Higher Physics Definitions
1/104
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
The Doppler Effect
The change in the observed frequency of a wave, when the source or the observer is moving
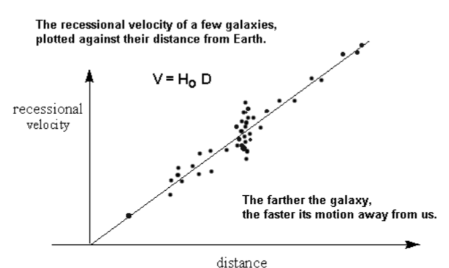
Hubble’s Constant
The gradient of the this graph
Big Bang Theory
Postulates that the universe began with as single burst of energy, in the beginning the universe was very small and very hot . It then cooled and condensed in matter which gradually formed atoms.
Cosmic Background Radiation (CMB)
Big Bang was pure energy in the form of radiation as cooled it emitted radiation as that radiation cooled had less energy and a lower frequency
Olber’s Paradox
Backs up the Big Bang theory, it explains why the sky is dark,the darkness we observe indicates that the universe is neither static nor infinite in the way previously thought. Factors contributing to this paradox include the finite age of the universe, the expansion of space which causes redshift, and the absorption of light by interstellar dust.
Dark Matter
Dark Matter is a mysterious and unseen form of matter that is believed to make up approximately 27% of the universe's total mass-energy content. Its presence is inferred from gravitational effects on visible matter, such as galaxies and galaxy clusters, as well as cosmic structures. For instance, the rotation speeds of galaxies and the gravitational lensing of distant objects suggest that there is much more mass present than can be accounted for by the visible components. Dark matter plays a critical role in shaping the large-scale structure of the universe and influences galaxy formation and evolution.
Dark Energy
Gravity should be an unbalanced force acting to slow down the expansion of the universe (a universe like this should eventually collapse in on its self).The universe is expanding at an accelerating rate suggesting there is a force acting against gravity pushing matter apar.
How to calculate rotational velocity of a galaxy
Measuring the amount of red or blue shift allows us to calculate that exact rotational velocity
Red Shift
Red Shift is a phenomenon observed in the light emitted from an object (such as a star or galaxy) that is moving away from an observer. As the object recedes, the wavelengths of the light it emits are stretched, causing them to shift towards the red end of the visible spectrum. This shift is a result of the Doppler Effect.
Blue Shift
Blue Shift refers to the phenomenon observed in the light emitted by an object moving towards an observer, where the wavelengths of light shorten, shifting toward the blue end of the visible spectrum. This shift occurs due to the Doppler Effect.
Escape Velocity
The speed required to escape from orbit
T (tera)
*1012
G (giga)
*109
M (mega)
*106
k (kilo)
*103
c (centi)
*10-2
m (milli)
*10-3
μ (micro)
*10-6
n (nano)
*10-9
p (pico)
*10-12
Random Uncertainty
Arise when measurements are repeated and slight variation occur. May be reduce by increasing the number of repeats
Systematic Uncertainties
Occur when readings are readings taken are either all too small or too large. This can arise due to improper measurement techniques are experimental design.
Scale Reading Uncertainty
An estimate of how accurately an instrument can be read.
Accurate Measurement
Measurements which are close to the expected value
Precise Reading
Measured to a large number of significant figures
Scalars
Magnitude only
Vectors
Magnitude and Direction
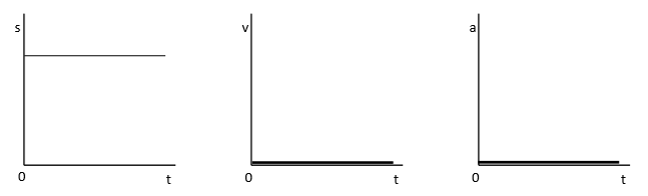
Constant Displacement Graphs
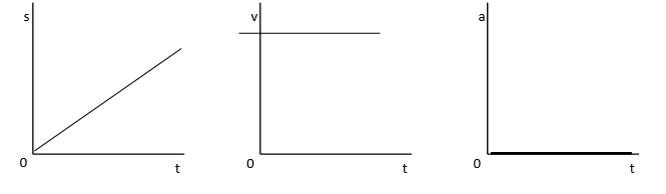
Constant Velocity Graphs
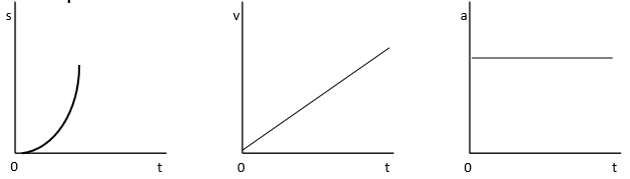
Constant Acceleration Graphs
Constant Deceleration Graphs
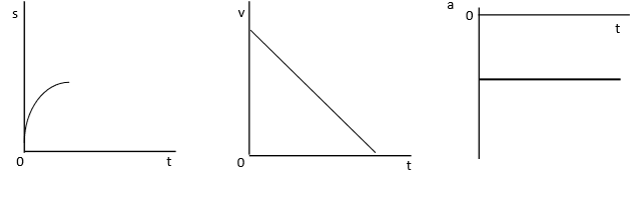
Terminal Velocity
When 2 forces are equal to each other and therefore you can’t accelerate any faster
Newtons Universal Law of Gravitation
Newton’s Law of gravitation states that the gravitational attraction between two objects is directly proportional to the mass of each object and is inversely proportional to their square of their distance apart.
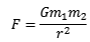
Gravitational Field Strength
The force of unit of mass placed in the field N/kg
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be converted or destroyed , only converted from one form to another.
Gamma Radiation
High frequency/energy waves/photons
Alpha Decay
The
Beta Decay
Fast moving electron
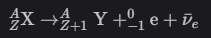
Fission

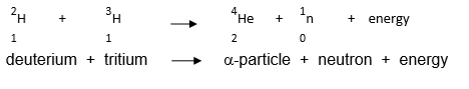
Fusion
Is the process where two lighter atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy in the process.
Antimatter
Same as a matter particle except it has the opposite charge but a lot less of them
Annihilation
When a matter and antimatter particle meet they annihilate giving of energy usually in the form of photons (gamma rays) and other particles.
Leptons
Electron, Electron Neutrino, Muon, Muon Neutrino, Tauon, Tauon Neutrino
Quarks
Up, down, charm, strange, top, bottom
Hadrons
Subatomic particle made of two or more quarks held together by the strong interaction.
Mesons
3 Quarks
Mesons
Quark, anti quark pair
Fermions
Matter Particles
Bosons
Force mediating particles
Gluons are responsible what force?
Strong Nuclear
Photons are responsible what force?
Electromagnetism
Z Bosons are responsible what force?
Weak Nuclear
W Boson are responsible what force?
Weak Nuclear
Gravitons are responsible what force?
Gravity
Critical Angle
Is the angle of incidence which produces an angle of refraction of 90o
Total Internal Reflection
Occurs when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
Constructive interference
When two sets of waves meet in phase to produce a larger wave
Destructive inteference
The waves are out of phase and combine to cancel each other out or reduce if the amplitude isn’t the same
Wave Particle Duality
Particles can both act as particles and waves.
Photovoltaic Effect
Is the process by which a material generates voltage and electric current when exposed to light.
Photoelectric Effect
Sometimes when electromagnetic radiation above a certain frequency strikes a service electrons are emitted and is the basis of photodiodes, solar cells, LDR.
Frequency (f)
The number of wavelengths produce by a source each second or the number of wavelengths passing a point each second
Wavelength (λ)
The minimum in which a waves repeats itself
Amplitude
The maximum displacement from zero to the crest or trough
Period (T)
The time taken for one complete wavelength to be produced by a source or the time for one complete wavelength to pass a point
Refractive Index
Is a measure of how much a material slows down light passing through that material and therefore gives a measure of direction the light change as it passes through a median.
Snell’s Law
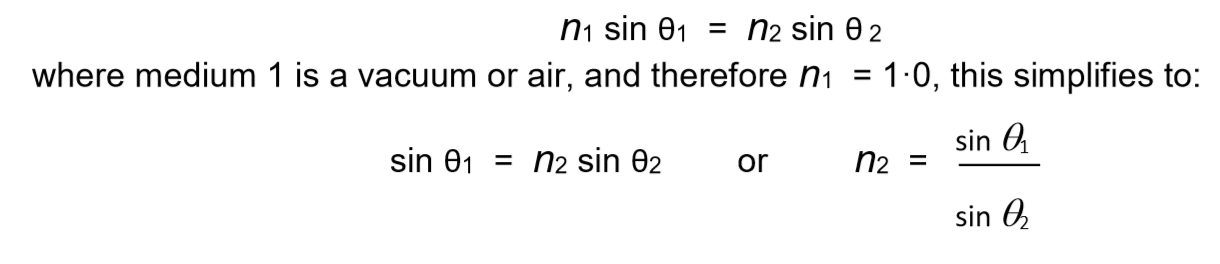
Diffraction
The spreading of waves as the pass through an aperture or around objects.
In Phase
Two points on a wave that are vibrating in exactly the same way, at the same time
Out of Phase
Two points that are vibrating in exactly the opposite way, at the same time
Coherence
If the they have constant phase difference .They will have the same frequency and often the same amplitude.
Interference
When two sets of waves meet, they combine and produce a new pattern.
Postulates of special relativity
When two observers are moving at constant speeds relative to one another, they will observe the same laws of physics.
The speed of light in a vacumm is the same for all observers
Time Dilation (t’)
Time is different for observers in different reference frames because the path the observe for a moving object is different
Length Contraction (l’)
Proper Length (l)
The length of of an object in its reference frame in which the object is stationary is it’s true length
Proper The time between (t)
The time between events that happen at the same place and it’s refence frame.
Irradiance
Power per unit area on a surface
Point Source
Irradiance Equation
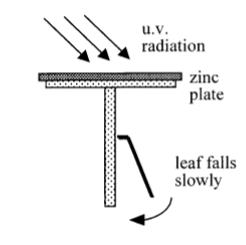
Photoelectric Effect Experiment
Can be demonstrated by using a negatively charged electroscope, when the zinc plate is exposed to u.v. radiation the leaf fall.
Threshold Frequency
In general there is a minimum frequency of electromagnetic in order to eject electrons from a particular metal.
Work Function (Eo)
The minimum energy required to release an electron from a surface
Spectra
Each elements as a gas emits an unique line spectra when excited and can be used to identify that element using a spectroscope or a spectrometer using a grating or prism.
Newton’s First Law
An object will remain at rest or continue to travel at a constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force.
Newton’s Second Law
When an unbalanced force is on an object it causes it to accelerate
Newton’s Third Law
For every reaction there is an equal but opposite reaction
Laws of Conservation of Momentum
Inelastic Collisions
When kinetic energy is not conserved
Elastic Collisions
When kinetic energy is conserved
EMF
Is defined as the work done on a unit charge
Potential Difference
Is defined as the energy which is dissipated as the unit charge pass through the components
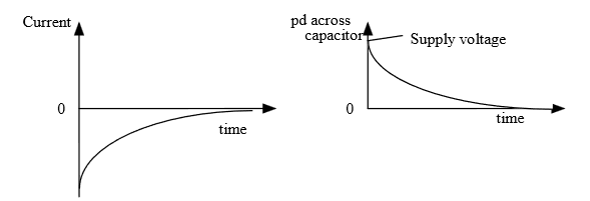
Capacitor Discharging Graphs
Conductors
Materials with many free electrons .These can easily be made to flow through the material.
Semiconductors
A Mix between conductors and insulators.
Insulators
Material that have very few free electrons.
Conduction Band
Is the highest occupied band which his not completely full
Valence Band
Band Gap
The distance from the valence band to the conduction band
Valence Band
Is a the highest full shell