Emotion Regulation Psy2001
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Emotions Generation - The Modal Model (Gross & Thompson, 2007)
Situation
Attention is directed to it
Appraisal evaluates its relevance to goals
Response: An emotion is generated involving: physiological, behavioral, and experiential components.
Emotion Regulation (Gross 1998)
Processes that influence which emotions, when they occur and how they are experienced/expressed
Regulation can be
Effortful/Explicit or Automatic/Implicit
Before the emotion arises (antecedent-focused) or after (response focused)
Process Model of Emotion Regulation (Gross,1998)
Situation Selection
Situation Modification
Attentional Deployment
Cognitive Change
Response Modulation
Situation selection
Avoid or seek emotional situations
Situation Modification
Change the environment
Attentional Deployment
Distract or shift attention
Cognitive Change
Reapparaise or reinterpret meaning
Motives for Emotion Regulation (Tamir, 2016)
Hedonic Motives
Instrumental Motives
Social Motives
Hedonic Motives
To feel better or avoid discomfort
Pro-hedonic: increase pleasure
Contra-hedonic: Increase discomfort for perceived benefits
Instrumental Motives
To achieve goals beyond pleasure:
Performance
Epistemic: wanting to understand
Social: to fit in
Eudaimonic: For meaning or self-actualisation
Positive Impact of Regulation on Outcomes
Better relationships, wellbeing, performance
Adaptive strategises like reappraisal and problem-solving linked to better mental health
Negative impact of Regulation on Outcomes
Maladaptive strategies like rumination, avoidance and suppression linked to anxiety, depression, ED
Common strategies of emotion regulation
Reappraisal
Distraction
Suppression
Evaluation of common strategies
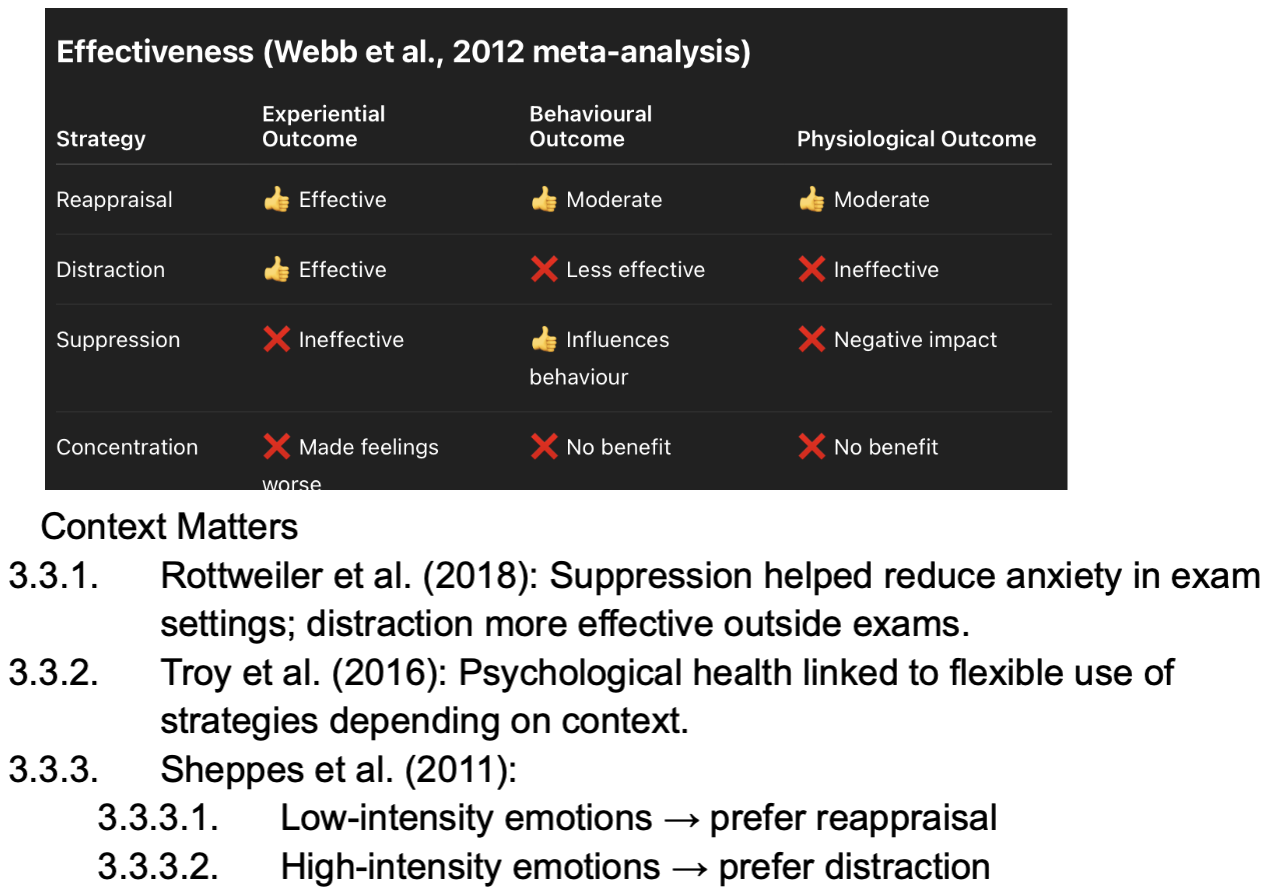
Intrapersonal vs Interpersonal Regulation - definition
Regulating your own emotions
vs
Regulating emotions through or for others
Intrapersonal - types
Situation selection, reappraisal, suppression etc.
Interpersonal Regulation - Types
Intrinsic IER; Extrinsic IER
Intrapersonal - strategies
Reppraisal, distraction, suppression
Interpersonal Regulation - strategies
Social sharing, co-reappraisal, humour, valuing
Intrapersonal - effectiveness
Reappraisal most effective; suppression least
Interpersonal Regulation - effectiveness
Extrinsic IER most effective
Intrapersonal - motives
Hedonic and instrumental
Interpersonal Regulation - motives
Prosocial or instrumental
Intrapersonal - outcomes
Wellbeing, psychological health, performance
Interpersonal Regulation - outcomes
Closer relationships, social supported, increased wellbeing
Intrapersonal - measurement
Experience sampling, lab tasks
Interpersonal Regulation - measurement
Diaries, ESM, partner feedback
Evidence for Interperonal Benefits
Zaki & Williams (2013): Emotion regulation often occurs socially.
Tran et al. (2023): People engage in IER multiple times per day.
Niven et al. (2016): People may make others feel worse if it benefits goal achievement (e.g., inducing anger for better performance).
Levy-Gigi & Shamay-Tsoory (2017): Extrinsic regulation was more effective than intrapersonal regulation in reducing distress