Ch 7- Fibrous Proteins Fibrous Collagen Protein
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Fibrous protein
Collagen Protein
Collagen
Fibrous protein with three intertwined polypeptide chains
Location of collagen
CT such as tendons, cartilage, bone, the cornea of the eye, skin etc
Function of collagen
provide strength to tissue
Most abundant fibrous protein
Collagen
Five groups of collagen depending on how the alpha chains are combined
1. Fibril forming chains
2. Network forming
3. Fibril-associated collagen
Fibril forming chains
linear with a banding pattern
Network forming
constitute basement of cellular membrane
Fibril-associated collagen
found in ECM
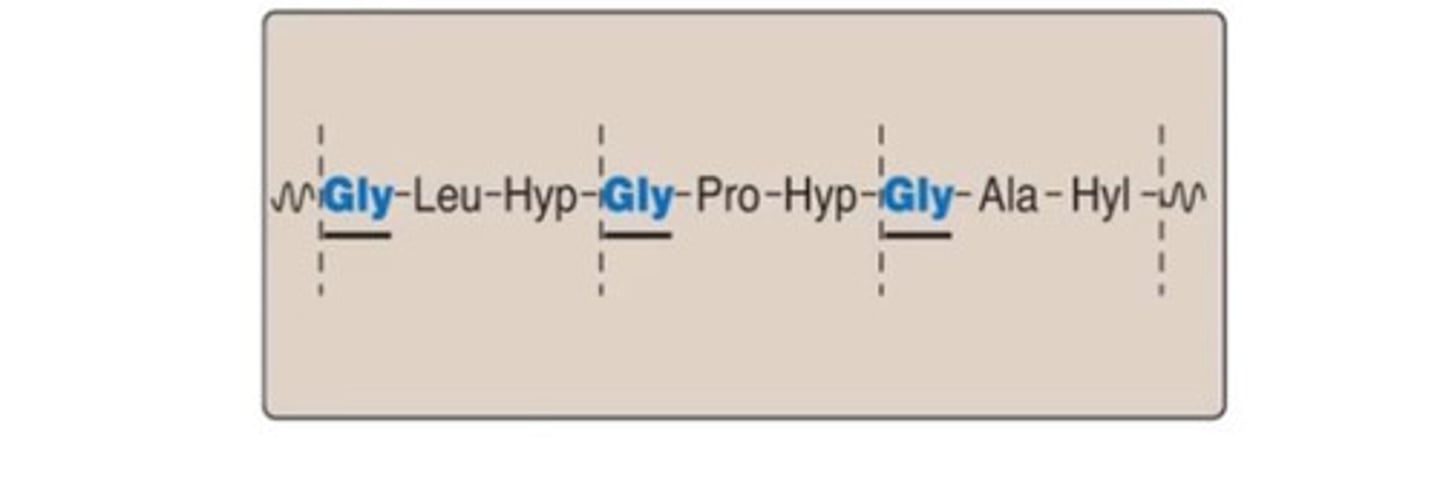
Collagen primary structure
- Repeating tripeptide unit
- Gly-X-Y, where X and Y are amino acids
- Often proline and 4- Hydorxy-proline in X and Y positions
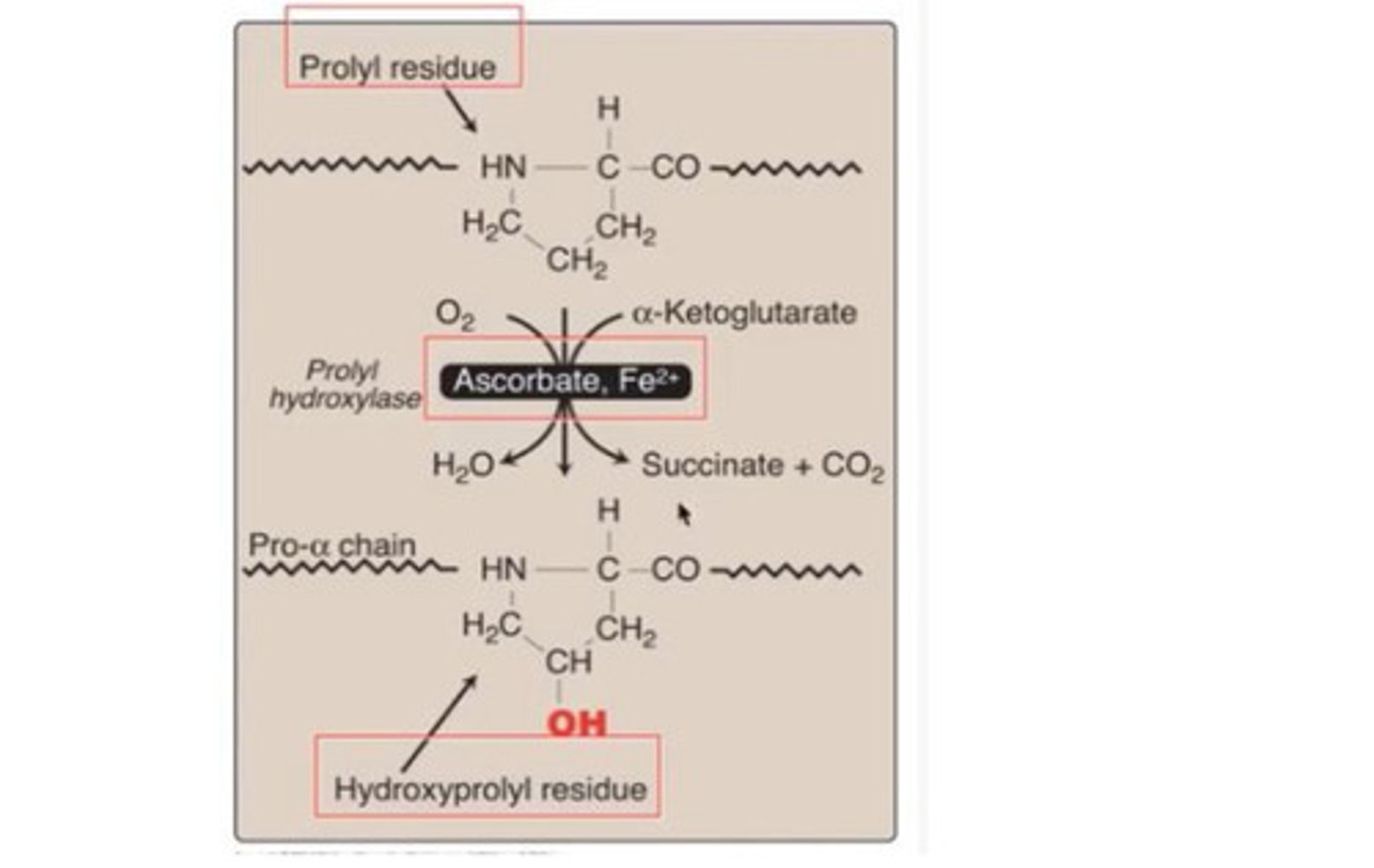
Hydroxylation of protein
post translational modification of protein eg formation of hydroxyprolyl residue
- Done by prolyl hydroxylase
- Vitamin C is extremely important for this modification
Secondary structure of collagen
- A chain (not a-helix)
- A left-handed helix, with three amino acid residues per turn
- Gly is ideal for this structure due to its very small side chain (one H) while the Pro and 4-Hydroxyproline residues permit the sharp twisting
- R- group exposed in this chain
Tertiary structure of collagen
The structure of a single collagen chain
Quarternary Structure of collagen
- first level- three separate collagen polypeptides (a-chains) are supertwisted about each other in a right-hand manner
- the formed triple helix is called tropocollagen
- tropocollagen can associate together to form higher order structure (fibril)
Synthesis of Collagen
1. In the nucleus the genes coding from pro alpha 1 and pro a2 chain are transcribed into mRNA
2. mRNA sent to rough endoplasmic reticulum where the translation occurs and the prepro a polypeptide chains are extruded into its lumen and the signal sequence is removed
3. Selected Proline and lysine are modified by hydroxylation
4. Selected hydroxylysine residues are glycosylated with glucose and galactose
5. the pro-a- chains begin to assemble
- Intrachain and interchain disulfide bonds form the C terminus propeptide extension
6. A triple helix is formed and pro collagen is formed
7. The pro collagen is secreted form a Golgi vesicle into the ECM (crosses the membrane)
8. The cleavage of the pro collagen the N (amino) and C terminus propeptides are removed so only the tropocollagen remains
Assembly of collagen fibrils
- Tropocollagen remains with sugar modification
- Self assembles as a collagen fibril
- Within this fibril the different tropocollagen molecules will be cross linked to make it very resistant
Structure-function relationship in fibrous proteins eg collagen
- Fibril: the tropocollagen molecules arranged into continuous long fibres
- Extremely high tensile strength
- Fibres cross linked by unusual types of covalent bonds involving Lys, OH-Lys (5-hydroxylysine) or His residues (X and Y positions)
- The cross links give strength and rigidity to collagen fibres
- Hydroxyproline can form H-bonds that provide stability to the fibres
Disease caused by defective collagen structure
Scurvy
Cause of scurvy
- Due to Vitamin C deficiency
- Vit C as a cofactor of the enzymes proline and lysine hydroxylase the enzymes generating hydroxylated proline and lysine
- General degeneration of CT
Symptoms of scurvy
- Numerous small haemorrhages caused by fragile blood vessels
- Tooth loss
- Poor wound healing and reopening of old wounds
- Bone degeneration
- Eventually heart failure
Collagenopathies
- Ehler-Danlos syndrome
- Osteogenesis imperfecta - brittle bone syndrome
Ehler Danlos Syndrome features
- Extremely loose joints, hyperelastic skin, skin that bruises easily and easily damaged blood vessels
What does Ehler Danlos Syndrome effect?
- Defect in processing collagen, no secretion of collagen and degradation
- Affects collagen 1. 3 or 5
Osteogenesis imperfecta - brittle bone syndrome
- Abnormal bone formation in babies
- Decrease production of type 1 (alpha 1 and 2) collagen
- Mutations often result in substitution of glycine by other amino acids eg Cys, Arg prevents formation of helix and final triple helix structure- no resistance