ESSC - test 3.3 Weathering and Mass wasting
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is weathering?
The disintegration and decomposition of material at or near the surface.
What is mass wasting?
The transfer of rock material downslope under the influence of gravity
What is erosion?
The incorporation and transporation of material by a mobile agent, usually water, wind, or ice.
Why do rocks break?
1. They have different temp and pressure conditions than how they were formed
2. Water can break down mineral bonds
3. Rock interacts with atmospheric oxygen
What are the two types of weathering?
Mechanical and chemical.
What is mechanical weathering?
There is some physical force. Include:
- frost wedging
- unloading
- biological activity
What is chemical weathering?
You're changing the chemistry of your rock somehow by removing or adding elements
What is the most important agent in chemical weathering?
Water. Oxygen dissolved in water oxidizes materials. and CO2 dissolved in it forms carbonic acid and alters the material.
What are joints?
Fancy science word for cracks. Basically, the rock is broken but there wasn;t any movement.
What is the difference between faults and joints?
With joints, there is no movement, but with rocks there is.
What are expansion joints?
The cracks in the sidewalk. These are expansion joints. On the causeway, the joints that you hit are expansion joints. You can see the lake between them at every joint. This allows the concrete to expand and go back. This preserves the concrete. Nature doesn't have this. If you keep expanding and contracting, rocks are going to form.
What are unloading joints?
often horizontal as well as vertical and form as a result of lower pressure near to the surface
What is unloading (unroofing)
remove the overline material (overburden) and the rock is now able to expand.
What is frost wegdging?
water goes into a joint, freezes. Water expands when it freezes. As it expands it pushes the joint open. Then water fills again. Ever so slowly, it breaks apart the rocks.
What is mineral wedging?
"like frost wedging, but way slower." - water runs across the surface picking up chemicals. WHen it gets into the joint it evaporates and deposits minerals.
WHat happens when rocks dissolve?
Pits
Rounded edges and corners
Wide joints
Looks like joints would capture runoff.
In general, continental crust is ______.
Granite
________ remains unaffected by chemical weathering because it doesn't really interact with anything
Quartz
Advanced mechanical weathering aids chemical weathering by increasing the
Surface area
In what ways are the rates of weathering effected?
Climate.
________ and __________ are the most crucial factors in rates of weathering.
temperature, moisture
Chemical weathering is most effective in areas of _____ temperature and _________ moisture
warm / abundant
What is differential weathering?
Different rocks weather at different rates. Even different parts of the same rock do. This is why we have different landforms. EX: Arches national park
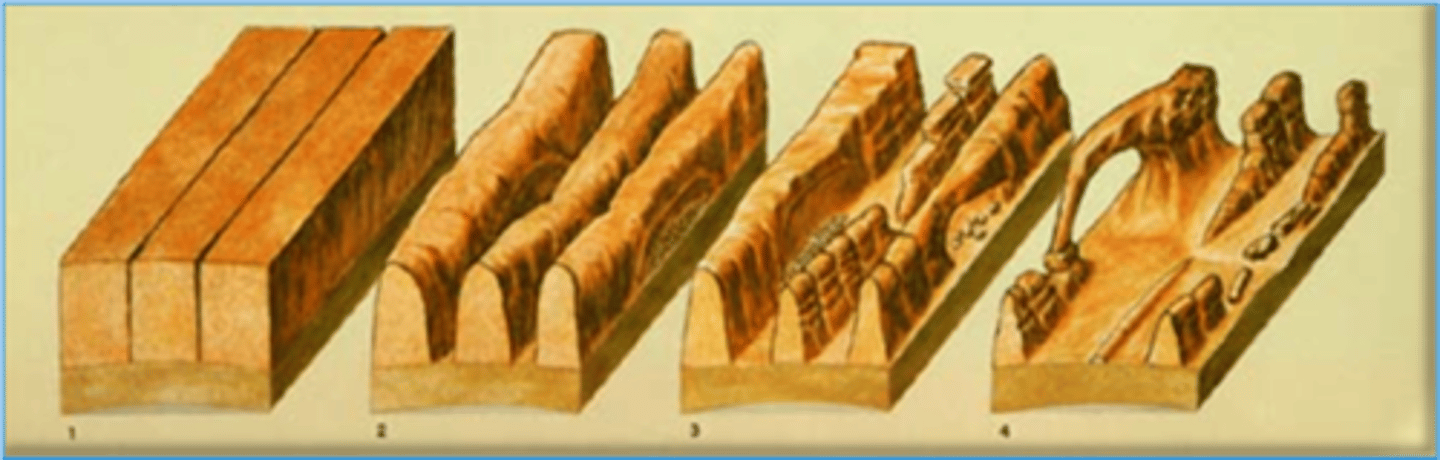
How do oceans get their salt?
Through weathering. Water with dissolved salt in it runs off into the ocean. Then water evaporates and the salt is left behind.
What are some other factors that influnce weathering?
Climate again - such as precipitation, elevation, ocean currents
Hillslope orientation
Steepness of slope
Time
_______ is a combination of mineral mater, water, and air
Soil
What is regolith?
the layer of unconsolidated rocky material covering bedrock.
What are the four types of soil, and how are they categorized?
Categorized by size.
Sand - large size
Silt - middle size
Clay - small size
Loam - mixture of all three
What is soil formation?
Refers to where the parent material came from (where is the OG rock?)
What are the two kinds of soil formations?
Residual and transported
What is residual soil formation?
The parent rock is bedrock (rock directly below you)
What is transported soil formation?
Parent rock has been brought in from somewhere else.
What is a horizone?
Zones of layers of soil
What are the horizones of residual soil? (OAEBC)
O - Organic matter
A - Mixture of organic and mineral matter
E - Basically a dead zone
B - Fine clay particles. Ions start to pile up here. (zone of accumulation)
C - Partially altered parent material.
I have no idea what the letters stand for, but he said this would be on the test.
Soil forming processes operate from the surface __(Up/Down)__
DOWN.
What are the controls of soil formation?
Slope (angle and orientation)
How does angle influence soil formaion?
Steep slopes often have poorly developed soils.
How does orientation (direction the slope is facing) influence soil formation?
Influences soil temperature and moisture level
Layers O and A together are called
Top soil
Layers O, A, E, and B together are called
solum, or "true soil"
What are some activities that threaten soil?
Overgrazing - too many sheep eating plant roots
Erosion - self explanatory
Removing vegetation - like the dust bowl
Soil contamination - like if you water your house plants with tap water
Why is natural soil erosion important?
Because that's how we recycle earth materials
What do natural rates of erosion depend on?
Soil characteristics
Climate
Slope
Type of vegatation
What can soil erosion and sedimentation cause?
reservoirs to fill with sediment, contamination by pesticides and fertilizers
What is liquefaction?
The process by which an earthquake's violent movement suddenly turns loose soil into liquid mud.
It's basically quicksand.
What is soil compaction?
When soil settles at different rates (such as underneath a house)