An Introduction to Metabolism
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
catabolism vs anabolism
catabolism = releases energy
anabolism = requires energy
_______________ is the sum of all chemical reactions in a cell, and it is essential for maintaining life.
Metabolism
_________________ involves the ________________ (like carbohydrates and fats) into simpler molecules (CO₂ and H₂O), releasing (yielding) energy in the process.
Catabolism, breakdown of fuels
_________________ is the process of ________________ from simpler precursors, which requires energy input
Anabolism, building complex molecules
________________ can function in both anabolic and catabolic roles, depending on the cell's needs.
Amphibolic pathways
Biosynthetic (anabolic) and degradative (catabolic) pathways are _____________, even though they may share intermediates and enzymes
distinct
Energy derived from catabolism is used for essential functions like ________________
- muscle contraction and work movements
- active transport of molecules
- biosynthesis of biomolecules from precursors
_______________ obtain energy through the _______________ of organic food, such as carbohydrates
Chemotrophs, oxidation
______________ derive energy from sunlight.
Phototrophs
Life needs energy: Living organisms are built from complex structures, and the ultimate source of energy on Earth is _______________
sunlight.
_____________ are organisms that can produce their own food using _____________ or chemical energy
Autotrophs, light
examples of autotrophs
plants, algae, phytoplankton, some bacteria
____________ do not make their own food and instead ______________ other organisms for energy
heterotrophs, consume
examples of heterotrophs
animals, fungi, most protozoa, most bacteria
applying the First Law of Thermodynamics to living organisms
Living organisms cannot create or destroy energy from nothing. They can only transform energy from one form to another.
applying the Second Law of Thermodynamics to living organisms
In the process of transforming energy, living organisms must increase the entropy (disorder) of the universe.
To maintain organization within themselves, living organisms must extract usable energy from their surroundings and release__________________ back into their surroundings
"useless energy" (in the form of heat)
_____________ are a series of reactions where molecules are ________________ in a stepwise manner.
Metabolic pathways, degraded or synthesized
ATP is the energy currency of life and can be produced through the _______________
oxidation of carbon fuels.
Metabolic pathways are highly ___________________ to ensure efficient energy use.
regulated
intermediary metabolism
metabolism at the cellular level
In order to construct a metabolic pathway, two criteria must be met:
1.) individual reactions must be specific.
2.) pathway must be thermodynamically favorable.
thermodynamically unfavorable reactions can be driven by coupling them with favorable ones, often utilizing ___________________
ATP hydrolysis
_________________ always have to _______________. If one molecule is oxidized, then another molecule has to be reduced
Redox reactions, occur together
oxidation vs reduction
Oxidation is loss of electrons
Reduction is gain of electrons
oxidizing agents are called ________________
electron acceptors
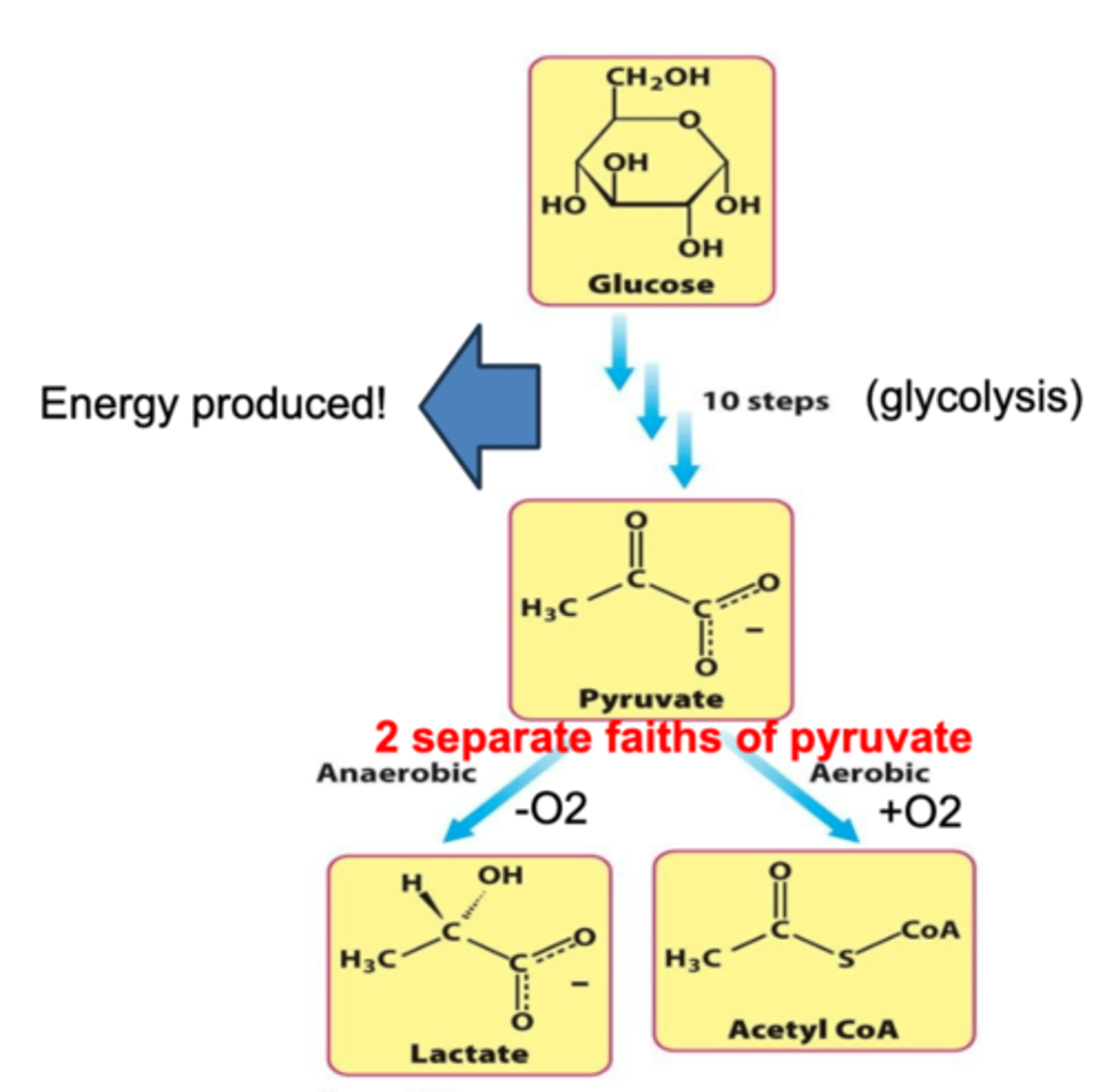
steps of glucose metabolism
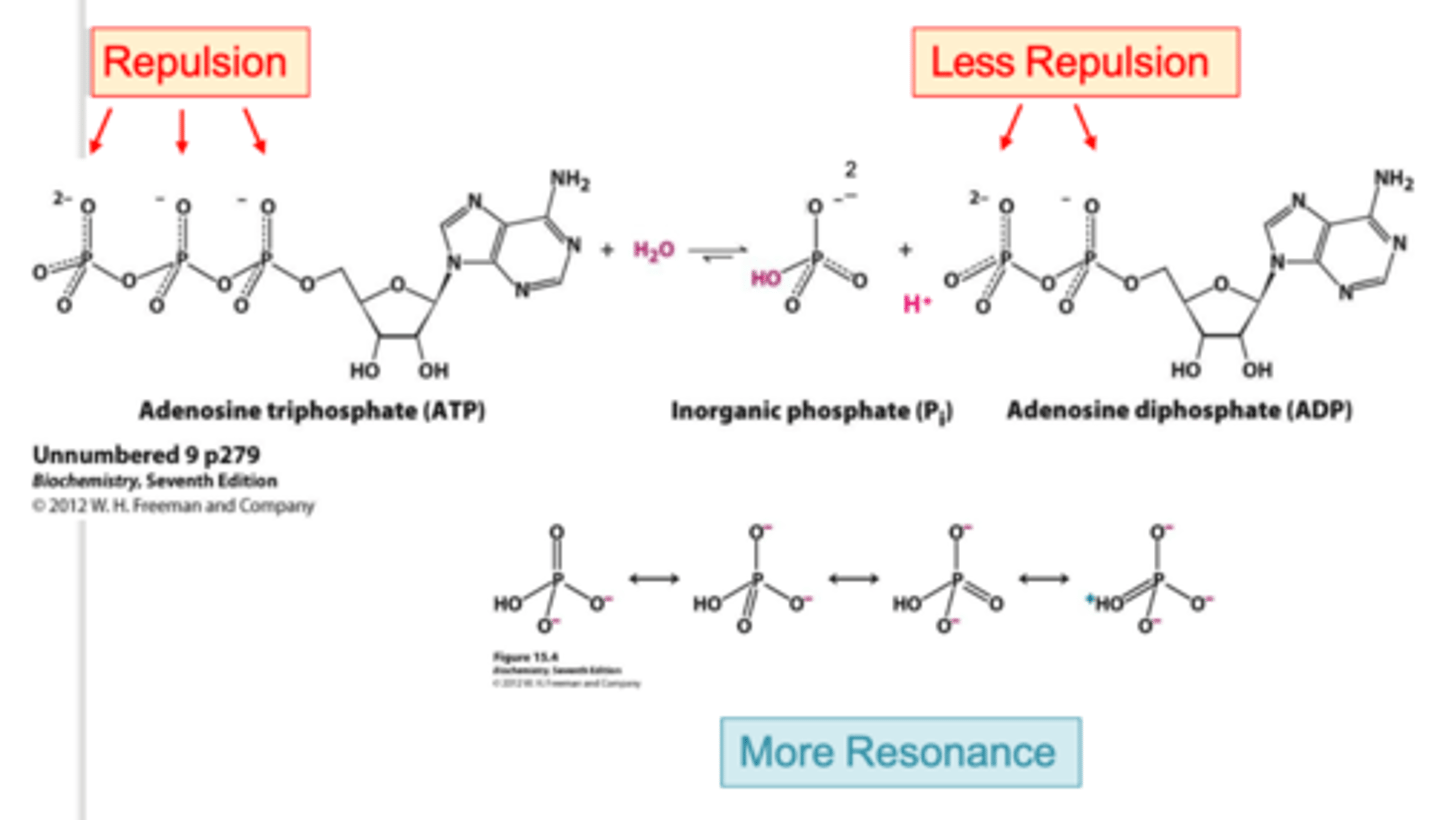
ATP hydrolysis releases energy, making ATP a critical energy source for various biological processes. The "high energy" of ATP is due to several factors:
- Electrostatic repulsion between negatively charged phosphate groups.
- Increased resonance stabilization of the products after hydrolysis.
ATP is often involved in ________________ processes
coupled
ATP hydrolysis releases energy, meaning that it's
exergonic
Energy derived from fuels or light is converted into ________________, the cellular energy currency.
adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
In biological organisms, the coupling mechanism typically involves _____________, a "high-energy" molecule. A stockpile of ATP is built up during _______________ for such coupling purposes
ATP, catabolism
The "high energy" of ATP is released upon _______________
its hydrolysis to either AMP or ADP.
exergonic vs endergonic reactions

ATP hydrolysis equation
provides the energy for glucose phosphorylation

_______________ is the standard free energy of hydrolysis, a measure of how easily a molecule can transfer a phosphate group to another molecule.
Phosphoryl-transfer potential
ATP has a _____________ phosphoryl-transfer potential than glycerol 3-phosphate.
higher
Compounds with high phosphoryl-transfer potential include
1.) phosphoenolpyruvate
2.) 1,3 biphosphoglycerate
3.) creatine phosphate
4.) ATP (to ADP)
Compounds with low phosphoryl-transfer potential include
1.) glucose 6-phosphate
2.) glycerol 3-phosphate
The ________________ ensures that ATP is constantly ________________ to provide energy to power the cell
ATP-ADP cycle, recycled
The _____________ of carbon atoms in fuels (like carbohydrates and fats) is a significant source of cellular energy.
oxidation
The more reduced a carbon atom is, the ____________________ is released upon oxidation.
more free energy
Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons. Such reactions must be coupled with reactions that gain electrons, terming the paired reactions:
oxidation-reduction (redox) reactions
During oxidation, carbon atoms lose electrons, which are then transferred to oxygen, forming ______________
CO₂ and H₂O.
cellular respiration equation

Compounds with the most to least energy

Fats are more efficient fuels than ________________
carbohydrates
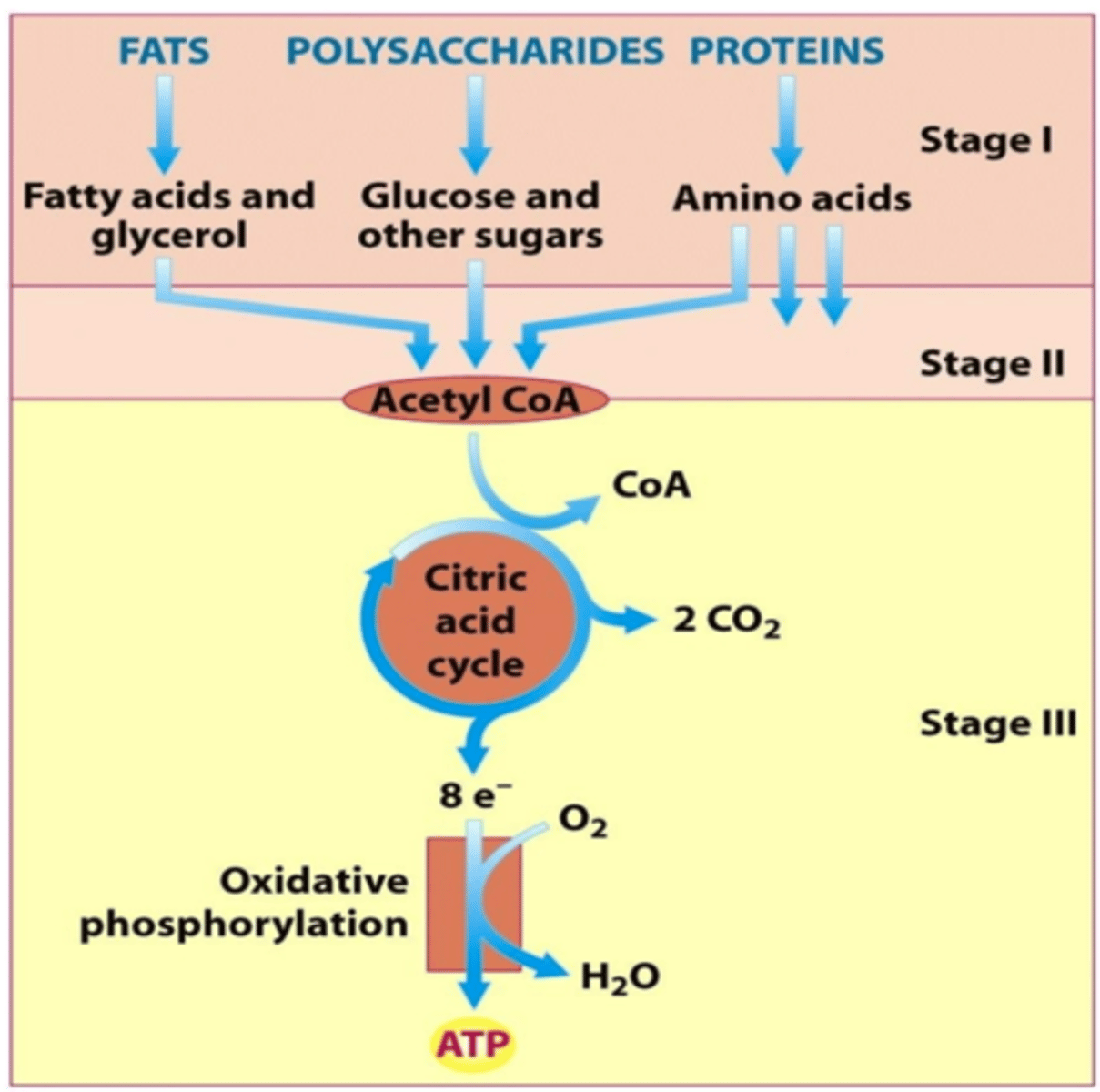
three stages of catabolism
Stage 1: Digestion of macromolecules into building blocks
Stage 2: Conversion of building blocks to acetyl-CoA
Stage 3: Oxidation of acetyl-CoA via citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation in the ETC
____________________ are activated carriers of electrons for fuel oxidation.
NADH/NAD+ and FADH2/FAD
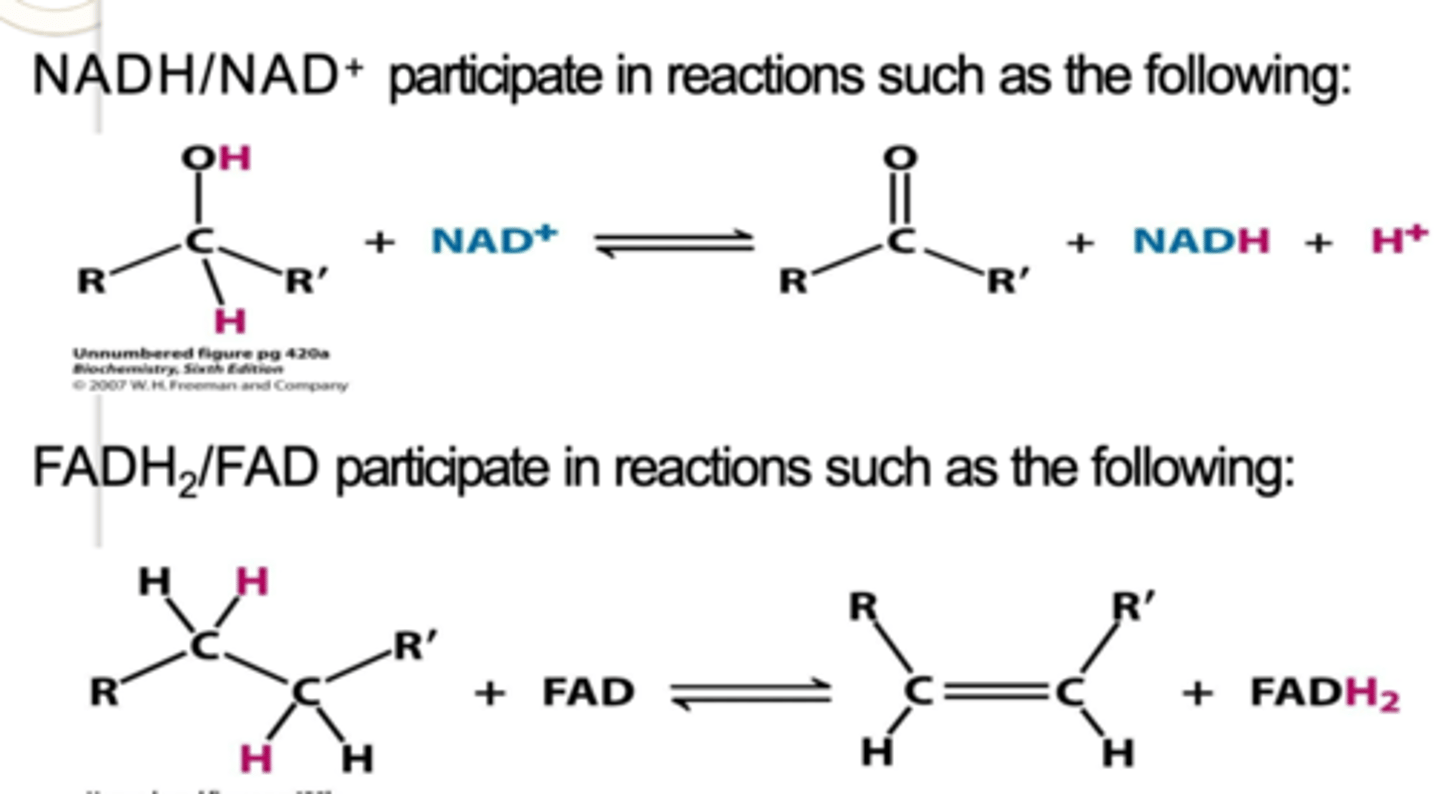
Many _________________, including NAD+ and FAD, are derived from water-soluble vitamins, particularly the B vitamins, which are the only type of vitamins that can function as ________________.
activated carriers, coenzymes
What type of vitamins play a variety of roles, but do NOT serve as coenzymes?
Vitamins A, C, D, E, and K
Water-soluble vitamins include
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin)
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenate)
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Vitamin C
ascorbic acid, functions as an antioxidant
Fat-soluble vitamins include
- Vitamin D (calciferol), for calcium metabolism
- Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol), an antioxidant
- Vitamin A (retinol), for vision
- Vitamin K, for blood coagulation
What are the 6 different types of metabolic reactions?
1.) Oxidation/reduction: (electron transfer)
2.) Ligation: (requiring ATP cleavage for the formation of covalent bonds)
3.) Isomerization: (rearrangement of atoms to form isomers)
4.) Group transfer: (transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another)
5.) Hydrolysis: (cleavage of bonds by the addition of water)
6.) Addition/removal of functional groups
Oxidation is considered by loss of electrons, loss of hydrogen, or ________________
gain of oxygen
Oxidation/reduction:
(electron transfer)

Ligation:
(requiring ATP cleavage for the formation of covalent bonds)
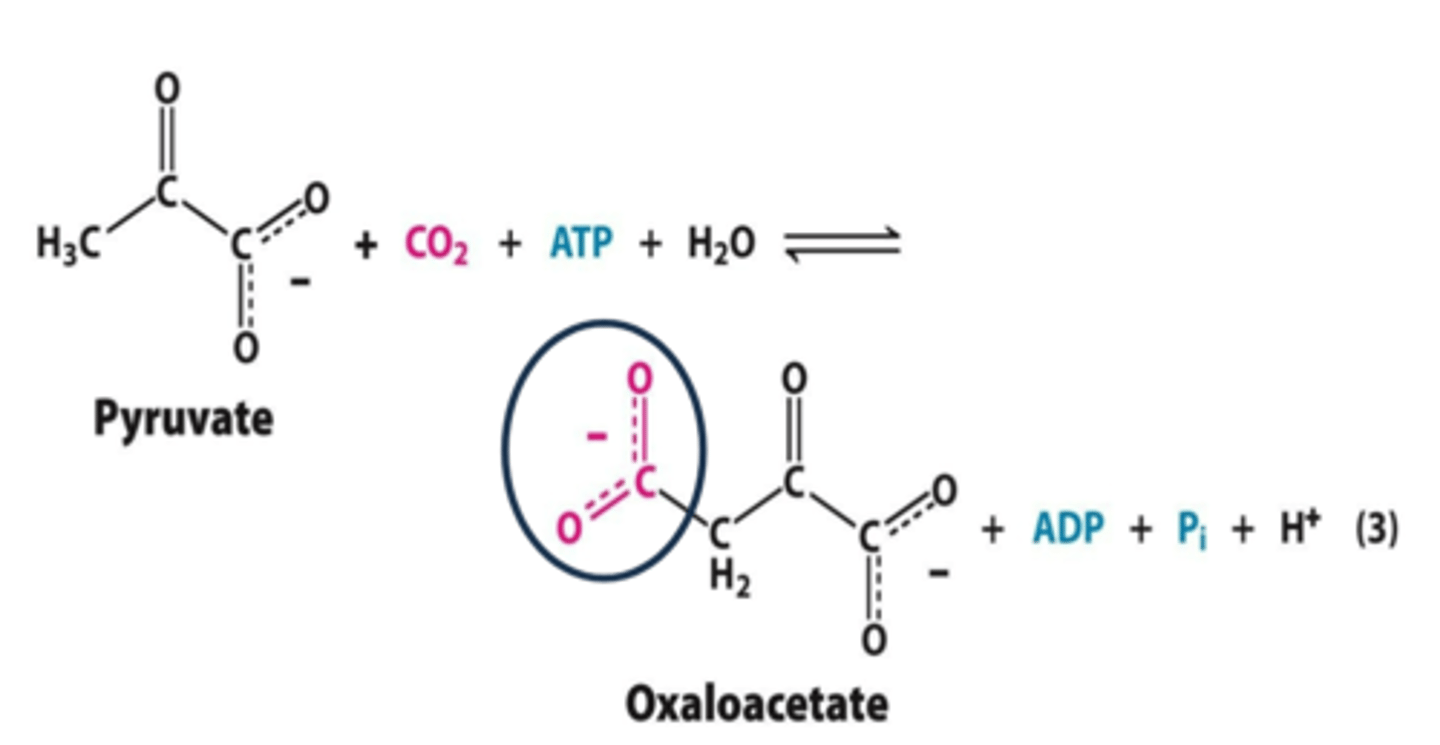
Isomerization:
(rearrangement of atoms to form isomers)
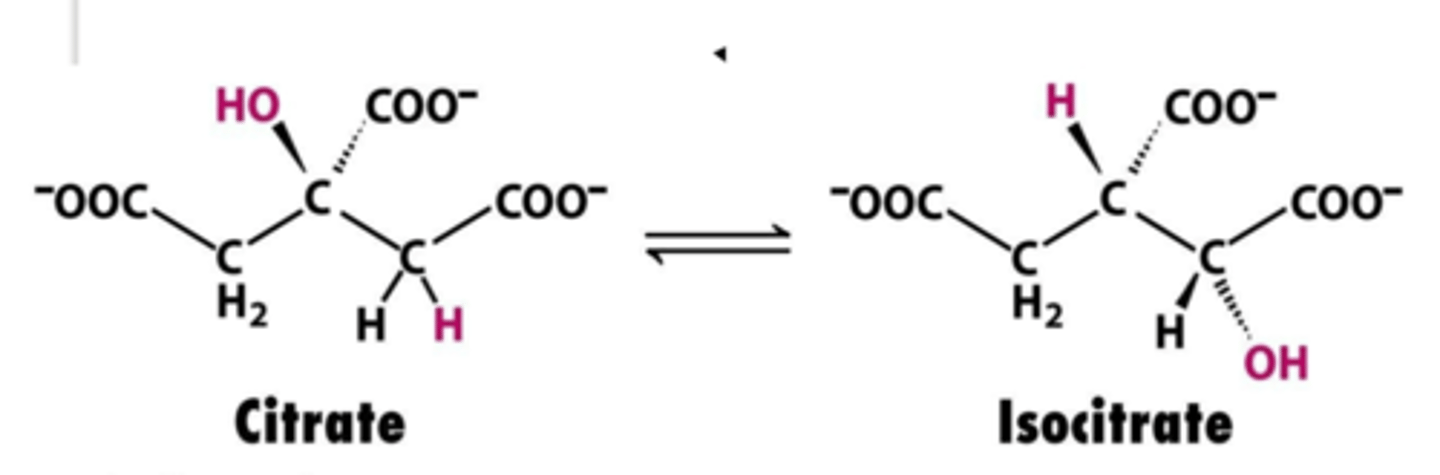
Group transfer:
(transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another)

Hydrolysis:
(cleavage of bonds by the addition of water)
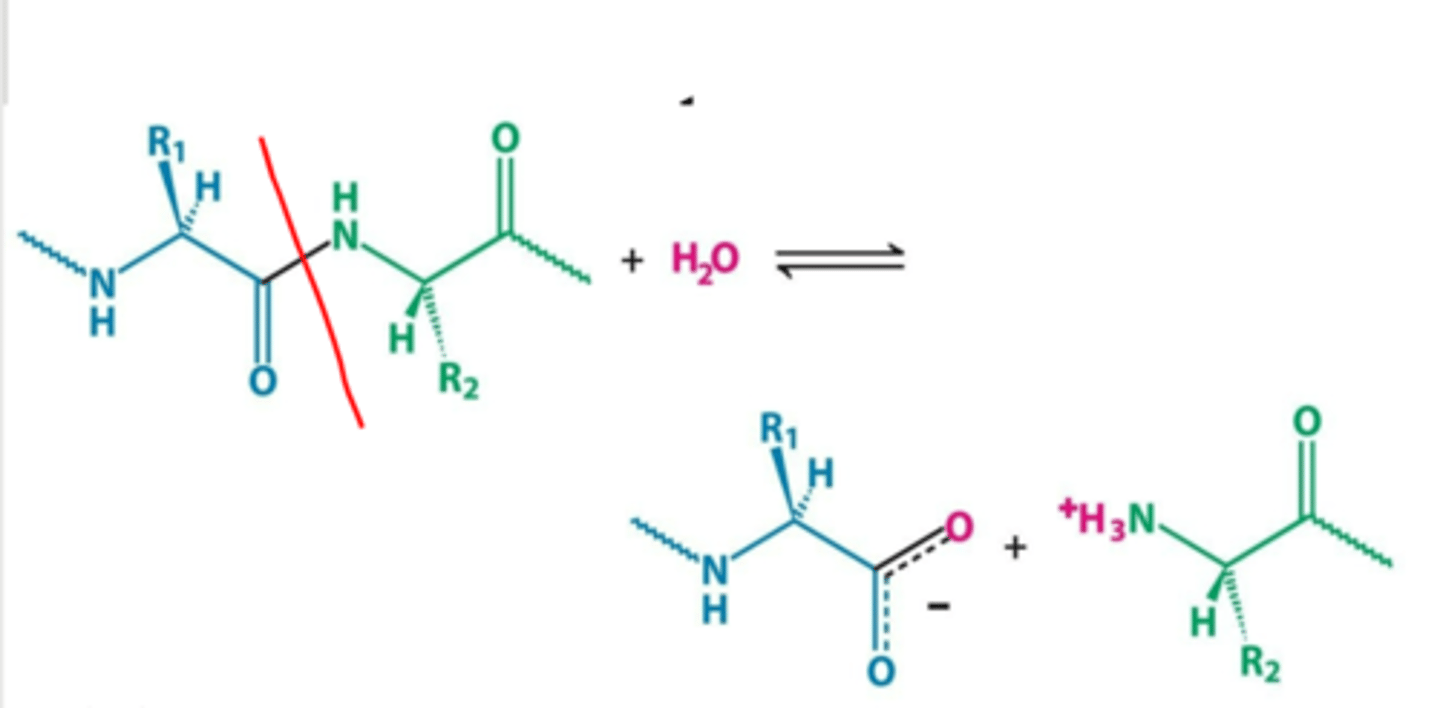
Addition/removal of functional groups
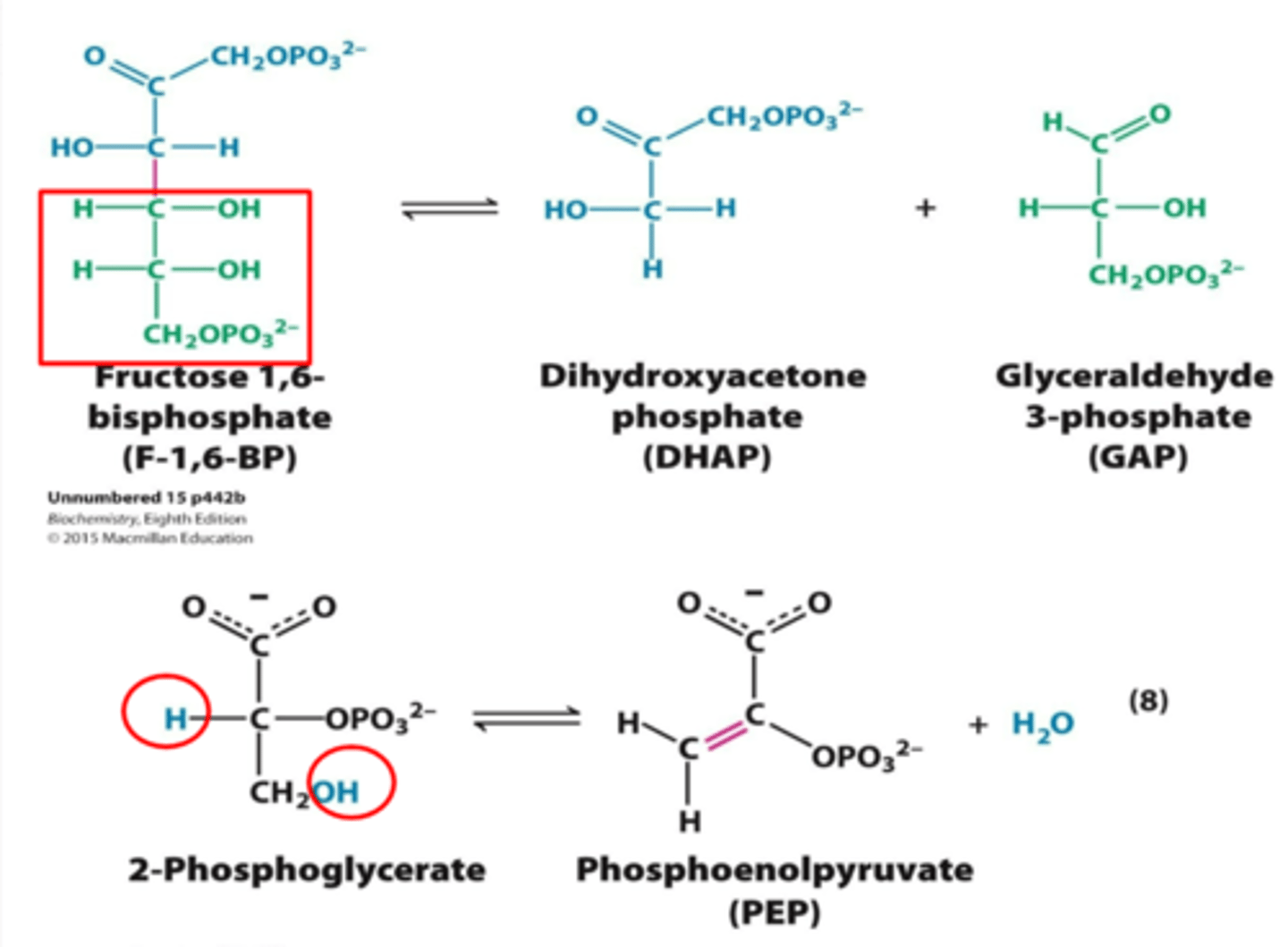
Two common means are used to assess energy status:
energy charge and phosphorylation potential
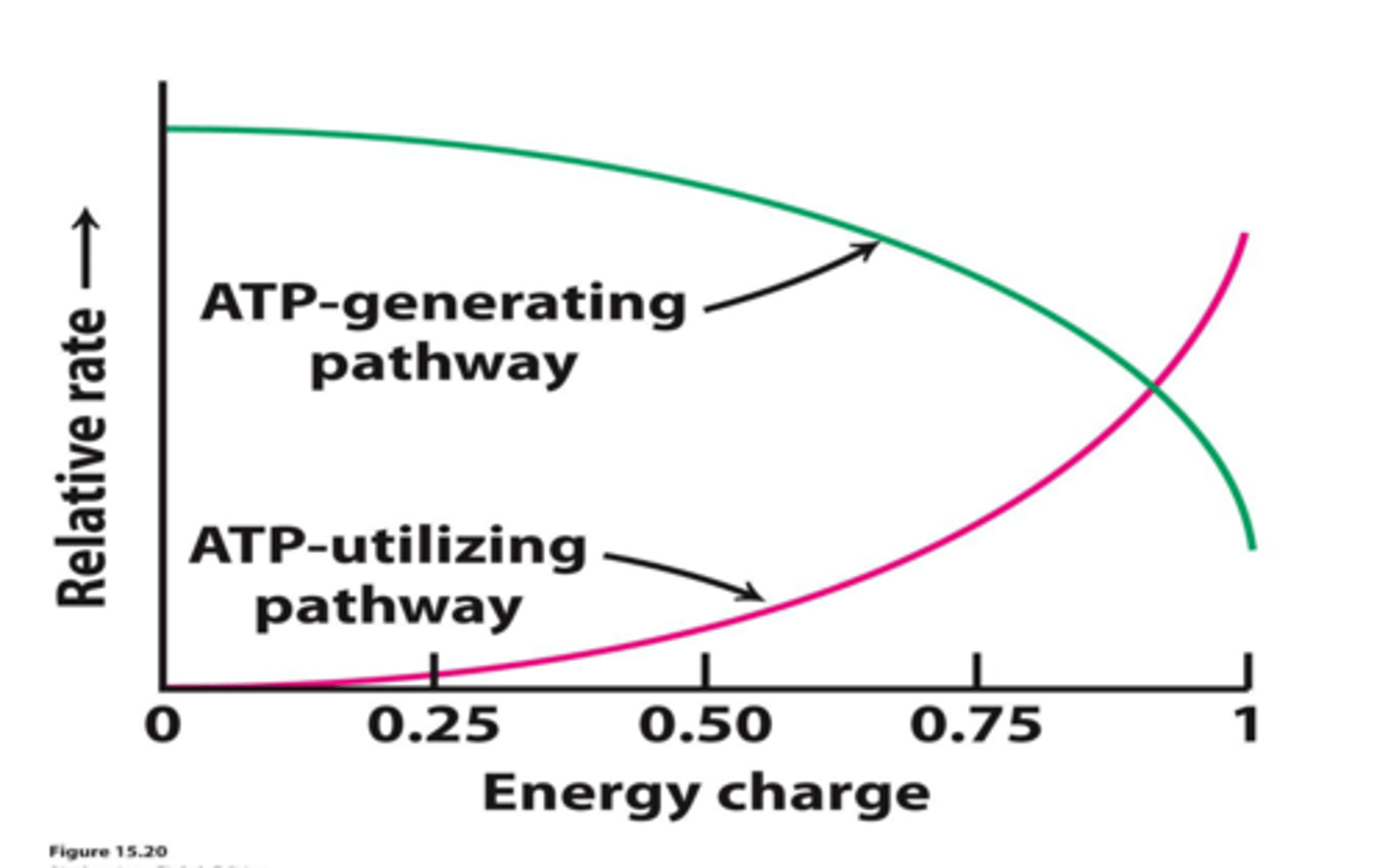
The __________________ is an indicator of the relative energy available to a cell as ATP.
energy charge (EC)
(EC = 0, minimal, or no ATP)
(EC = 1, maximum ATP)
Many reactions in metabolism are controlled by the
energy charge
Aspects of metabolism may have evolved from
an RNA world
The fact that ATP, NADH, FADH2 and coenzyme A all contain ______________ may be a reflection of the role of RNA in early metabolism.
adenosine diphosphate units
In the postulated RNA world, RNA served both as ______________
a catalyst and an information storage molecule.