BMS 302 Exam 4
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
The source of calcium in cardiac muscle is:
the sarcoplasmic reticulum and extracellular sources
Starling's law of the heart
states that, within physiological limits, the heart pumps out the blood that returns to it within each cycle; is the result of the length-force relationship also observed in skeletal muscle; can also be described as autoregulation; is demonstrated by a decreased force of contraction with decreased stretch of cardiac muscle
Starling's law of the heart holds that the _____, the greater the force of contraction.
greater the venous return, edv, and longer myocardial fibers
What parts of the heart are innervated by both the Parasympathetic and Sympathetic nervous systems?
the SA and AV nodes and the atria
The ventricles are innervated by:
the Sympathetic nervous system only
The ______ Nervous System increases the intracellular Ca++, which permits a more rapid & forceful contraction, _____ the rate of re-uptake of Ca++ by sarcoplasmic reticulum following contraction, which _____ plateau phase of ventricular fast response action potential or QT interval making it possible to cause a _____ heart rate.
Sympathetic; increases; shortens; faster
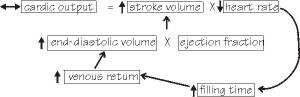
The flow chart shown below best represents:
The turtle heart experiment in which the temperature of the fluid bathing the sinus venosus is decreased.
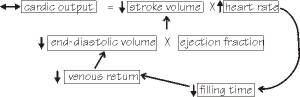
The flow chart shown below best represents:
The turtle heart experiment in which the temperature of the fluid bathing the sinus venosus is increased.
Decreasing the temperature of the fluid bathing the sinus venosus:
decreases heart rate; decreases the rate of diffusion of ions across the membrane during the prepotential; makes the prepotential slope more shallow; follows ficks law
Increasing the temperature of the fluid bathing the sinus venosus:
increases heart rate; increases the rate of diffusion of ions across the membrane during the prepotential; makes the prepotential slope steeper
Vagal tone
affects the heart rate during rest and repose conditions; reduces the inherent rate of contraction by about 20-30 beats per minute in humans; is a tonic stimulation by the PANS of the SA-node
Cutting the right vagus nerve:
eliminates vagal tone; causes the heart rate to increase
Stimultion of the right vagus nerve innervating the turtle heart:
causes the heart rate to decrease
Vagal arrest is the result of:
continuing vagal stimulation that causes the prepotential slope of action potentials in the sinus venosus to approach zero; binding of large quantities of acetylcholine to cholinergic receptors in the sinus venosus
Vagal stimulation following the addition of atropine results in
no change
The effect of atropine is the result of:
cholinergic receptors being blocked by the atropine so acetylcholine cannot alter heart function.
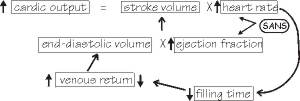
The flow chart shown below best represents:
The turtle heart experiment in which the ventricle is injected with epinephrine.
With an injection of epinephrine into the heart, heart rate and force of contraction (stroke volume) both increase, leading to an increased cardiac output. This is because
increased heart rate helps compensate for the decreased stroke volume that can be the result of an increased heart rate which decreases filling time and ejection fraction increases when the ventricles are stimulated by the SANS and that helps keep stroke volume from falling due to the increased heart rate
Which of the following statements are true for both increasing the temperature of the fluid surrounding the sinus venosus and stimulating the heart with epinephrine?
HR increases and filling time decreases
During the cardiac cycle, an extra systole can be induced by electrical stimulation during:
the relative refractory period.
The compensatory pause is seen because:
the wave of depolarization from the sinus venosus reaches the ventricular muscle during the absolute refractory period of the extra-systole.
When Stannius Ligatures I and II are tied on a turtle heart, the ______ the lowest (shallowest) prepotential slope, the ______ an intermediate prepotential slope and the ______ the greatest (steepest) prepotential slope.
ventricles have; atria have; sinus venosus has
When taking a blood pressure, the first sound that you hear represents the _____, and is the pressure that is generated during _____.
systolic reading; contraction of the ventricles
Mean arterial pressure must be homeostatically maintained why?
to insure adequate perfusion of all vascular beds, to insure sufficient pressure so that the forces of gravity can be overcome, to prevent one from passing out if the brain is insufficiently perfused, to allow one to change positions such as going from reclining to standing without feeling faint, through the baroreceptor reflex.
As the heart to brain distance becomes greater, the MAP at the level of the heart _____ , while the MAP at brain level _____ when compared with different species.
increases; remains about the same
Systolic blood pressure is reflected or influenced by _____, whereas diastolic pressure is reflected by _____.
cardiac output; peripheral resistance
You are measuring the blood pressure in a patient using a sphygmomanometer. You could detect an increase in venoconstriction by observing _____________, and you could detect an increase in vasoconstriction of the arterioles by observing ______________.
an increase in systolic pressure; an increase in diastolic pressure
if heart rate doubles and stroke volume doubles, cardiac output will:
quadruple (4X).
what factors can affect stroke volume?
end diastolic volume, venous return, heart rate, ejection fraction, ventilation, sympathetic stimulation and excersize
List three mechanisms the body has developed to maintain the return of blood (venous return) to the heart from the extremities.
skeletal muscle pump, thoracic pump, venoconstriction
What facilitates venous return?
increase in venous tone, skeletal muscle pump, thoracic pump, postural changes, fainting
skeletal muscle pump
muscle contraction squeezes veins forcing blood back toward the heart past one way valves
thoracic pump
negative pressure in chest "pulls" blood into the thorax (and heart) with each inhalation
venoconstriction
smooth muscle in the elastic venous vessels contracts forcing blood from the venous system back toward the heart
What branch of the Autonomic Nervous System innervates the veins?
Sympathetic
What autonomic output leads to venoconstriction?
Increased Sympathetic
What is the effect of venoconstriction on venous return?
increases
What autonomic output leads to venodilation?
Decreased Sympathetic
What is the effect of venodilation on venous return?
decreases
Increased sympathetic activity stimulates the smooth muscle (effector) in the wall of the veins to ________ and therefore ______ the diameter of the vessel.
contract; decrease
List three factors that can alter peripheral resistance.
viscosity, length, diameter
What vessels play the most important role in altering peripheral resistance?
arterioles
Decreased sympathetic activity stimulates the smooth muscle (effector) in the wall of the veins to ________ and therefore ______ the diameter of the vessel.
relax; increase
What branch of the Autonomic Nervous System innervates the arterioles?
Sympathetic
What is the effect of arteriolar vasoconstriction on peripheral resistance?
increases
What autonomic output leads to arteriolar vasoconstriction?
Increased Sympathetic
What autonomic output leads to arteriolar vasodilation?
Decreased Sympathetic
What is the effect of arteriolar vasodilation on peripheral resistance?
decreases
Increased sympathetic activity stimulates the smooth muscle (effector) in the wall of the arterioles to ________ and therefore ______ the diameter of the vessel.
contract; decrease
Decreased sympathetic activity stimulates the smooth muscle (effector) in the wall of the arterioles to ________ and therefore ______ the diameter of the vessel.
relax; increase
Sympathetic tone
Veins and arterioles are in a partially contracted state under rest and repose conditions which is the result of a tonic sympathetic stimulation of the smooth muscle in the walls of the vessels.
baroreflex arc stimulus
decreased MAP
baroreflex arc receptor
baroreceptors located in carotid artery and aortic arch
baroreflex arc Afferent Pathway
decreased frequency of impulses along sensory neurons
baroreflex arc integrator
cardiac and vasomotor centers of medulla
baroreflex arc efferent pathways
sympathetic neurons to heart & vessels and parasympathetic neurons to heart
baroreflex arc effectors
cardiac muscle and smooth muscle of vessels
baroreflex arc response
increased MAP
During moderate exercise, systolic pressure increases because cardiac output _____ and diastolic pressure is maintained close to resting levels or decreases as blood flow to exercising skeletal muscle _____, and blood flow to the digestive tract _____.
increases; increases; decreases
Hypertension (high blood pressure)
can be diagnosed with repeated blood pressure measurements using a sphygmomanometer and stethoscope, is diagnosed when blood pressure readings exceed 140/90, has no symptoms in the early stages of development and goes unnoticed until damage to the cardiovascular system has occurred
Total Lung Capacity formula (6.0 L in men, 4.6 in women)
IRV + TV + ERV + RV
vital capacity formula
IRV + TV + ERV
Functional Residual Capacity formula
ERV + RV
Inspiratory Capacity formula
IRV + TV
Tidal volume
amount of air inhaled per breath during normal breathing, at rest 0.5 L
Inspiratory reserve volume
amount of air that can be inspired above and beyond that inspired during a normal quiet inspiration
Expiratory reserve volume
maximal amount of air that can be expired following a normal quiet expiration
FEV1 and FEV3
75-85%, >97%
BTPS refers to
body temperature, standard pressure (760 mm Hg)
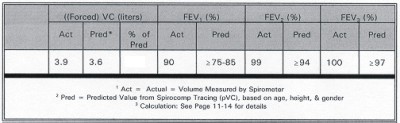
Evaluate this subject's airway resistance.
Airway resistance is less than expected.
In subjects with normal lung function at sea level or moderate altitudes, ___________ has the greatest effect on increasing ventilation.
hypocapnia
Hyperventilation results in _____ levels.
decreased blood carbon dioxide, no change in blood oxygen
What is the effect of hypocapnia on ventilation?
decreases
What is the effect of hypercapnia on ventilation?
increases
What is the effect of hypoxia on ventilation?
increases
Typical values for an end-expiratory sample of gas collected following a one minute breathold might be:
5-6% CO2
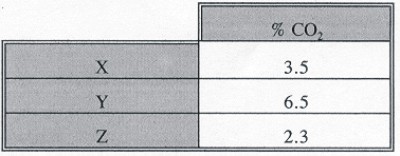
The data in the table below was collected from a subject using a small balloon to collect an Haldane-Priestly end-expiratory gas sample. Sample___ represents an end-expiratory sample collected following a breath-hold, sample ___ represents an end-expiratory sample collected following hyperventilation, and sample ___ is the control resting sample
Y, Z, X
What happens to oxygen levels in the blood during a breath-hold?
decrease
What happens to carbon dioxide levels in the blood during a breath-hold?
increase
Hyperventilation results in _____blood CO2 levels, which ____ breath-hold time, while breath-holding ______ blood CO2 levels resulting in _____ urge to breath.
decreased; increases; increases; an increased
The Sympathetic Nervous System _____ smooth muscle contraction, which _____ diameter and _____ airway resistance.
decreases, increases, decreases
The Paraympathetic Nervous System _____ smooth muscle contraction, which _____ diameter and _____ airway resistance.
increases, decreases, increases
What is the most appropriate type (cholinergic or adrenergic) of agonist and/or antagonist for decreasing airway resistance? Select all appropriate drug classes.
Cholinergic Antagonists and Adrenergic Agonists
Prevention of bronchitis
remove source of irritation
Prevention of asthma
anti-inflammatory drugs and bronchodilators
A Calorie or kilocalorie unit is used to measure food energy and is equal to the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a __________ of water by ______________.
kilogram; 1o Centigrade
Conversion factors for metabolism
1L-1000 mL; 1 kg- 1000 g; 1kcal- 1000 cal
What statements best describes the approximate efficiency of the body in utilizing energy?
initially 80% converted to thermal energy, 20% converted to work energy, eventually all (100%) energy is converted to thermal energy
The amount of energy put into a system is _____ the energy put out by the system.
the same as
In the laboratory _____ was used to measure the metabolism of the Mr. Faust, the laboratory mouse and _____ was used to determine the metabolism of the human subject.
indirect calorimetry, indirect calorimetry
When we measure actual heat produced by a subject to determine metabolic rate, we are using_____ calorimetry, and if we measure oxygen consumption, we are using _____ calorimetry.
direct; indirect
The _____ gives us a relationship between heat production and oxygen consumption in the body that allows us to indirectly determine metabolic rates.
energy equivalent of oxygen
The energy equivalent of oxygen is:
4.8 kcal heat produced for every liter of oxygen utilized
As age increases, metabolic rate____ .
decreases
Ingestion of food:
consisting primarily of proteins has a greater effect on metabolism than lipids or carbohydrates, increases resting metabolic rates.
As circulating thyroxine (thyroid hormone) levels increase, metabolic rate ______.
increases
Metabolic rate increases following the ingestion of caffeine because caffeine:
inhibits phosphodiesterase activity causing more cAMP to be present and therefore enhance sympathetic pathways
What is required for the measurement of a Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)?
fasting subject (12 or more hours), reclining subject, early morning testing, quiet and thermoneutral room
metabolic rate (units used in human measurements)
kcal/m2 x hr
metabolic rate (all species)
volume O2 /time or kcal/time