Surgery/Hospital Care 597: Wounds
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are acute vs. chronic wounds?
Acute: Normal stages of healing within 4 weeks
Chronic: Do NOT progress through normal healing (often stalled); minimal healing within 4 weeks
What are the phases of wound healing? (4)
1. Hemostasis: Within minutes post-injury; platelets aggregate at injury site to form fibrin
2. Inflammation: Bacteria & debris are phagocytized and removed; factors released that cause migration & division of cells involved in proliferative phase
3. Proliferation: Angiogenesis, collagen deposition, granulation tissue formation, epithelialization, and wound contraction
4. Remodeling: Collagen is remodeled and realigned along tension lines; cells that are no longer needed are removed by apoptosis
What is healing by primary intention? (2)
Occurs when tissue is cleanly incised and anatomically re-approximated
Healing usually proceeds WITHOUT disruption/complication
What is healing by secondary intention? (2)
Wound is left open and eventually heals through granulation tissue + eventual coverage of defect (migration of epithelial cells)
Granulation tissue composed of new capillaries, fibroblasts, and provisional extracellular matrix
Epithelialization happens in which direction?
Horizontally ONLY
Granulation happens in which direction?
Bottom-to-top
What are the biggest comorbidities that interfere with wound healing?
Smoking
Diabetes (hyperglycemia)
What is the progression of a normal surgical scar? (4)
Sterile dressing left in place at least 48 hours
Swelling (by 6 days)
Rebuilding (healing ridge normal after 1st week)
Remodeling (6 mos-2 years)
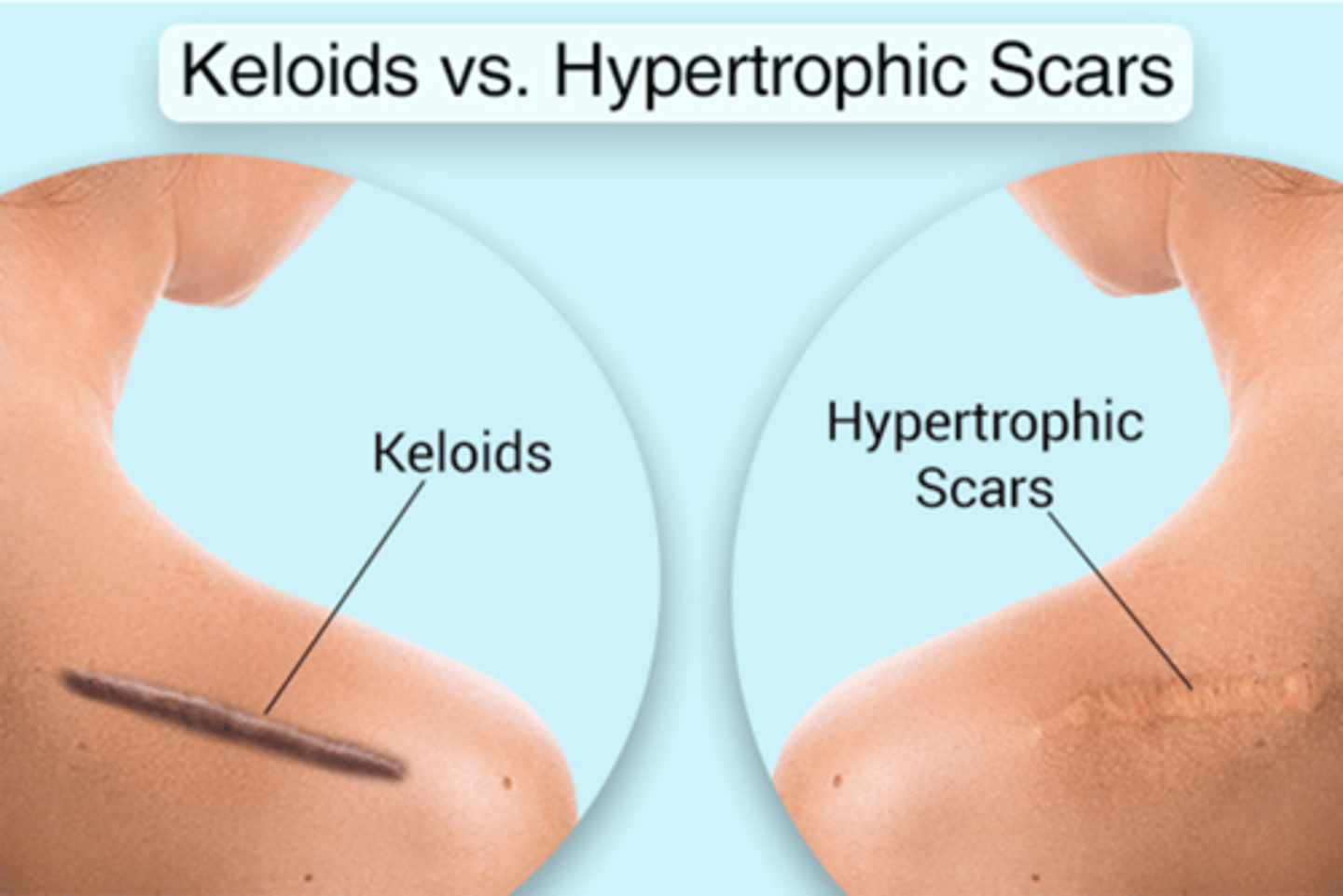
What are 2 types of atypical scars?
Hypertrophic scar (erythematous, thickened, raised; WITHIN boundaries of original surgical incision)
Keloid scar (erythematous, bulging, firm, focally raised; EXTENDS past boundaries of original surgical excision)
What are pressure/decubitus ulcers?
Ulcers caused by pressure, friction/shear
Stage 1 occurs in as little as 2-6 hours
What are skin grafts vs. flaps?
Grafts: Do NOT maintain original blood supply (must rely on recipient region for nutrients/blood supply)
Flaps: Comes with blood supply
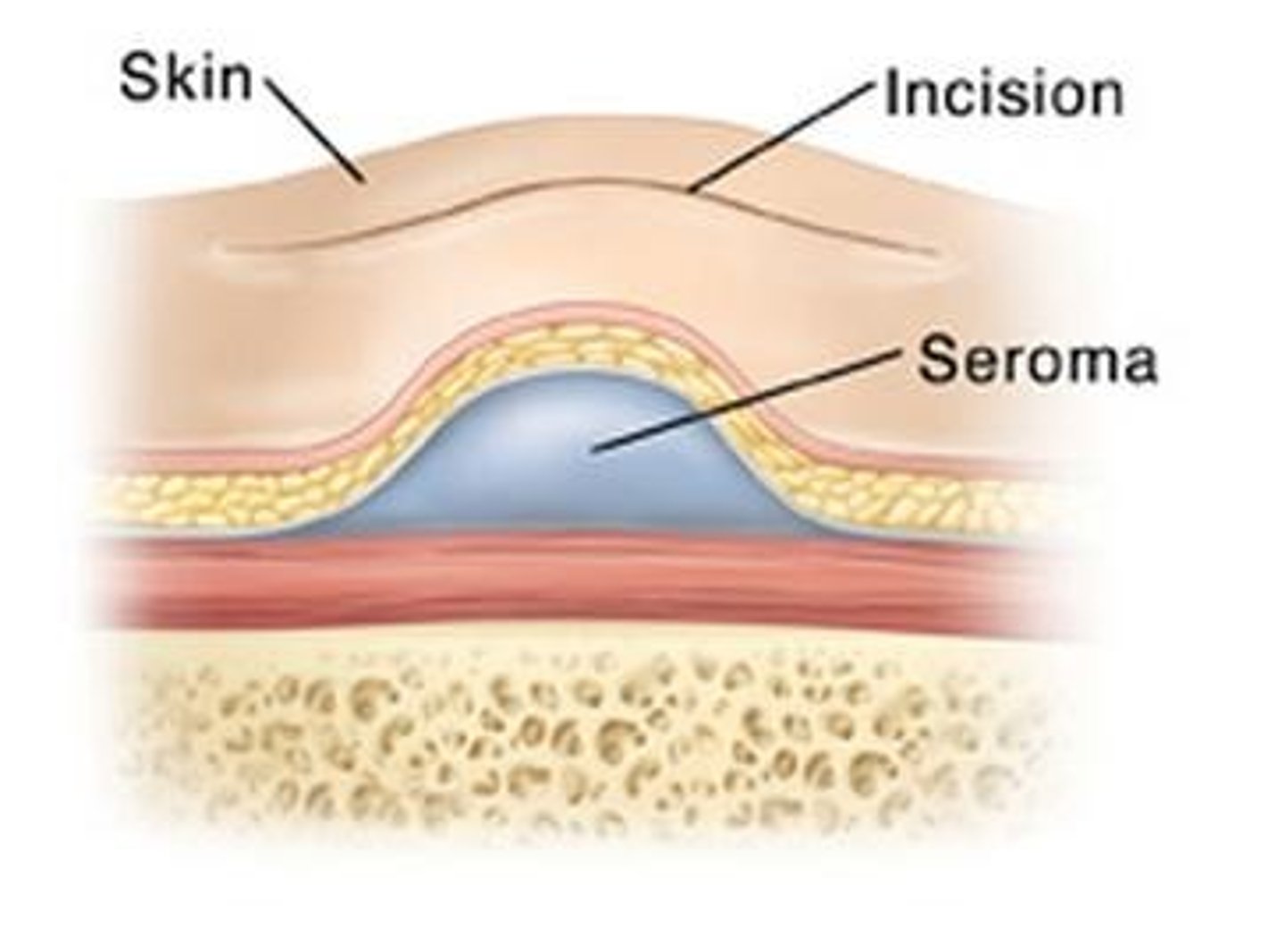
What is a seroma?
- define
- tx
Pocket of inflammatory fluid/secretions produced by injured and dying cells
Tx: Observation (most resorb) vs. aspiration
What is a hematoma? (2)
Abnormal collection of blood OUTSIDE blood vessel that impairs wound healing
Need to address and evacuate expanding hematomas
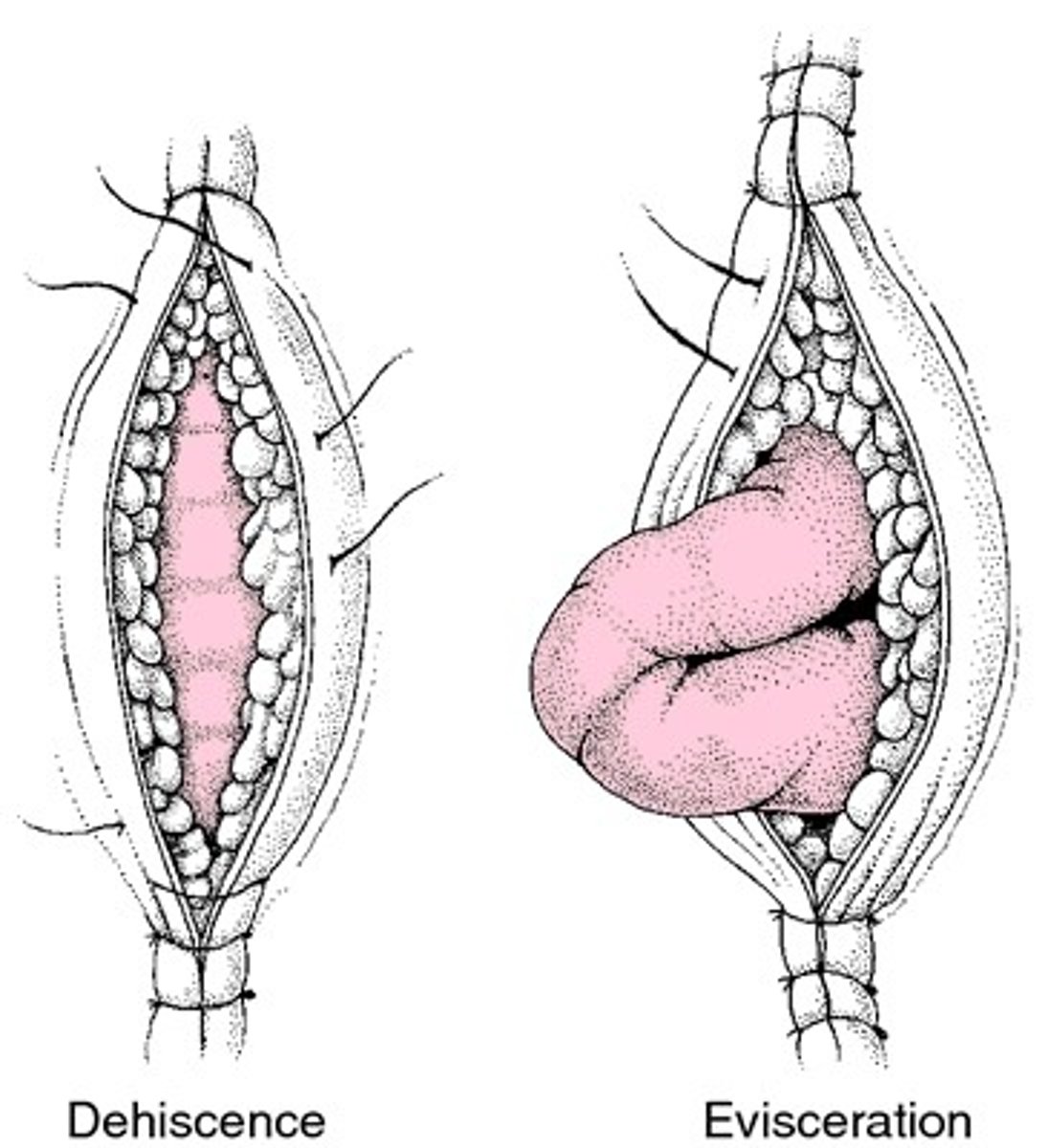
What is dehiscence?
- define
- timeline
Separation of wound incision d/t improper closure
Typically occurs 5-8 days after surgery
When do surgical site infections (SSI) typically happen?
- superficial
- deep
Superficial: Day 4-5 post-op
Deep: Day 7 post-op
What is an eschar vs. a scab?
Eschar: Dead tissue found in a full thickness wound
Scab: Crust has formed by coagulation of blood/exudate on superficial/partial thickness wounds
What are the options for debridement? (4)
Sharp (dead tissue removed with sharp instrument)
Autolytic (moist dressing allows body to break down dead tissue)
Enzymatic (chemical applied to break down dead tissue)
Mechanical (taking off top layer - wet-to-dry)
What is Wound VAC?
Vacuum-controlled assisted wound closure where negative pressure is continuously applied
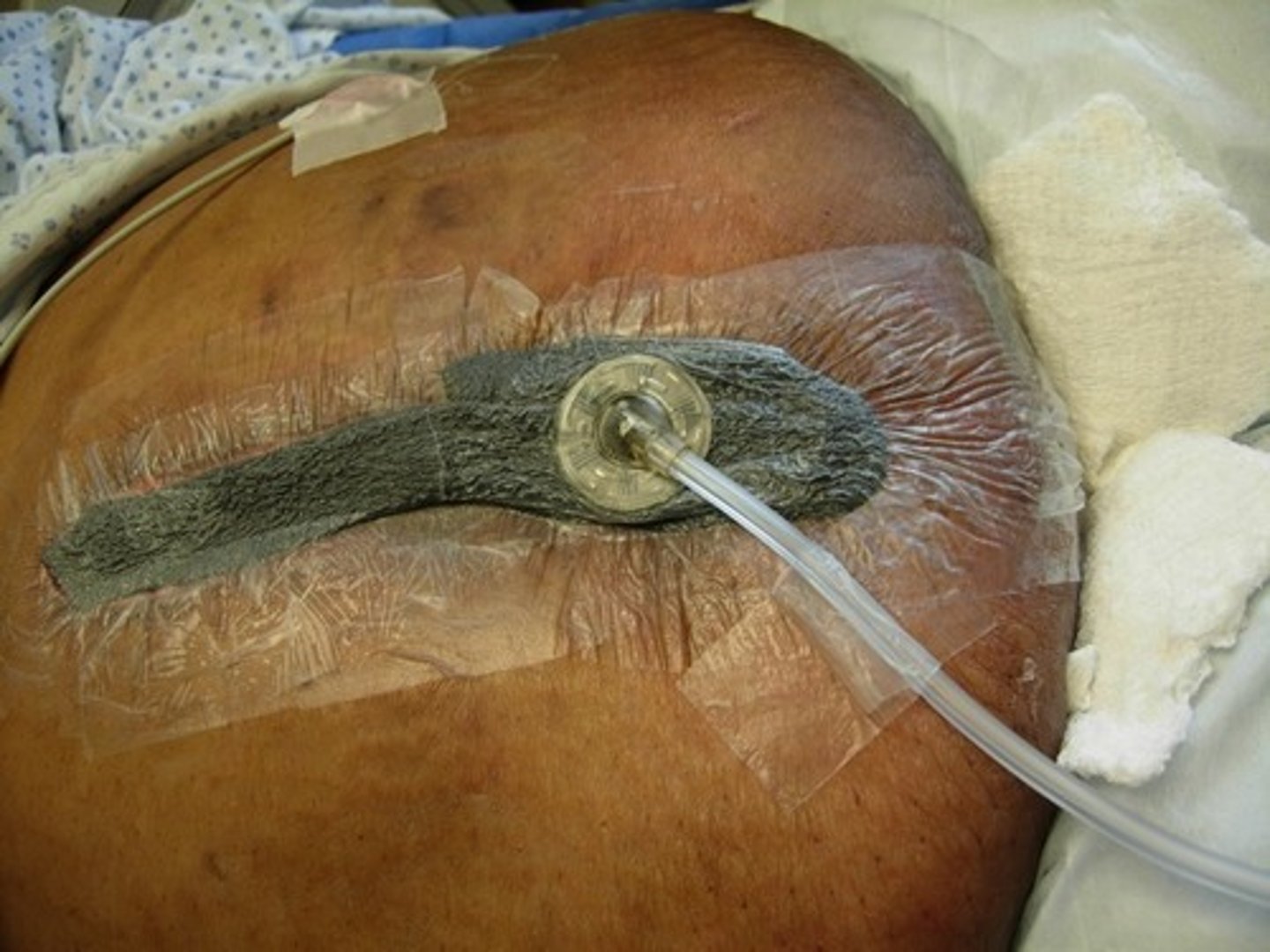
What is a surgical drain?
Tube used to remove pus/blood/other fluids from a wound, space, or body cavity to prevent fluid accumulation
What is an ostomy?
Surgical opening resulting in a stoma, used to drain waste products OR provide food/medicine/hydration
What are the most common causes of fistulas? (3)
Prior trauma/surgery
Cancer
Infection/inflammation