IB Chem Unit 2: Equilibrium
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is equilibrium?
when the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction in a closed system, resulting in constant concentrations of reactants and products.
What must be the case for equilibrium to be achieved?
The system must be closed!!!
What is phase equilibrium?
rate of one phase change is equal to the rate of the same change in opposite direction
eg: H2O (l) ←→ H2O (g)
What is chemical equilibrium?
the rate of the forward chemical reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse chemical reaction
eg: NsO4 (g) ←→2 NO2 (g)
What is solution equilibrium?
the rate of dissolving is equal to the rate of crystallization, must be a saturated solution
What happens to the amount of reactants and products once a reaction reaches equilibrium?
the concentration of the reactants and products remains constant once you reach equilibrium (in a closed system)
What is true in dynamic equilibrium?
macroscopic properties (like concentration) are constant and the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction
What is the equilibrium constant?
Keq or Kc, the ratio of reactants to products at a particular temperature
Does the equilibrium constant depend on the reaction mechanism?
no, the equilibrium constant is independent of the reaction mechanism
this means we can use the cooeficents of the reaction to calculate Keq (aka Kc)
Consider the general reaction:
aA + bB → cC + dD
What is the equation to calculate the equilibrium constant?
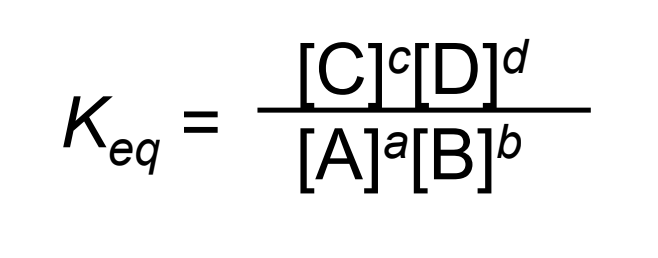
What are the units for equilibrium constant?
you do not need units
What do we need to do before we can plug concentrations into the formula for Keq?
you have to determine the concentrations of solution when at equilibrium
What does it mean if Keq > 1?
the reaction is product favored, product predominates at equilibrium, equilibrium lies to the right
What does it mean if Keq < 1?
the reaction is reactant favored, reactant predominates at equilibrium, equilibrium lies to the left
How can we calculate the equilibrium constant even if we don’t know all the concentrations?
tabulate the known initial and equilibrium concentrations for each species in he expression, calculate the change in concentration, use stoichiometry to calculate the changes in the unknown concentrations, calculate the initial concentrations
How does the equilibrium constant change if you reverse the reaction?
it is the reciprocal of the Keq of the original reaction
How does the equilibrium constant change if you multiply the reaction by some number, x?
the equilibrium constant is the original raised to the power of that number, x
How does the equilibrium constant get calculated if it is for a net reaction made of 2 or more steps?
the equilibrium constant is the product of each equilibrium constant at each step
How can you determine the direction of the reaction?
compare the initial concentrations to the equilibrium concentration, a measure used in chemistry to compare the current state of a chemical reaction to its equilibrium state
What is the reaction quotient?
Q, allows us to look at initial concentrations
How does temperature affect Keq?
for endothermic reactions, increasing temperature increases Keq
for exothermic reactions, increasing temperature decreases Keq
(LeChatelier’s Principle)
For the general reaction:
aA + bB → cC + dD
What is the equation for the reaction quotient?

What does it mean if Q < K ?
the reaction has to shift towards the products to reach equilibrium, reaction shifts right
What does it mean if Q=K ?
the reaction is at equilibrium, there is no shift to reach equilibrium since you are already there
What does it mean is Q > K ?
the reaction has to shift towards the reactants to reach equilibrium, the reaction shifts left
What does the reaction quotient basically tell you?
Where the reaction is at now (in terms of concentration of reactants and products)
what does equilibrium constant basically tell you?
Where the reaction is at equilibrium (in terms of concentration of products and reactants)
What is LeChatelier’s Principle?
if a system at equilibrium is disturbed by a change in temp, pressure, or concentration, the system will shift its equilibrium position so as to counteract the effect
What is the effect of an increase in concentration of a reactant on equilibrium?
if there is an increase in the concentration of one of the reactants that causes an increase in the number of collisions on the reactant side which causes an increase in the rate of the forward reaction leading to a shift of equilibrium to the product side
What is the effect of a decrease of concentration of a reactant on equilibrium?
a decrease in reactant concentration will cause a decrease in the number of collisions on the reactant side which causes a decrease in the rate of the forward reaction resulting in a shift toward the reactant side
What effect does an increase of temperature have on the position of equilibrium?
an increase in temperature causes a greater increase in the number of collisions on the energy side (the side that has the heat) which causes an increase in the rate of the endothermic reaction resulting in a shift in the direction of the endothermic reaction
What is the effect of a decrease of temperature on the position of equilibrium?
a decrease in temperature causes a greater decrease in the number of collisions on the energy side which causes a decrease in the rate of reaction in the endothermic direction resulting in a shift in the direction of the exothermic reaction (equilibrium shifts towards the heat side)
What is the effect of an increase of pressure on the position of equilibrium? (gases only)
an increase in pressure causes a greater increase in number of collisions on the side with the greater number of moles, resulting in a shift toward the side with fewer moles
What is the effect of a decrease of pressure on the position of equilibrium? (gases only)
a decrease in pressure causes a greater decrease in the number of collisions on the side of the reaction with more moles o gas, resulting in the equilibrium shifting towards the side with more moles of gas
How does a catalyst affect the position of equilibrium?
a catalyst has no effect on the position of equilibrium, it just ensures that equilibrium can be reached more quickly but does not result in a shift in either direction
What is Gibbs Free Energy used for?
can be used to determine if a reaction is spontaneous
When is a reaction spontaneous?
only if ΔG is negative
If ΔH is - and ΔS is +, at what temperatures is that reaction spontaneous?
all temperatures
If ΔH is + and ΔS is -, when is that reaction spontaneous?
no temperatures, never spontaneous
If ΔH is + and ΔS is +, when is that reaction spontaneous?
only at high temperatures
If ΔH is - and ΔS is -, when is the reaction spontaneous?
at low temperatures
When is equilibrium achieved in terms of G and S?
equilibrium is achieved when G is at a minimum and S is at a maximum
What is G?
free energy
What is S?
entropy
What is free energy under any conditions?
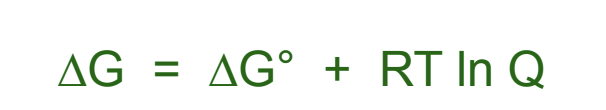
How can we manipulate the energy for free energy under standard conditions?
under standard conditions all concentrations are 1 mol/dm³ so Q=1 and ln(1)=0 so the last term drops out
How can we manipulate the equation for free energy at equilibrium?
at equilibrium Q=K, so we get
