General Pathology
1/300
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
301 Terms
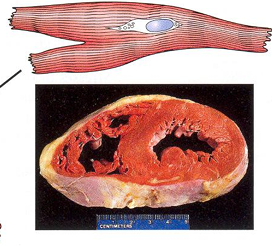
Normal myocyte
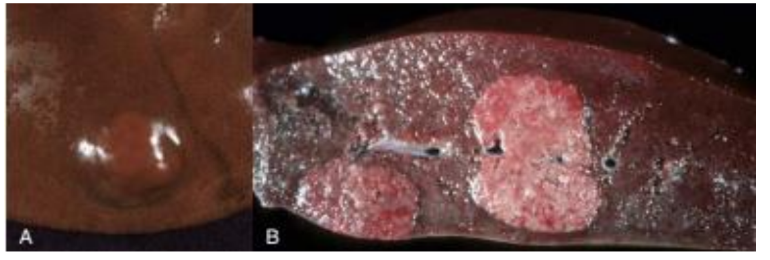
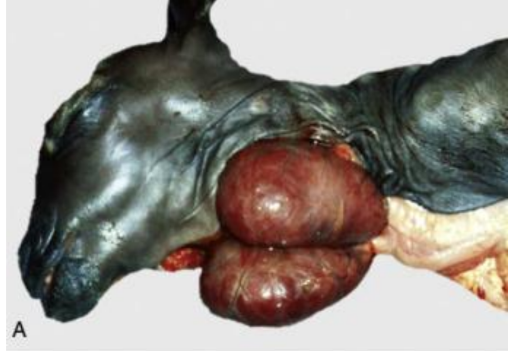
Nodular hyperplasia of the liver (dog)
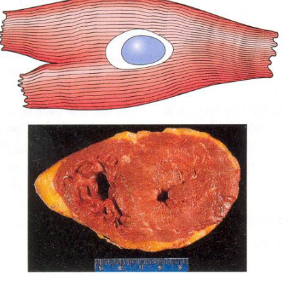
Hyperthrophy (adapted myocyte)
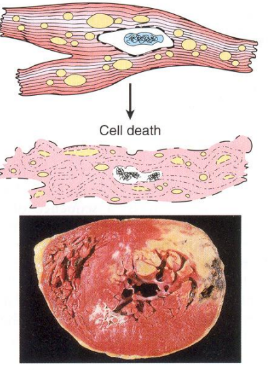
Reversible injured myocyte, cell death
What is Acute Cellular Swelling ?
Macroscopic = Organ is enlarged, heavier, pale, rounded edges. Kidneys, liver are particularly affected. In the brain, a small change can be fatal
Microscopic = Cells are swollen, pale, finely vacuolated with water vacuoles (swollen mitochondria/ER/Golgi cisternae)
Ballooning degeneration is the extreme from, due to poxiviruses in keratinocytes
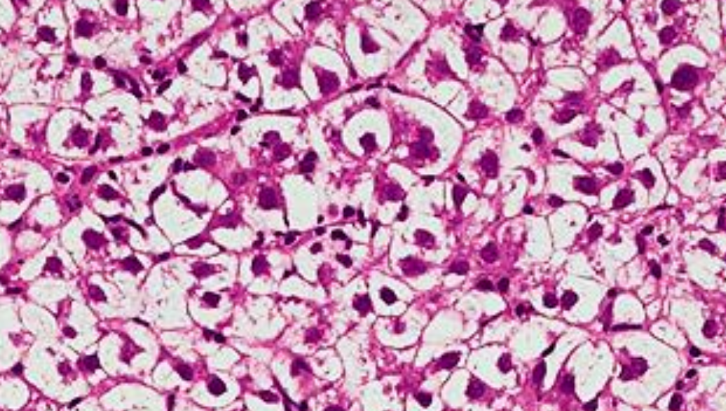
Hepatocytes swelling
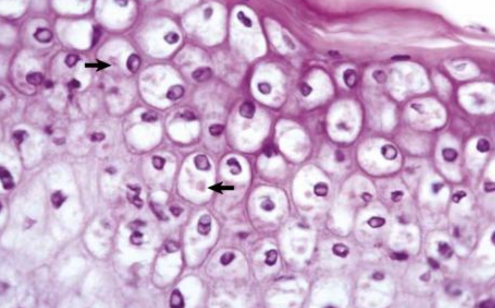
Ballooning degeneration
Hyperthrophy
Enlargement of an organ, as a result of increase in cell size ( amount of structural prot, organelles)
Cells that lack ability to replicate, no new C are formed
Due to: increased functional demand (myocardial hyperthrophy), hormonal stimulation, stimulation by GH
Hyperplasia
Increase in volume of tissue and/or organ, result in increase of number of C
Occurs often with hyperthrophy, especially as a consequence of hormonal stimulation
Hyperplasia affects C that CAN divide
Pathologic hyperplasia —> significant risk factor for tumor dvlppt (papillomaviruses, pyometra, goiter, prostatic hyperplasia, pathological wound healing with formation of keloid = chronic irritation)
Hyperplasia of the thyroid and hypertrophy in goat = massive enlargement = goiter
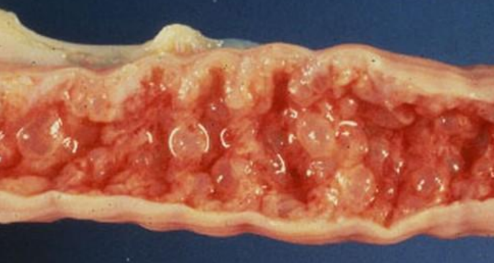
Pathological hyperplasia of uterus
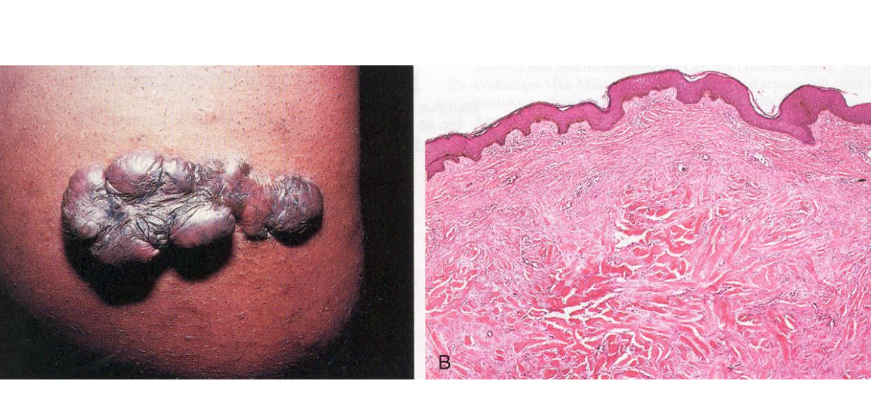
Chronic irritation = wound healing with keloid formation = Pathological Hyperplasia of skin (dermin with loads of collagen)
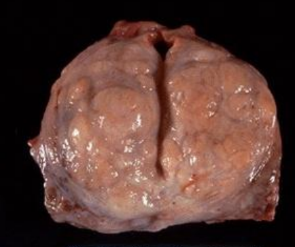
Prostatic hyperplasia

Hepatic Lipidosis = fatty liver = hepatic steatosis (fat degeneration)
Metaplasia
Replacement of mature (differenciated) C with another C type often with less differentiated ones), always pathological,
most common = squamous epithelial metaplasia or mesenchymal metaplasia with formation of bone/cartilage
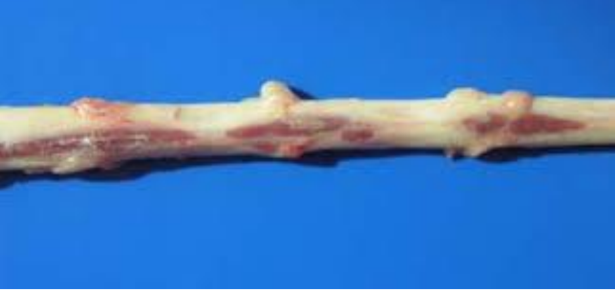
Osseous dural metaplasia = ossifying pachymeningitis
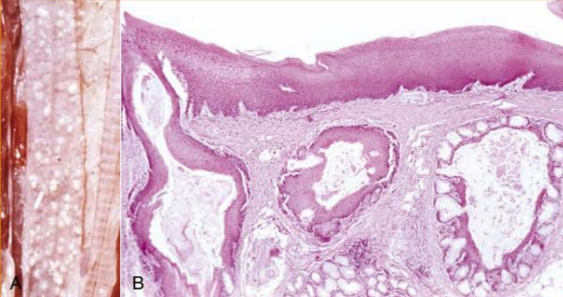
A = esophagus mucosa with white nodules, squamous metaplasia of glandular mucosa (due to avitaminosis A)
B = Avitaminosis A, replacement of mucosal epith and goblet C in glands, with keratinizing stratified squam epit
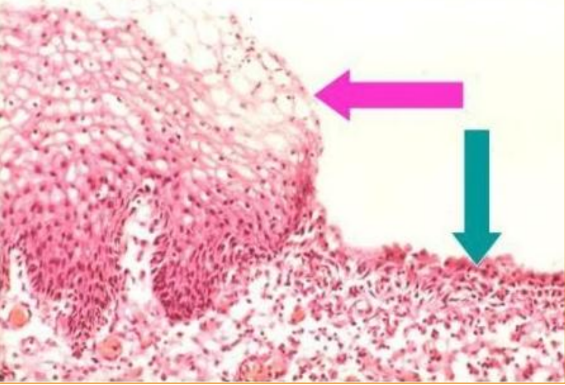
Squamous metaplasia of urinary bladder (from transitional to squamous epith)
Dysplasia
Abnormality in dvlppt/disorder of growth/differenciation
C are pleomorphic (C have various distinct forms), increase in nb of poorly differientiated C/immatue C (could be precursor of neoplasia)
Always pathological
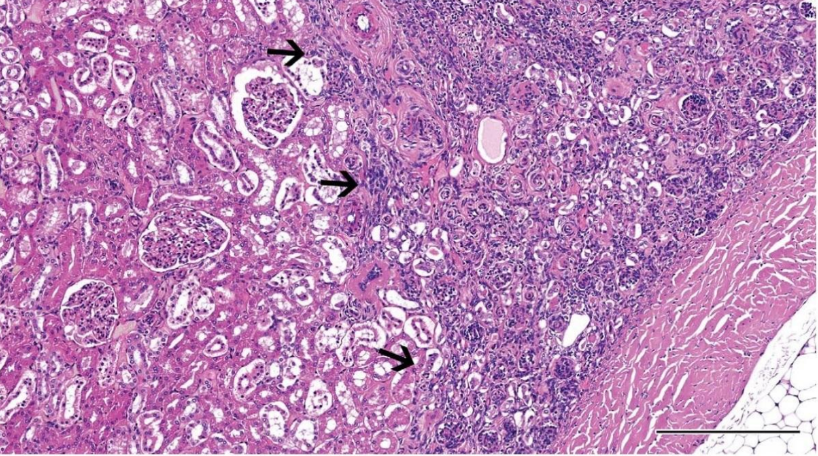
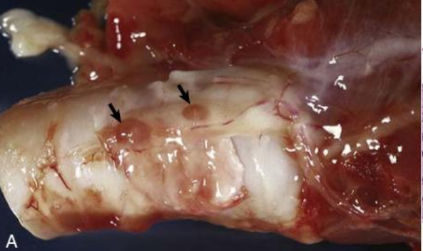
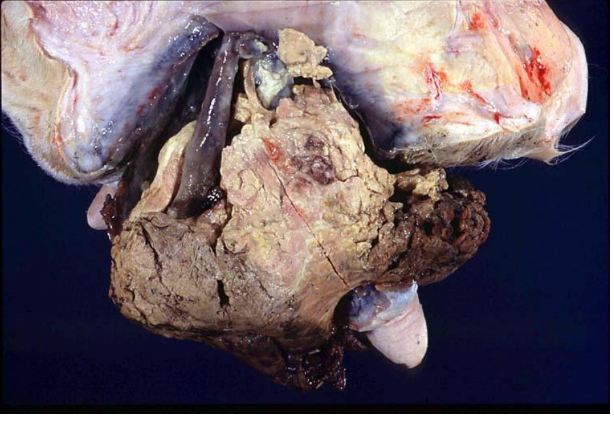
Renal dysplasia (dog)
(immature glomeruli, proliferation of arterioles)
Atrophy
Decrease in the mass of a tissue/organ, that have previously reached NORMAL size.
Reduction in size and/or nb C (volumetric and/or numerical atrophy)
Differs from hypoplasia, where organ NEVER reaches its normal size
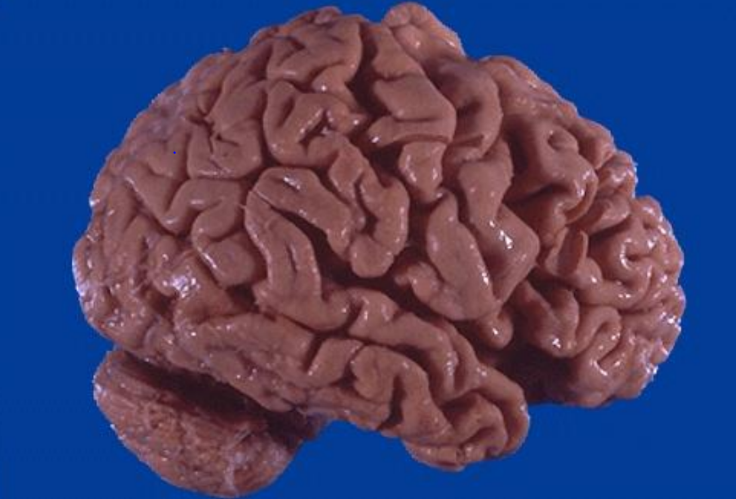
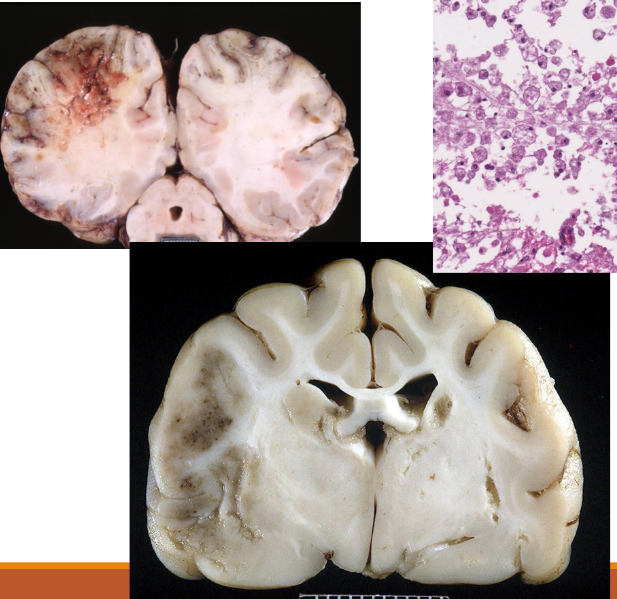
Atrophy of the brain
atrophic C (smaller/reduced functions), atrophic organs (reduced V and weight)
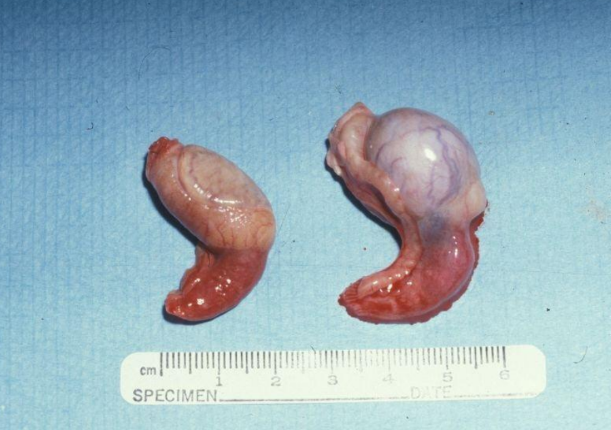
Atrophy of the testicle on the left
Atrophy of the thyroid (dog)
transparent and barely noticeable
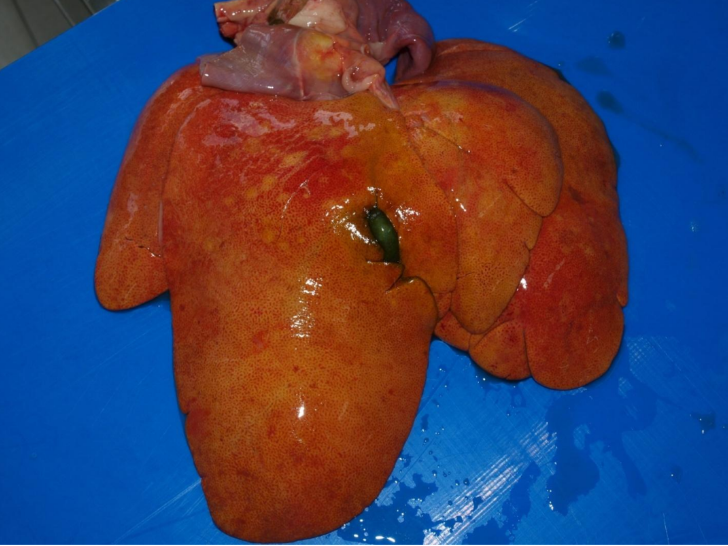
Hepatic lipidosis or hepatic steatosis
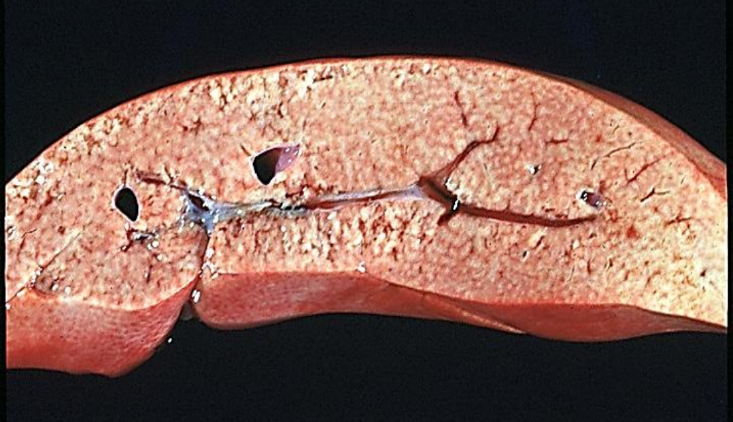
Hepatic lipidosis or hepatic steatosis
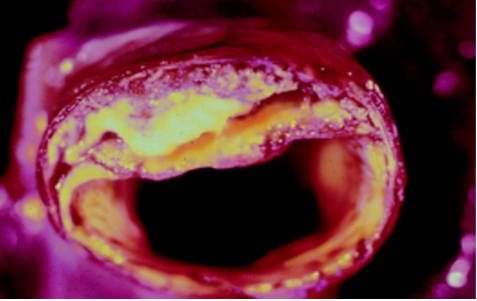
Atherosclerosis (accumulation of cholesterols and lipids in arteries)
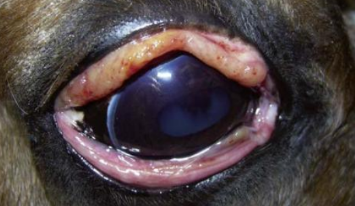
Amyloidosis (deposition of abnormal fibrillar proteins in tissue) conjunctiva (horse)
Palpebral conjunctiva, waxy yelllow noodules of amyloid in subepithelial tissue
Amyloid
Primarily extraC accumulation of prot
Gout
Deposition of sodium urate crystals in various tissues
Pseudogout
Deposition of Ca2+ pyrophosphate crystals
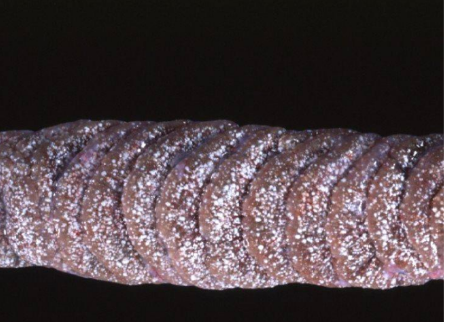
Renal Gout (boa)
Multifocal to coalescing severe urate deposition
Exogenous pigments
Coal dust (Anthracosis) due to polluted air, smoke, smog
Plant pigments (carotenoids)
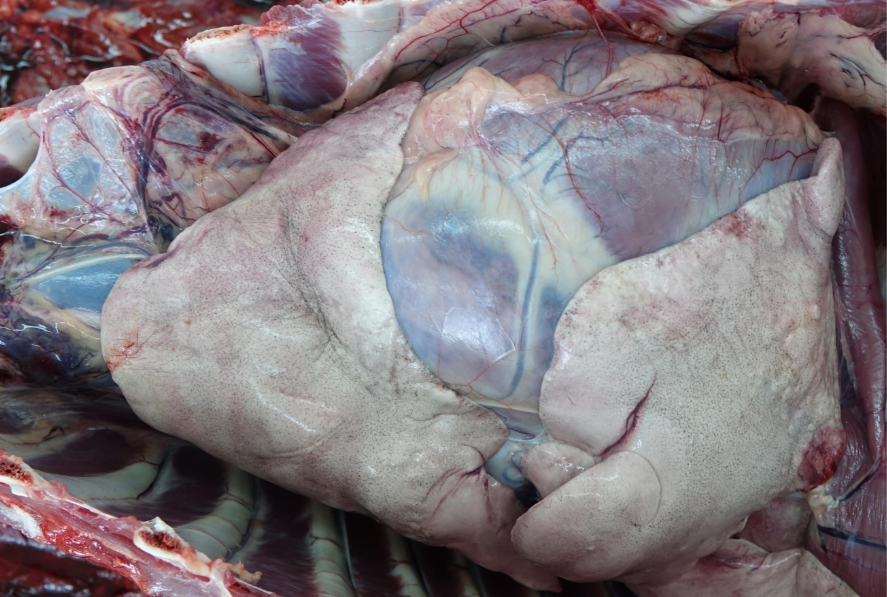
Anthracosis (lungs)
Endogenous Pigments
Lipofuscin (wear and tear/aging pigment)
Melanin (black)
Hemosiderin (golden yellow, granular pigment)
Bilirubin (excess leads to icterus/jaundice)
Urobilinogen and urobilin
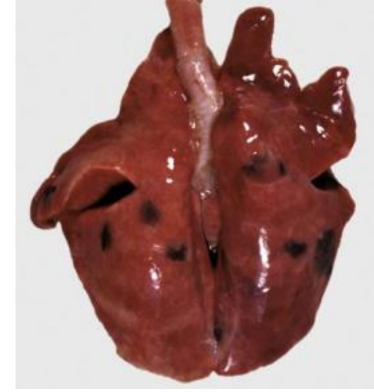
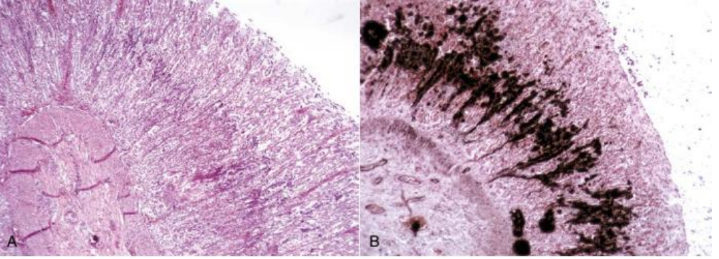
Congenital melanosis lungs (pig)
Melanin deposits are subpleural and spread to the lung parenchyma
Jaundice/icterus
Due to the accumulation of the bile pigments (primarily billirubin)
could be:
Prehepatic (hemolytic, unconjugated billirubin and hemolysis) lemon yellow
Hepatic (hepatocellular jaundice, unconjugated/conjugated billirubin) orange
Posthepatic(obstructive/retentive, can’t excrete conjugatd billirubin) greenish yellow
Calcification
Deposition of Ca2+ salts in tissue that physiologically don’t contain Ca
Could be dystrophic and metastatic (hypercalcemia or problem in Ca metabo occuring in normal tissue)
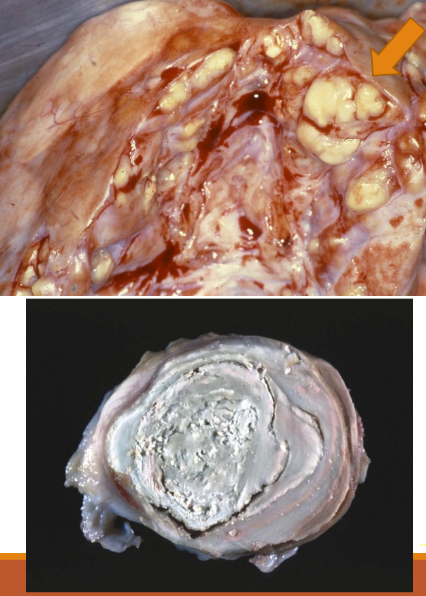
Uremic calcification stomach (dog)
Dystrophic calcification, not associated with Ca homeostasis (serum Ca concentration), Ca deposits occur in damaged/necrotic C and tissues
Present in myocardial infarction, caseous necrosis (tuberculosis), old thrombi
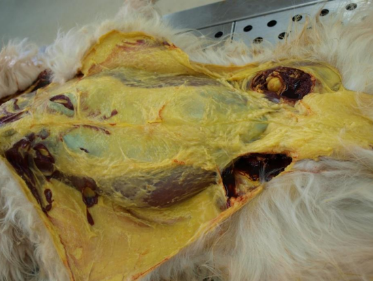
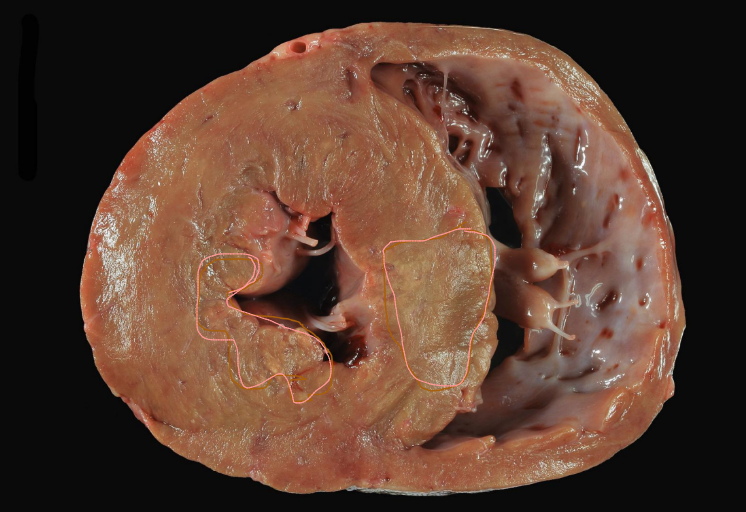
Calcification, vit E or selenium deficiency (calf)
Myocardial necrosis that undergone calcification
Necrosis types
Coagulative necrosis
Caseous necrosis
Liquefactive necrosis
Gangrenous necrosis (dry, wet and gas gangrene)
Fat necrosis
Fibrinoid necrosis or change
Necrosis of epithelium (ulcers and erosions)
Coagulative necrosis
Due to hypoxia, ischemia, toxic injury
Coagulative necrosis
Caseous necrosis
Liquefactive necrosis
Wet Gangrene, mammary gland (cow)
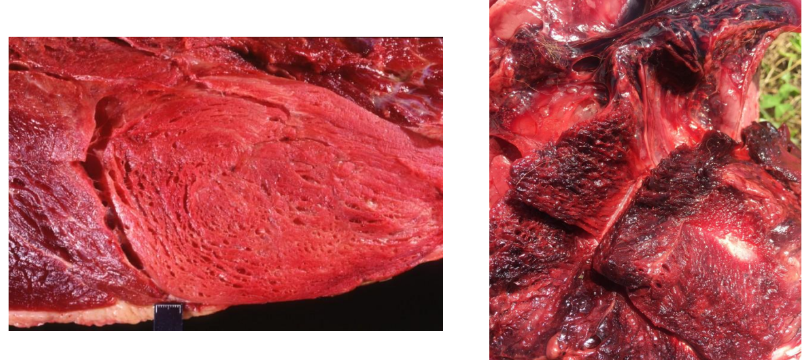
Gas Gangrene (in fact a subtype of wet gangrene, the difference is that the putrefactive bact contaminating the dead tissue are gas forming bact (Clostridium spp)
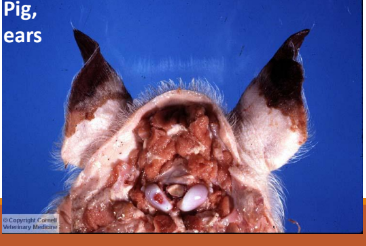
Dry Gangrene
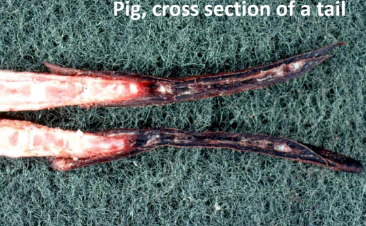
Dry Gangrene
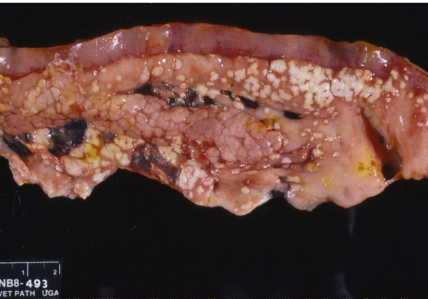
Fat necrosis
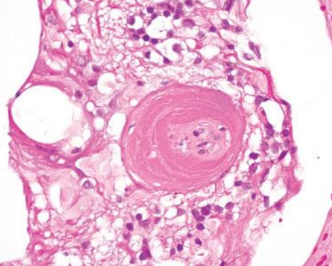
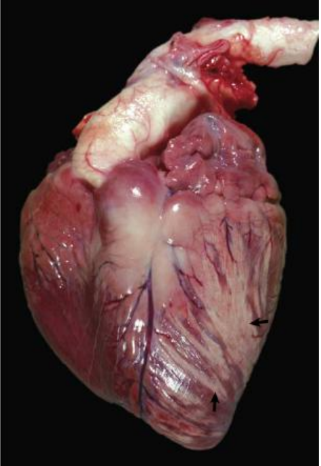
Hypertensive retinopathy (dog)
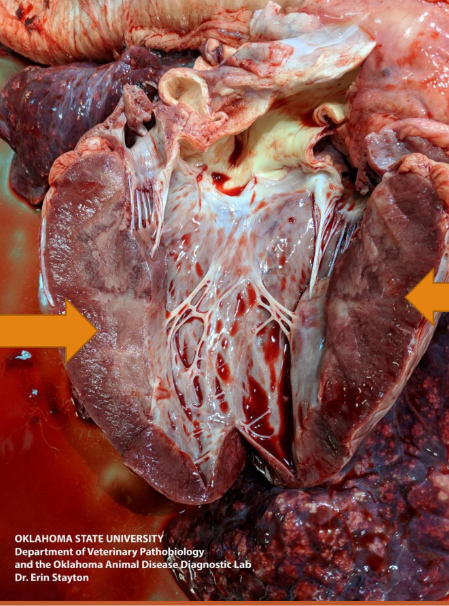
Fibrinoid necrosis or change
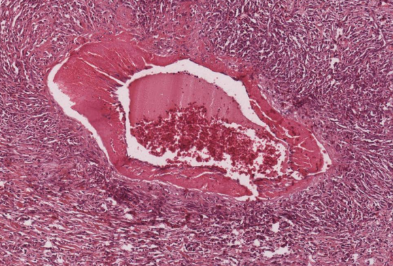
Polyarteritis nodosa (rat)
Fibrinoid necrosis or change
Necrosis of epithelium
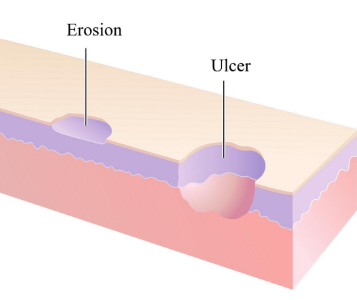
Affect epidermis or epithelial lining (respiratory, GI or repro tracts)
Erosion (necrosis of superficial layer of the epithelium)
Ulceration (full thickness necrosis)
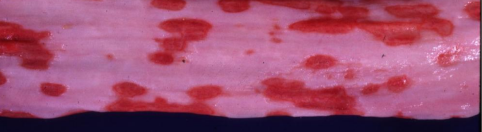
Multifocal to confluent Necrosis of the epithelium, erosion on the esophagus
Apoptosis
Edema
Imbalances of the fluid microenvironment or of the microvasculature itself —> shift in the location of normally intravascular water, electrolytes and plasma prot —> accumulation of fluids at extraC space or extraC sites
Hyperemia
Too much blood is actively or passively forced into diff tissues sites
Hemorrhage
Blood escapes from the vascular system and enters the tissues or the outside world
Thrombosis
The delicately balanced hemostatic mechanism responsible for the lifesaving blood clot sometimes assumes major pathological importance when intravascular coagulation or thrombosis occurs
Embolia
Part of thrombi (or other substance) can break off from initial point and sail downstream —> lodge in a smaller, distant vascular site
Infarction
Intravascular coagula can occlude the blood supply to vital tissues and produce ischemic necrosis
Differents types of Cardiac failure
Right heart failure = congestion and increased hydrostatic P occur in the portal venous system —> ascites
Left heart failure = pulmonary edema
Generalized heart failure = generalized edema
Hydrothorax
Collection of edema fluid in the pleural cavity
Hydropericardium
Collection of edema fluid in pericardium
Ascites/Hydroabdomen
Collection of edema fluid in the peritoneal cavity
Anasarca
Subcutaneous edema
Hydrarthros
Collection of edema fluid in joint
Hydrocele
Collection of edema fluid in scrotum
Hydrocephalus
Collection of edema fluid in cerebral chambers
Iterstitial edema in lungs
Alveolar edema, accumulation of white fluid in bronchi and trachea
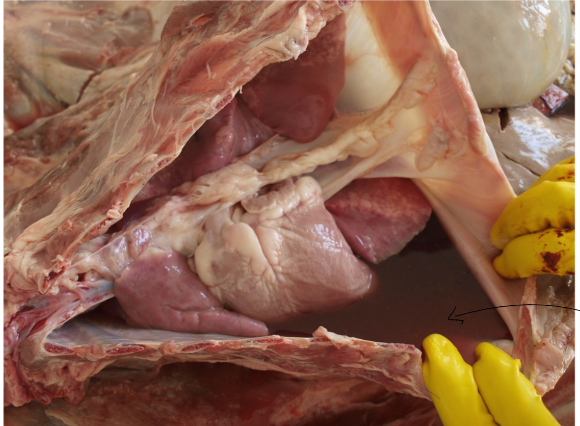
Hydrothorax (accumulation of edema fluid in pleural cavity)
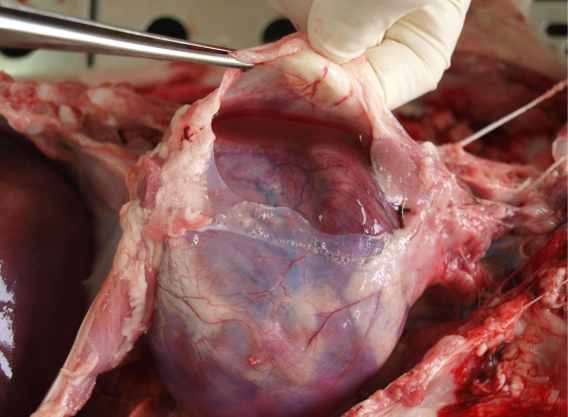
Hydropericardium (accumulation of edema fluid in pericardium)
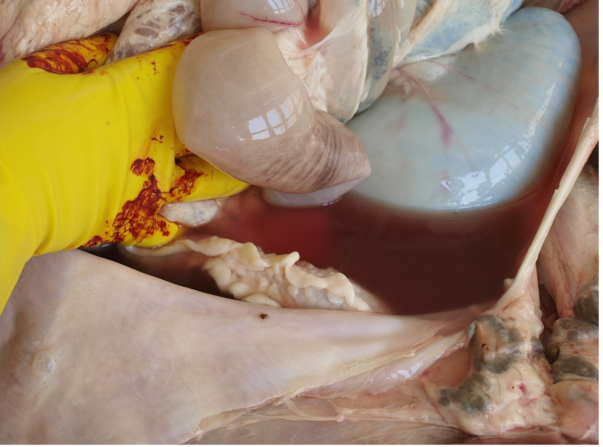
Ascites, Hydroabdomen (accumulation of edema fluid in the abdominal cavity)
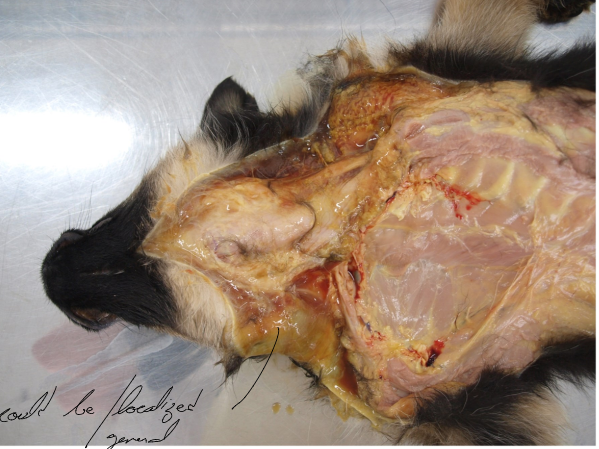
Anasarca or oedema subcutis (Subcutaneous edema)
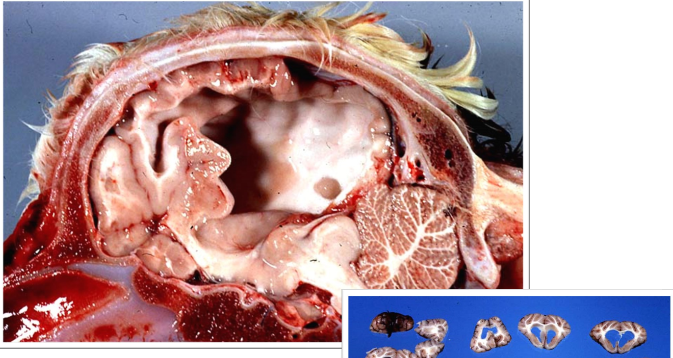
Hydrocephalus (internus) (accumulation of edema fluid in the cerebral ventricles)
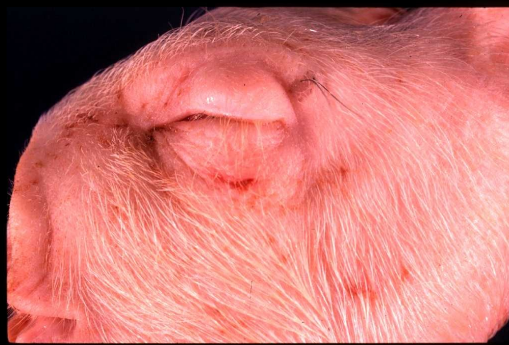
Eyelid edema (due to E.coli spp.)
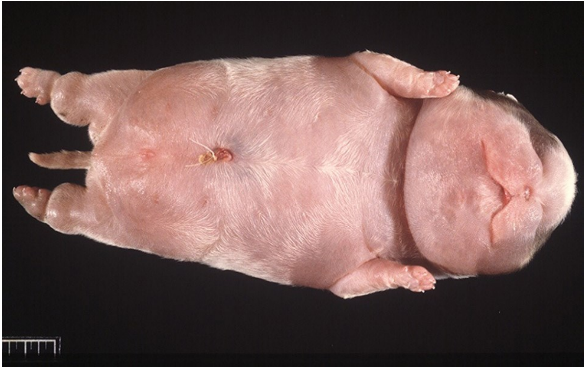
Anasarca (subcutaneous edema)

Anasarca (subcutaneous edema) on the face

Brisket disease, (dvlppt of subcutaneous edema in the brisket, due to high altitude)

Hydroabdomen
Hyperemia
Active engorgement of vascular bed within a normal or increased outflow of blood
in lat hyperemia means accumulation of blood
Congestion
Passive engorgement of a vascular bed generally by a decrease outflow with a normal or increased inflow blood (venous blood)
Differents hyperemia
Acute local active hyperemia
Acute local passive hyperemia/congestion
Chronic local passive hyperemia/congestion
Chronic generalized passive hyperemia/congestion
Acute local active hyperemia
Increased arteriolar blood flow into the area
Hyperemia of inflammation - chemically mediated response to inflammatory mediators
Tissue is bright red and warm
Acute local passive hyperemia/congestion
Local obstruction to venous drainage —> passive negorgement of the drainage area
Causes = thrombosis, acute venous obstruction (intestinal displacement)
Tissue is dark red (venous blood)
Chronic local passive hyperemia/congestion
Development of venous obstruction is slow —> the vascular system has an opportunity to adjust to obstruction - collateral flow are opened
Chronic generalized passive hyperemia/congestion
Causes : diseases of heart (congestive heart failure) or disease of lungs
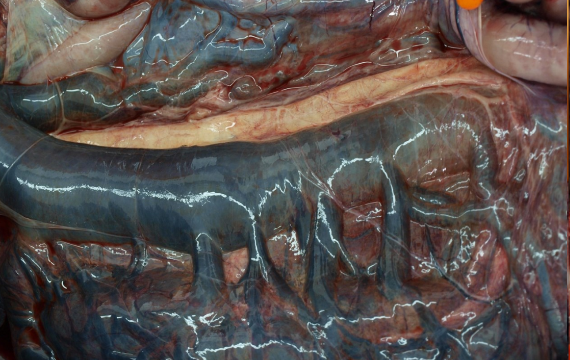
Severe congestion in the veins
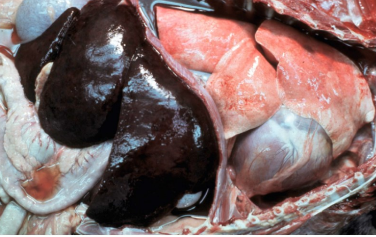
Acute passive congestion (enlarged, dark red, consequence of sudden interruption of the return of blood to the heart)
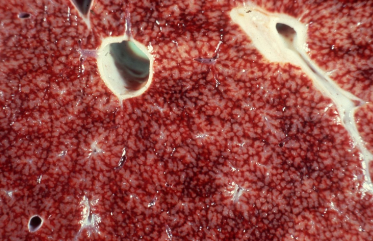
Chronic passive congestion (repeating pattern of red and tan molting, accentuated lobular pattern, nutmeg liver)
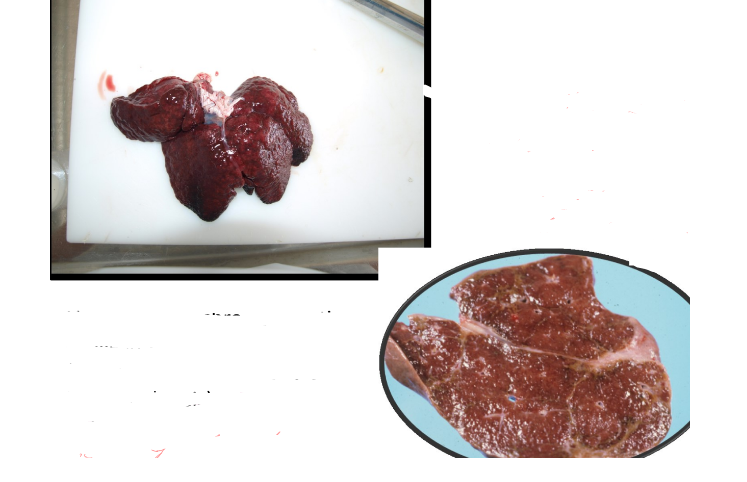
Chronic hepatic congestion = liver fibrosis (congestion —> hypoxia and C injury —> fibrosis = Cardiac cirrhosis)
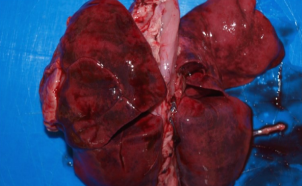
Prolonged lung congestion (alveolar capilaries become engorged with blood, dilated and tortuous —> may rupture —> intraalveolar hemorrhages —> extravascular RBC phagocytosed by intraalveolar macrophages —> laden with the Hg-breakdown pigment hemosiderin —> heart failure C)
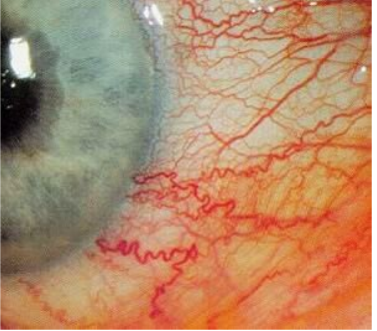
Active hyperemia
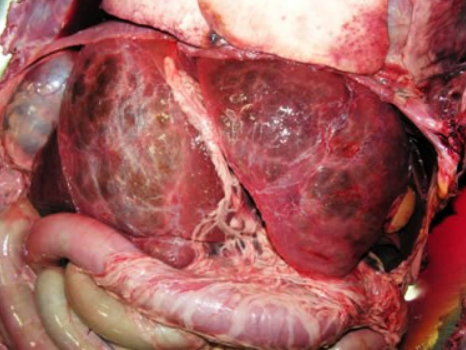
Liver congestion —> cardiac cirhosis
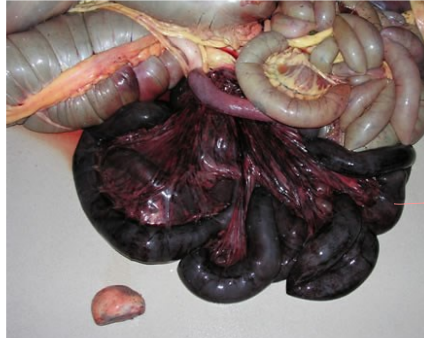
Severe congestion and hemorrhagic necrosis
Events that contribute to hemostasis
Transient vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation (to form platelet plug at the site of damage (1ry hemostasis))
Coagulation to form a meshwork of fibrin (2ndary hemostasis)
Fibrinolysis to remove the platelet/fibrin plug (thrombus retraction)
Tissue repair at the damaged site
Anatomical site of hemmorage
Bleeding from the heart (through the damaged heart wall, usually due to trauma)
Arterial bleeding (due to damaged aorta and arteries, blood leaks in streams (synchronous with the pulse), blood is oxygenated and bright red, VERY EXTENSIVE
Venous bleeding (due to damaged veins, blood leaks more uniformly and slower, blood is dark red colour)
Capilary bleeding (due to damaged capilaries, parenchymal (small pink dots) bleeding)
Haemorrhage by rhexis
Physical dissruption of vessel (rhexis means bursting)
due to:
trauma
vascular erosion (haemorrhagiae per diabrosin) by inflammatory reactions or invasive neoplasms
blood vessel caused by elevated blood pressure
Haemmorrhagiae per diabrosin
Vascular erosion by inflammatory or invasive neoplasms