Plant Tissues
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary related to plant tissues, their structures, and functions.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
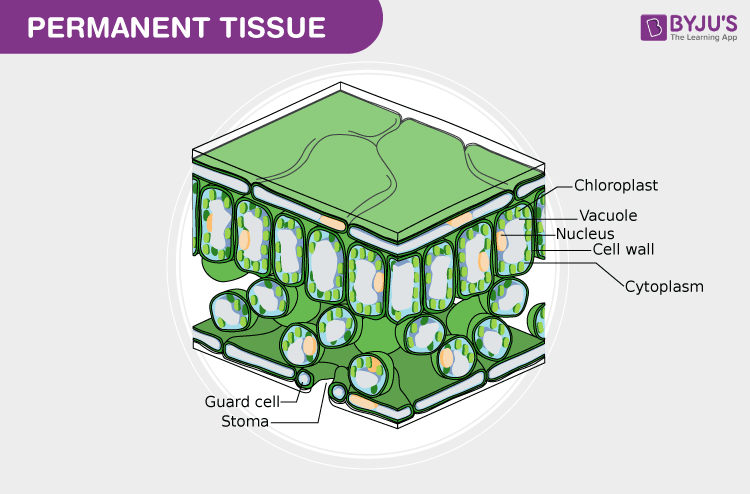
Tissue
A group of cells more or less alike in size and shape, performing the same function and having a common origin.
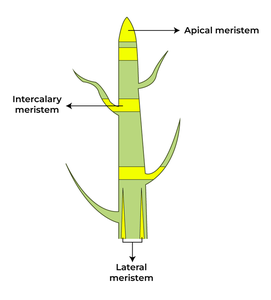
Meristematic Tissue
A group of actively dividing cells, mainly located at the growing tips of the roots, stem, and leaves.
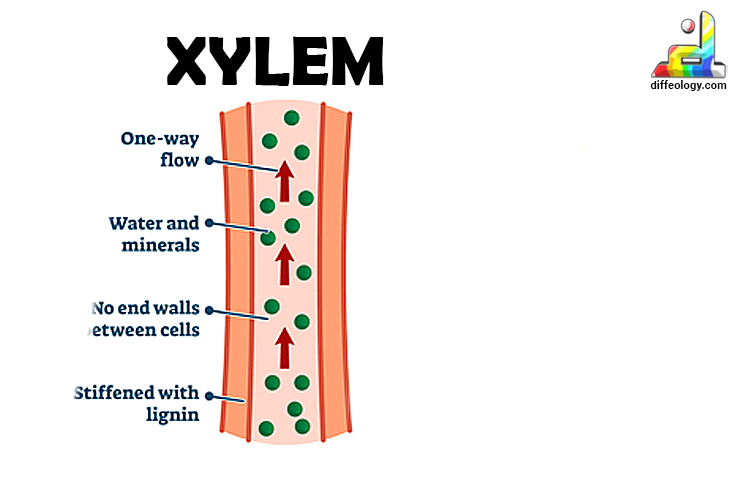
Xylem
The water-conducting tissue of plants, responsible for conducting water and dissolved minerals from the roots to various parts.
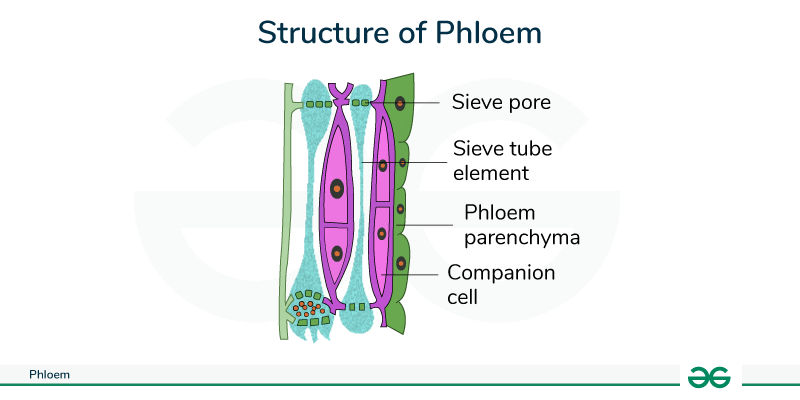
Phloem
The living tubular cells in plants that transport prepared food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
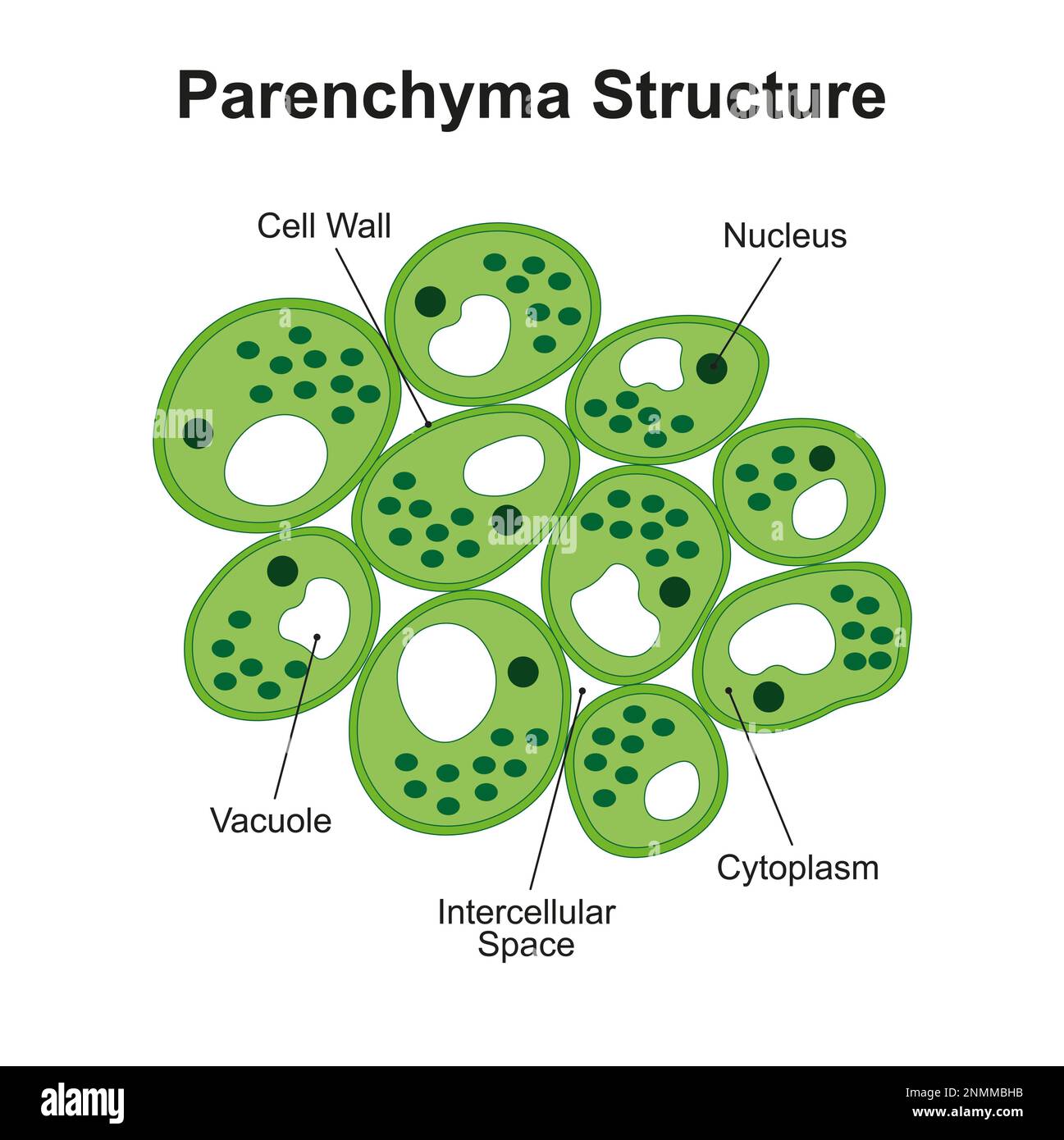
Parenchyma
The most common type of plant tissue made of thin-walled living cells, involved in storage and photosynthesis.
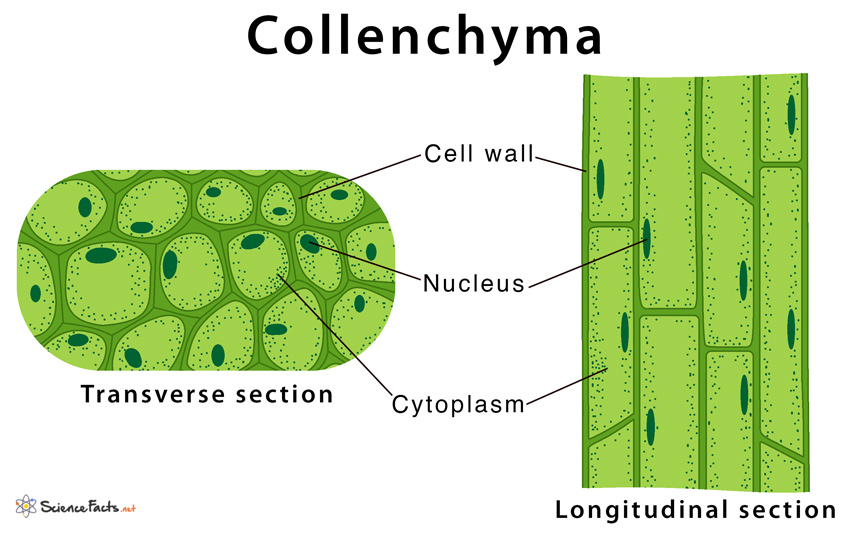
Collenchyma
Living cells found in bands that provide mechanical strength and support to growing parts of the plant.
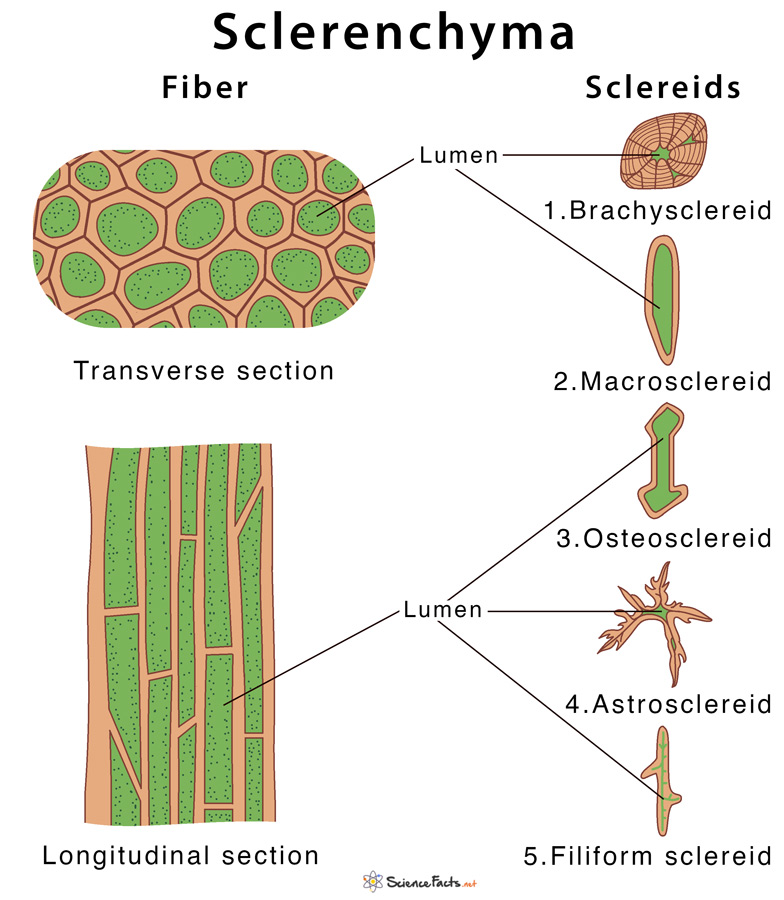
Sclerenchyma
Dead cells with thickened cell walls, providing rigidity and toughness to different parts of the plant.

Histology
The study of tissues and their functions.
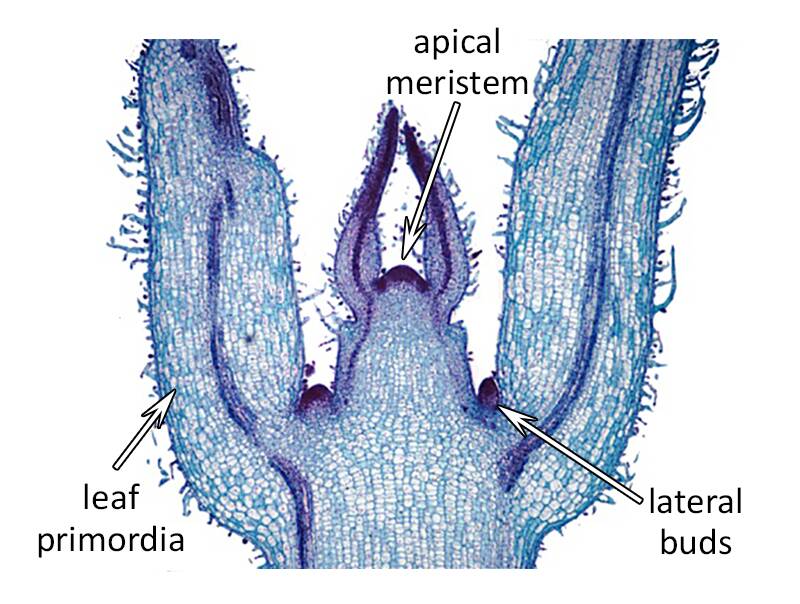
Apical Meristem
Found at the tips of shoots and roots, responsible for elongation of the plant.
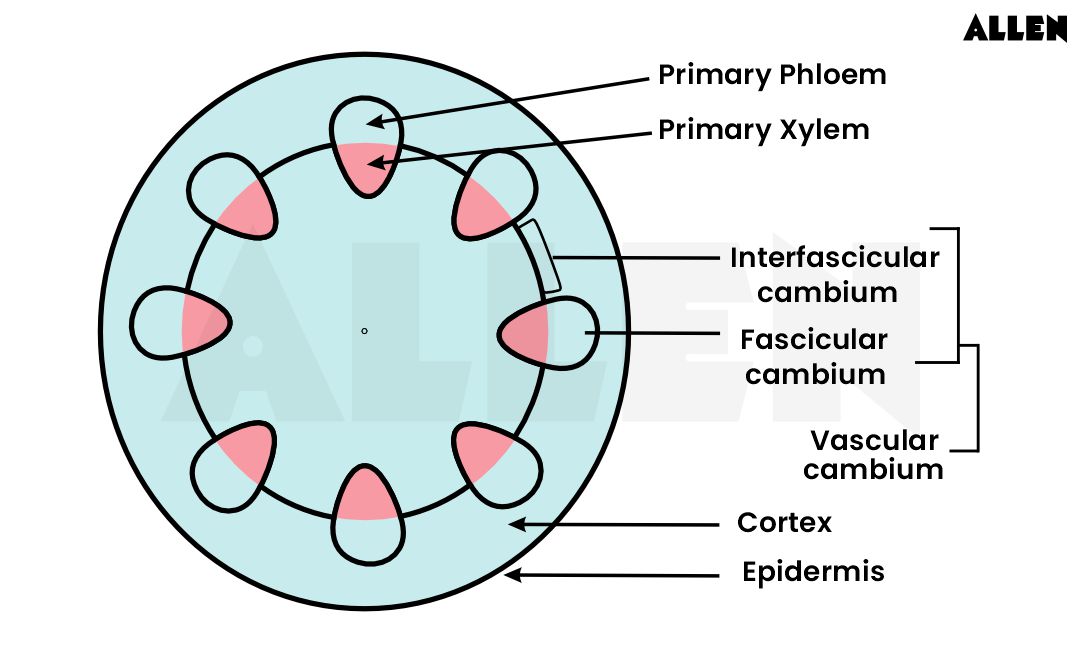
Lateral Meristem
Located beneath the bark and increases the diameter of plant organs.
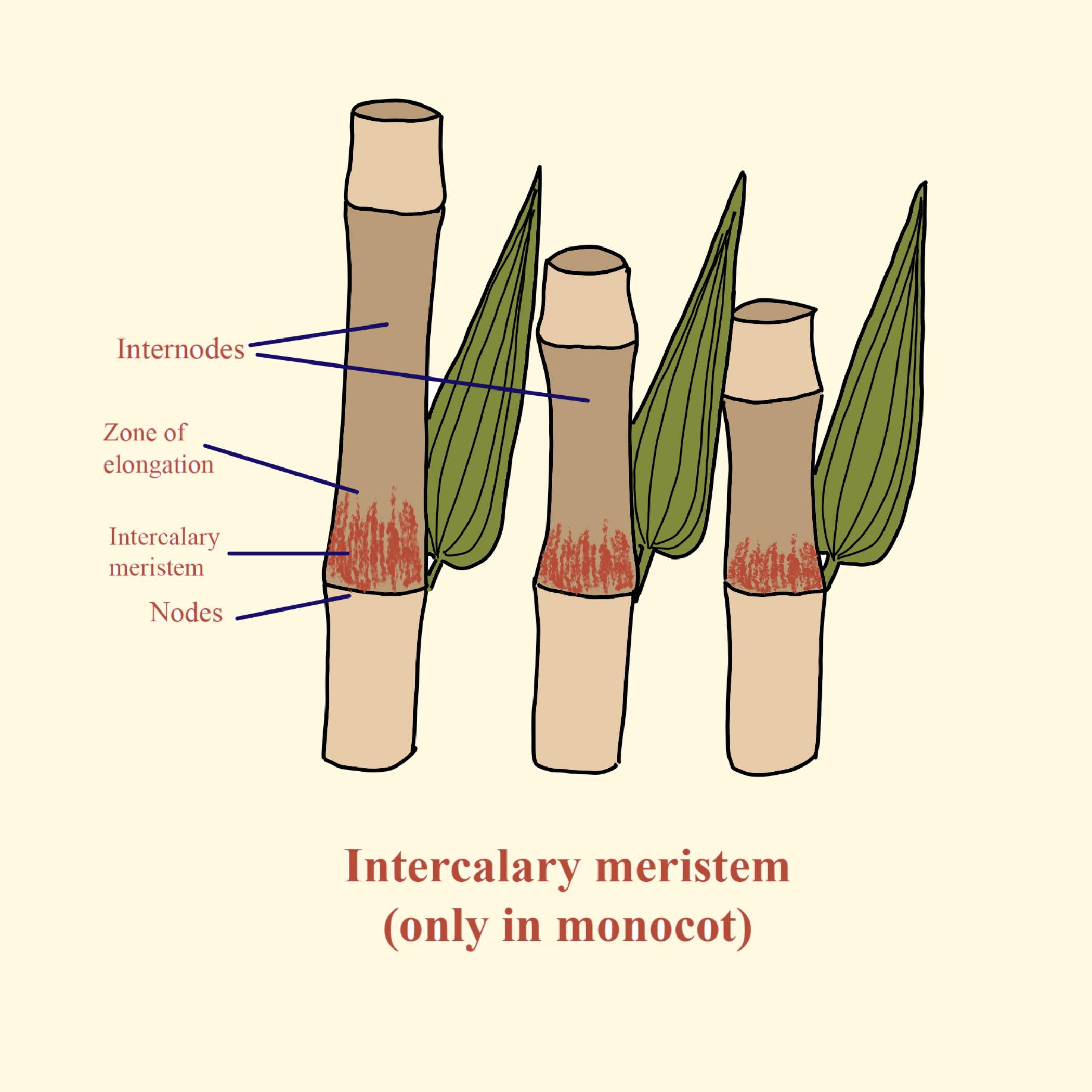
Intercalary Meristem
Found at the base of internodes, contributes to the increase in length of plant organs.
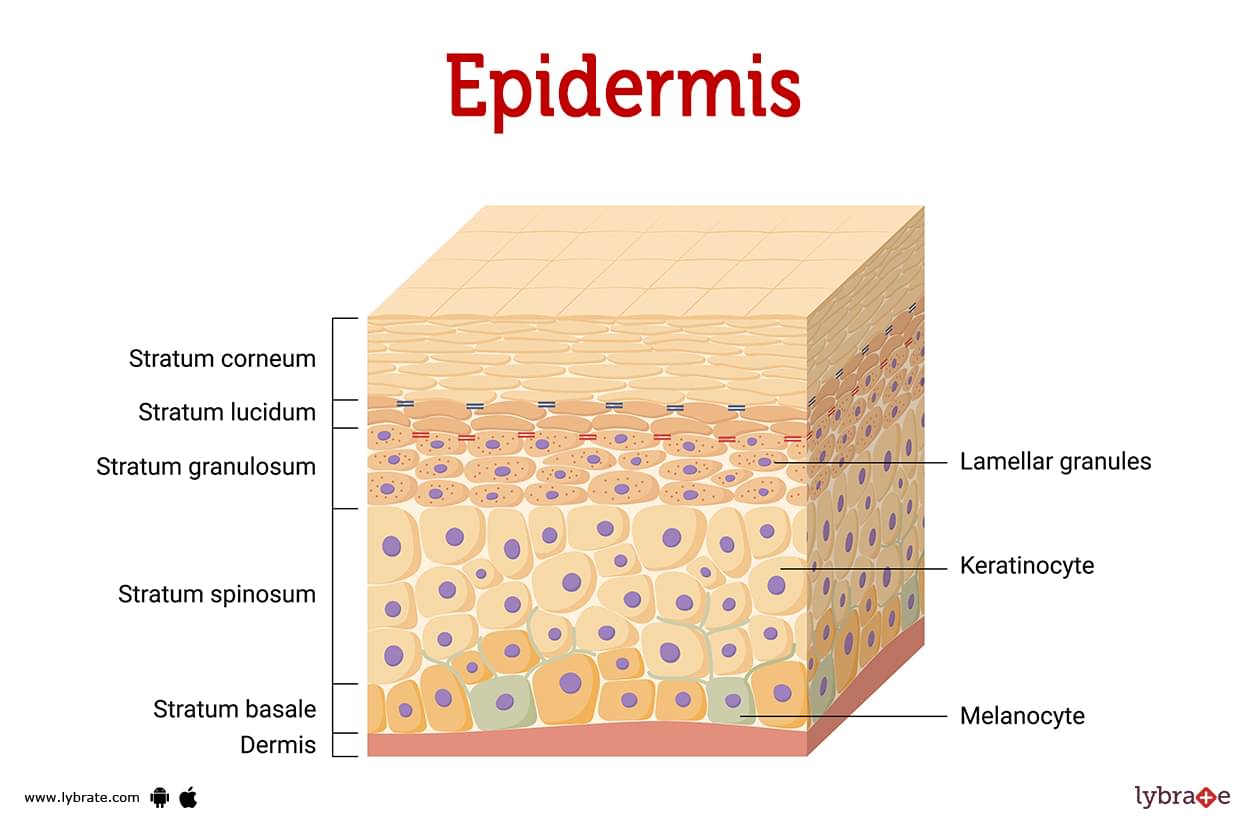
Epidermis
The outermost layer of plant cells that provides protection against external influences.
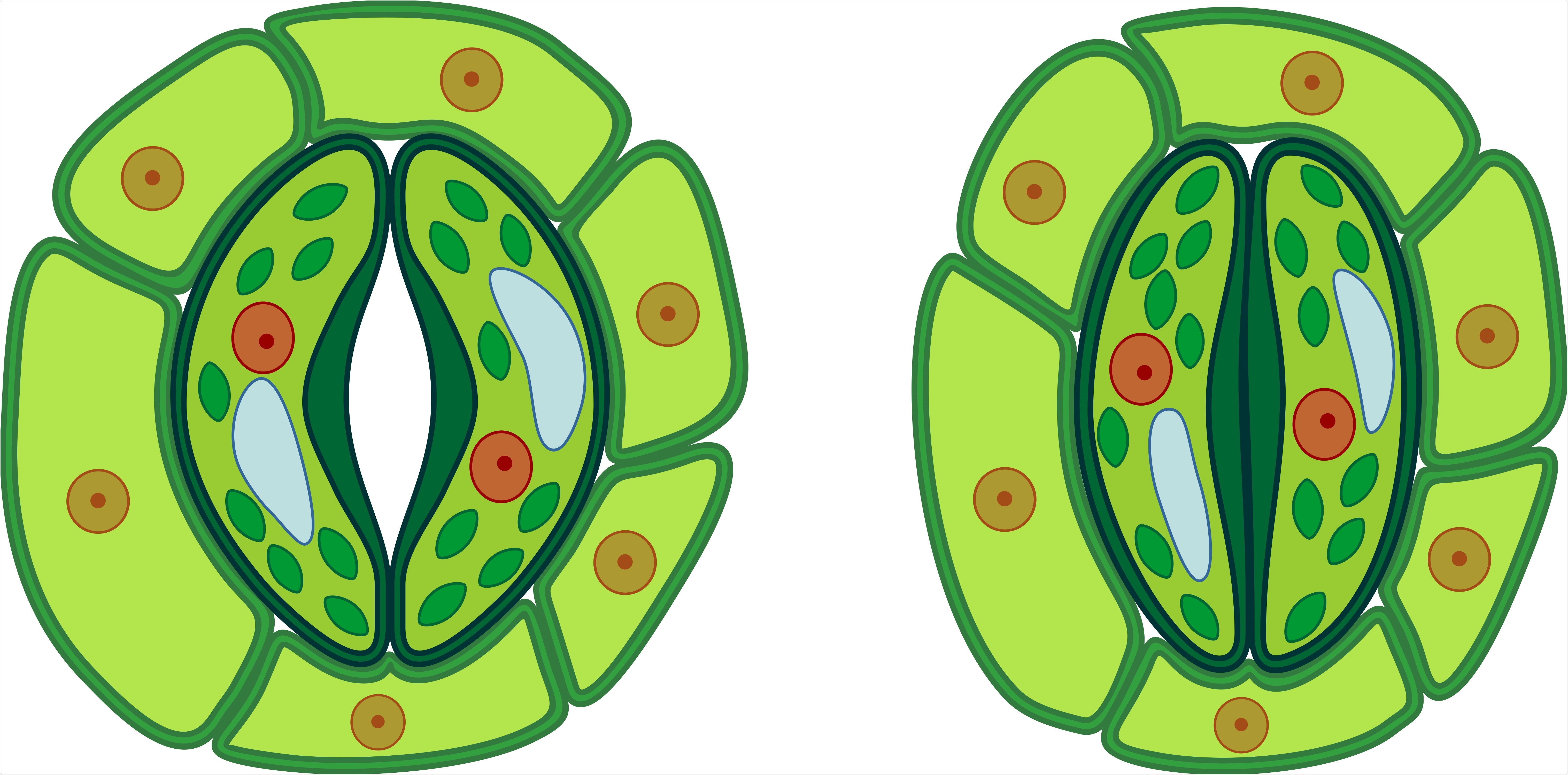
Guard Cells
Special cells in the epidermis that control the opening and closing of stomata for gas exchange.
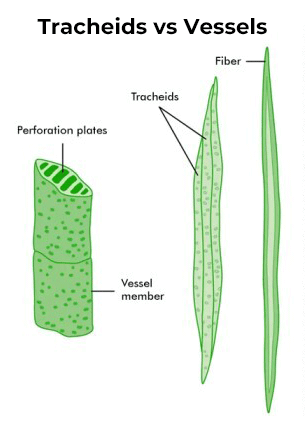
Tracheids
A type of xylem cell that helps in the conduction of water.
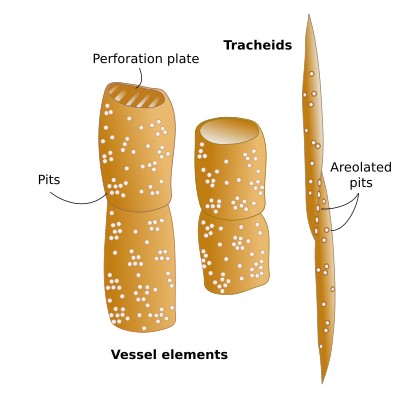
Vessel Elements
Another type of xylem cell that transports water and provides structural support.

Cork Cells
Dead cells that form a protective layer in older roots and stems.
Secretory Tissues
Plant tissues that secrete substances such as tannins, gum, and mucilage.

Cutin
A waxy substance that covers the protective tissues of the plant.
Chlorenchyma
Chloroplast-containing parenchyma cells that help in photosynthesis.
Cell Wall
The rigid outer layer of a plant cell, providing structure and protection.

Lignin
A hard substance within the cell wall of sclerenchyma that provides rigidity.

___ tissue is a group of actively dividing cells, mainly located at the growing tips of the roots, stem, and leaves.
Meristematic Tissue
The water-conducting tissue of plants is called ___.
Xylem
___ are the living tubular cells in plants that transport prepared food from the leaves to other parts of the plant.
Phloem