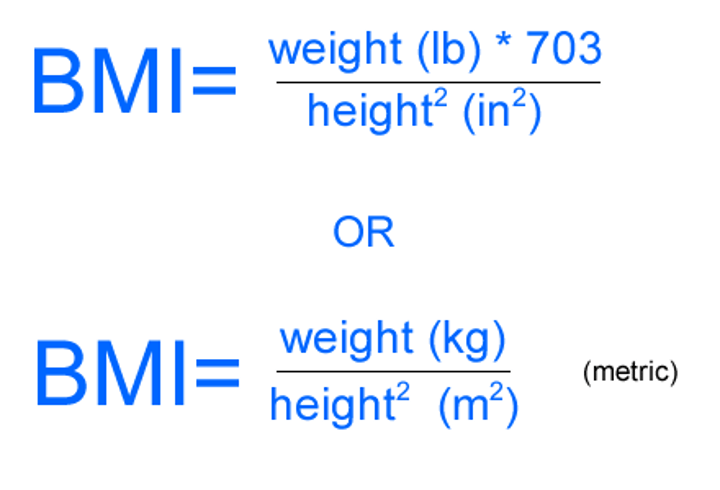
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD)
buildup of plaque in the arteries of the heart
- cis unsaturated raises HDL and lowers LDL :)
- trans unsaturated lower HDL and LDL rises :(
- saturated fats raises HDL in most cases :/
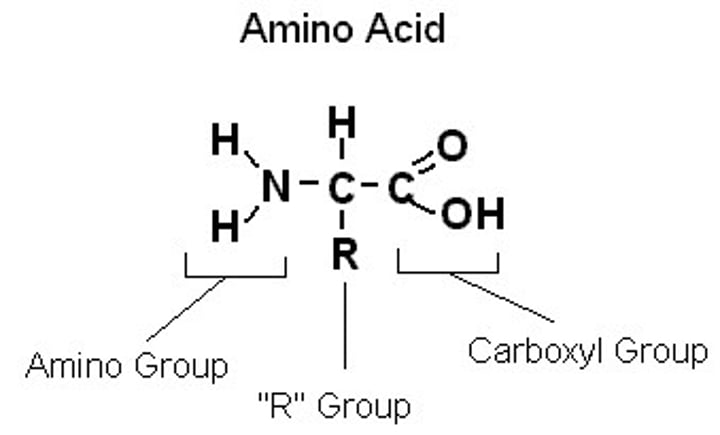
amino acid structure
a carboxyl group, amine group, and R group
gene
sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait
proteome
an organism's complete set of proteins
amino acid diversity
the R group of amino acids vary and thus determines the trait
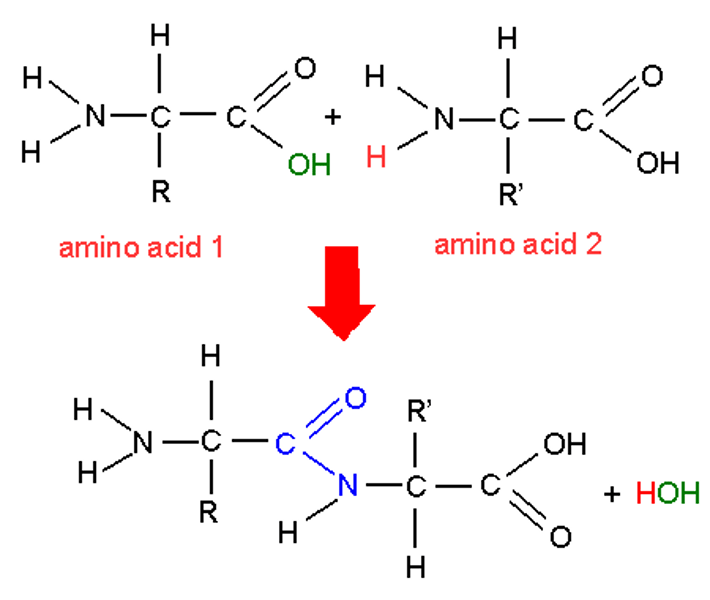
dipeptide
two amino acids bonded together by a condensation reaction between the carboxyl group and amino group; they form a peptide bond
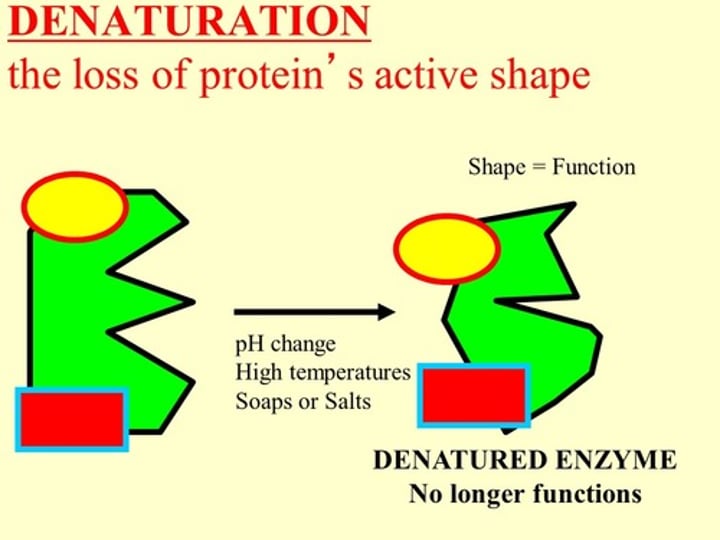
denaturation
loss of normal shape of a protein due
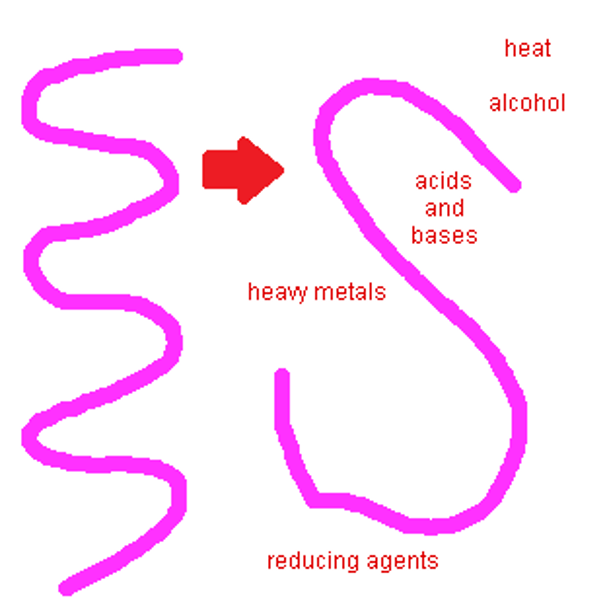
causes of denaturation
temperature, pH, substrate concentration
- the active site of an enzyme loses its structure and makes it unavailable for a substrate to bind
- hydrogen and ionic bonds are disrupted
levels of protein organization
1. primary structure
2. secondary structure
3. tertiary structure
4. quaternary structure
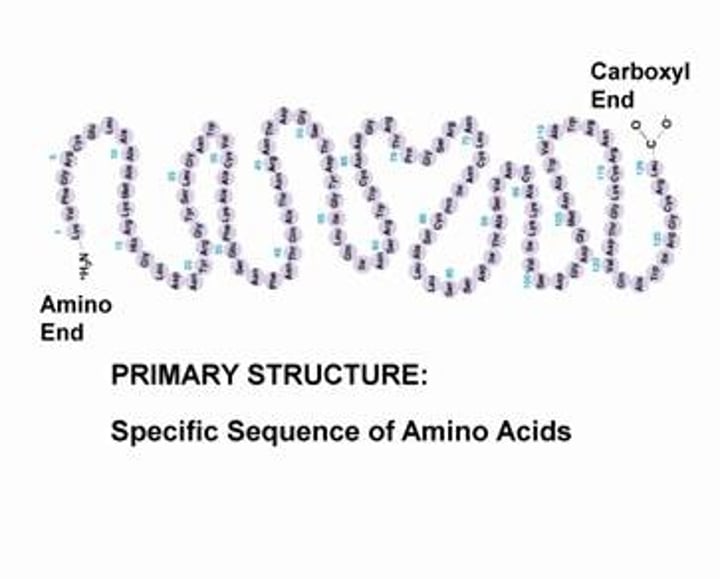
primary structure
sequence of amino acids
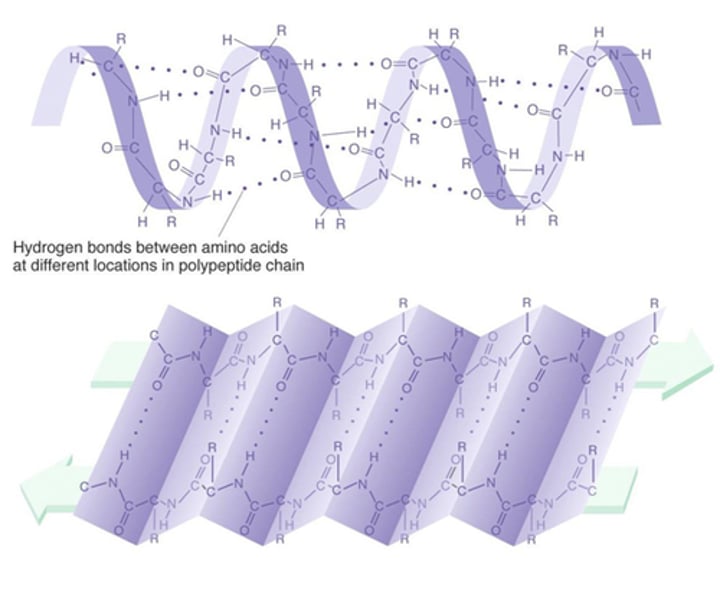
secondary structure
occurs when H-bonds react to construct alpha helics or beta sheets
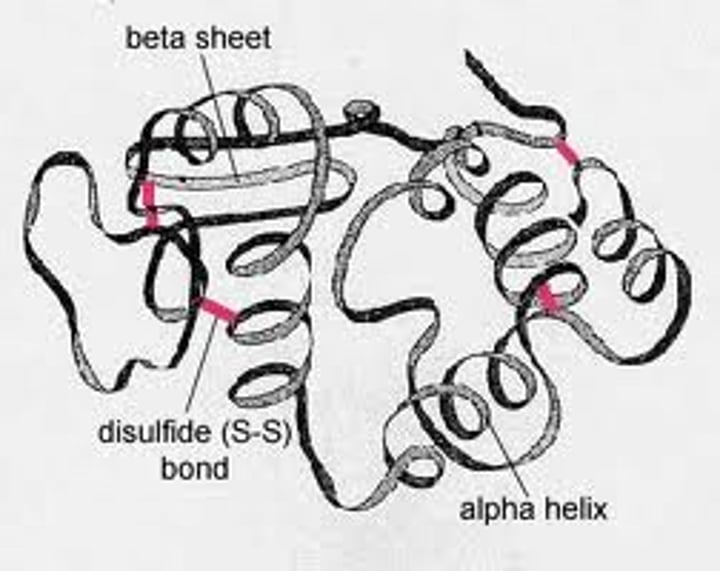
tertiary structure
Results from interactions between alpha helices and beta and creates a 3D shape
quarternary structure
when multiple polypeptides interact with each other and are held by H-bonds that form its 3D structure
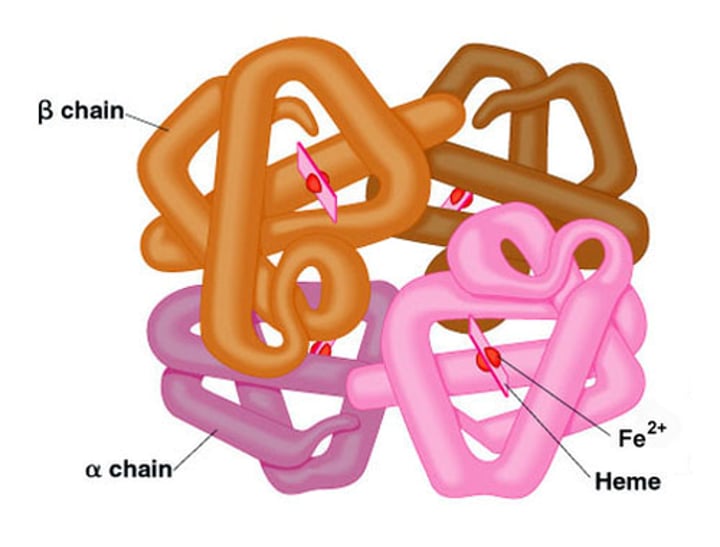
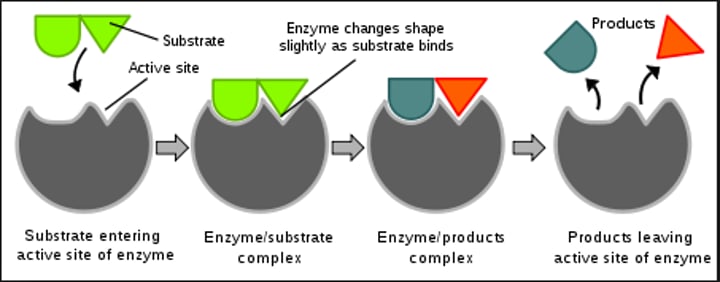
enzymes
proteins that speed up specific chemical reactions but lower activation energy
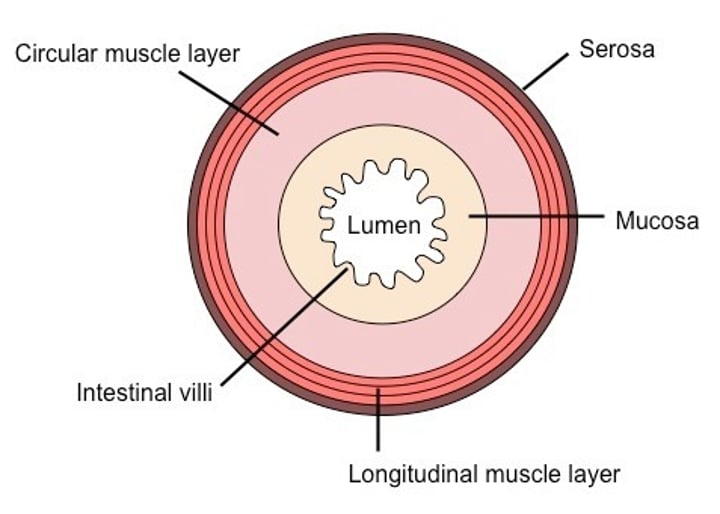
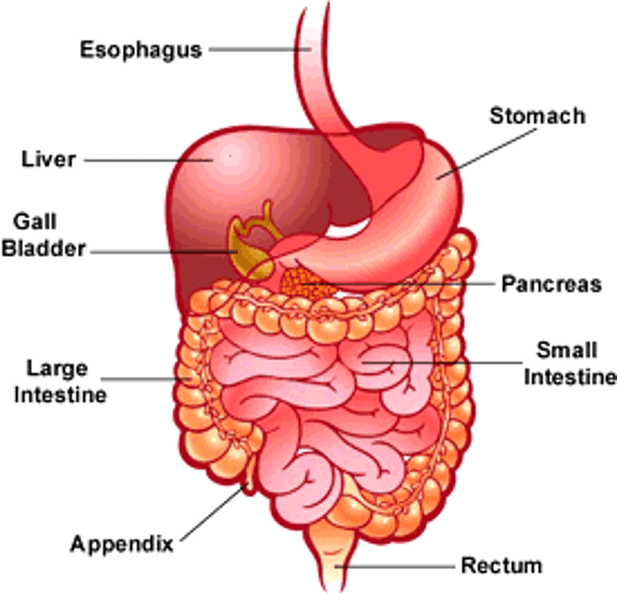
structure of the small intestine
lumen, mucosa, submucosa, circular muscle, longitudinal muscle, serosa
peristalsis
a wave of muscle contractions that push food through the gut
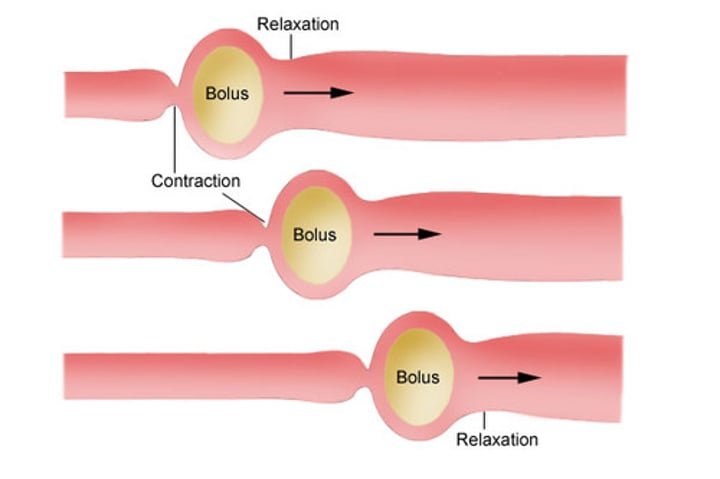
circular muscle
muscle that prevents the bolus from moving backwards
longitudinal muscle
a muscle that contracts ahead of the bolus to shorten the distance for food to move
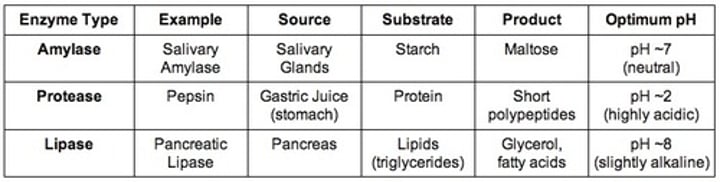
lipase
enzyme that breaks down fat (lipids) to make fatty acids+glycerol
- occurs in the pancreas and excretes into the small intestine
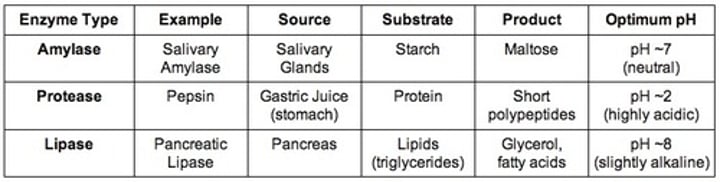
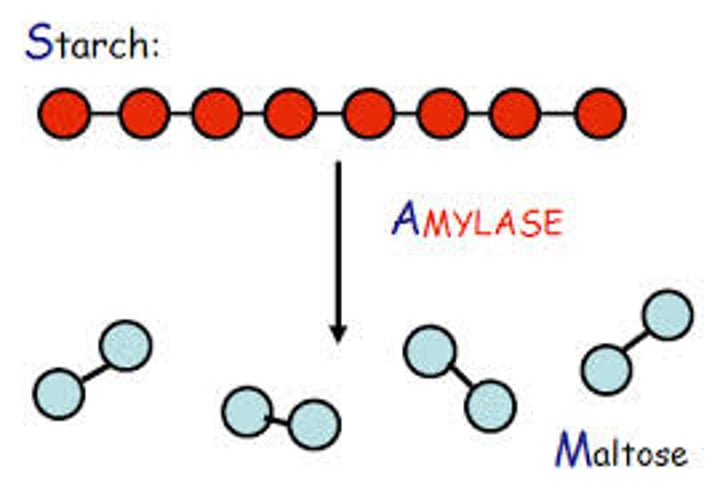
salivary amylase
enzyme in the mouth that breaks down starch to maltose
protease
enzyme that breaks down proteins in the stomach and small intestine
absorption
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of the digestive system into the blood
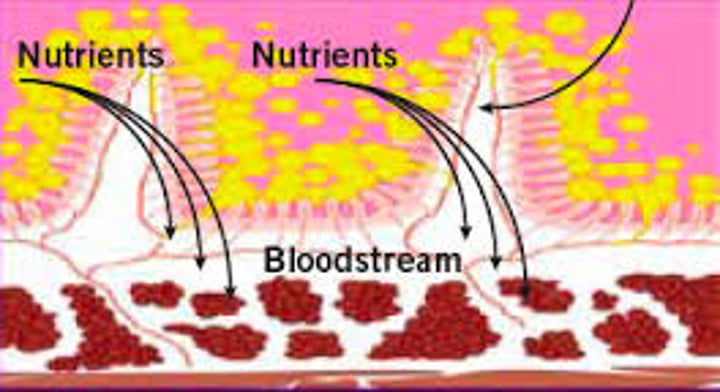
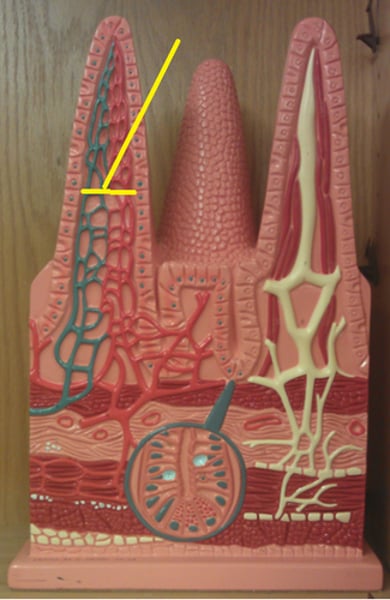
villi
are finger like structures of the mucosa on the inner intestinal wall
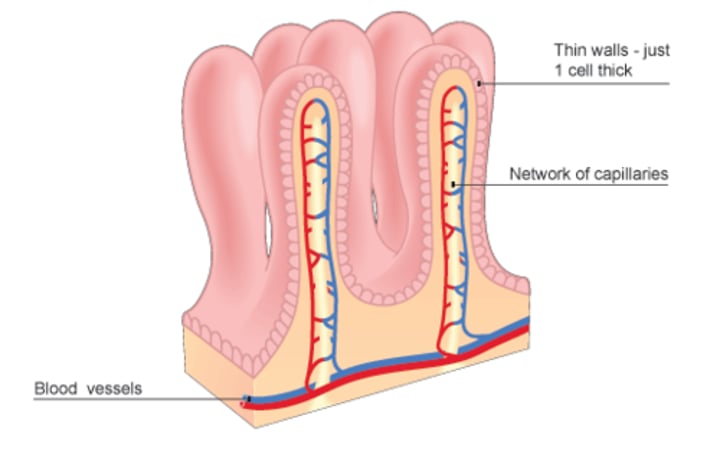
lacteal
a lymph tubule located in the villus that absorbs fatty acids
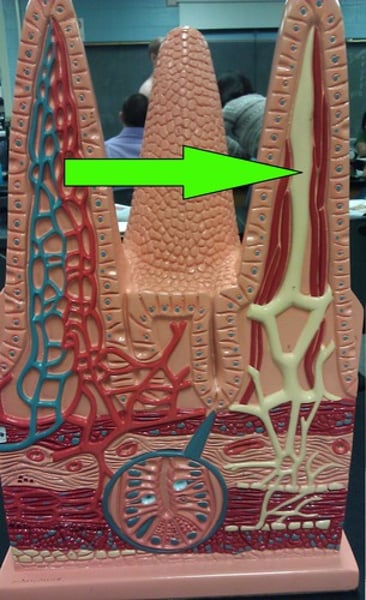
blood capillaries
absorbs glucose/amino acids
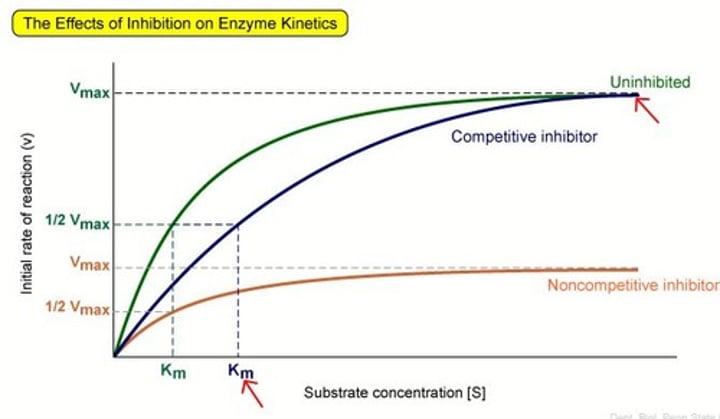
enzyme inhibitors
are molecules that slow an enzymes ability to catalyze a reaction by interfering with a substrates access to the active site
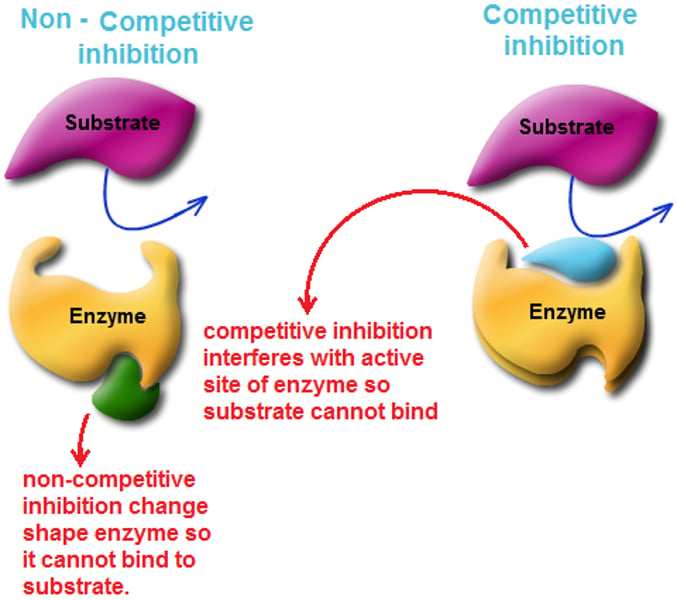
competitve inhibition
an inhibitor competes with the normal substrate for binding to an enzyme's active site; it slows the overall rate of reaction but can equal the normal optimum max
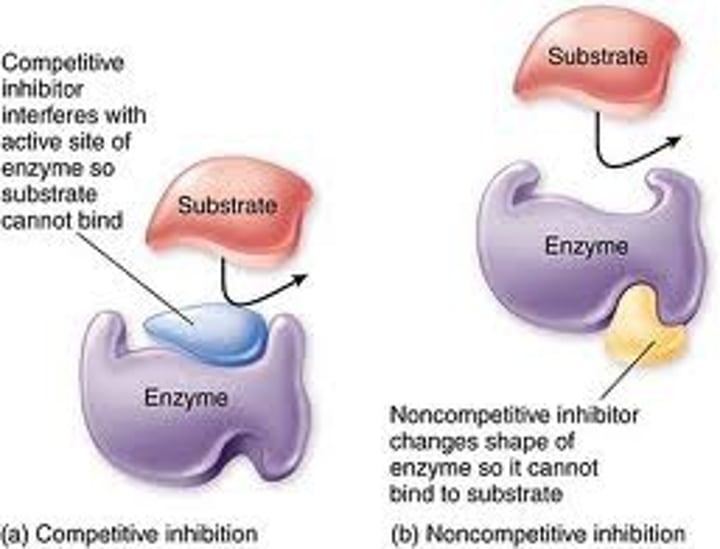
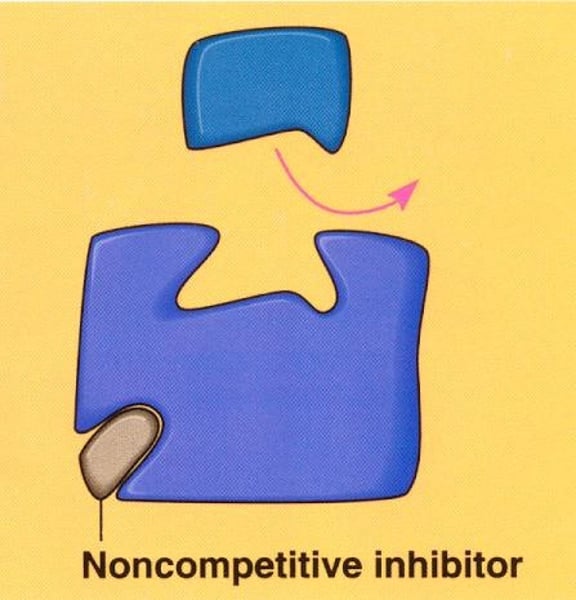
noncompetitive inhibitor
inhibit enzyme activity by binding to a secondary site called the allosteric site; this causes the active site to change formation and stops a substrate from binding
- it decreases the max rate of reaction permanently and plateaus
anatomy of the digestive system
Graph of non-competitive inhibitor
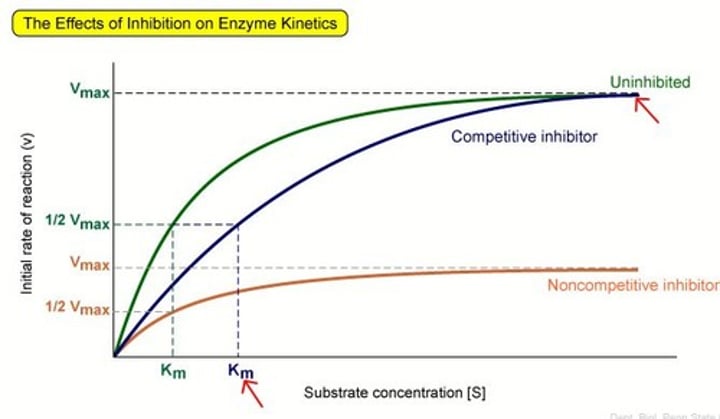
graph of competitive inhibitor
why are cis and trans fatty acids unsaturated?
they either have hydrocarbon bonds on the same side or either side. this includes the double bonds between carbon atoms.