WIND and ATMOSPHERIC CIRCULATION
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is atmospheric pressure?
The force exerted by the weight of air. (At sea level, it's 14.7 psi (1 kg/cm²) and 1013.2 mb)
How does atmospheric pressure change with altitude?
Atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude.
What does rising atmospheric pressure indicate?
Rising pressure indicates "fair" weather.
What does dropping atmospheric pressure indicate?
Dropping pressure indicates "bad" weather.
What is wind?
Wind is the horizontal movement of air from high to low-pressure areas.
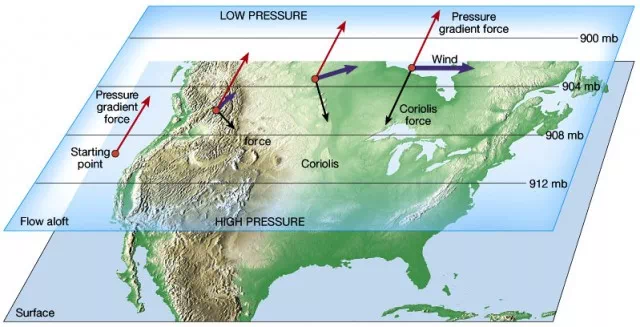
What causes wind to move from high to low-pressure areas?
The pressure gradient force drives this movement.
What are isobars?
Isobars are lines on a map that represent equal air pressure.
What is the Coriolis effect?
The apparent deflection of wind due to Earth’s rotation, deflecting winds to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and left in the Southern Hemisphere.
What is a geostrophic wind?
A wind that moves parallel to isobars, occurring at high altitudes without friction.
What is a jet stream?
A high-speed river of air at high altitudes, moving 120–240 km/h.
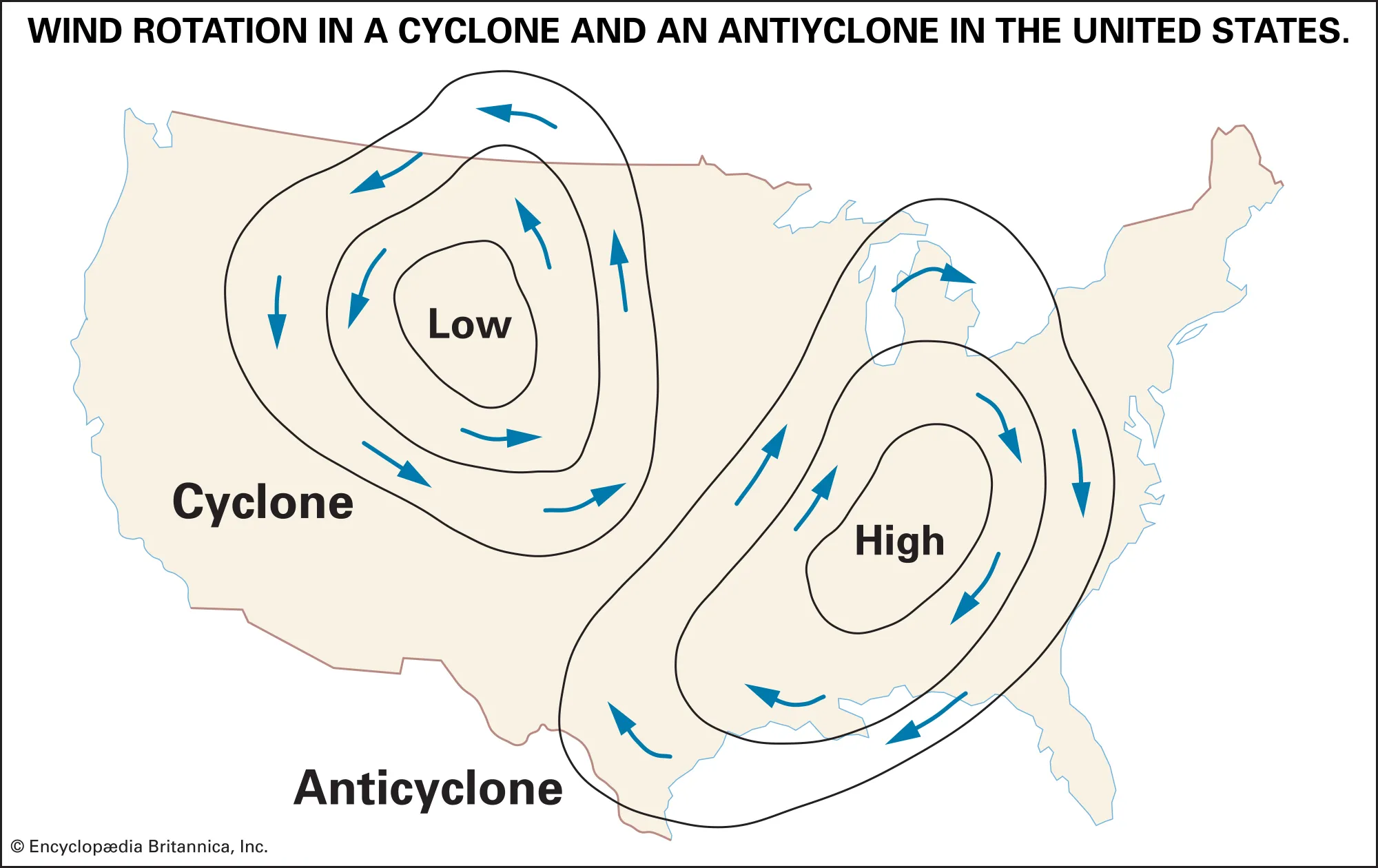
What is a cyclone?
A low-pressure center where air rises, causing inward (convergence) and counterclockwise winds in the Northern Hemisphere.
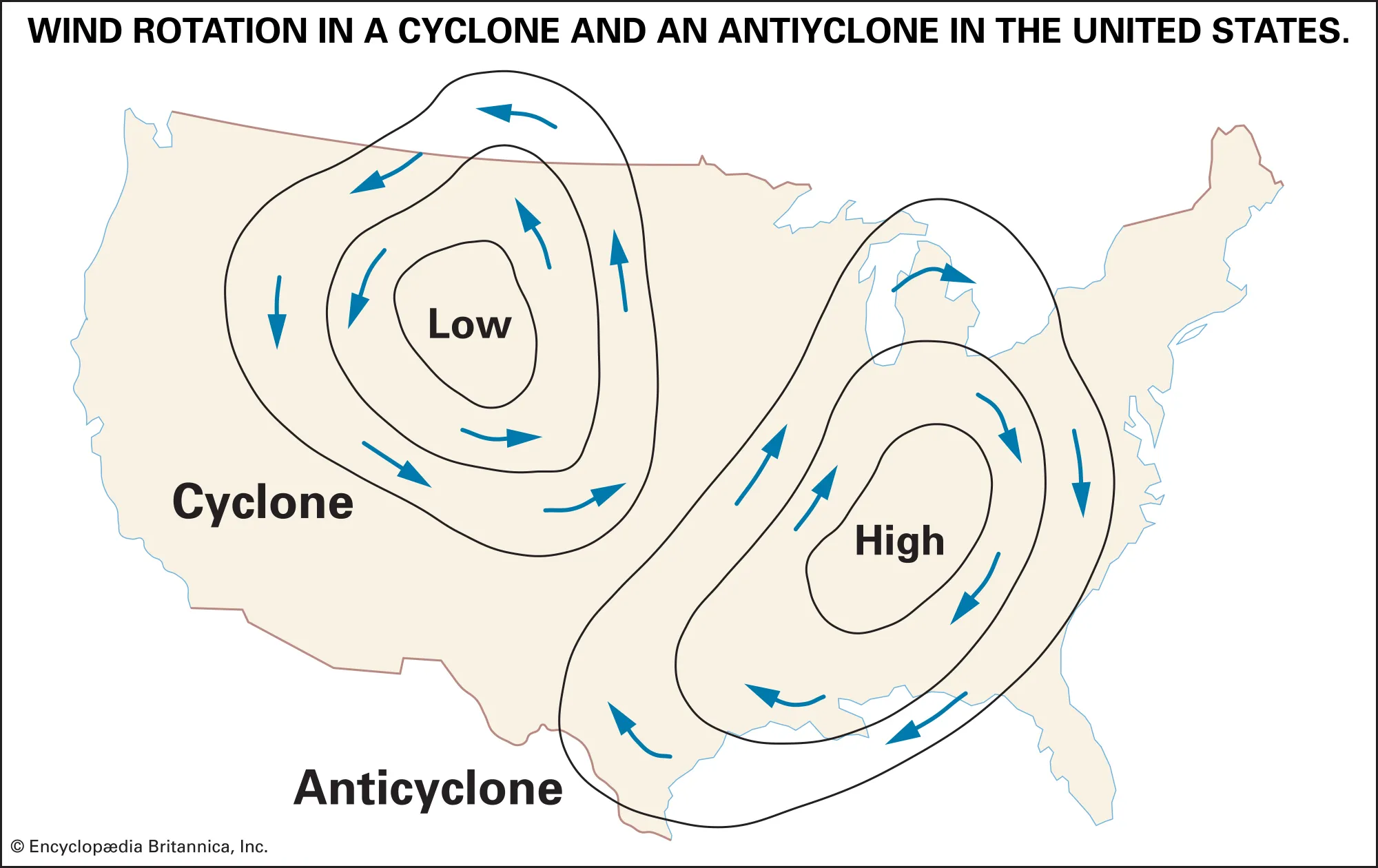
What is an anticyclone?
A high-pressure center where air sinks, causing outward (divergence) and clockwise winds in the Northern Hemisphere.
What weather is associated with a cyclone?
Cyclones usually bring clouds and precipitation.
What weather is associated with an anticyclone?
Anticyclones usually bring fair weather.
What are local winds?
Small-scale winds, such as land and sea breezes, mountain and valley breezes, and chinook winds.
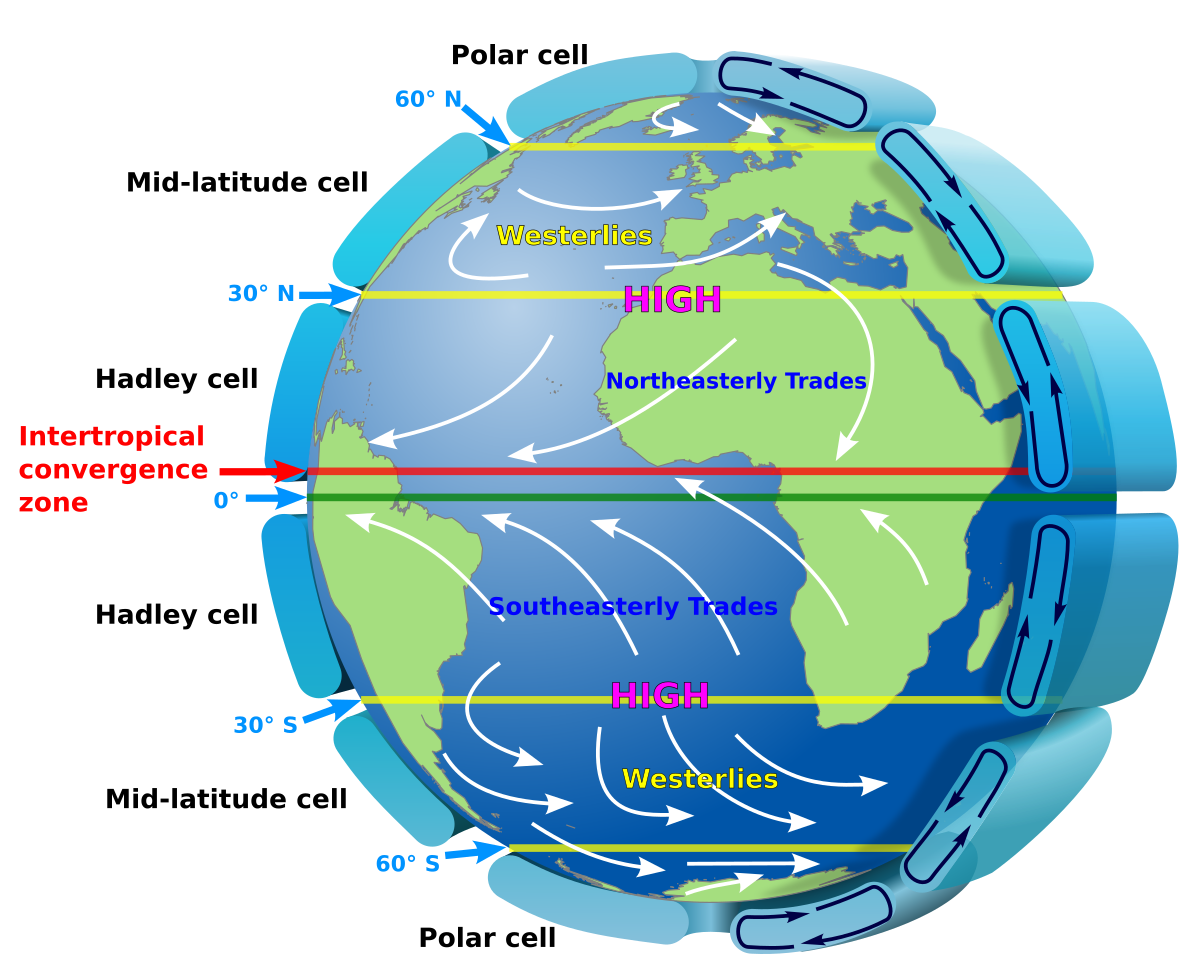
What causes global atmospheric circulation?
Unequal surface heating causes global atmospheric circulation.
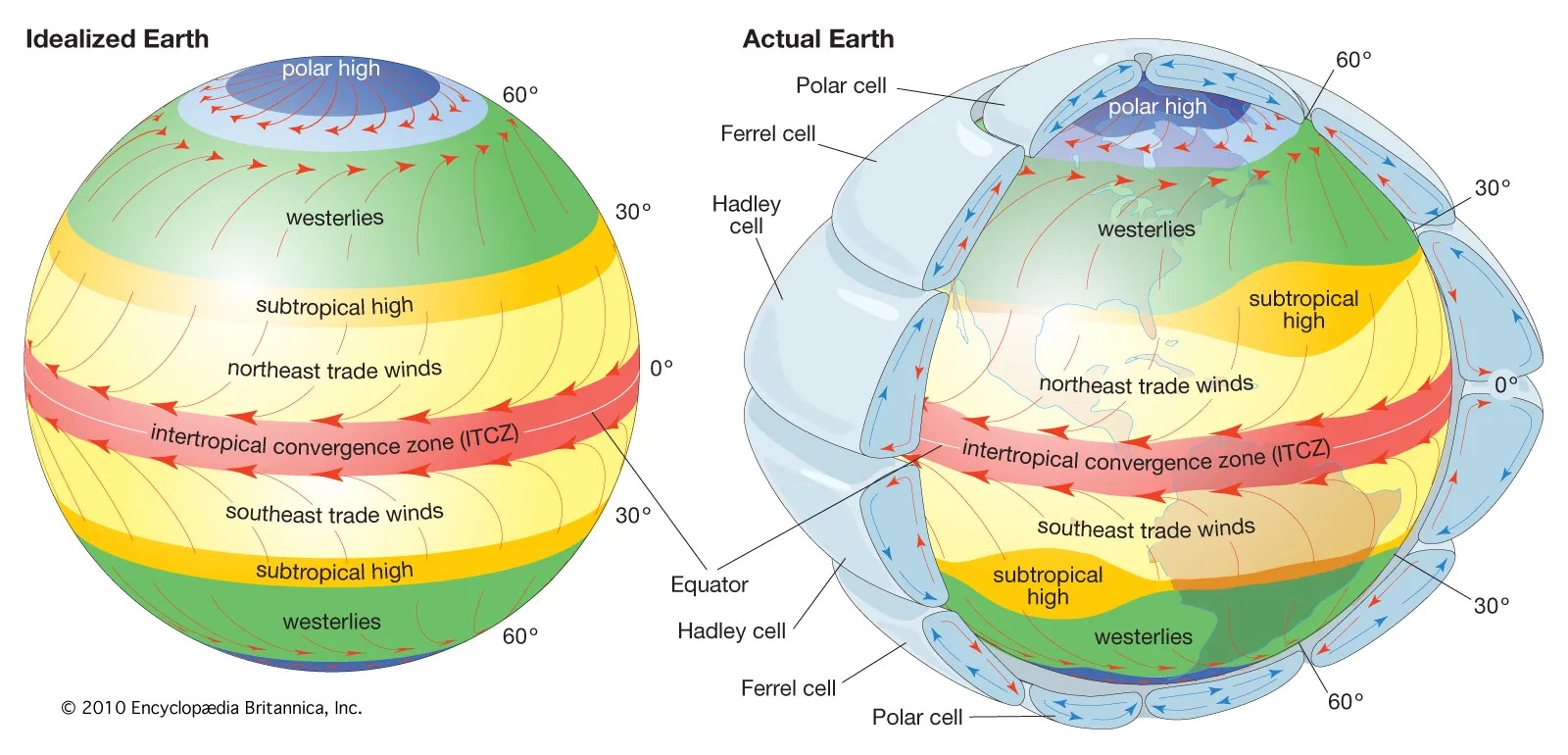
What are Hadley cells?
Three pairs of atmospheric cells on a rotating Earth that redistribute heat.
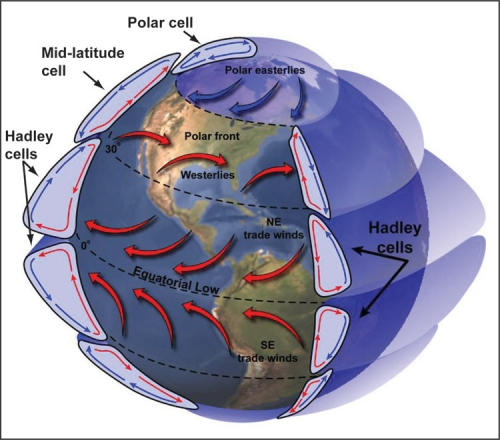
What is the ITCZ (Intertropical Convergence Zone)?
A low-pressure zone near the equator where air rises and causes abundant precipitation.
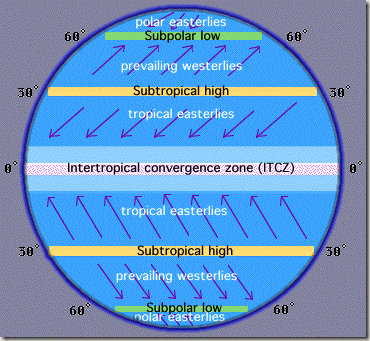
What are the subtropical highs?
High-pressure zones near 30° latitude with sinking, dry air; locations of great deserts.
What are trade winds?
Winds that travel from the subtropical highs toward the equator.
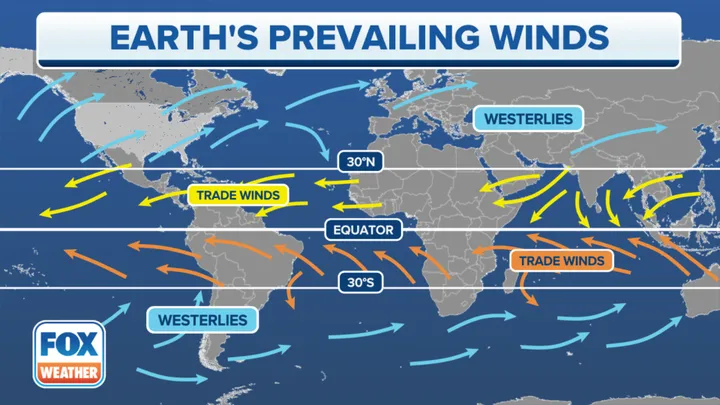
What are westerly winds?
Winds that travel from the subtropical highs toward the poles.
What is the polar high?
A high-pressure zone at the poles where cold, sinking air creates polar easterlies.
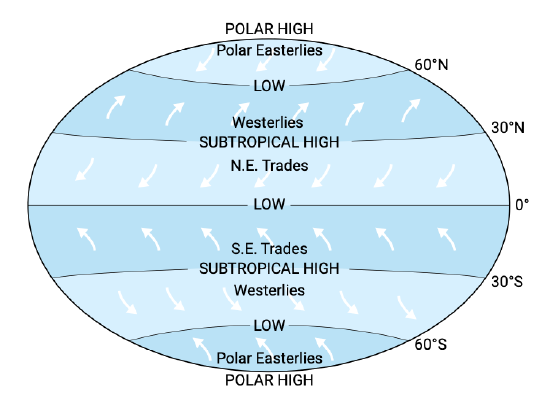
What is a monsoon?
A seasonal change in wind direction, bringing warm, moist air during summer and dry air during winter.
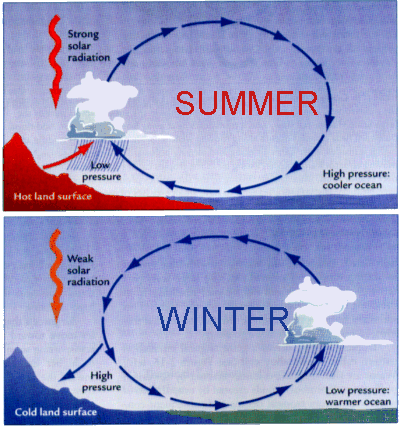
What are the westerlies?
Winds that blow from west to east in the mid-latitudes (30° to 60°).
What are the 4 types of air masses?
Continental Polar (CP), Continental Tropical (CT), Maritime Polar (MP), Maritime Tropical (MT).
What is an occluded front?
A front where a warm front is overtaken by a cold front.
What is El Niño?
A warm current in the Pacific that disrupts normal ocean circulation, causing changes in weather patterns.
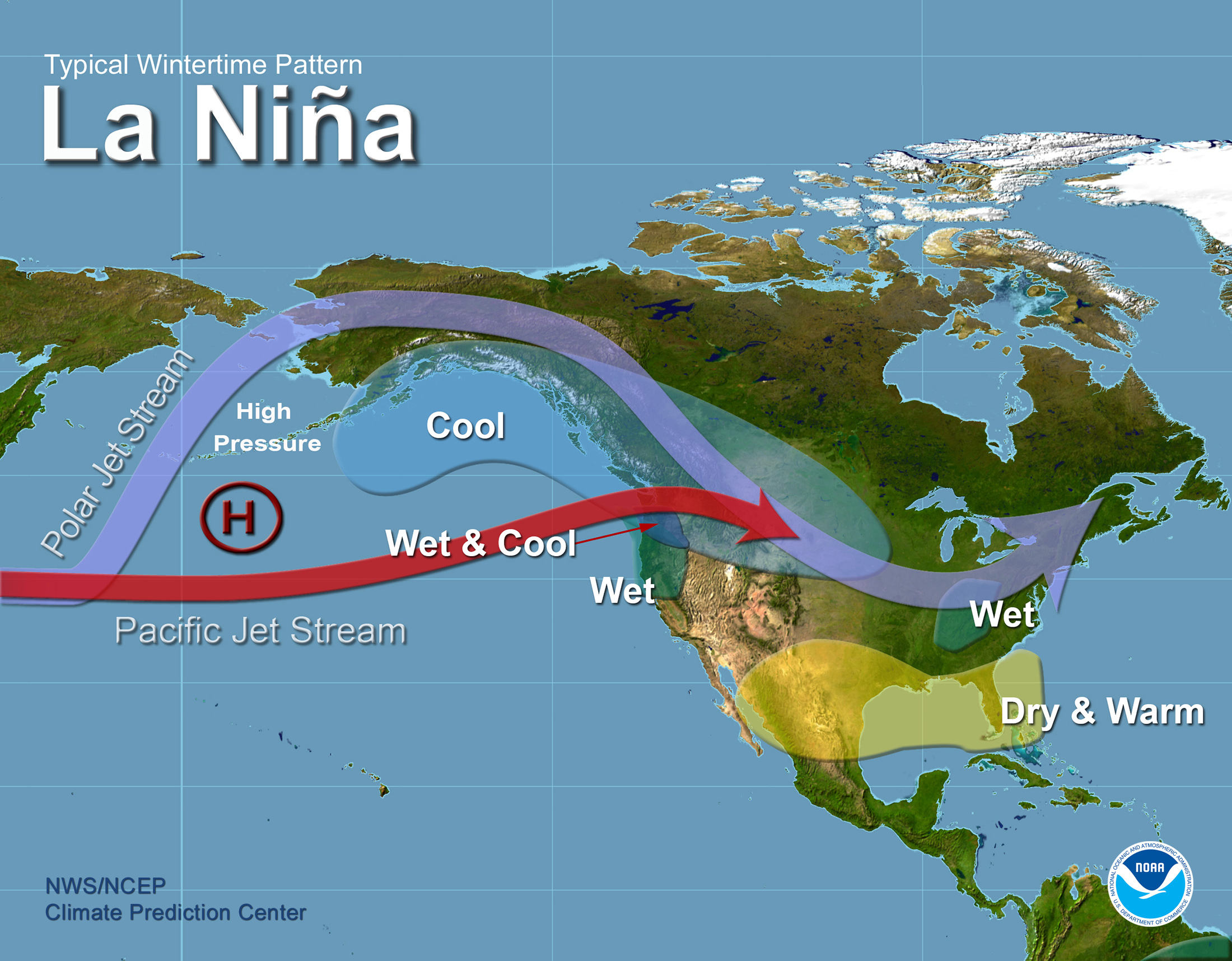
What is La Niña?
A cooling of sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific, opposite of El Niño