Unit 4
4.8(8)
Card Sorting
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:18 AM on 12/14/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
1
New cards
caravel
small, highly maneuverable used by the Portuguese and Spanish in the exploration of the Atlantic; used for long voyages at great speed from 15th - 17th centuries; used for exploration, not trade

2
New cards
carrack
large trading merchant ship operating in European waters (especially by the Portuguese) 14th- 17th century

3
New cards
fluyt
Dutch sailing vessel that allowed them to control the Baltic trade; designed to facilitate transoceanic delivery with max space and crew efficiency; used from 16th to 17th centuries

4
New cards
Henry the Navigator
(1394-1460) Portuguese prince who promoted the study of navigation and directed voyages of exploration down the western coast of Africa; sponsored seafaring expeditions to search for an all-water route to the east; imported enslaved Africans

5
New cards
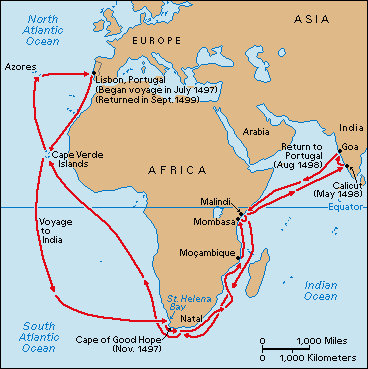
Vasco da Gama
Portuguese explorer.; 1497-1498 he led the first naval expedition from Europe to sail to India, opening an important commercial sea route for Europeans
6
New cards
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese navigator who led the Spanish expedition of 1519-1522 that was the first to sail around the world.
7
New cards
trading post empire
imperial dominance based on control of trade rather than on control of subject peoples; practiced by Europeans in the Indian Ocean as they took over trade from Arab and Muslim merchants
8
New cards
Christopher Columbus
Italian navigator who discovered the New World (in 1492) in the name of Spain while searching for a direct sea route to access Indian Ocean trade
9
New cards
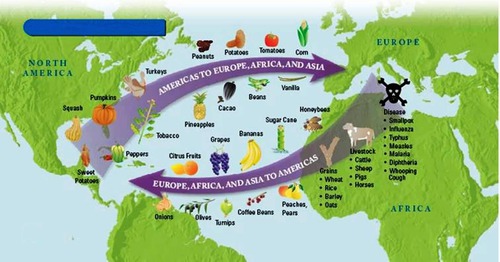
Columbian Exchange
exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus' voyages.
10
New cards
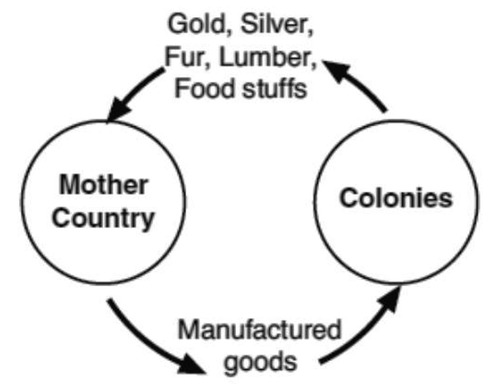
Mercantilism
economic system where nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold/silver and by exporting more goods than they imported; colonies were crucial in the accumulation of wealth; prevalent from 16th - 19th centuries.
11
New cards
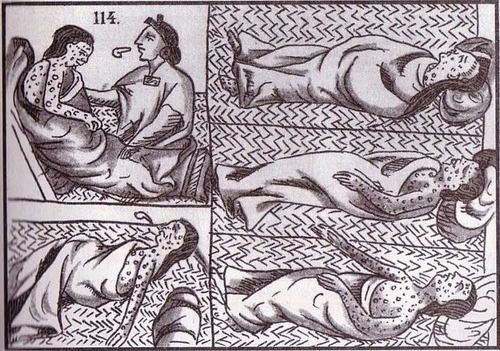
The Great Dying
the devastating demographic impact of European-borne epidemic diseases (like smallpox and measles) in the Americas following European conquest; anywhere from 50-90% of indigenous peoples were killed by European diseases
12
New cards
chattel slavery
absolute legal ownership of another person, including the right to buy or sell that person; the form of slavery utilized in the Americas during the transatlantic slave trade
13
New cards
mita system
economic system in Inca society where Inca subjects paid "taxes" with their labor and what they produced for a set period of time each year; later exploited by the Spanish as they forced Incas to mine silver

14
New cards
indentured servitude
worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination; before 1800 (19th century) most were Europeans; after 1800 most indentured laborers were South or East Asians

15
New cards
encomienda
grant of land made by Spain to a Spanish settler in the Americas, including the right to use local indigenous peoples as laborers on the farm

16
New cards
hacienda
Spanish estates in the Americas that were often plantations; they represent the gradual removal of land from peasant ownership and a type of feudalistic order where the owners would have agreements of loyalty but would retain control over the actual land; continued into the 20th century.
17
New cards
joint-stock company
exploration company made up of a group of shareholders; each shareholder contributed money to the company and received some share of the company's profits and debts; used by European rulers to finance exploration and were used by rulers to compete against one another in global trade
18
New cards
royal chartered monopoly companies
groups of private investors who paid an annual fee to France and England in exchange for a monopoly over trade to Indian Ocean colonies
19
New cards
Vodun
New World syncretic faith that combines the animist faiths of West Africa with Roman Catholic Christianity; evidence of the syncretism created when European and African beliefs merged in the Americas; AKA voodoo
20
New cards
Santeria
originated in Cuba, a religion that blends African traditions and Roman Catholic beliefs/practices; evidence of the syncretism created when European and African beliefs merged in the Americas
21
New cards
casta paintings
Spanish-commissioned paintings that showed the racial mixing of New World families; illustrated the importance of European ancestry in the social hierarchy of Latin America

22
New cards
mestizo
term used by Spanish authorities to describe someone of mixed native American and European descent
23
New cards
mulatto
term used in Spanish and Portuguese colonies to describe someone of mixed African and European descent.
24
New cards
Creoles
Descendants of Spanish-born but born in Latin America; resented inferior social, political, economic status.
25
New cards
peninsulares
Spanish-born upper class individuals who immigrated to Latin America; highest social class and given special privileges and the highest political positions in Latin American governments
26
New cards
the Fronde
series of violent uprisings during the early reign of Louis XIV (1648 - 1653) caused by growing royal control and increased taxation; inspired Louis XIV to take total political control in fear of a future uprising
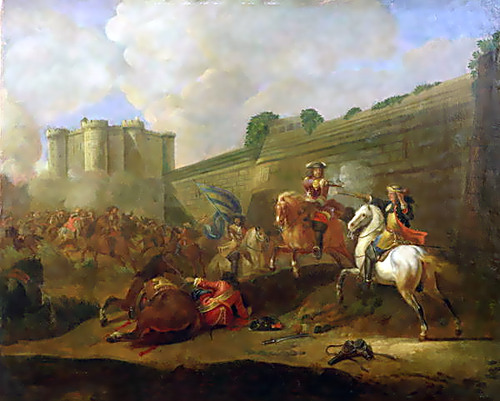

27
New cards
Nat Turner's Rebellion
a rebellion of enslaved Virginians that took place in Southampton County, Virginia led by former enslaved person Nat Turner in 1831; one example of resistance to existing authorities in the Americas
28
New cards
British East India Company
British joint-stock company that controlled most of India during the period of imperialism.; controlled the political, social, and economic life in India for more than 200 years.

29
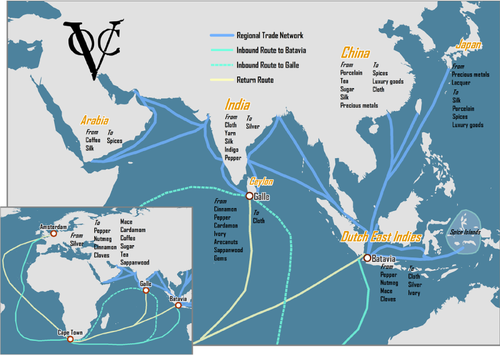
New cards
Dutch East India Company
Dutch-chartered joint-stock company that controlled the spice trade in the East Indies.
30
New cards
Triangular Trade
three-way system of trade during 1600-1800s whereby Africa sent enslaved people to the Americas, the Americas sent raw materials (like sugar, tobacco) to Europe, and Europe sent guns and rum to Africa in exchange for enslaved Africans
31
New cards
coercive labor
any labor system that involves force (slavery, chattel slavery, serfdom, Spanish run mita system, and indentured labor)
32
New cards
bullion
gold and silver in the form of bars