CHP 12 neurological intervention
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
contemporary task-oriented approaches for motor control training
principles
occupational performance emerges from interaction of multiple systems (personal & performance, etc.)
behavioral changes represent attempt to compensate and achieve functional goal
use varied strategies
top-down approach (look at occupational performance first)
interventions focus on
adjusting to role and performance limitations
creating optimal environment
use of functional task and occupational based activities
practice, practice, practice
adapt and remediate
Carr and Shepherd’s Motor Relearning Program (MRP)
person is active participant whose goal is to relearn effective strategies for performing functional movement
postural adjustments and limb movements linked
skill development does not follow developmental sequence
intervention focus
general strategies for solving motor problems NOT individual movements (problem solve rather than memorize)
successful task relearning = activities performed automatically and efficiently
compensatory strategies limits functional recovery > repeated use can cause further limitations and abnormal movements
motor learning principles
learning is contingent on type of task being learned
discrete, continuous, serial, closed (task w/planned movements > bowling), open (driving), variable motionless, consistent motion
law of practice refers to performance changing linearly with amount of time spent in practice
massed (rest < practice), distributed (practice = rest), blocked, random, whole (dressing), part (don/doff shirt)
key feature of practice is information learner receive about attempts to learn (trial/error, feedback)
inherent/intrinsic, augmented/extrinsic, concurrent (during), terminal (end), immediate (after), delayed, knowledge of results (you did this much), knowledge of performance (next time keep your shoulders back, but good job)
motor learning stages
skill acquisition
cognitive stage, occurs during initial instruction and practice of skill
teach back, demonstrate, highlight key points, select appropriate feedback and task, reflection, adapt
skill retention
associative stage, involves carryover as individual demonstrate newly acquired skill after initial practice
practice, feedback, structure
skill transfer
autonomous stage, individual demonstrates skill in new context
practice, feedback, structure
factors to promote generalization of motor learning
capacity of intrinsic feedback
high knowledge of performance feedback
low extrinsic > knowledge of results
practice in variety of natural settings and conditions
whole task practice
near transfer
alternate form of initial task
very similar to initial task but has minimal changes in task parameters
near > intermediate > far > very far transfer
sensorimotor approaches
utilized for CNS dysfunction
general principles
controlled movement preceded by stereotypic reflex response
facilitation and inhibition patterns
sensory input regulates motor output (need sensation for movement)
centralized motor programs determine muscle activation patterns (cortex > middle brain > SCI)
higher level and lower level centers; higher level > lower
damage to higher control centers release primitive reflexes and movement patterns from inhibition
lower level integration (SCI) occurs by higher level righting and equilibrium responses
includes
neurodevelopmental tx approach (NDT)
proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)
Brunnstrom’s approach
Margaret Rood’s approach
neurodevelopmental treatment approach (NDT)
Bobath technique
focus is on improving quality of movement through
normalization of movement patterns
integration of both sides
establishment of ability to weight bear and weight shift
establishment of normal righting and equilibrium patterns
primary intervention is handling
principles
normalization of postural and limb tone is prerequisite to normal movement
eliminate tone abnormalities (hypo-hypertonia, flaccidity, spasticity, etc.)
loss of postural control > overuse of uninvolved side and limited fxnal movement
avoidance of movements and activities that increase tone
associated reactions (nonfxnal and involuntary changes in uninvolved limb position & tone) should be avoided
inhibition of primitive reflexes and abnormal postural and limb movements

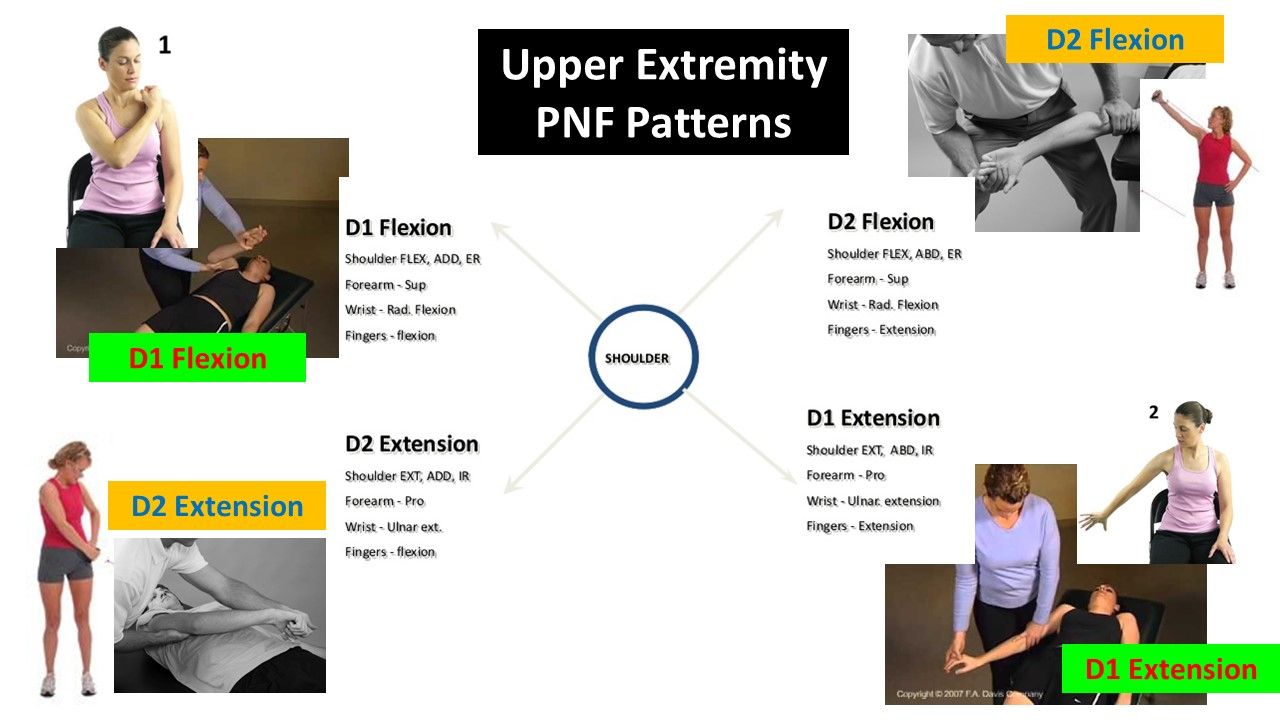
proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)
superimposed movements (diagonals) and posture focusing on sensory stim from manual contacts, visual cues, and verbal commands
goal directed ax w/facilitation techniques; reversing movements
D1 flexion/extension and D2 flexion/extension
diagonal patterns and mass movements during fxnal activities
cross midline and rotary movement
principles
neuromuscular mechanisms can hasten with stimulation of proprioceptors
early motor behavior is dominated by reflex ax; mature motor behavior supported by integrated postural reflexes
spontaneous movement; extreme flexion to extension
developing motor behavior expressed in orderly sequence
shifts btw flexor or extensor dominance
locomotion depends on reciprocal contractions
PNF D1 and D2 patterns
D1 = shopping cart
D2 = Disco
D1 flexion (EX: comb left side of heat w/R arm, reach for cup in UR cabinet w/LE) (shopping cart dance)
scap: abduct, up rotate
shoulder: flex, add, ER
elbow: flex
forearm: sup
wrist: flex, radial
finger/thumb: flex, add
D1 Extension (EX: reach for R arm rest w/RUE; place cup in dishwasher, reach back to wash RLE w/RUE)
scap: add, down rotate
shoulder: ext, abd, IR
elbow: ext
forearm: pro
wrist: ext, ulnar
finger/thumb: ext, abd
D2 flexion (EX: raising hand to ask Q; reaching for cup in front you; fist pump)
scap: add, up rotate
shoulder: flex, abd, ER
elbow: ext
forearm: sup
wrist: ext, radial
finger/thumb: ext, abd
D2 extension (EX: wash L thigh w/RUE; putting on seatblet, don belt)
scap: abd, down
shoulder: ext, add, IR
elbow: flex
forearm: pro
wrist: flex, ulnar
finger/thumb: flex, abd
Brunnstrom’s movement therapy
focused on facilitating recovery through specific sequence that promotes movement from reflexive to volitional
focus on developing movmt in hemiplegia
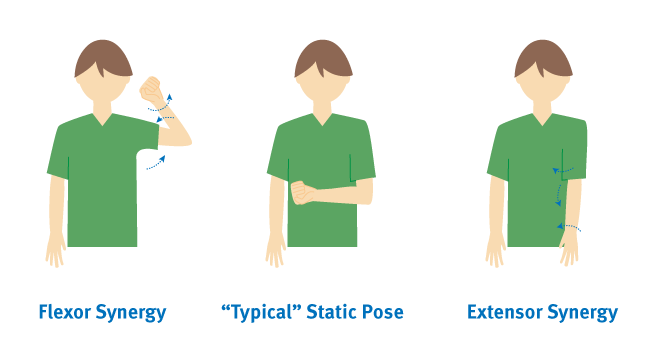
stages
I: flaccid, no vol movement
II: synergies and spasticity
III: incr spasticity and beginning of vol movmt in synergy
IV: decr spasticity and vol move beginning move out of syngery
V: spasticity continues to decr, vol movmt more complex w/out synergistic pattern
VI: spasticity almost gone, isolated vol movmt
VII: normal movement
Margaret Rood’s Approach
sensorimotor control is developmentally based and tx must begin at current level
four phases of motor control
reciprocal inhibition/innervation
early mobility pattern primarily a reflex governed by spinal and supraspinal centers (protective, stepping reflex)
co-contraction
simultaneous contraction of agonist and antagonist that provides stability in static pattern
prolonged holding of object, standing at concert, prop arm to stand
heavy work/mobility superimposed on stability
proximal muscles contract and move and distal segments are fixed
downward dog to upward dog, stance phase in gait
skill
highest level of control and combines stability and mobility
consist of stabilized proximal segment w/distal segment move in space
changing lightbulb, writing on chalk board kicking ball
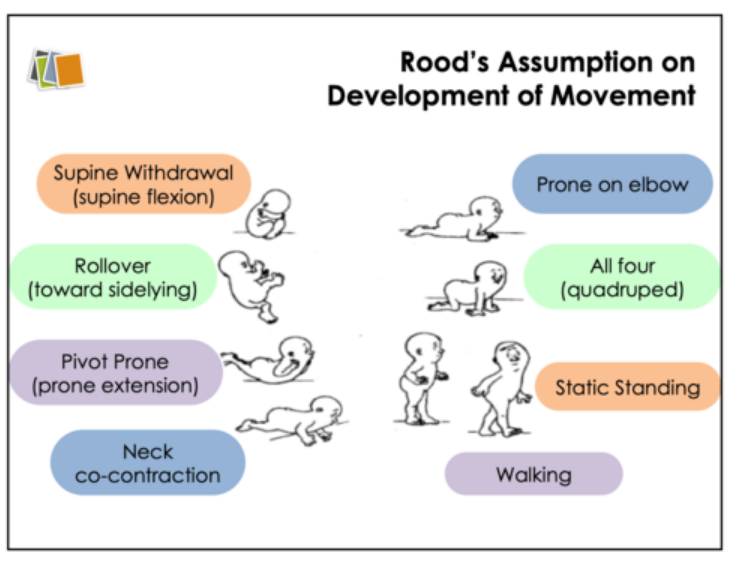
ontogenic motor patterns: sequence of motor development
supine withdrawal
rollover
prone extension
neck co-contraction
prone on elbows
quadruped
standing
walking
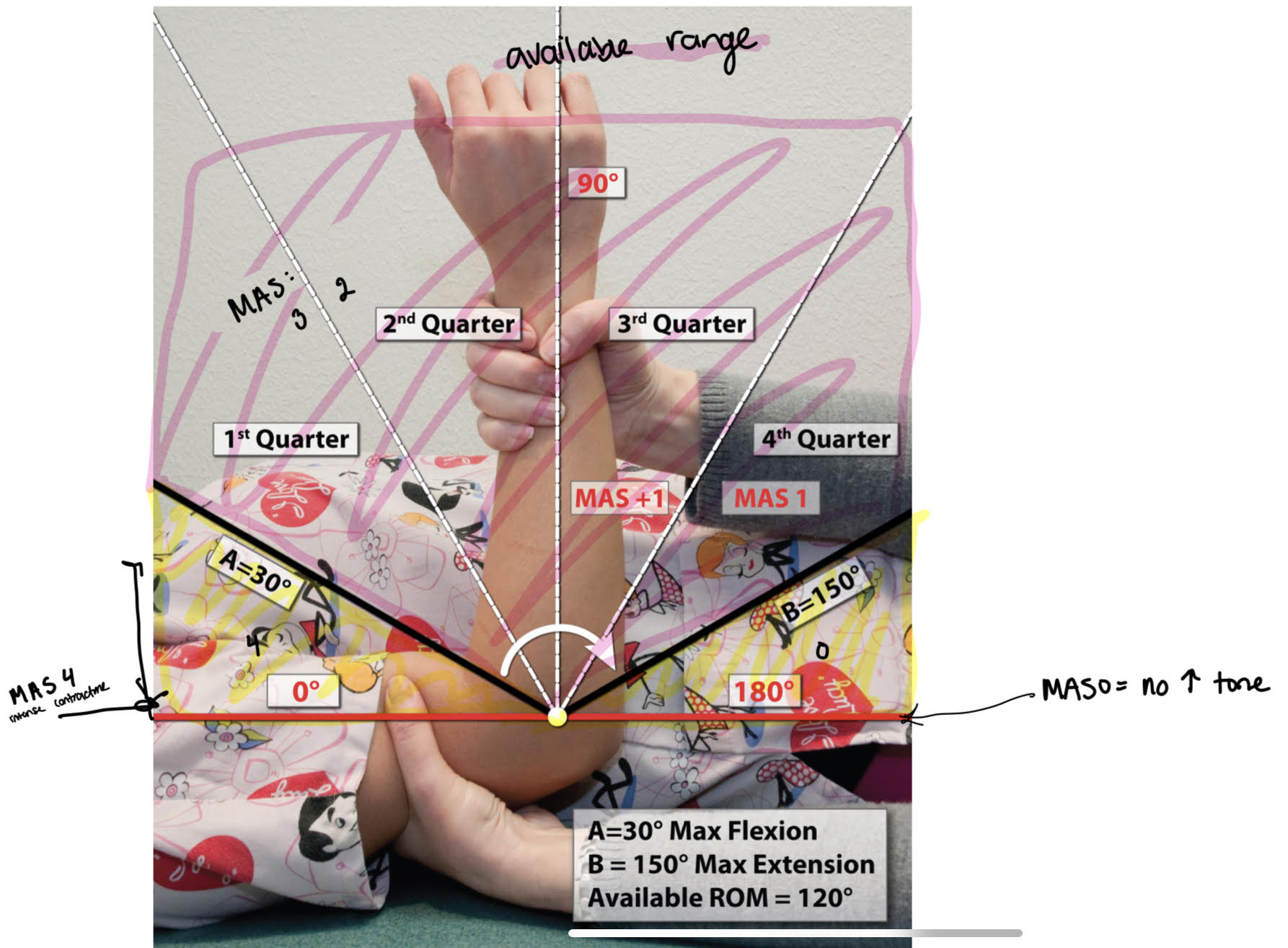
modified Ashworth scale (MAS)
measures resistance to passive movements of joint which is not exclusive to measure of spasticity
evaluation of hypertonia and spasticity
velocity dependent stretch reflexes
standardized extension time: one second duration
PROCEDURE
full PROM
document max ext & flex
find full range and divide by 4 for quadrants
quick stretch in direction opposite of pull for 1 sec x3
document point of catch/angle manifestation
DOCU:
muscle group tested and rating
EX: R elbow flexors: MAS 2
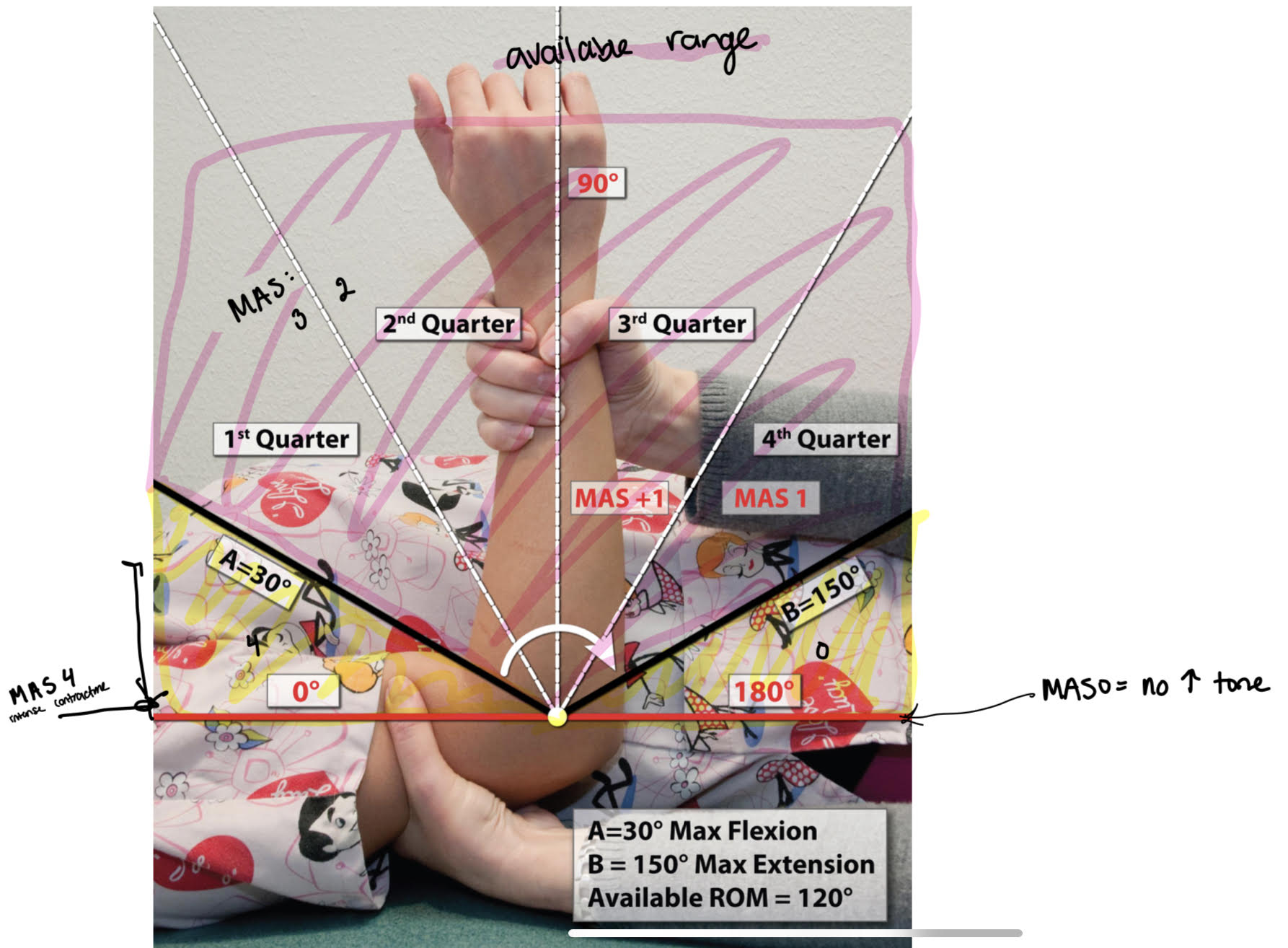
MAS scoring
0: no increase in muscle tone; normal muscle tone
full range
1: slight increased tone, catch & release, minimal resistance @ end of range
4th quarter
1+: slight increased in tone, catch > minimal resistance throughout remainder (less than half)
3rd quarter
2: more marked increase in muscle tone through most ROM, affected parts move easily
2nd quarter
3: considerable increase in muscle tone, PROM difficult
1st quarter
4: affected part rigid
cant get range
reflex testing
utilized to evaluate involuntary stereotyped responses to particular stimulus
may be present since fetal life or re-emerged after brain injury
response = positive
common reflexes tested
grasp: pressure at palm of hand > finger flex
flexor withdrawal: stim at sole of foot > flex of stimulated leg
ATNR: flex extended leg while opposite leg is flexed > ext of opposite leg w/add and IR
STNR: flex head followed by head etx > flex of head result in flex of arms/ext of legs and vice versa
tonic labyrinthine: prone to supine > prone = flex of arm/legs and supine = ext of arm/legs
intention tremor
worsening of action tremor as limb approaches target in space
dysmetria
undershooting (hypometria) or overshooting (hypermetria) of target
dyssynergia
breakdown in movement resulting in joints being moved separately to reach desired target as opposed to moving in smooth trajectory
decomposition of movement
dysdiadochokinesia
impaired ability to perform rapid alternating movements
(patty cake on thighs)
rigidity
increased resistance to passive movement throughout the range
may be..
cogwheel: alternative contraction/relaxation of muscles being stretched
lead pipe: consistent contraction throughout range
akinesia
inability to initiate movements
kinesia = movments
athetosis v dystonia v chorea
athetosis: dyskinetic condition includes inadequate timing, force, and accuracy of movements in trunk/limbs; movements are writhing and worm like
dystonia: involuntary sustained distorted movement or posture involving contraction of groups of muscles
chorea: involuntary movements of face and extremities which are spasmodic and short duration
huntingtons!
hemiballismus: unilateral chorea > violent, forceful movements of proximal muscles
assessment of GHJ inferior subluxation
allow person arm to dangle into gravity
palpate space underneath acromion process with index finger
compare intact side and document width of pace in terms of finger breadths
using orthosis for neuro pts
prevent deformities and contractures (CVA, CP, etc)
control spasticity
correct malalignment
compensate for weakness
provide support
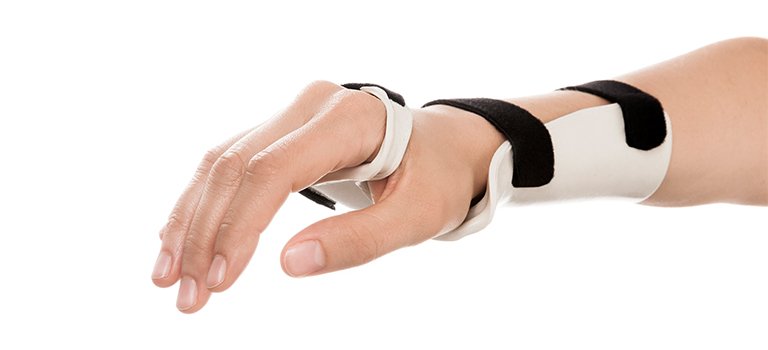
cock-up orthosis
supports wrist in 10-20 ext to prevent contractures
allows digits to function
volar or dorsal
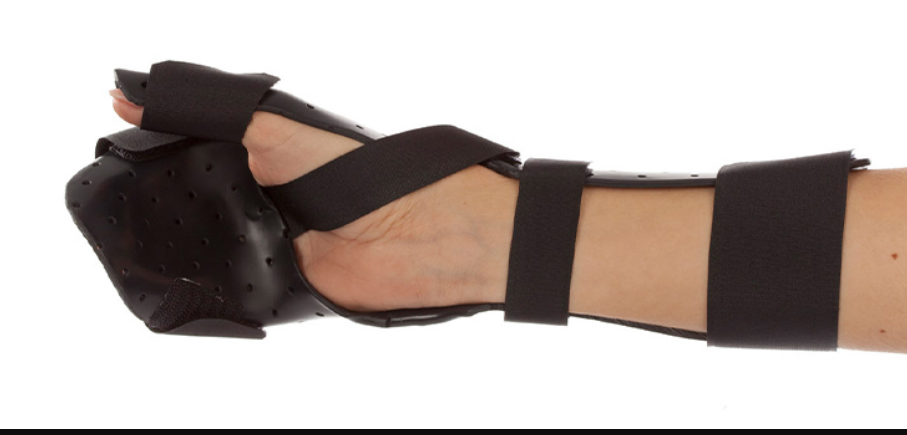
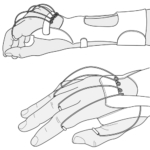
bobath finger spreader (abduction orthosis)
soft orthosis positions digits and thumb in abduction to reduce tone

rood cone
based on Rood’s inhibitory principles of sustained deep pressure
utilized to reduce flexor spasticity in hand

orthokinetic orthoses
utilizes tactile input (elastic bandages) to facilitate and/or inhibit appropriate muscle group
any static orthosis that is used to decrease tone in neuro hand pts may…
cause hand deformity
increase w/severity of spasticity
use with cautions and frequently monitor
consider fabricating orthosis w/wrist separate from fingers to reduce sustained flexor that could increase tone
SaeboStretch good option for minimal to moderate tone
overhead suspension sling
incorporates arm support that is supported by sling and suspended by overhead rod
can be used for exercises or to engage in functional task
candidates
proximal weakness w/ muscle grades in 1/5 to 3/5 range
EX: ALS, guillain-barre, MD
balanced forearm orthoses
mobile arm supports or ball-bearing forearm orthoses
consists of arm trough, proximal and distal arms, and support bracket that can be placed on w/c or table
allows person with weak proximal musculature to utilize available control of trunk and shoulder to engage in functional tasks for exercise
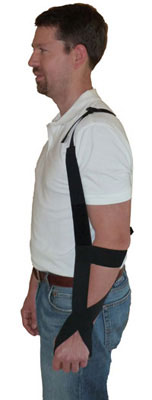
shoulder slings
utilized to support flaccid arm after neurologic insult for short and controlled periods of time
long term use may be detrimental
prevents traction injuries during upright ax (flaccid arm will begin to sublux!!! use sling for support when moving about)
types:
arm pouch: supports weight of arm holds arm in flexor pattern; short periods
only use during fxnal mobility and transfers
shoulder saddle: supports distal weight of arm with forearm cuff; worn under clothes; allows elbow flex/ext
hemi shoulder: arm supported with humeral cuff; allows elbow flex/ext and distal fxn
GivMohr: supports distal weight of arm; allows elbow flex/ext; pictured
oral motor dysfunctions
may result in speech impairments (dysarthria), swallowing impairments (dysphagia), drooling, facial asymmetry, etc.
evaluate each stage
pre oral: food set up, sensory awareness of food, food to mouth
oral-preparatory: open mouth, muscles of mastication, bolus in oral cavity, bolus formation
oral stage: lips, buccal muscles, and tongue propel bolus
pharyngeal: swallow reflex, laryngeal elevation, soft palate elevation, pharyngeal peristalsis
esophageal: propulsion of bolus through esophagus
signs of aspiration (6)
change in color due to airway obstruction
prolonged coughing
gurgling voice, extreme breathiness, loss of voice
nasal drip
profuse drooling
fever
swallowing stages (5)
pre-oral or anticipatory stage
voluntary; psychological, social, environmental, cultural, emotional aspects of eating
oral-preparatory stage
voluntary; food to mouth, salivation, mastication, bolus formation
oral stage
voluntary; lips, cheeks, tongue move bolus to pharynx
pharyngeal stage
involuntary; swallow response, vocal cords close, elevation of structures
esophageal stage
involuntary; bolus enters esophagus, peristalsis
primitive reflexes impacting oral motor function
rooting reflex
test: stroke from corner of mouth along cheek to ear > head turns and tongue protrusion
jaw jerk (phasic bite reflex)
test: tap center of mandible 1-2 times > jaw closes/opens
fxn: allows for jaw movements of eating
bite reflex (tonic bite reflex)
test: tongue depressor placed btw upper and lower teeth > strong closure of mouth
fxn: present when unable to chew foods, utensil use is difficult
ATNR
test: rotate head 90 > limb ext on face side, flex on skull side
STNR
test: flex head then ext head > flex of head = flex arms & ext of legs; ext of head = ext of arms & flex of legs
testing CNIII
oculomotor n
pupil size, pupillary reflex, visual tracking
testing CNIV
trochlear n
visual tracking, smooth pursuit
testing CNVIII
vestibulocochlear n
tuning fork, balance
testing CNIX
glossopharyngeal n
gag and swallow reflex
taste to posterior tongue
testing CNXI
spinal accessory n
shoulder (sternocleido, trap m) testing
testing CNXII
hypoglossal n
stick out tongue
oral motor interventions
direct therapy for strategies and eating techniques
modification of food consistency, amount, placement
slow oral transit time > cold & sour bolus
weakness > soft solids & thick fluids to posterior mouth
delayed swallow > high flavor foods
reduced laryngeal elevation > mendelsohn & supraglottic
postural interventions!!
chin tuck, supraglottic swallow, mendelsohn’s maneuver
indirect therapy not including bolus practice
thermal (cold) stimulation to swallow receptors
reflex facilitation
strengthening and coordination of oral movements
positioning
constraint induced movement therapy (CIMT)
task-oriented approach for neuro pts with control of wrist and digits
BP injuries
criteria for affected side
20 ext of wrist and 10 ext of each digit
10 ext of wrist, 10 abd of thumb, 10 ext any 2 other digits
able to lift washrag off tabletop using any type prehension then release it
major components
massed practice and shaping of affected limb w/repetitive fxnal ax
3-6hrs a day; shaped ax for increasing difficulty
environmental/task modifications allowed to enhance performance
contemporary motor learning principles (random, variable, natural, problem solving)
restraint of less affected UE to prevent use
transfer package: adherence based behavioral method to promote transfer to ADL training (logs, contracts, homework, etc.)
ayres sensory integration
inherent neural organization of sensory information creates pathways for increasing mature and effective adaptive responses
interventions…
aim to modify regulatory state without having lasting neurophysiological impact
are tailored sensory experiences and sensory tools that support function
may be passive or active
passive: weighted vest during class, steamrollers in prone
active: alternative seating, fidget toys, chew toys
should not disrupt routine
may or may not be playful
group based or individualized
equipment used is minimal w/no training required
assumptions
plasticity of CNS
therapeutic environment = just right challenge + sensory motor learning experiences + active problem solving + mature adaptive responses
higher cortical processing dependent on organization of sensory info at lower brain centers
adaptive responses!! allow adequate modulation and supports optimal development
sensory integration and praxis tests (SIPT)
measures sensory integration skills that are associated w/learning disabilities, emotional disorders, and minimal brain dysfunction
standardized; 4-8.11yrs
seventeen tests
address tactile processing, vestibular-proprioceptive processing, visual perception, and practicability
DeGangi-Berk test of sensory integration (TSI)
standardized; 3-5yrs
measures sensory integrative fxn with focus on vestibular system
three areas:
bilateral motor coordination, postural control, reflex integration
test of sensory functions in infants
standardized; 1-18mos
assess level of sensory responsiveness to variety of sensory stimuli
sensory processing measure (SPM)
elementary school aged children
measures sensory processing, praxis, and social participation across different environments
assesses all 7 senses
visual, auditory, tactile, olfactory-gustatory, proprioceptive, and vestibular behaviors
Ayres sensory integration intervention OT role
control sensory input that is child driven and play based
create environment to facilitate active participation for just right challenge
ensure registration of meaningful sensory input
balance structure and freedom (tap into inner drive of child)
gradually introduce new activities and grade up
promote organized adaptive responses
general sensory integration intervention principles
grade and apply appropriate sensory combo
firm pressure and resistance > light touch
linear movement > angular
slow movement > rapid
combo of stimuli must be used to elicit adaptive response for effective intervention
starting point
closely monitor response to stimuli and adhere to precautions (hyper/hypo responses)
tactile interventions
modulation/responsiveness
self-applied stimuli is more tolerable than passive
use firm pressure
use controlled sensory activities with simultaneous tactile and vestibular-proprioceptive input
start w/slow linear and deep pressure
apply tactile stimuli in direction of hair growth
follow tactile stimuli with joint compression
discrimination
deep touch to hands and body
usually simultaneously with deficits in motor planning
graded ax requiring discrimination
proprioception interventions
modulation/responsiveness
firm touch, pressure, joint compression, traction
resistance to active movement for learning force for task
use various body positions (yoga, obstacle courses, etc.)
slow linear movement, resistance, and deep pressure
use adaptive techniques (weight vests)
discrimination
all above w/activities requiring ability to grade force or effort of movements
vestibular interventions
modulation/responsiveness
grade type and rate of movement
slowly introduce linear movement with touch pressure in prone and provide resistance to active movement
gravitational insecurity!
use linear vestibular stimuli to increase spatial orientation
use rapid rotary and angular movements with deceleration/acceleration to increase ability to distinguish pace of movement (semicircular canals)