PHYS 335: Cell Physiology and Membrane Transport Info (Week 2)
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
cell organelles
Structures within a cell that perform specific functions.
cytoplasm
The jelly-like fluid that fills a cell.
cytosol
The liquid component of the cytoplasm where the organelles are suspended.
fluid-mosaic model
A model describing the structure of cell membranes as a mosaic of components including phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins, and carbohydrates.
integral membrane proteins
Proteins that are permanently attached to the cell membrane.
intracellular fluid
Fluid inside the cell.
nucleus
The central organelle that contains the cell's genetic material.
peripheral membrane proteins
Proteins temporarily associated with the cell membrane.
phospholipids
Lipids that form the basic structure of a cell membrane.
plasma membrane
A semipermeable membrane that surrounds the cell.
transmembrane proteins
Proteins that span the entire lipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
channel gating
The opening and closing of ion channels to control the flow of ions.
diffusion
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
diffusion equilibrium
When the concentration of a substance is the same throughout a space.
Fick's first law of diffusion
A mathematical equation describing the rate of diffusion of a substance.
flux
The rate of flow of a fluid, particles, or energy.
ion channels
Proteins that allow specific ions to pass through a cell membrane.
net flux
The overall flow of particles from one place to another.
active transport
The movement of molecules across a cell membrane against their concentration gradient, requiring energy.
aquaporins
Proteins that facilitate the transport of water across cell membranes.
cotransport (symport)
A type of mediated transport where two substances are transported in the same direction.
countertransport (antiport)
A type of mediated transport where two substances are transported in opposite directions.
endocytosis
The process of a cell engulfing material by wrapping extensions of its plasma membrane around the material.
exocytosis
The process of releasing material from a cell by vesicle fusion with the cell membrane.
facilitated diffusion
The passive movement of molecules across a cell membrane facilitated by transport proteins.
hypertonic
A solution with a higher solute concentration compared to another solution.
hypotonic
A solution with a lower solute concentration compared to another solution.
isotonic
A solution with the same solute concentration as another solution.
Na+/K+-ATPase pump
An enzyme that helps maintain the sodium-potassium balance within cells.
nonpenetrating solutes
Solutes that cannot freely cross a semipermeable membrane.
osmol
A unit of measurement for the number of solute particles in a solution.
osmolarity
The concentration of solute particles in a solution.
osmosis
The movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration.
primary active transport
Active transport that directly uses energy to transport molecules.
secondary active transport
Active transport that uses the energy from an ion concentration gradient to transport molecules.
semipermeable membrane
A membrane that allows certain molecules or ions to pass through while blocking others.
transporters
Proteins that transport specific substances across cell membranes.
afferent neurons
Neurons that carry signals towards the central nervous system.
astrocytes
Glial cells that support neuronal function and help maintain the blood-brain barrier.
axon
The long, slender projection of a nerve cell that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body.
axon collaterals
Side branches of the axon that also conduct electrical impulses.
axon hillock (or initial segment)
The region where the axon originates from the cell body and where action potentials are initiated.
axon terminal
The end of an axon where neurotransmitters are released to communicate with other neurons.
axonal transport
The process by which materials are moved along the axon.
blood-brain barrier
A protective barrier formed by specialized endothelial cells that limits the passage of substances from the bloodstream into the brain.
cell body (or soma)
The part of the neuron that contains the nucleus and other organelles.
central nervous system (CNS)
The part of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord.
dendrites
Branch-like extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons.
efferent neurons
Neurons that carry signals away from the central nervous system to muscles and glands.
ependymal cells
Cells that line the fluid-filled cavities of the brain and spinal cord.
glial cells
Supporting cells in the nervous system that provide various functions, including insulation and nourishment of neurons.
interneurons
Neurons that transmit signals between other neurons.
microglia
Immune cells in the central nervous system that protect against pathogens.
myelin
A fatty substance that insulates/protects axons and speeds up the transmission of electrical signals.
nerve
A bundle of axons in the peripheral nervous system.
neuron
A specialized cell that transmits electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system.
neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across synapses between neurons.
nodes of Ranvier
Gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon where action potentials can be generated.
oligodendrocytes
Glial cells in the central nervous system that produce myelin.
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The part of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord that connects the central nervous system to the limbs and organs.
postsynaptic neuron
The neuron that receives signals at a synapse.
presynaptic neuron
The neuron that sends signals at a synapse.
Schwann cells
Glial cells in the peripheral nervous system that produce myelin.
sensory receptors
Specialized neurons that detect stimuli from the environment.
synapse
The junction between two neurons where communication occurs.
varicosities
Swollen regions along autonomic nerve fibers that release neurotransmitters.
afferent division of the PNS
carries sensory information from PNS sensory receptors to CNS
basal nuclei (basal ganglia)
gray matter areas located deep within the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres
brainstem
the oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull
- responsible for automatic survival functions
cerebellum
a large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres
- the body's ultimate control and information-processing center
cerebral hemispheres
the two sections of the cortex on the left and right sides of the brain
cerebrum
area of the brain with four lobes responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
- subcortical structures include the hippocampus, basal ganglia and olfactory bulb.
commissure
nerve fibers that connect neurons in the central nervous system (CNS) and are confined to the spinal cord
corpus callosum
a thick band of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres and acts as a communication link between them.
cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
- need to know optic nerve (2), glossopharyngeal nerve (9), vagus nerve (10), accessory nerve (11)
optic nerve
the nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
glossopharyngeal nerve
provides motor, parasympathetic and sensory information to your mouth and throat, and helps raise part of your throat, enabling swallowing.
vagus nerve
responsible for the regulation of internal organ functions, such as digestion, heart rate, and respiratory rate, as well as vasomotor activity, and certain reflex actions, such as coughing, sneezing, swallowing, and vomiting
accessory nerve
a motor nerve that controls the muscles in the neck and shoulders, and the larynx, which are responsible for tilting, rotating, and flexing the neck, and elevating the shoulder
diencephalon
thalamus and hypothalamus
- helps with coordinating with the endocrine system to release hormones, relaying sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex, and regulating circadian rhythms (the sleep wake cycle)
dorsal horns
- functions as an intermediary processing center for information, comprising a complex network of excitatory and inhibitory interneurons as well as projection neurons that transmit the processed somatosensory information from the spinal cord to the brain
- receives sensory information from the body's skin and deeper tissues through primary afferent fibers
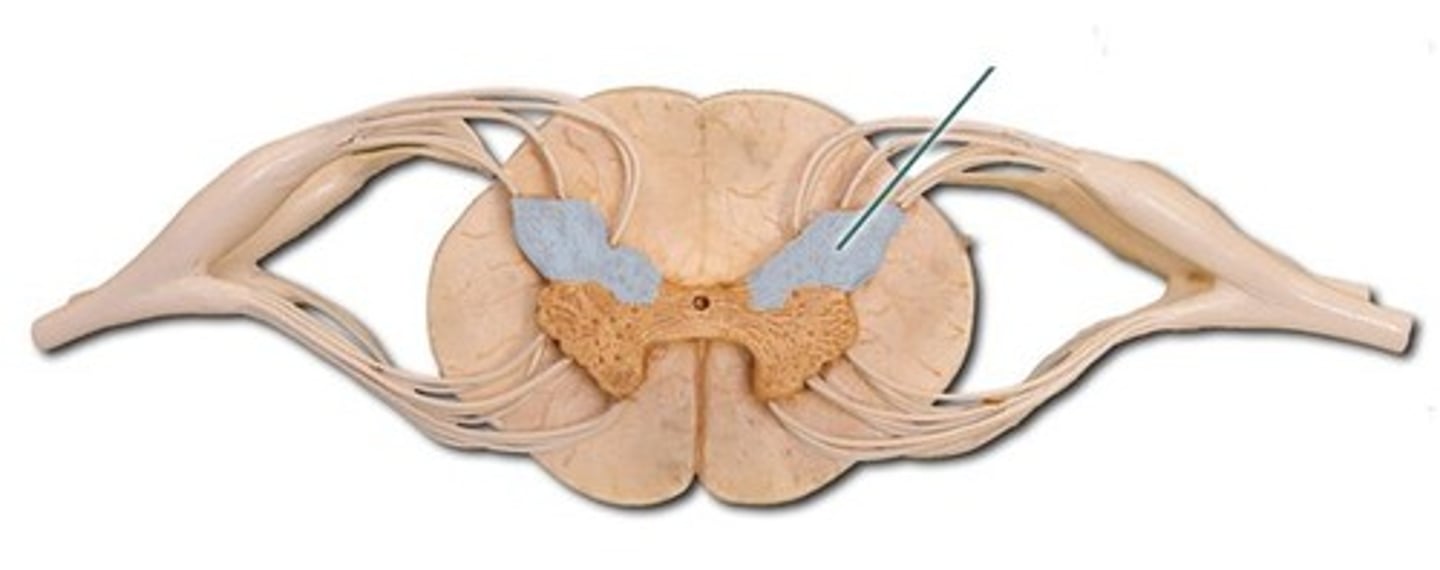
dorsal roots
contain sensory (afferent) fibers from sensory neurons in dorsal root ganglia and conduct impulses from peripheral receptors
dorsal root ganglia
a set of nodule-like structures in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that play a key role in pain perception and sensory information transmission
- transmit sensory information from the periphery to the central nervous system (CNS) such as touch, temperature, itch, pain, and proprioception
efferent division of the PNS
carries motor commands from the CNS to muscles, glands, and adipose tissue
forebrain
the largest and most complicated region of the brain, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, and cerebrum.
- helps with function in thinking, senses, movement, sleep, emotions, and pain
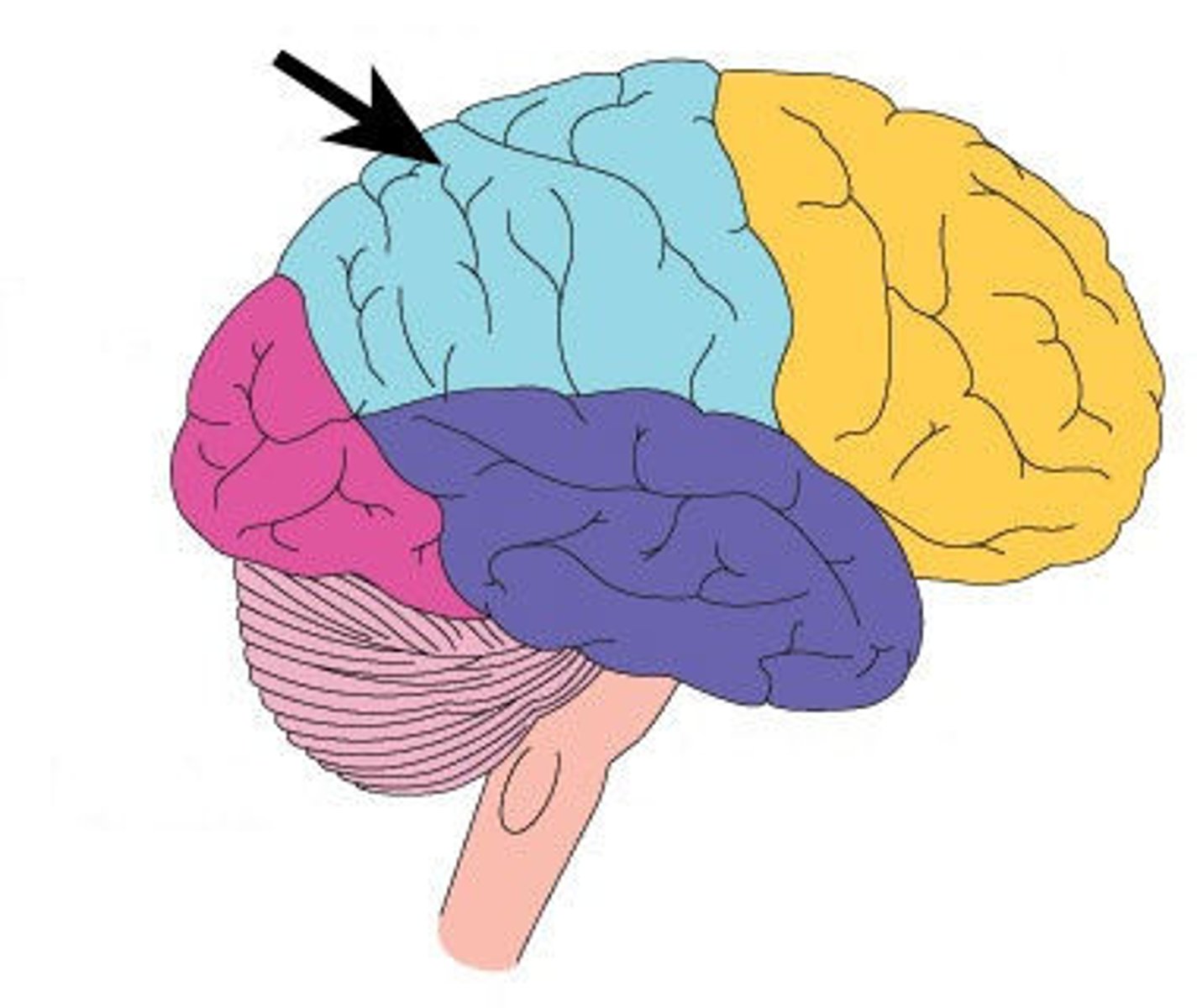
frontal lobe
a region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
ganglion
a cluster of nerve cell bodies, often of similar function, located in the PNS.
gray matter
brain and spinal cord tissue that appears gray with the naked eye; consists mainly of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) and lacks myelinated axons.
gyrus
a ridged or raised portion of a convoluted brain surface.
hindbrain
medulla, pons, cerebellum
- an area of the brain that coordinates information coming into and out of the spinal cord
hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
limbic system
neural system (including the hippocampus, amygdala, and hypothalamus) located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives.
medulla oblongata
part of the brainstem that controls vital life-sustaining functions such as heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, and digestion.
midbrain
a small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
occipital lobe
a region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
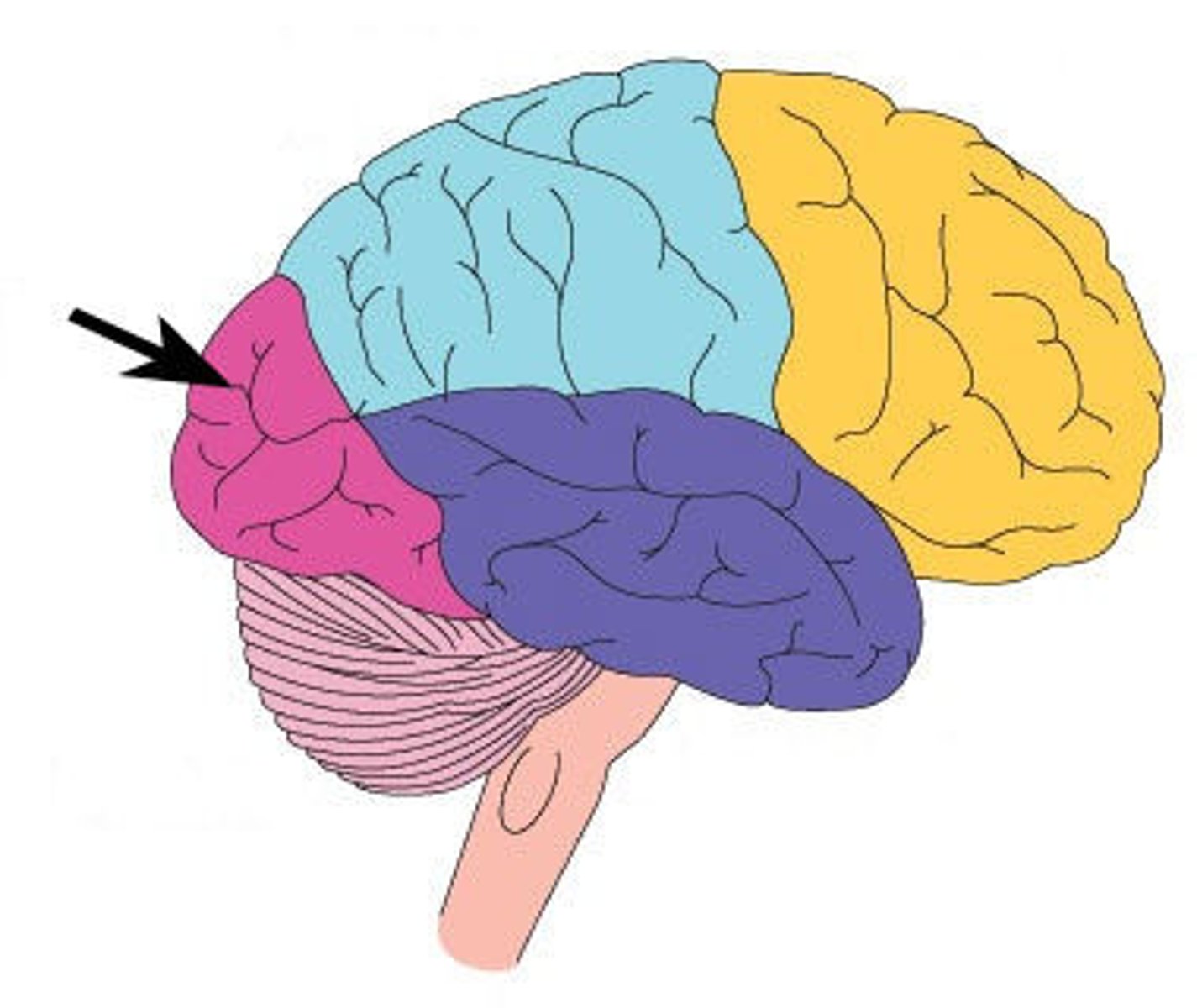
parietal lobe
a region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch.
pathway
centers and tracts that connect the CNS with body organs and systems
pituitary gland
referred to as the "master gland" because it monitors and regulates many bodily functions through the hormones that it produces, including:
- Growth and sexual/reproductive development and function
- Glands (thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and gonads)
- Organs (kidneys, uterus, and breasts)
pons
a part of the brainstem that connects the brain to the spinal cord and medulla oblongata
- a key merging point for several cranial nerves, works with the medulla oblongata to regulate breathing, handles unconscious processes and jobs such as the sleep-wake cycle