Bone Tissue
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
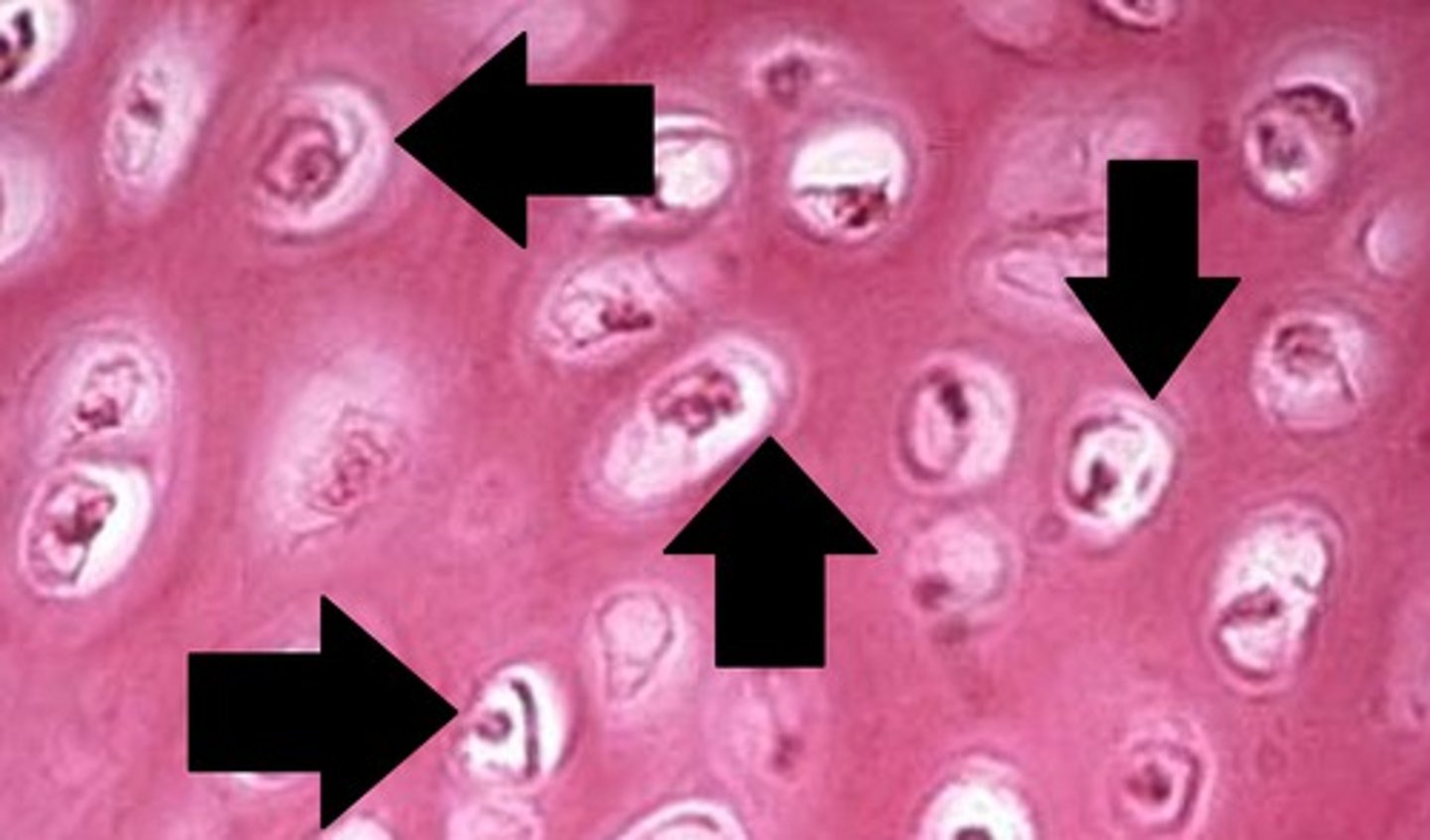
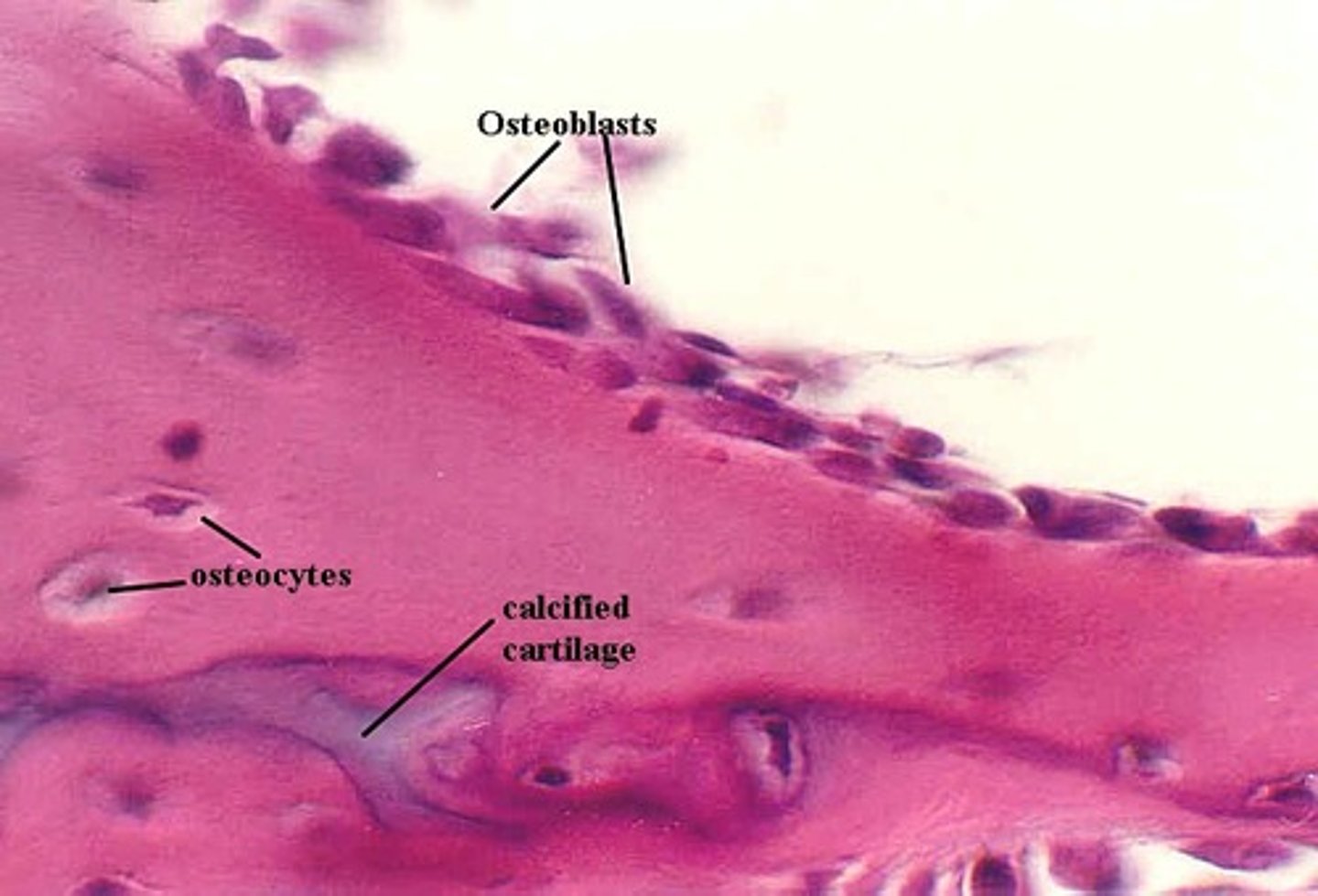
Osteocytes
mature bone cells trapped in matrix that sit in a lacuna
Canaliculi
Hairlike canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
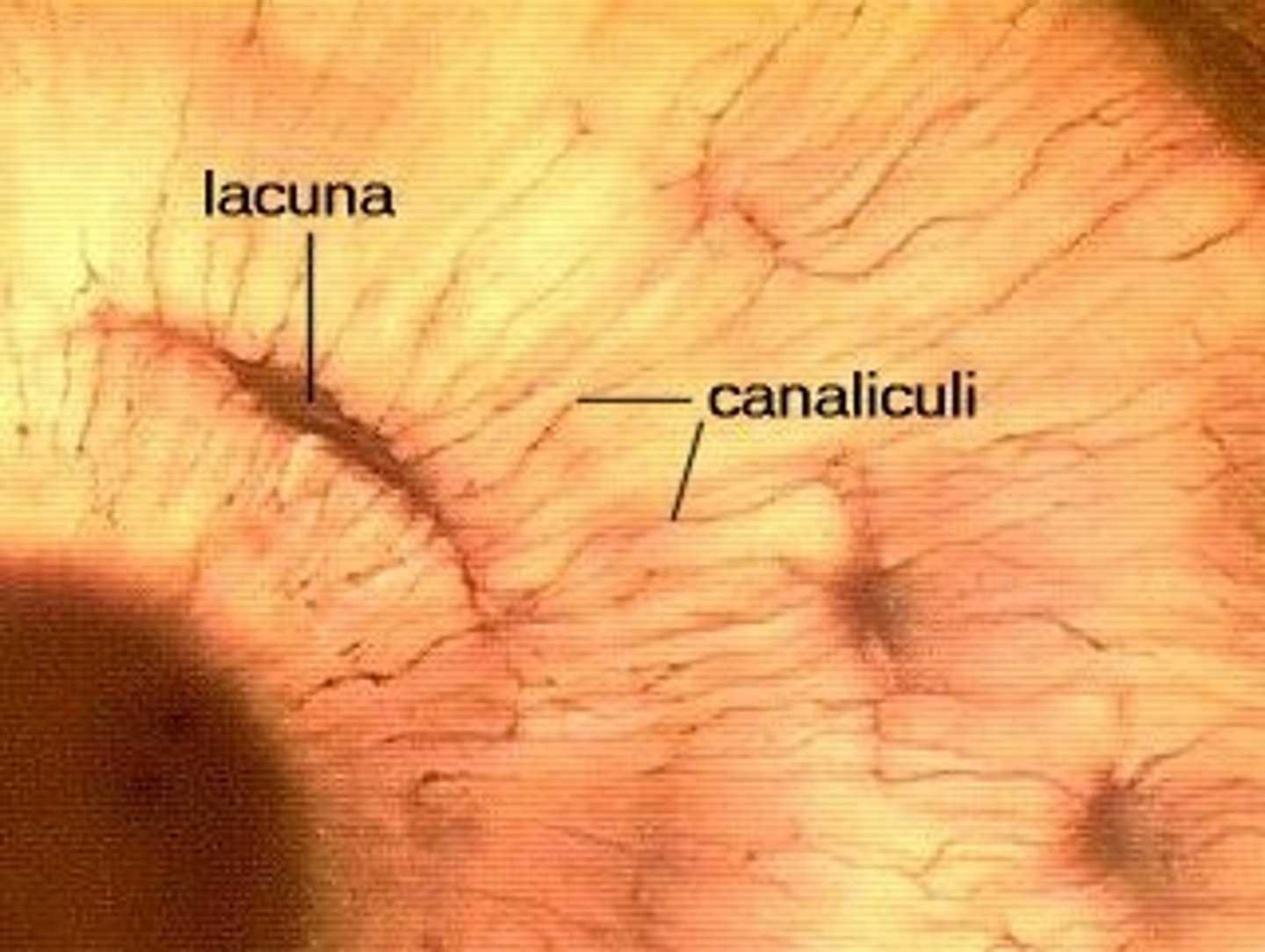
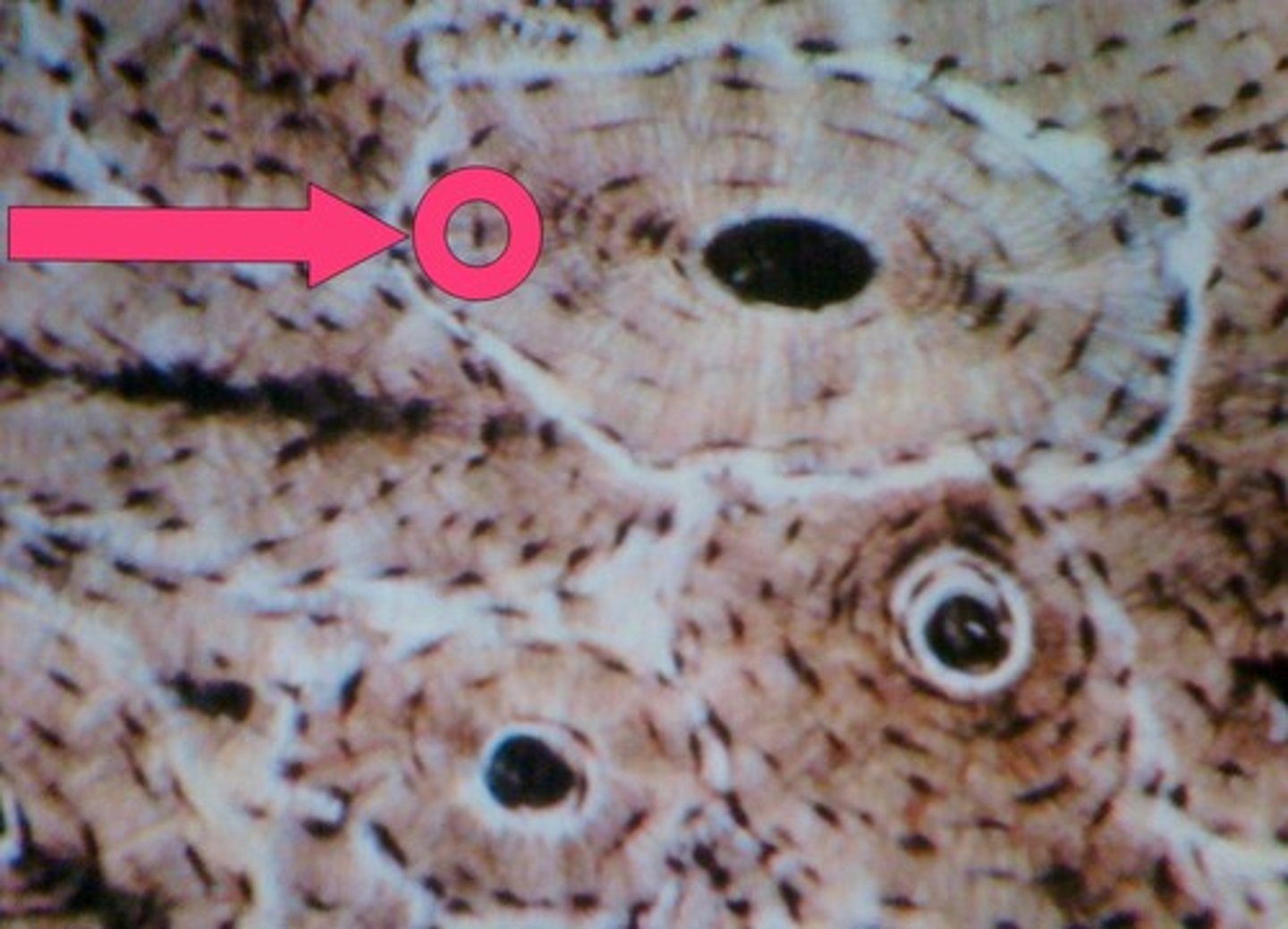
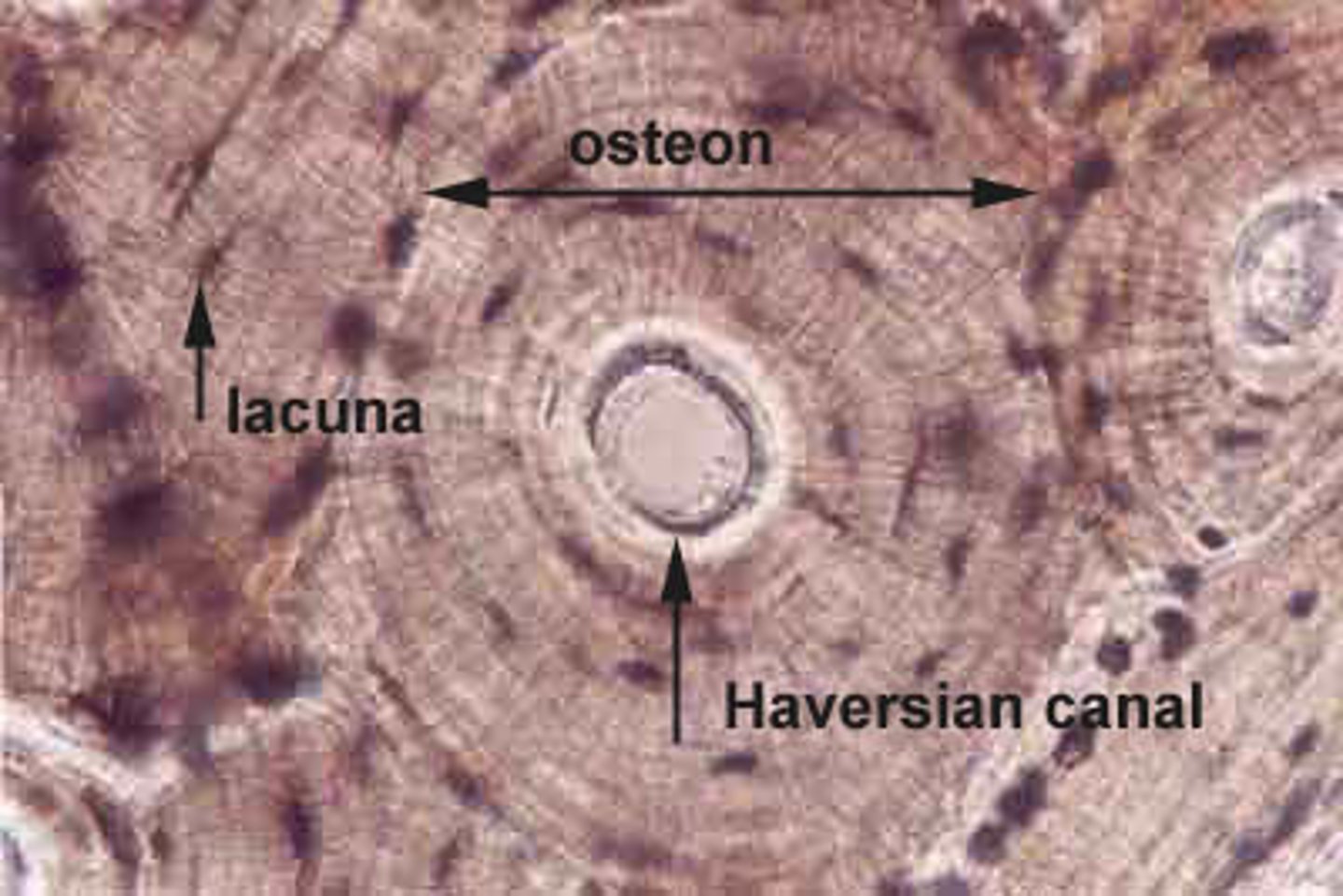
Lacunae
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes
Osteoblasts
Bone building cells
Osteoclasts
large cells that resorb or break down bone matrix
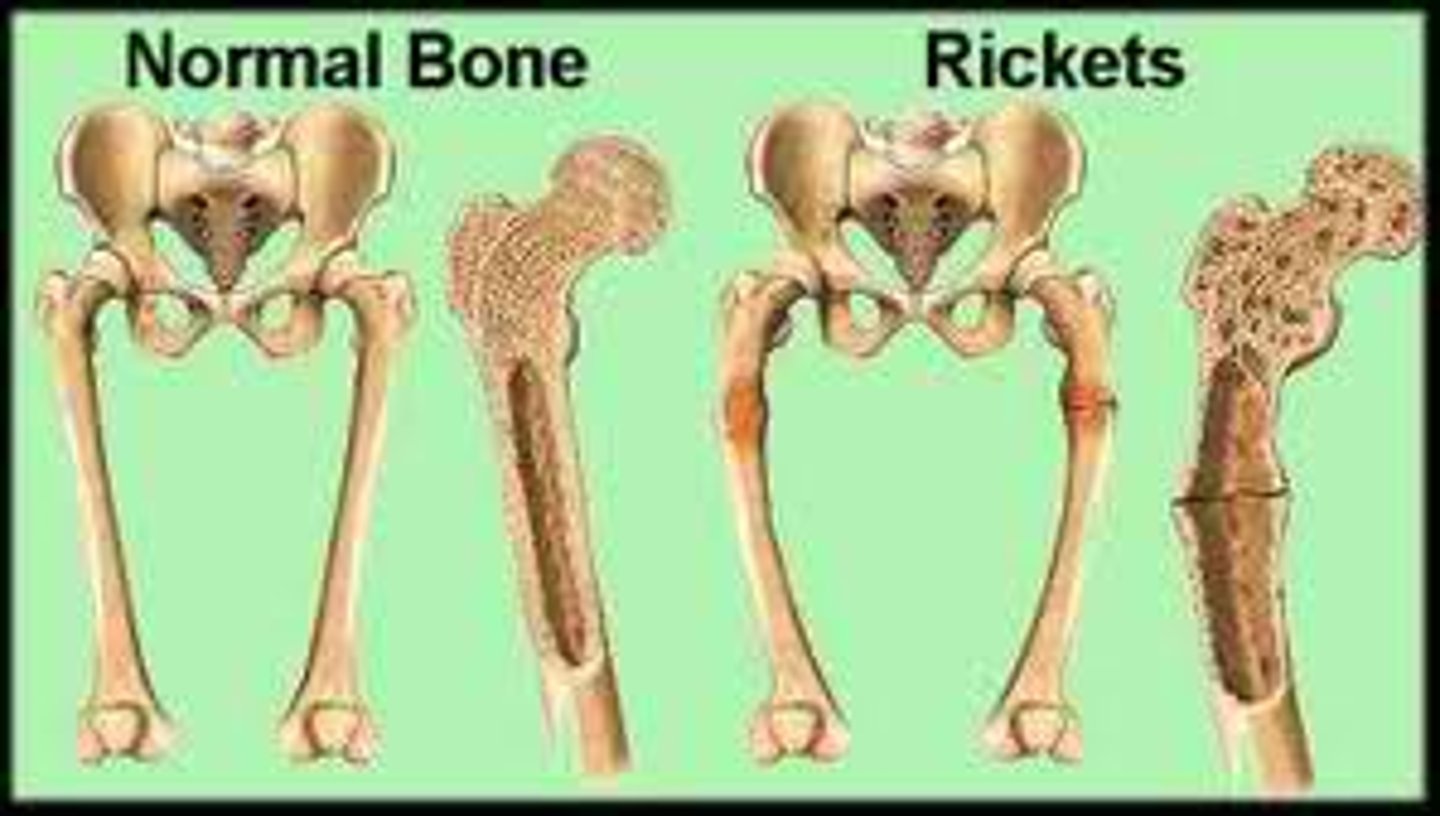
osteomalacia
disease marked by softening of the bone caused by calcium and vitamin D deficiency
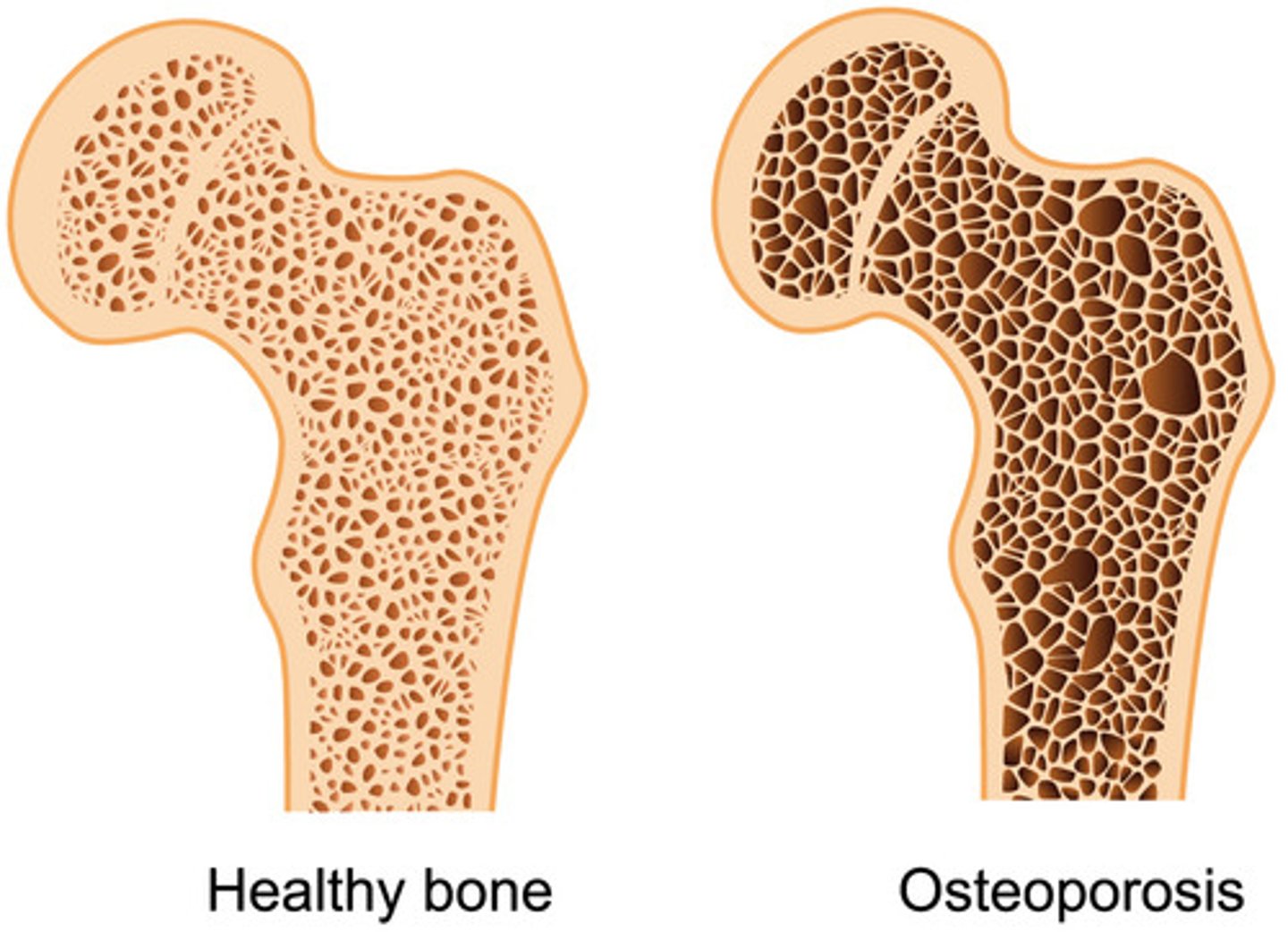
osteporosis
loss of bone density caused by excessive absorption of calcium from bone
Hydroxyapatite
Hardy crystals consisting of calcium and phosphate that form the bone matrix.
Osteoid
unmineralized bone matrix composed of proteoglycans, glycoproteins, and collagen
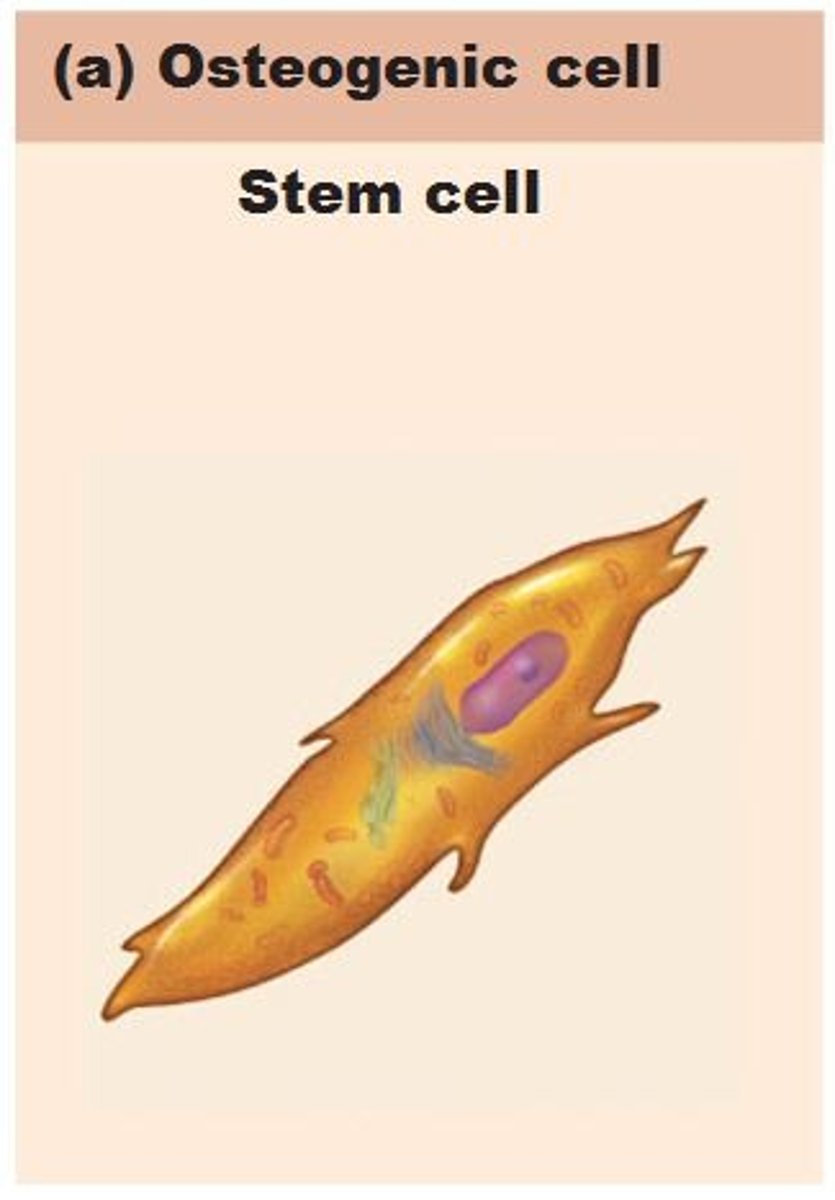
osteogenic cells
stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts
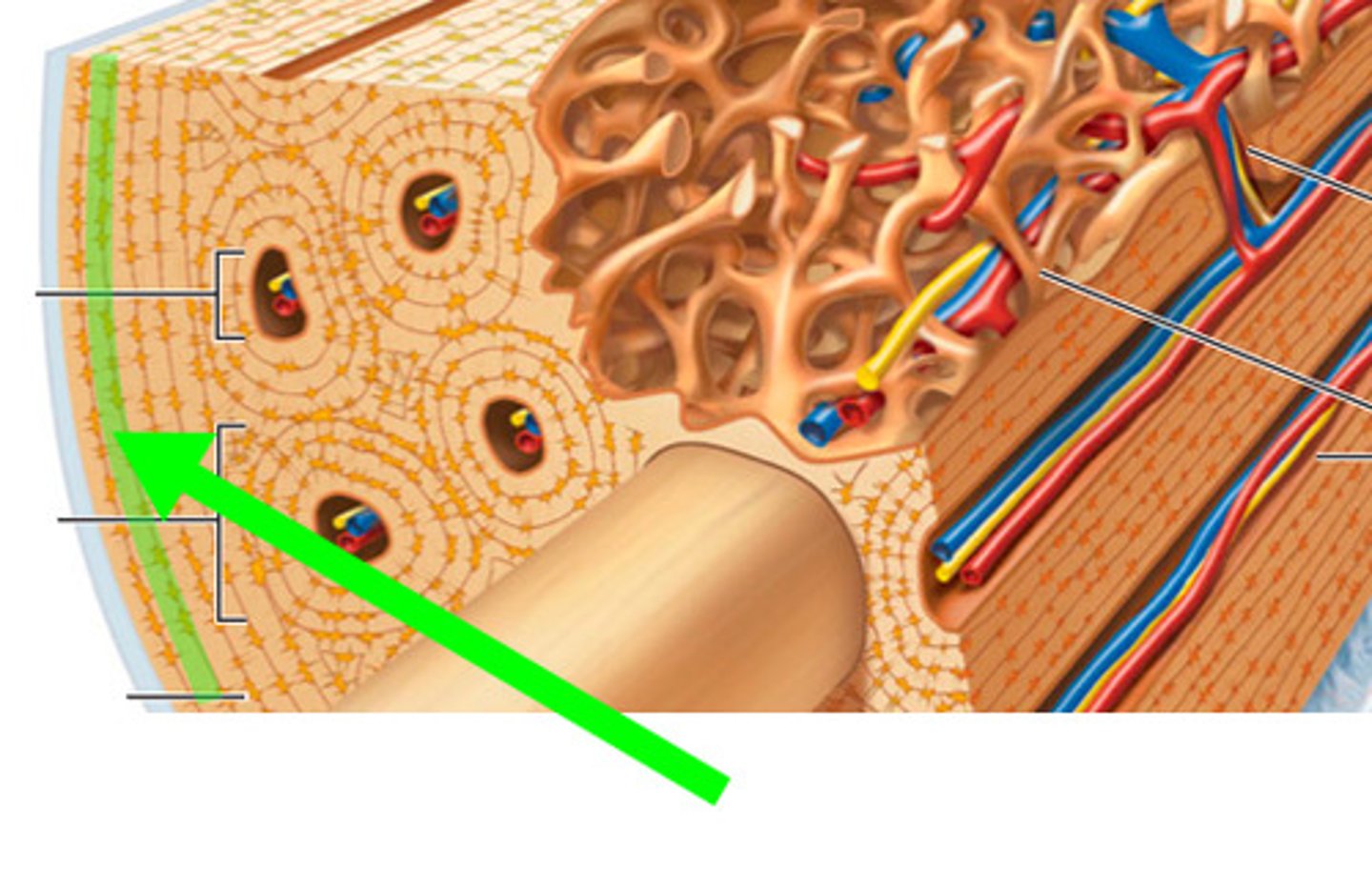
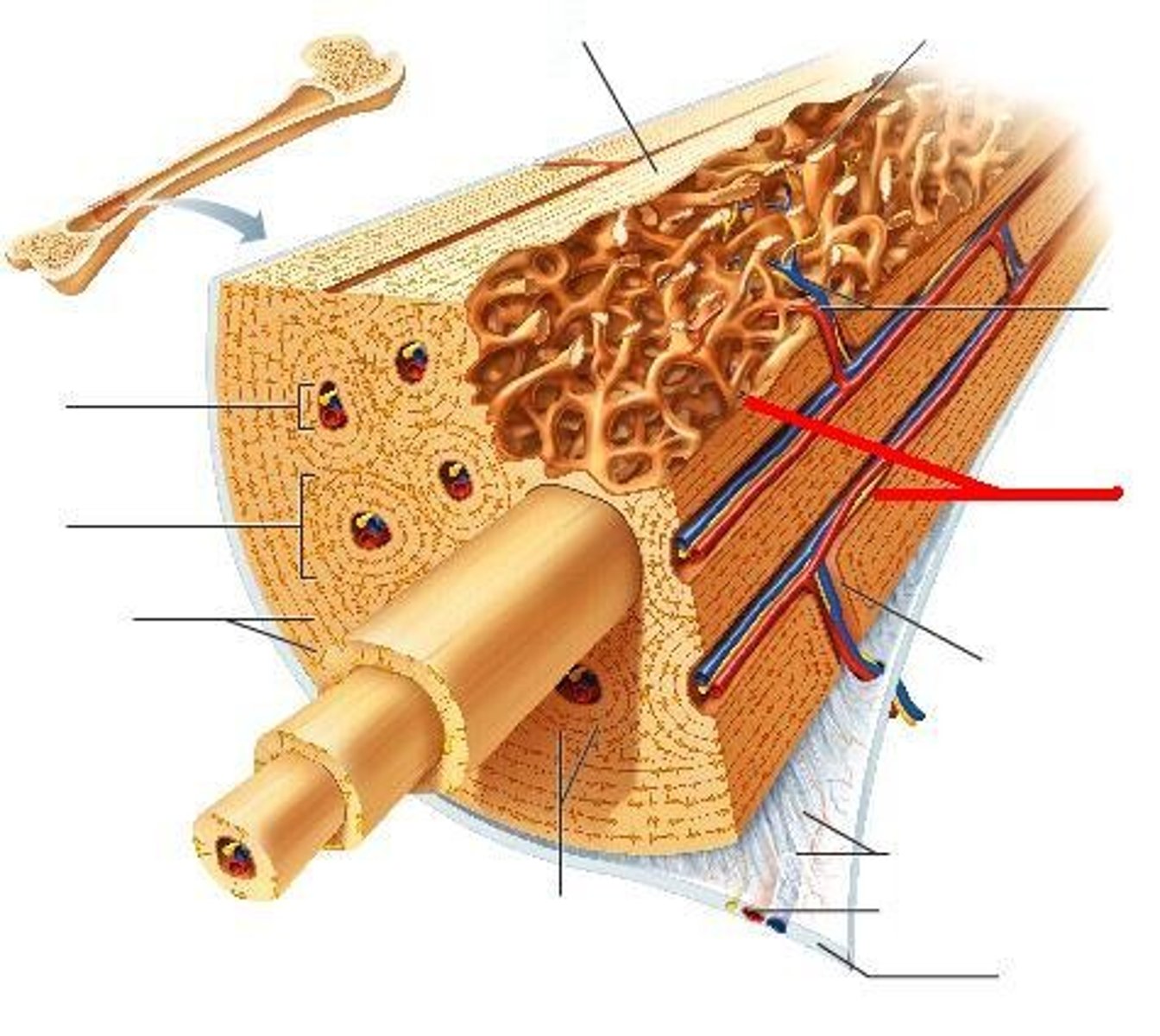
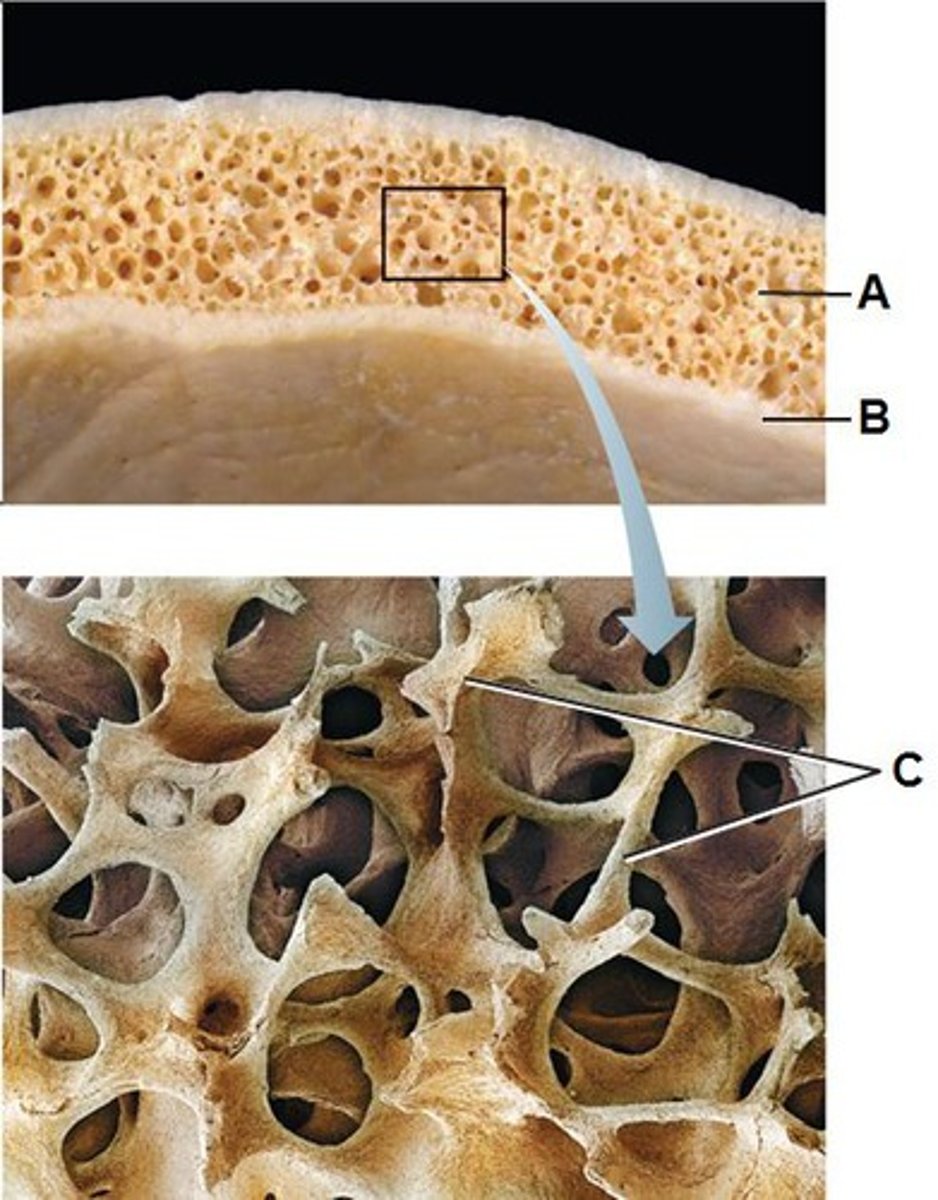
Osteon
structural unit of compact bone
Lamellae
Concentric rings made up of groups of hollow tubes of bone matrix
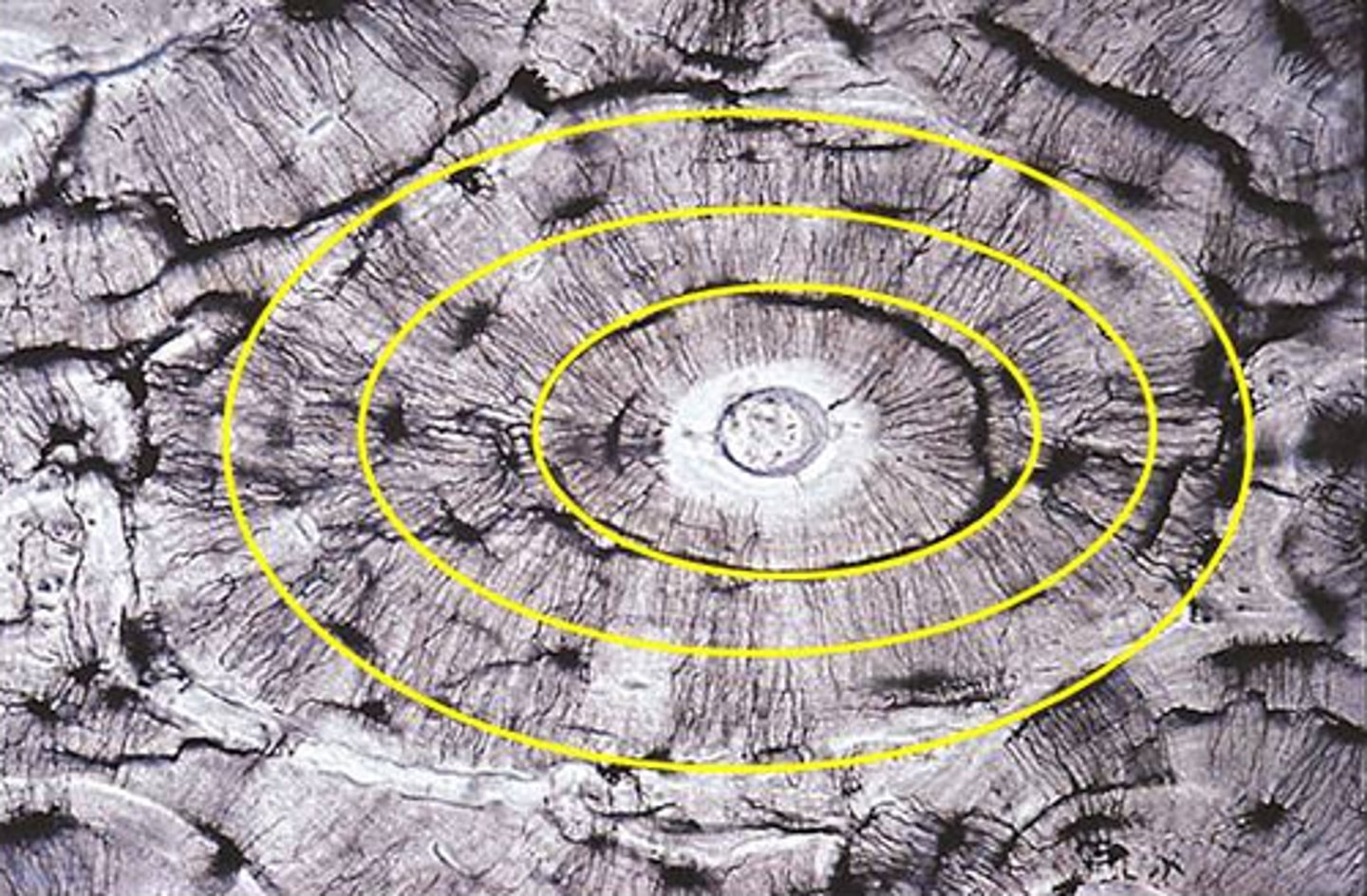
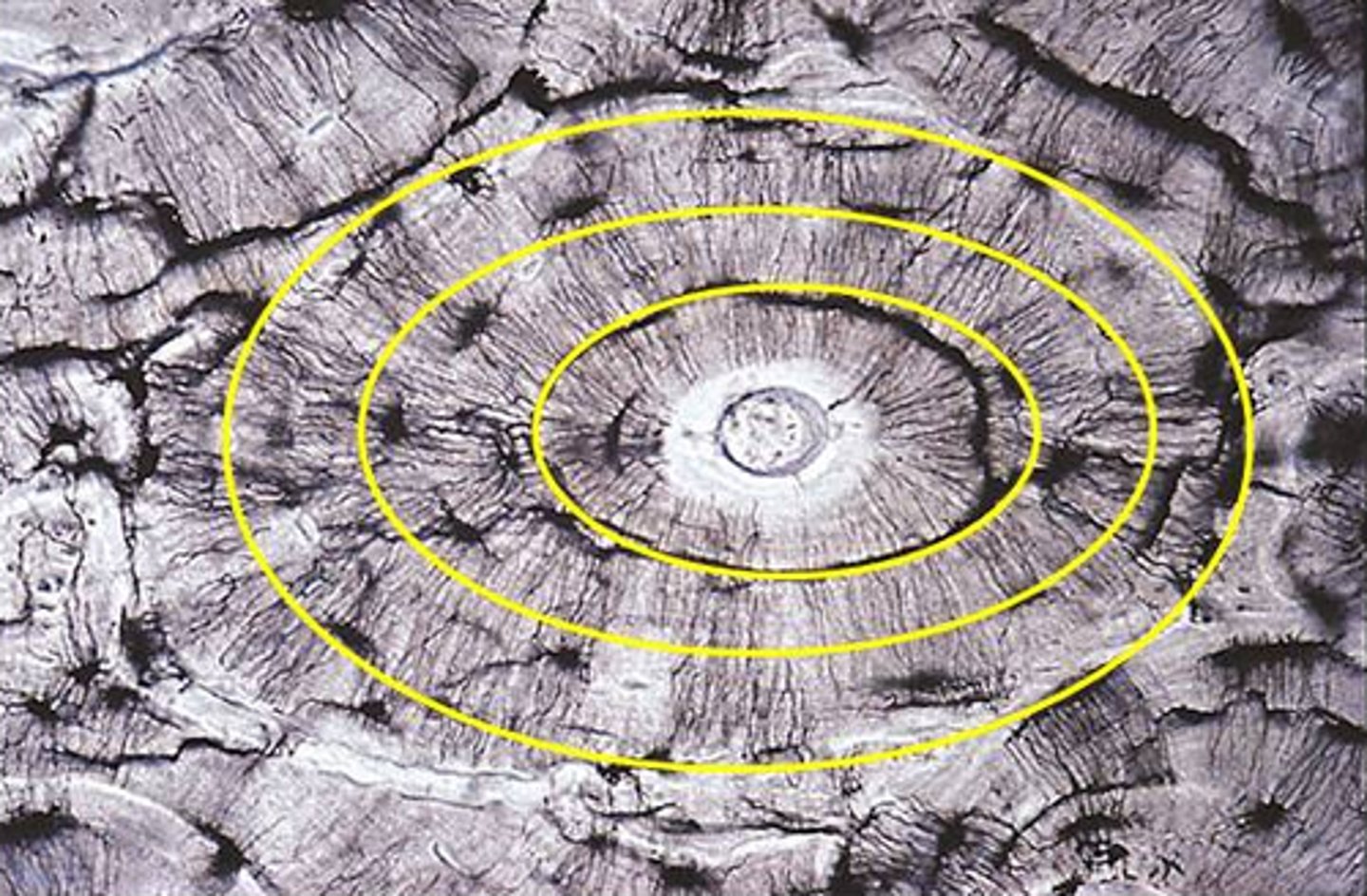
Haversian (central) canal
central channel containing blood vessels and nerves
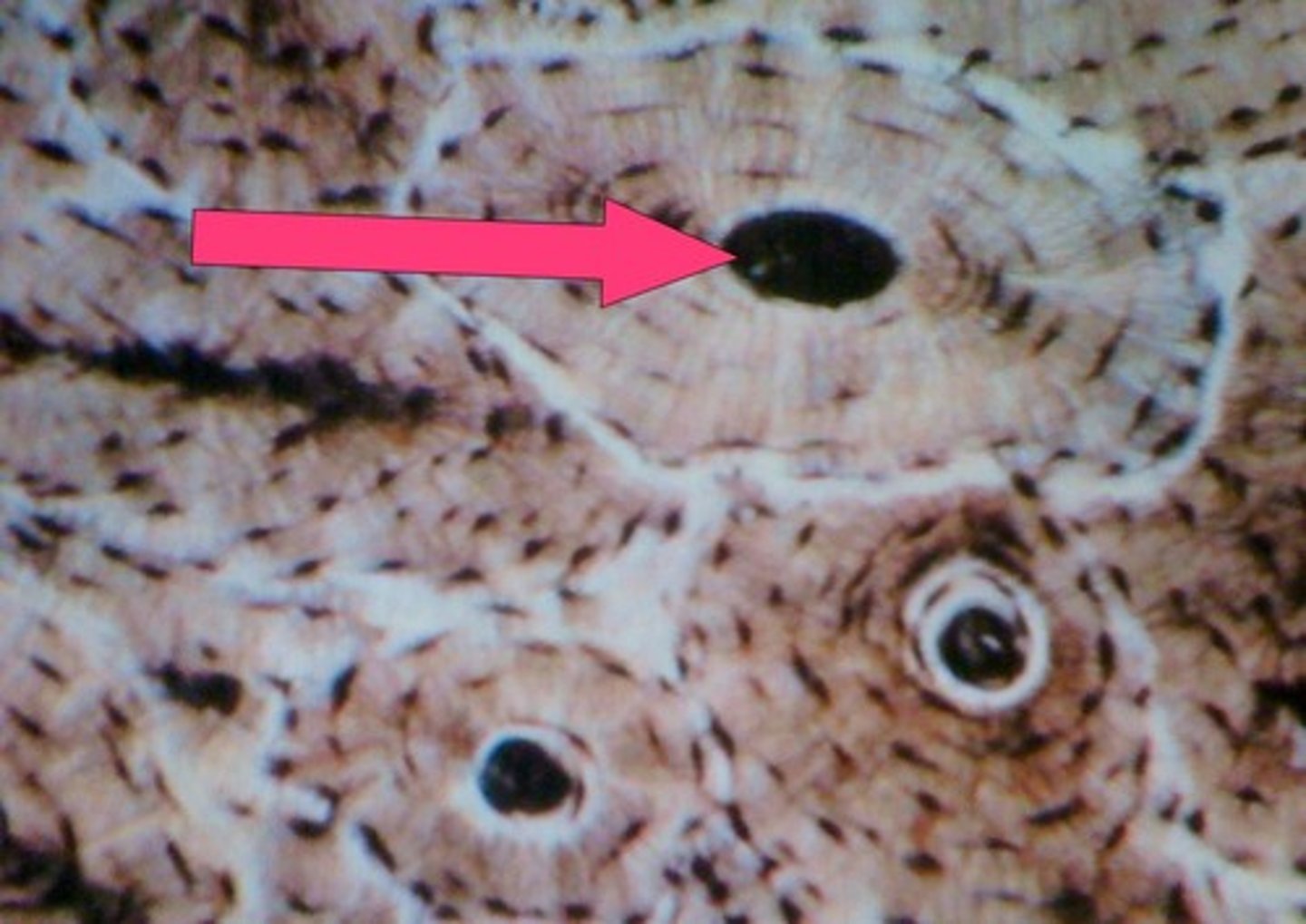
Volkmann's canals
channels lying at right angles to the central canal, connecting blood and nerve supply of the periosteum to that of the Haversian canal
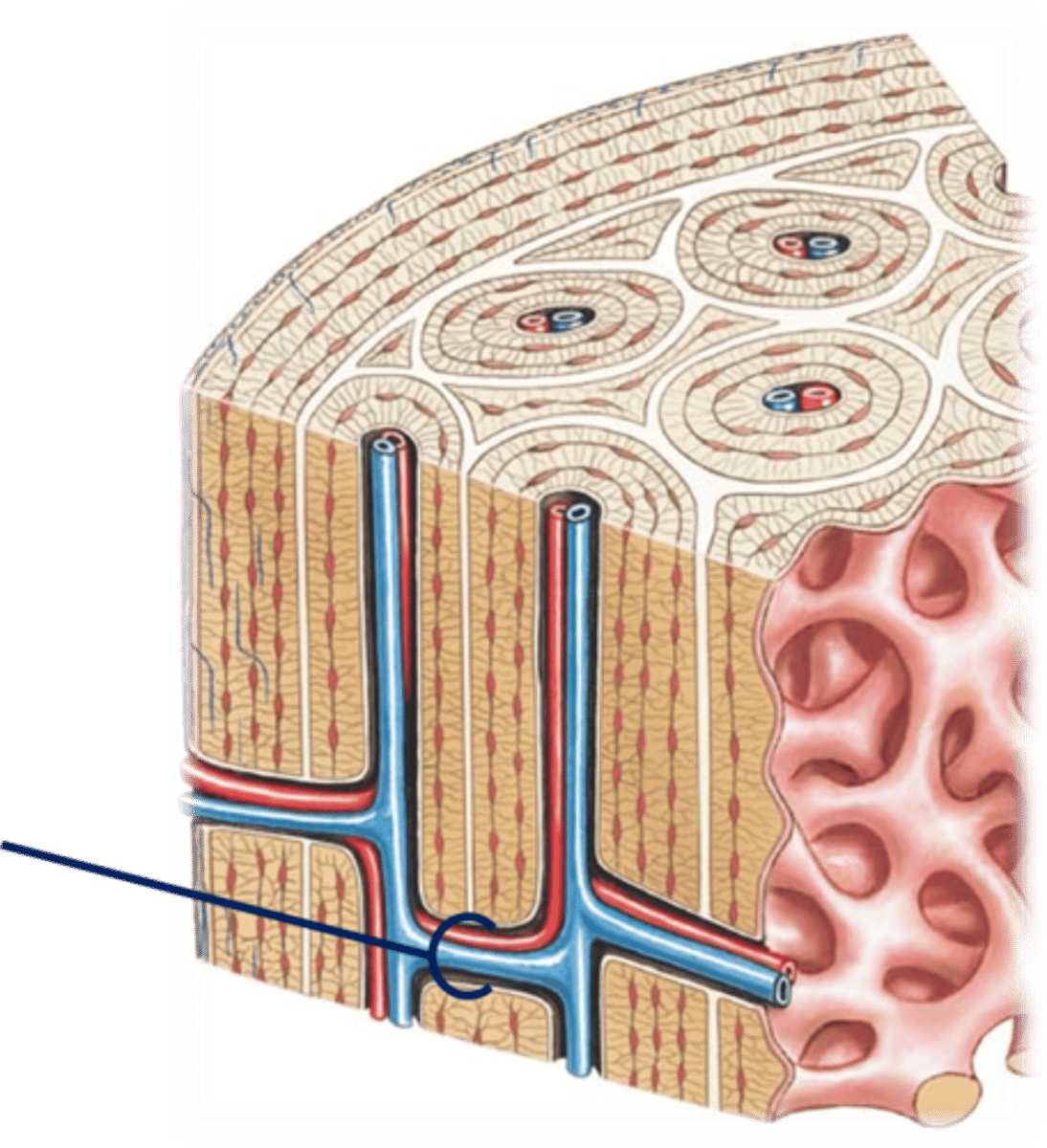
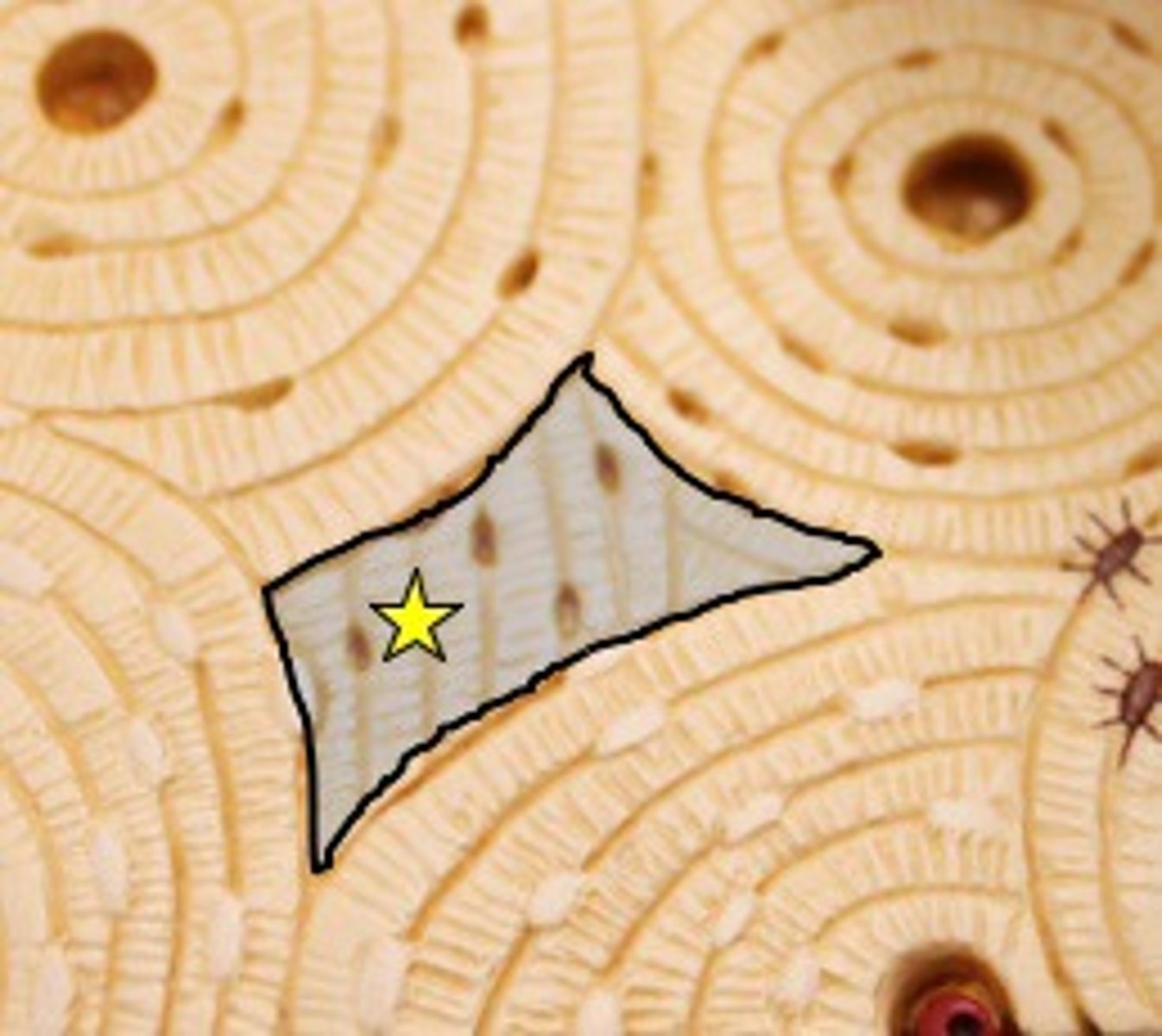
interstital lamellae
fill gaps between forming osteons

concentric lamellae
layers of bony matrix around a central canal
circumferential lamellae
located deep to periosteum and superficial to endosteum and extend around entire circumference of the diaphysis and resist twisting of long bone
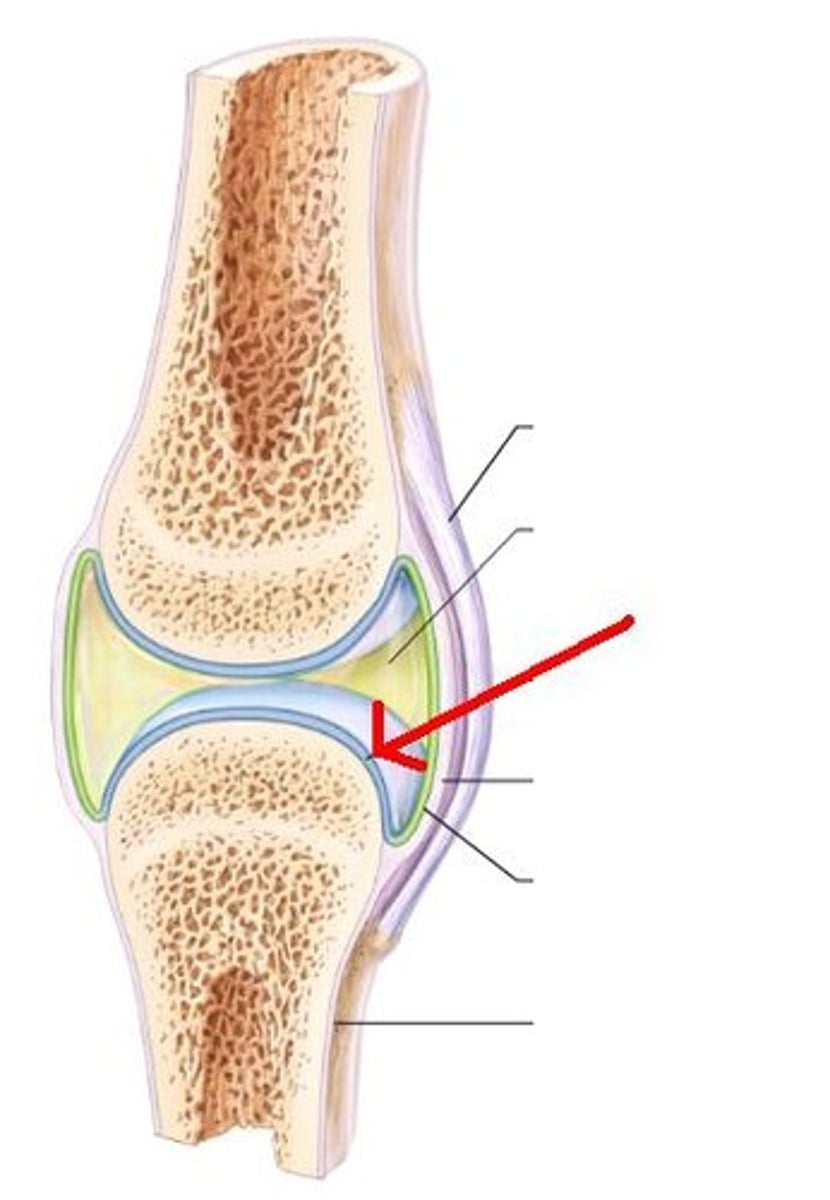
Periosteum
A dense fibrous membrane covering the surface of bones (except at their extremities) and serving as an attachment for tendons and muscles.
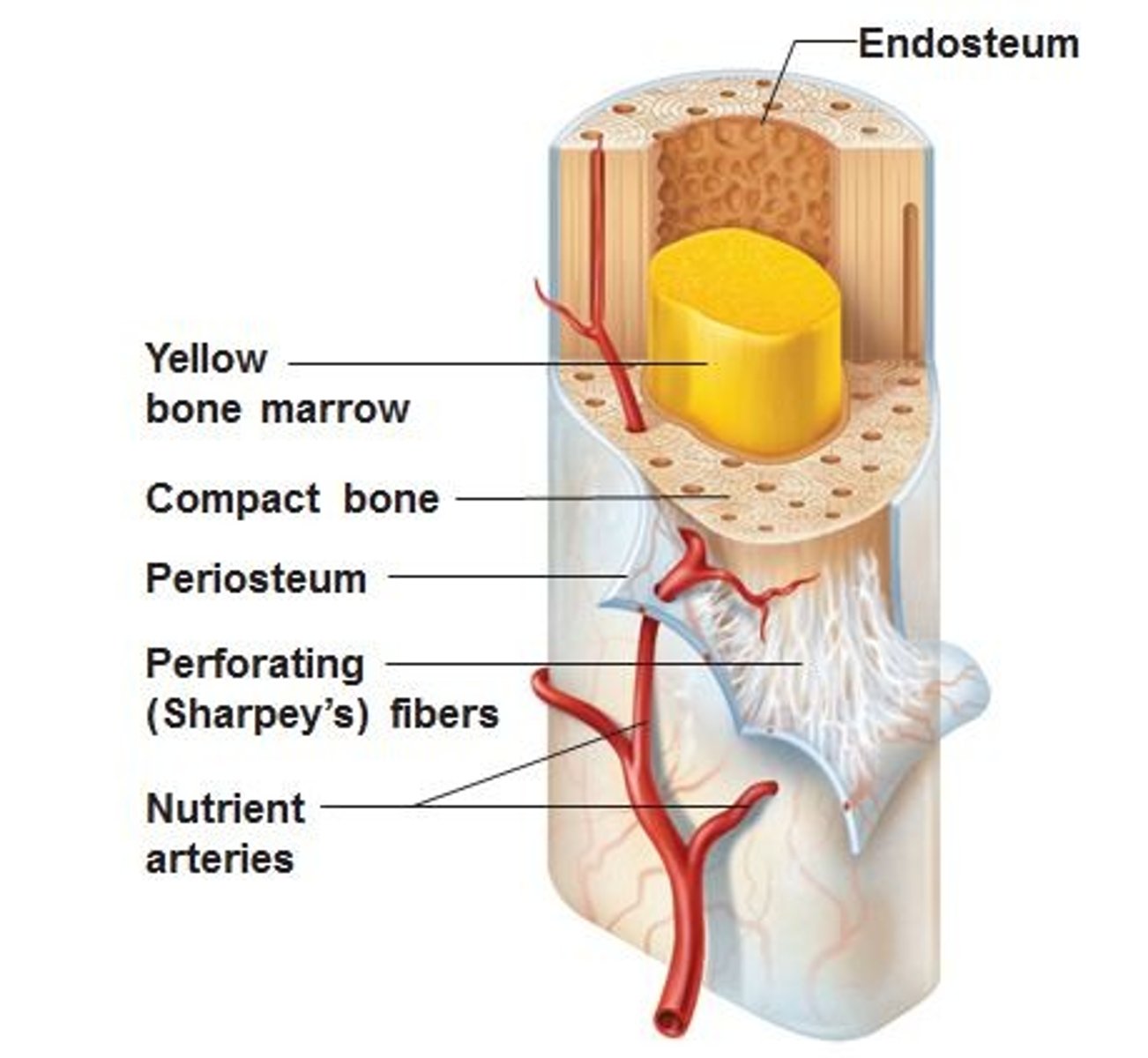
Endosteum
lines the medullary cavity
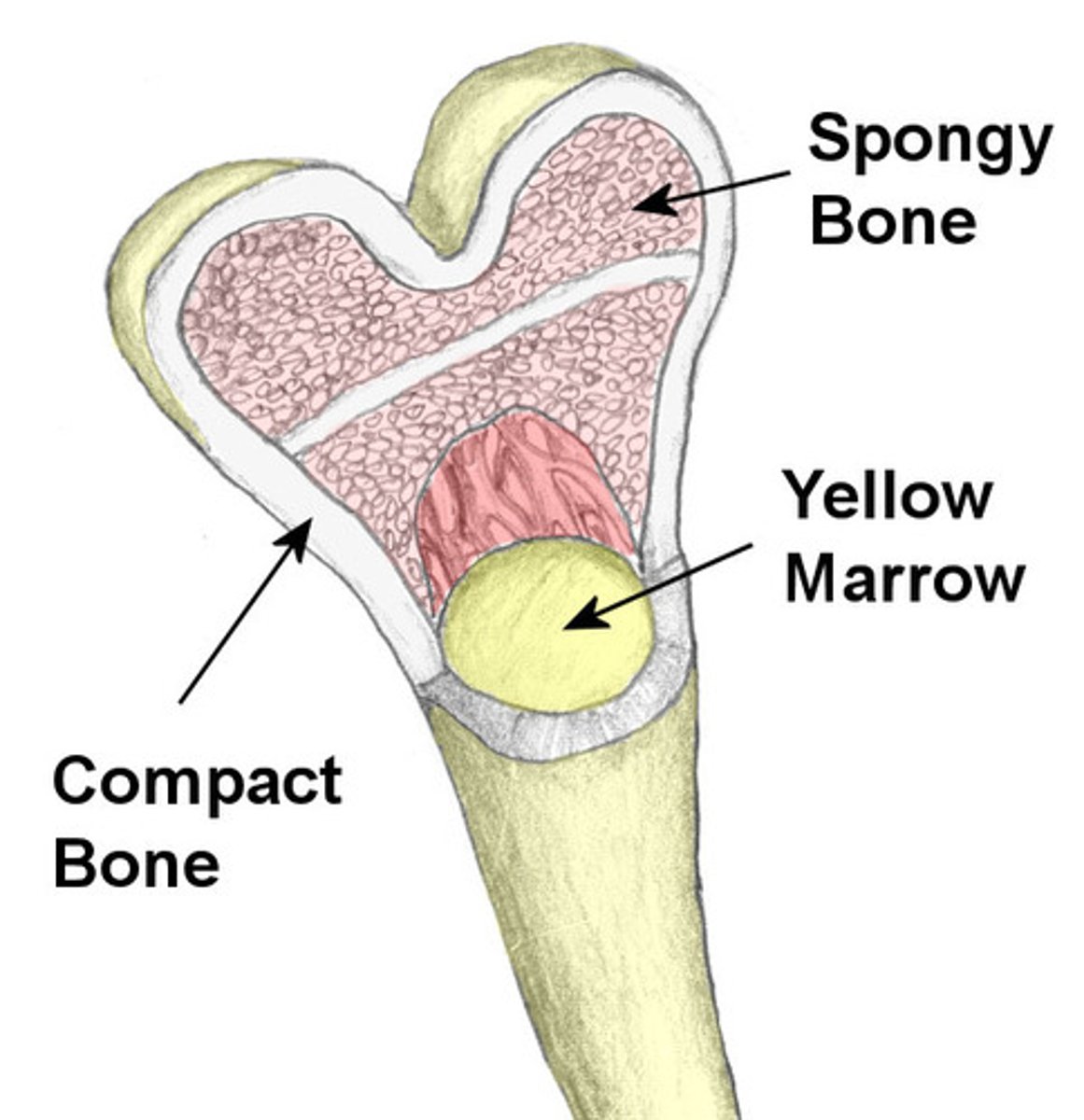
medullary cavity
cavity within the shaft of the long bones filled with bone marrow
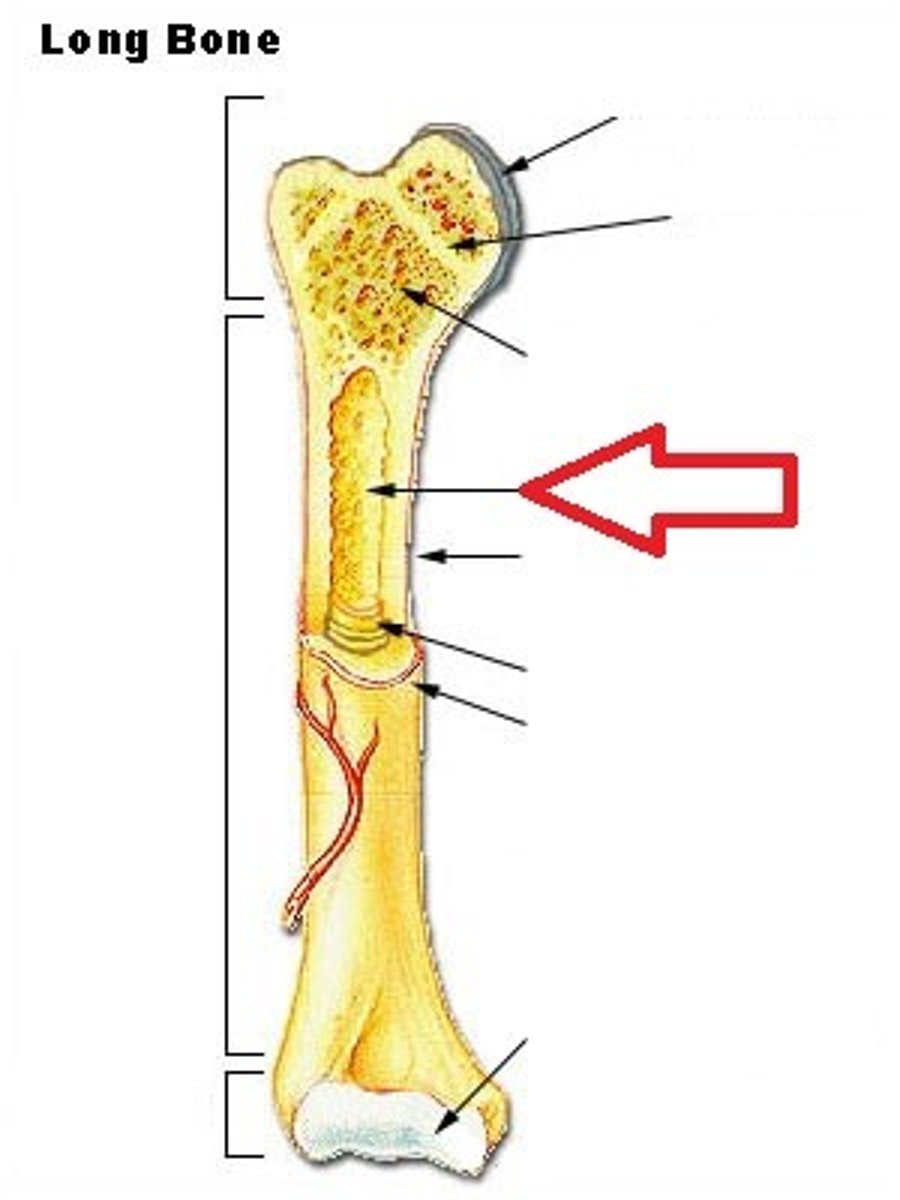
Diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
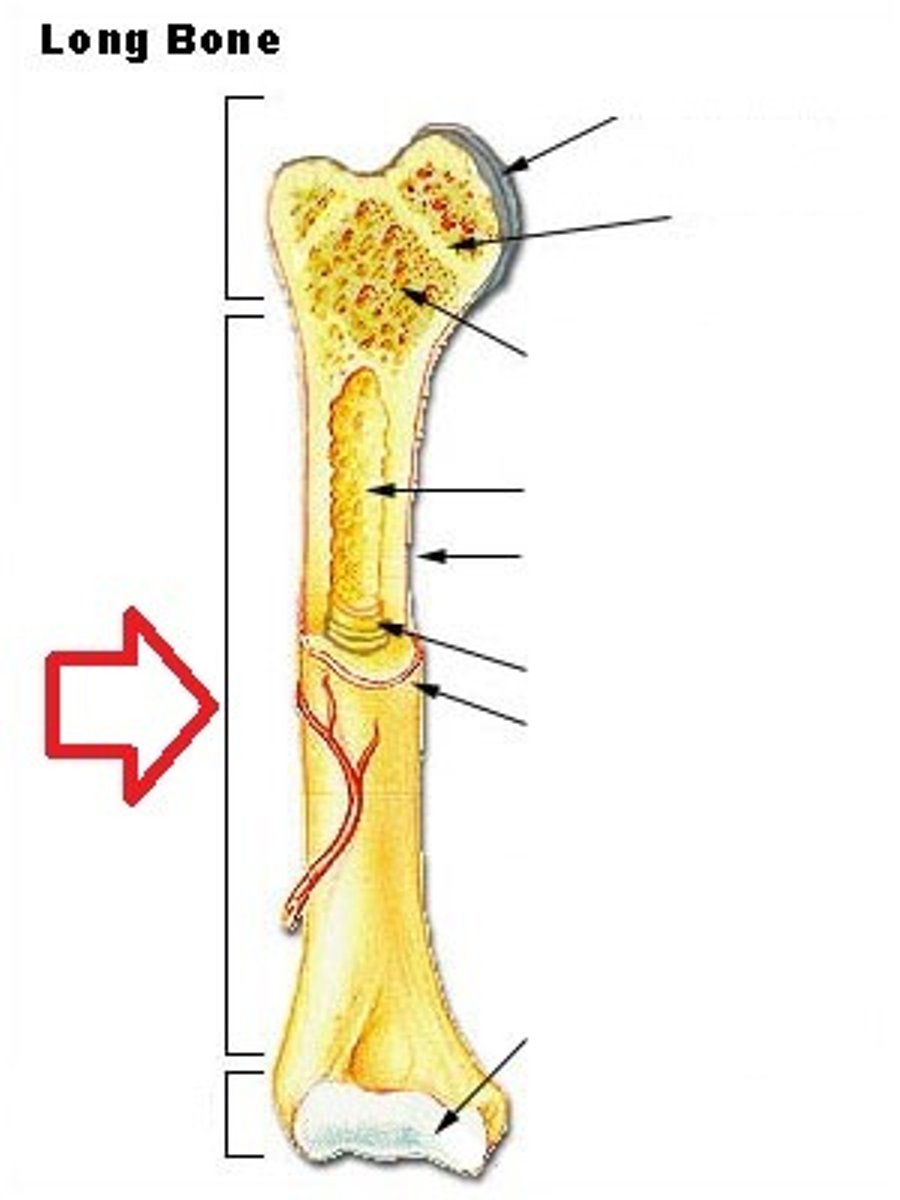
Epiphysis
End of a long bone
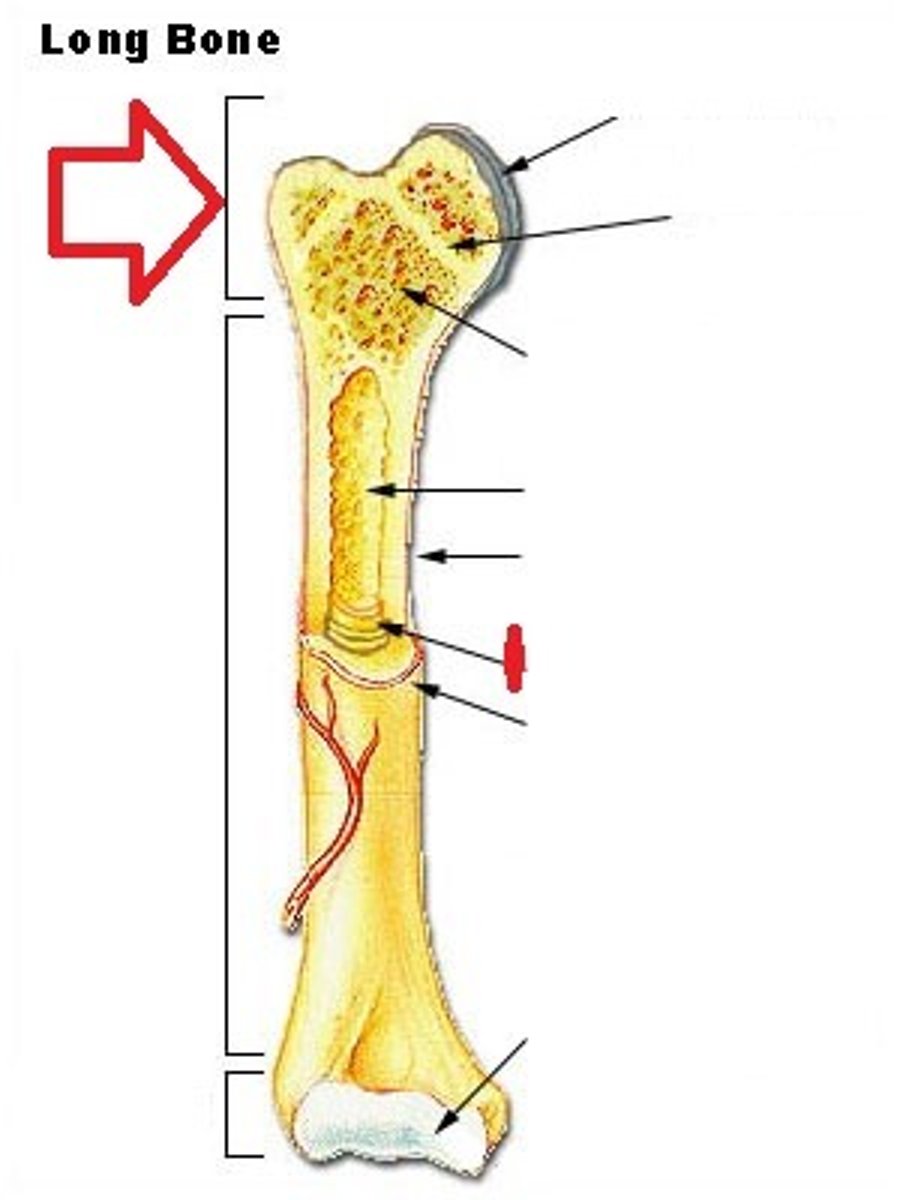
hyaline cartilage
Most common type of cartilage; it is found on the ends of long bones
Epihyseal plate
Growth plate located at the ends of long bones.
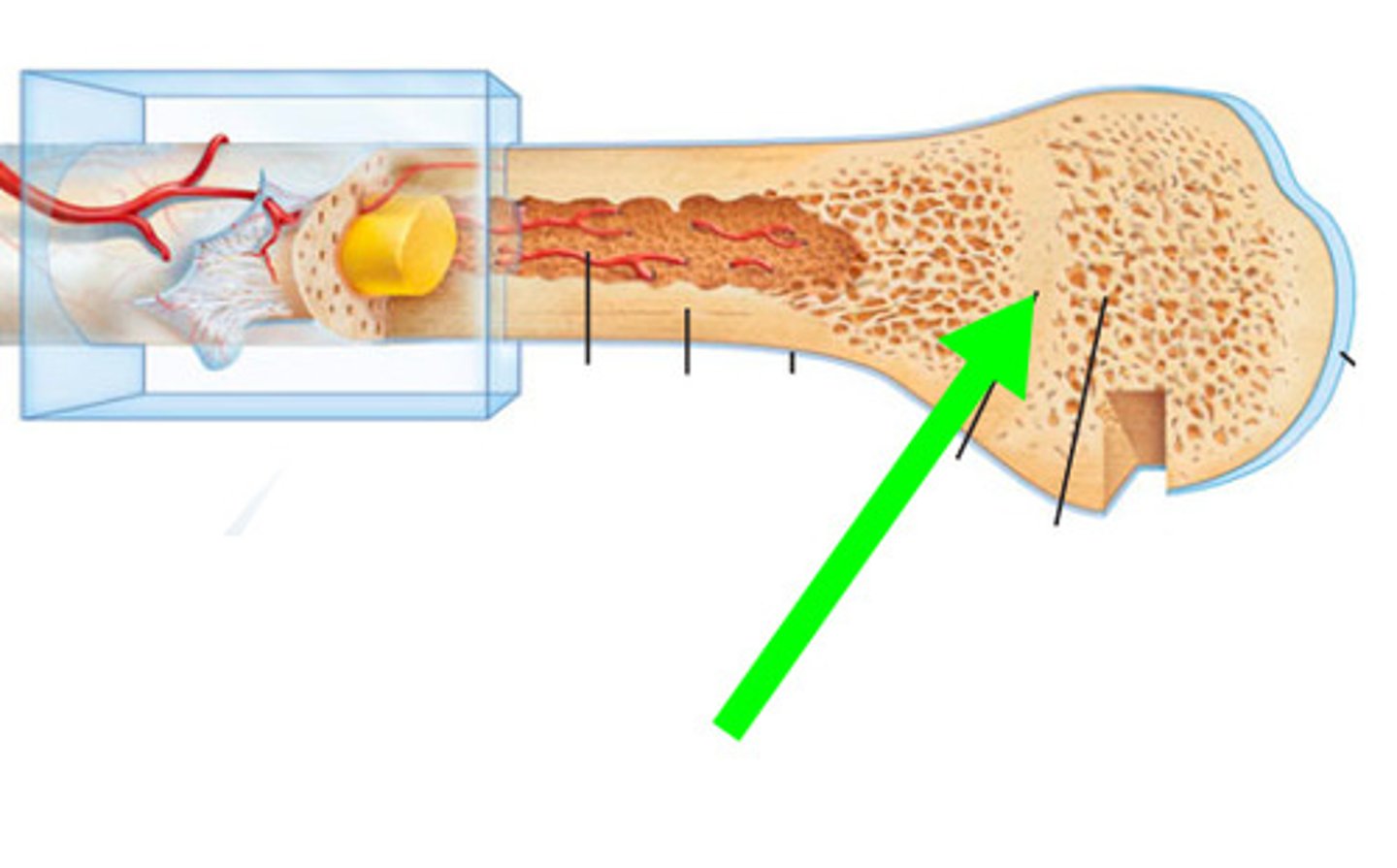
spongy bone
composed of small needle-like pieces of bone and lots of open space. irregularly spaced lamella and no osteons
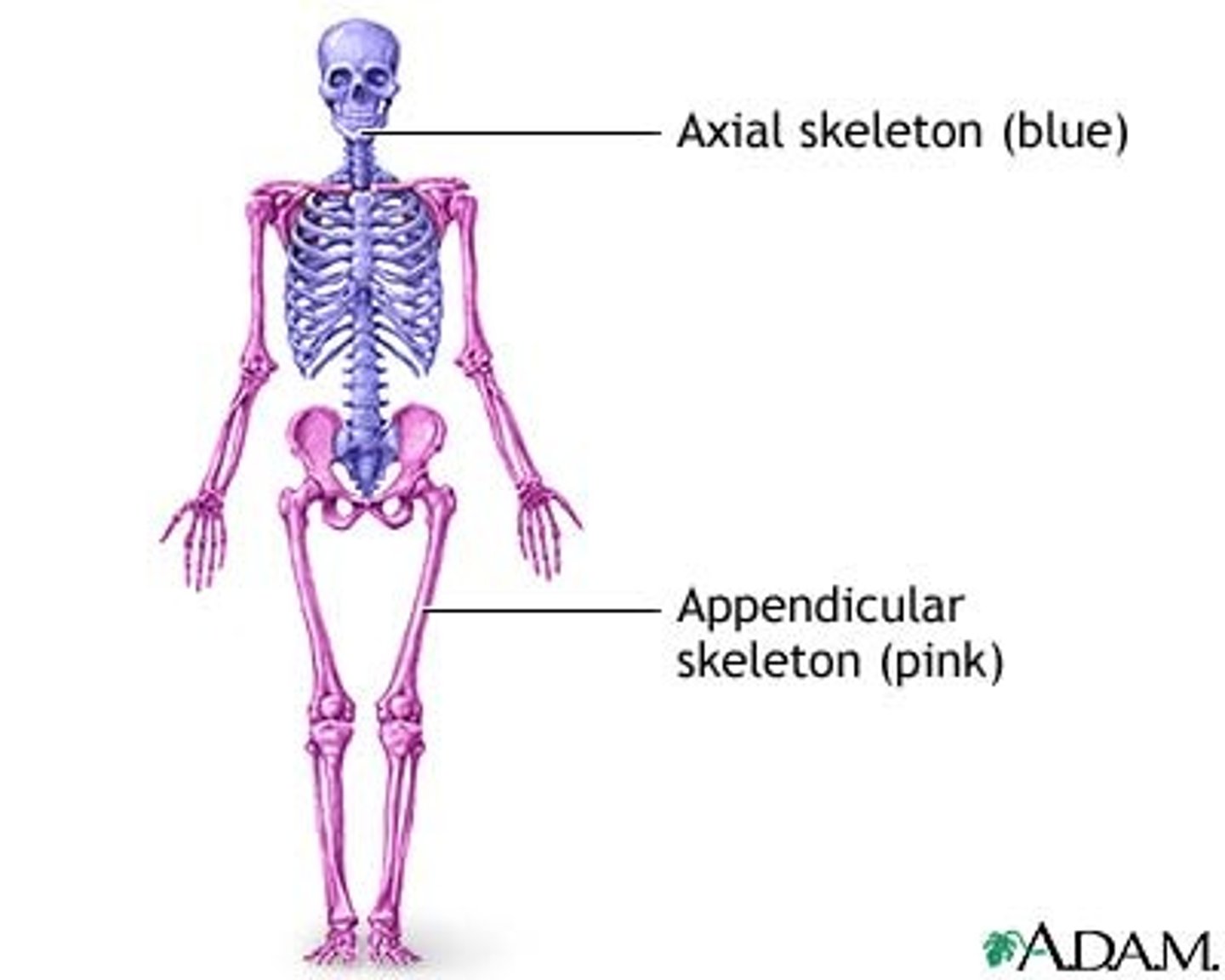
axial bones
Skull, rib cage, and spine
appendicular skeleton
Bones of the limbs and limb girdles that are attached to the axial skeleton
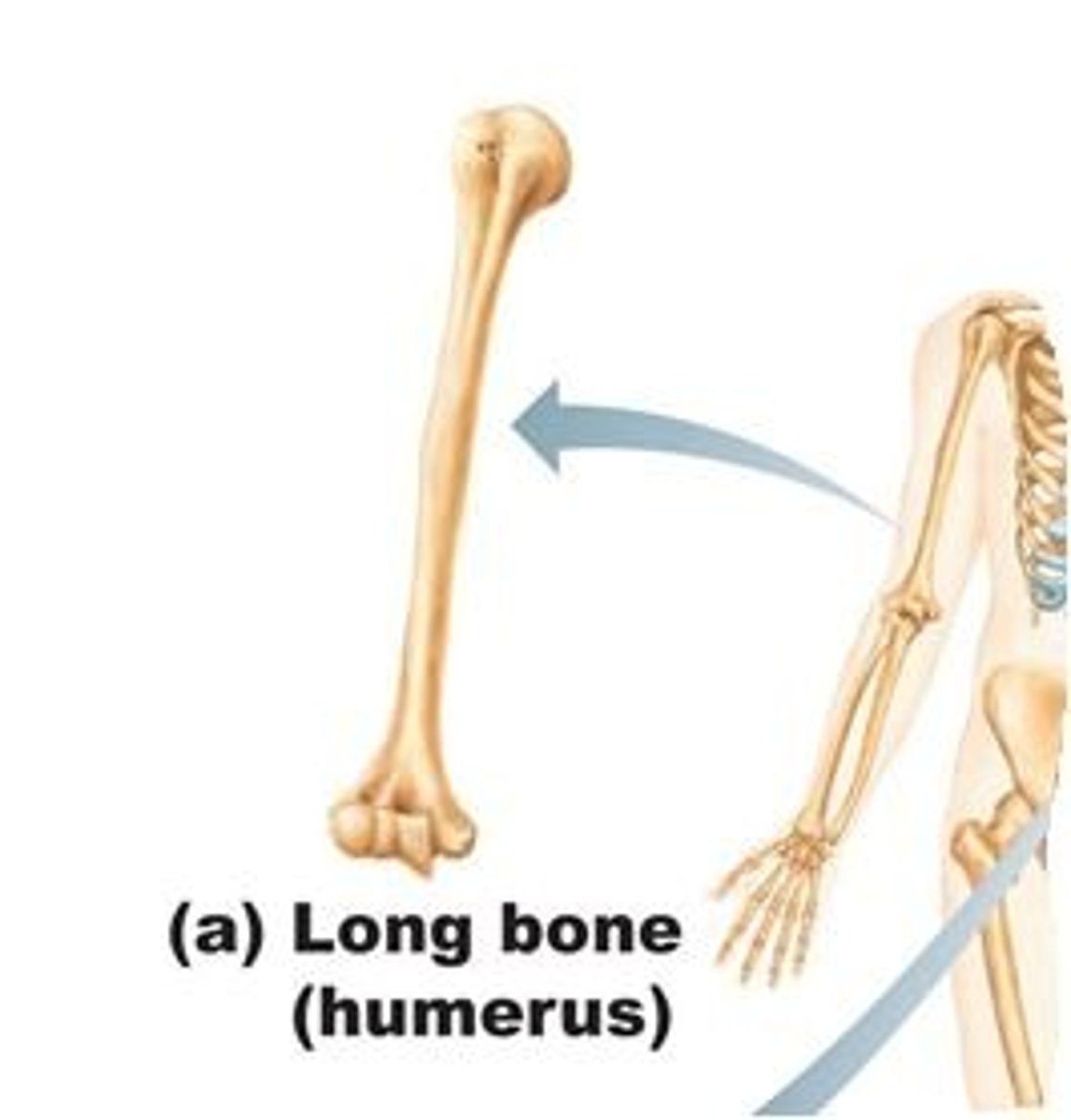
long bones
longer than they are wide
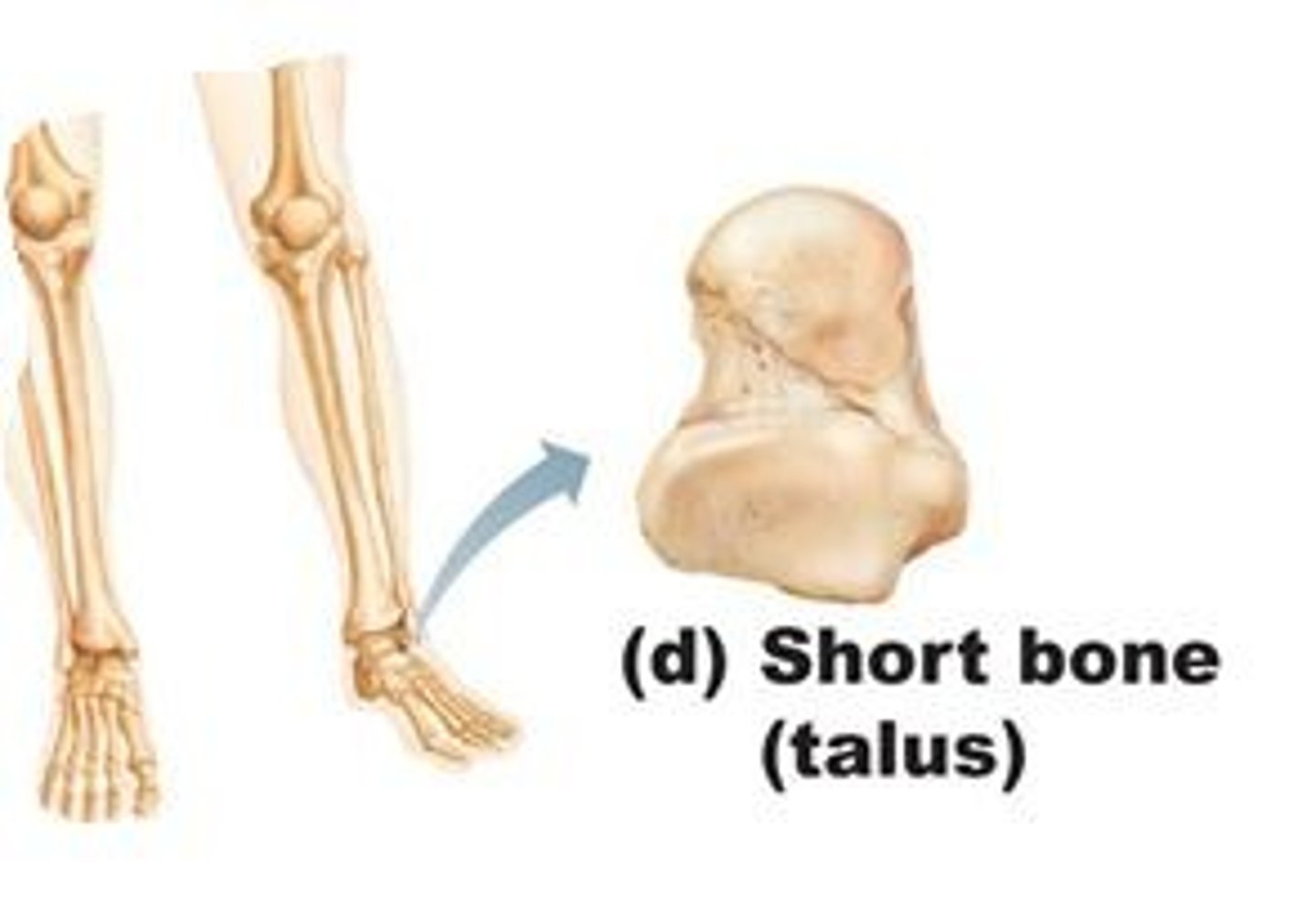
short bones
carpals and tarsals
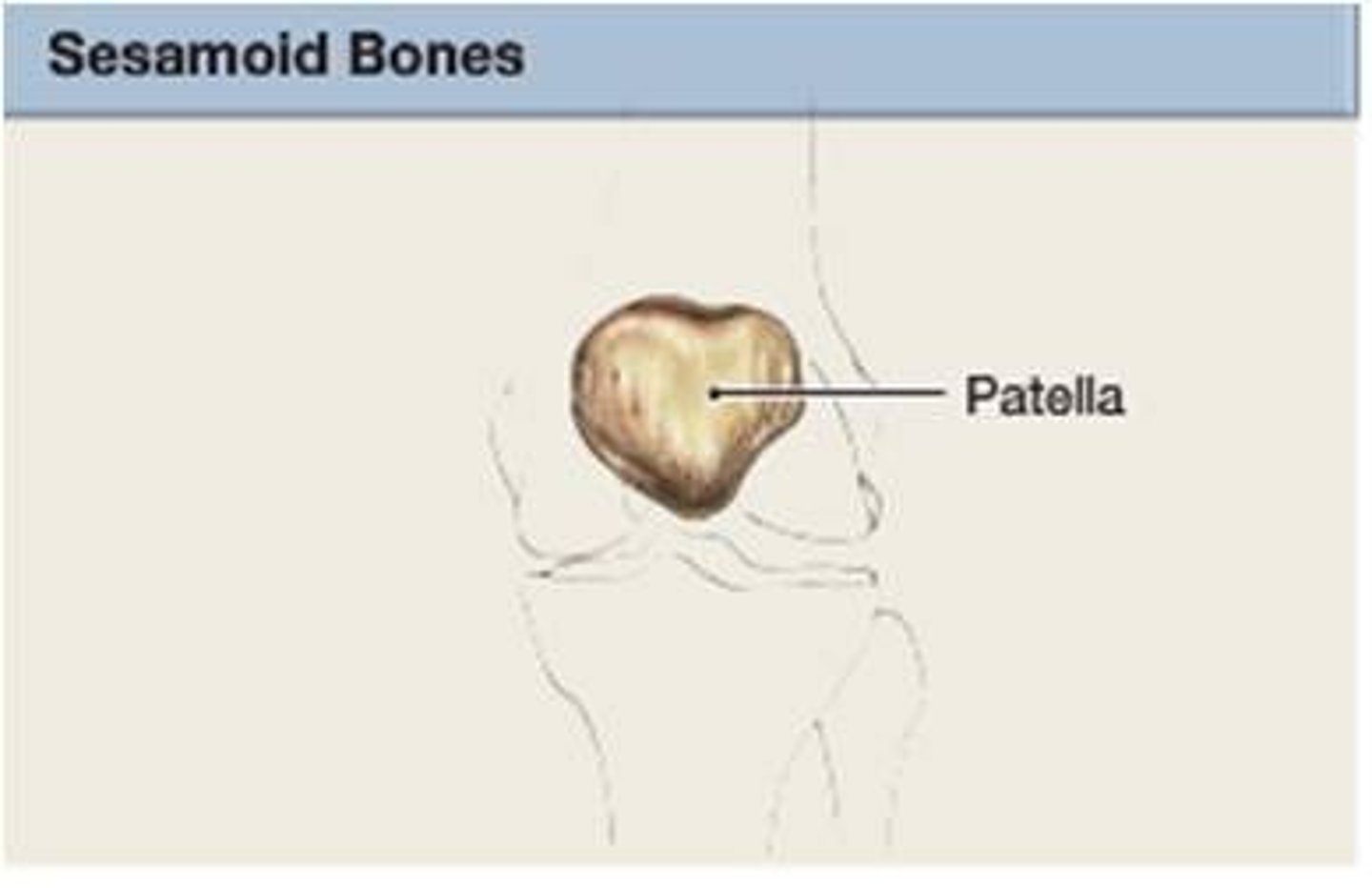
sesamoid bones
round bones found near joints
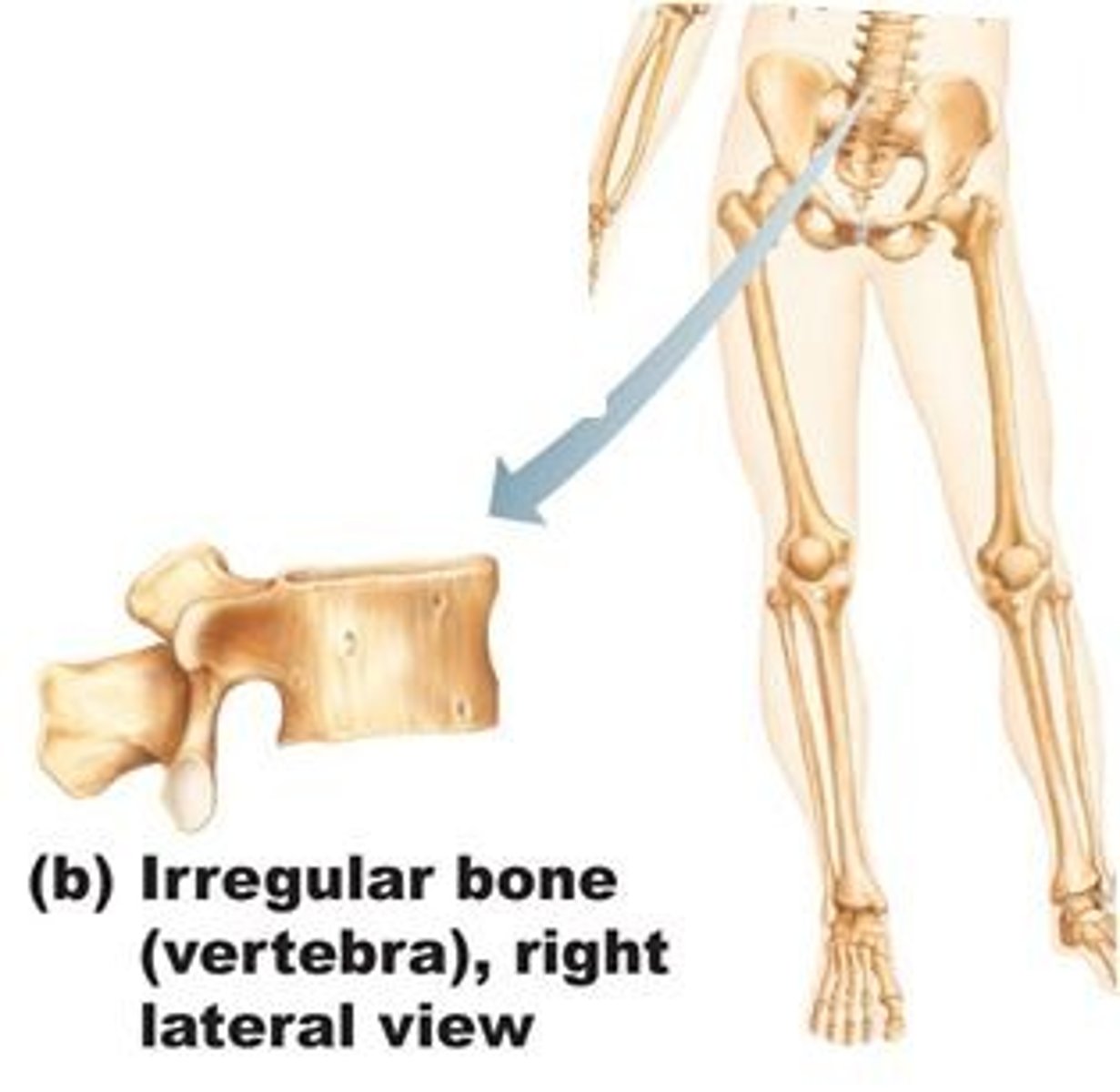
irregular bones
bones of the vertebrae and face
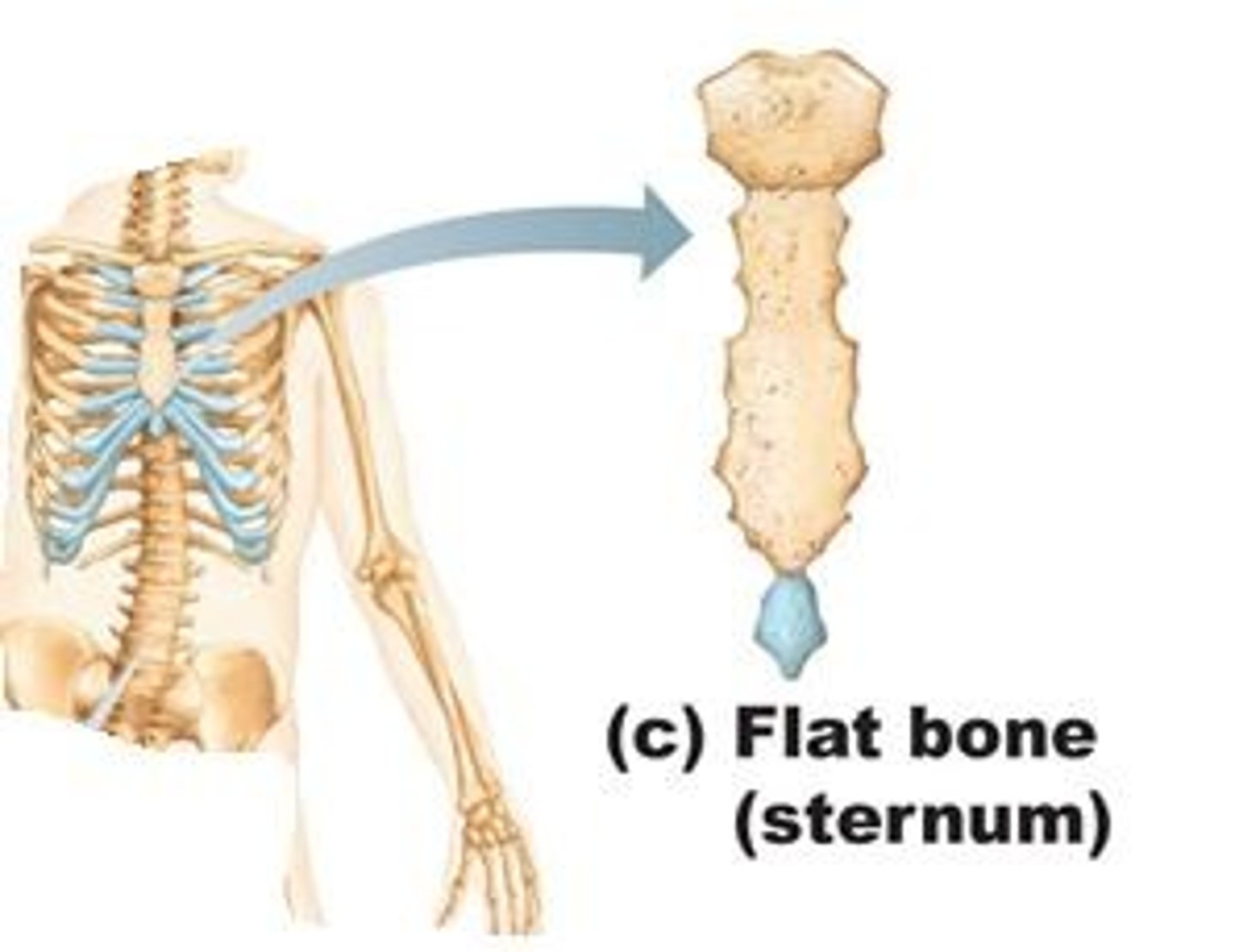
flat bones
thin, flattened, and usually curved
pneumatic bones
sinus-containing bones (i.e., frontal bone)
trabeculae
supporting bundles of bony fibers in cancellous (spongy) bone
yellow marrow
soft, fatty material found in the medullary cavity of long bones
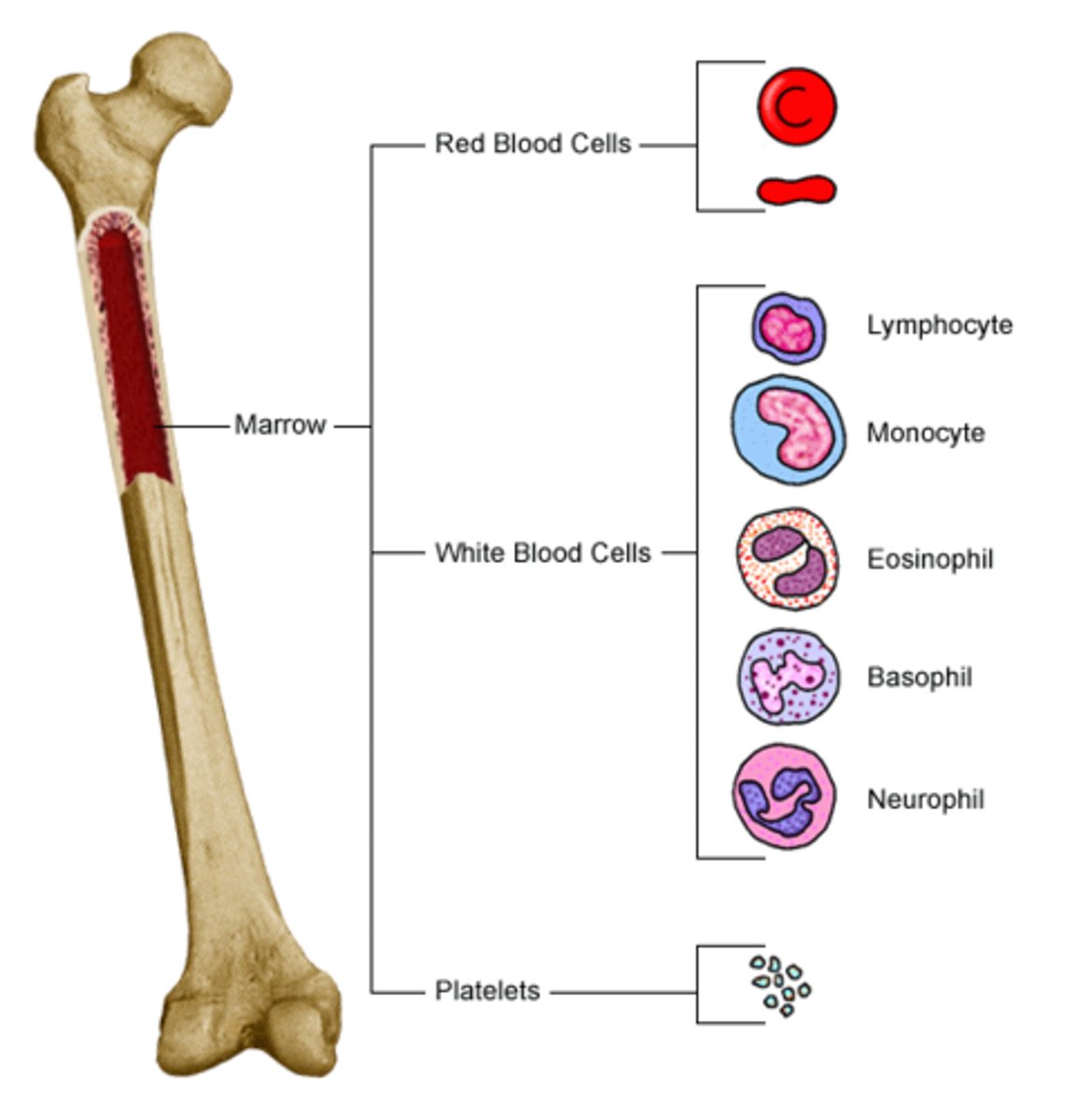
red marrow
produces blood cells
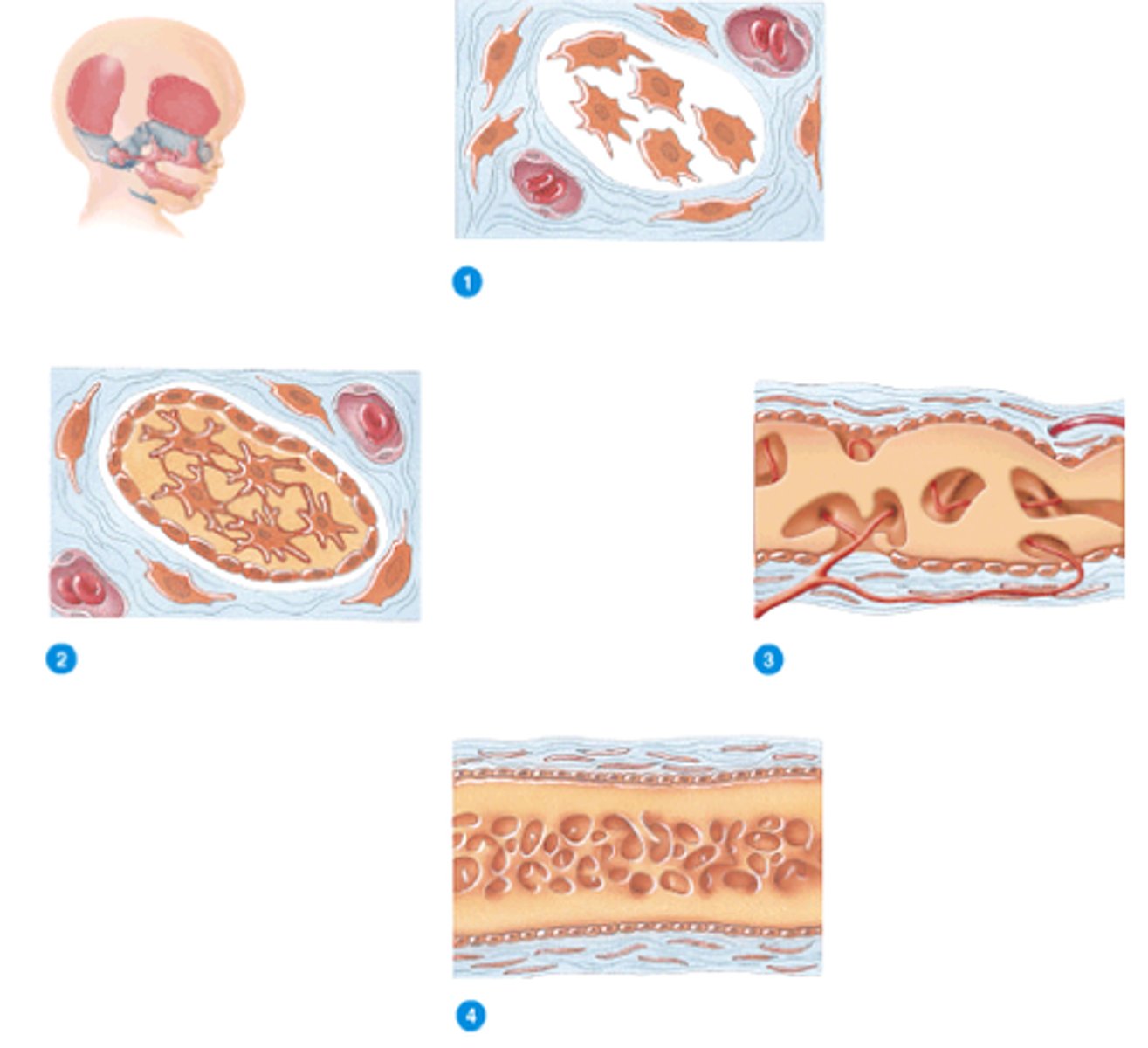
Ossification
process of bone formation
Calcification
process that hardens bones by adding calcium phosphate and collagen
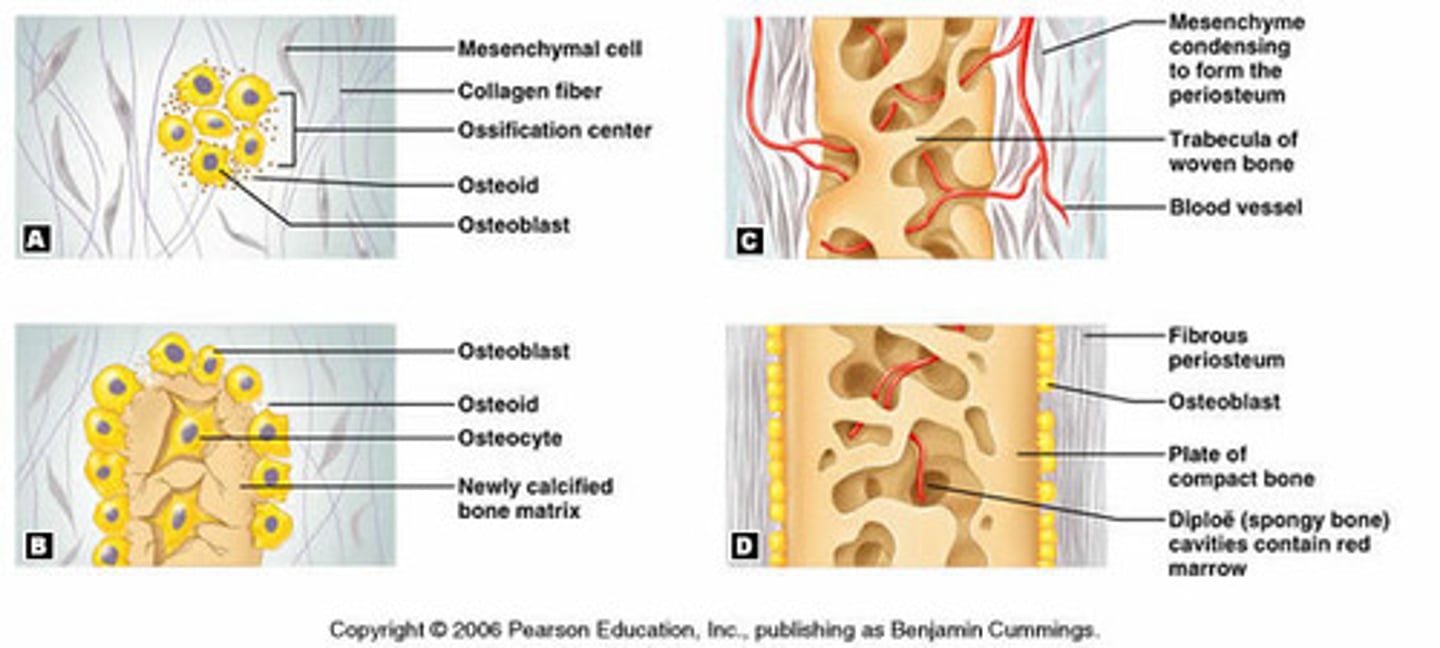
intramembranous ossification
process by which bone forms directly from mesenchymal tissue (flat bones of skull, and clavicle)
endochondral ossification
Process of transforming cartilage into bone.
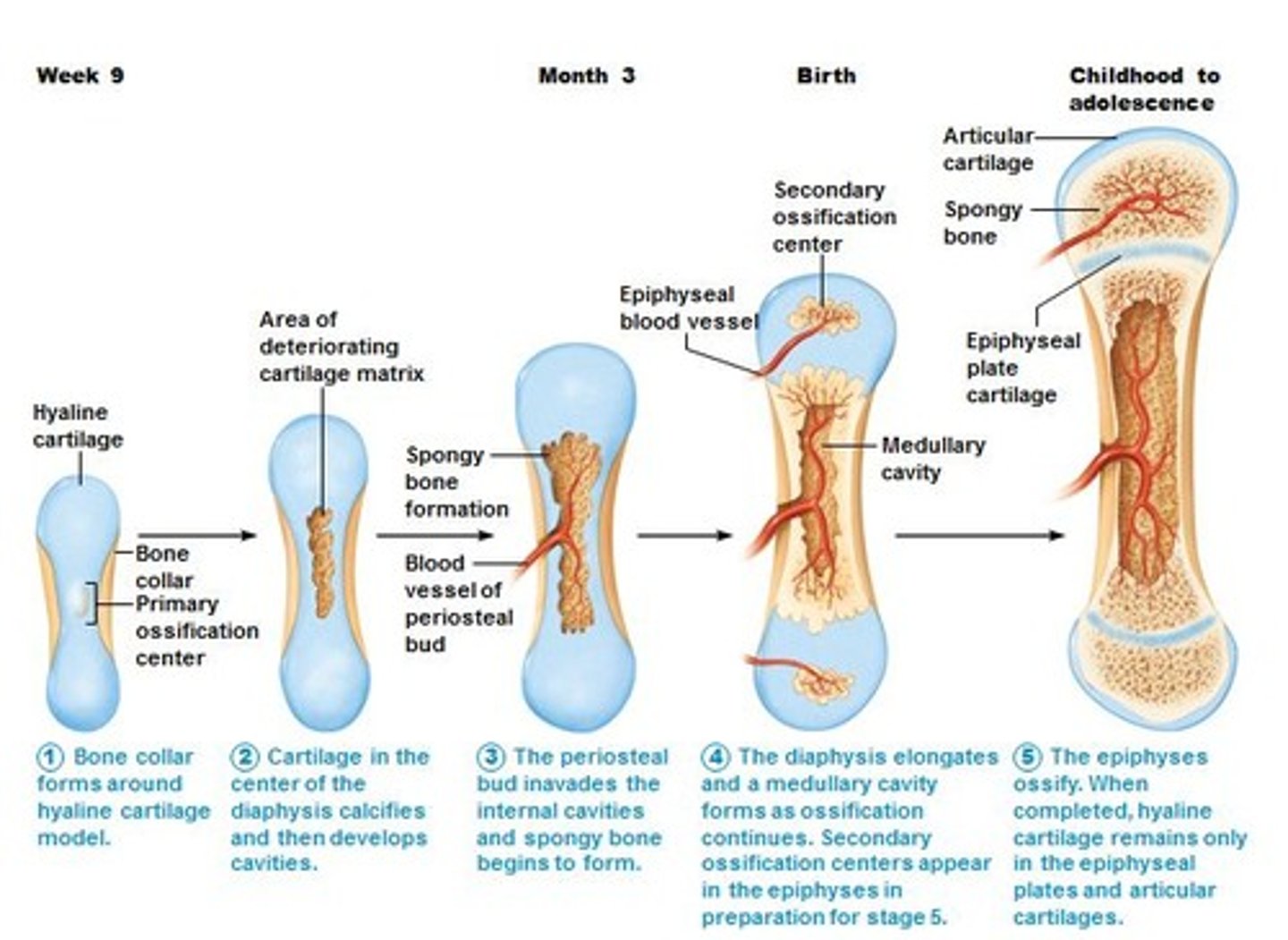
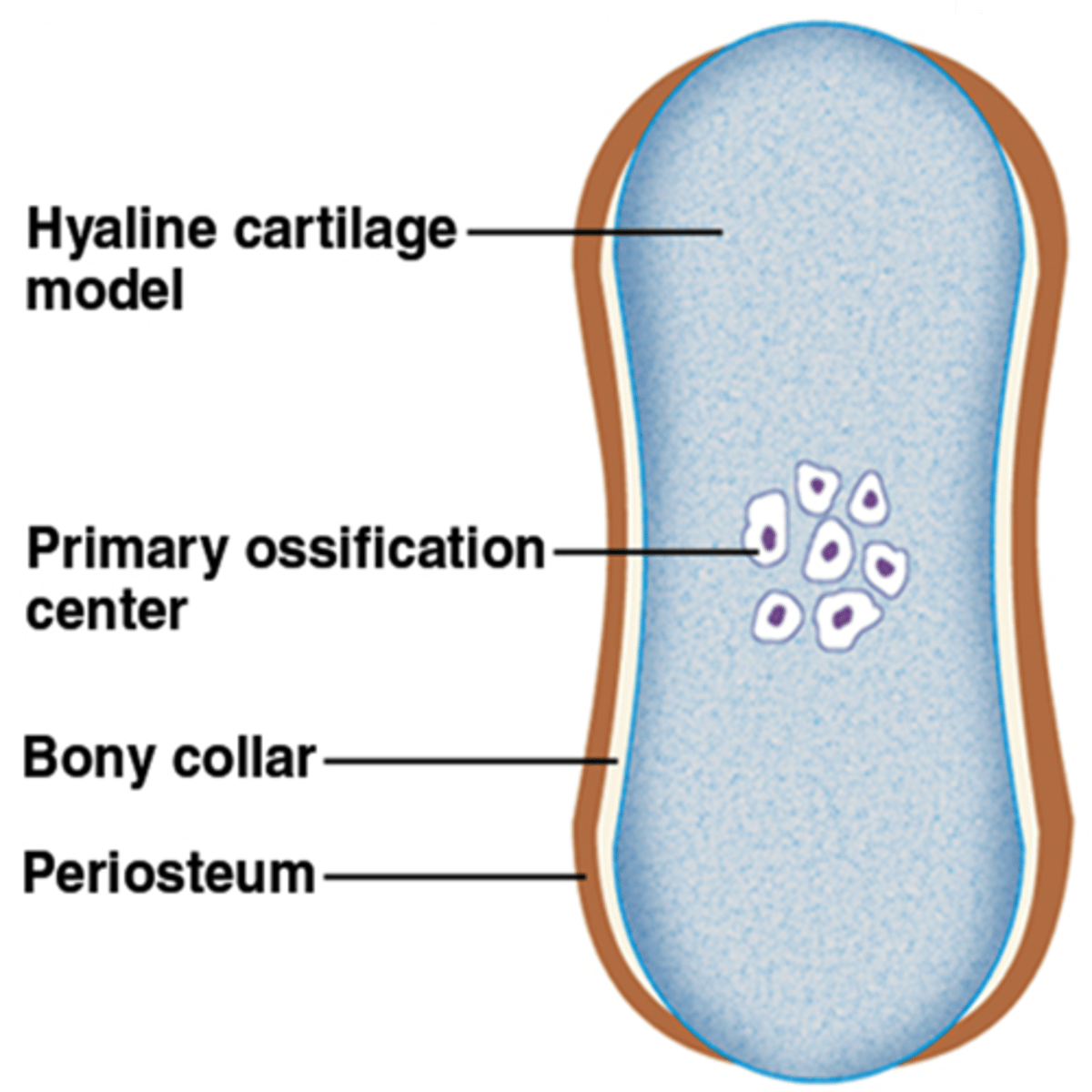
primary ossification center
region, deep in the periosteal collar, where bone development starts during endochondral ossification
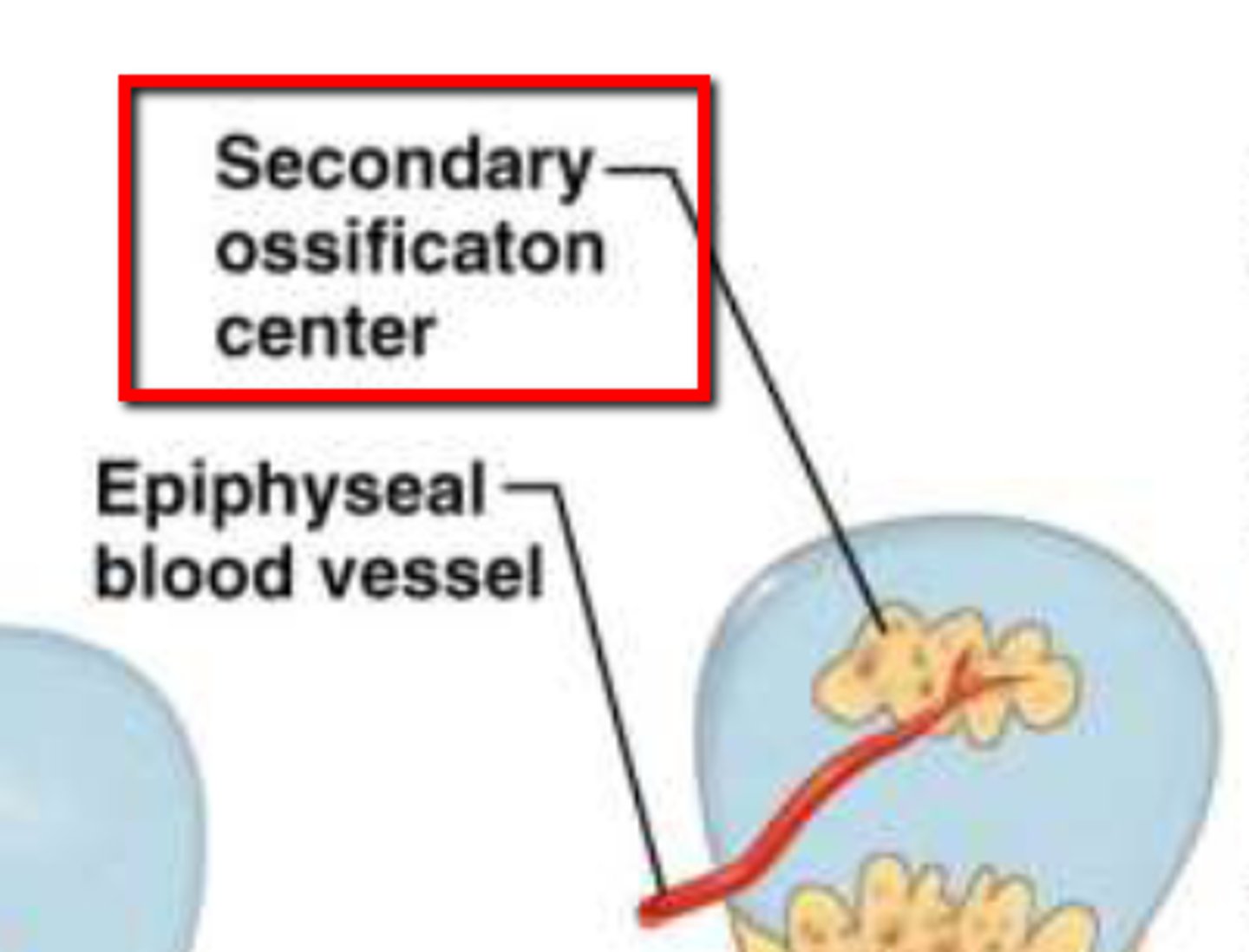
secondary ossification center
this develops in the epiphyses of bone during endochondral ossification
ossification center
cluster of osteoblasts found in the early stages of intramembranous ossification
mesenchymal cells
stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts
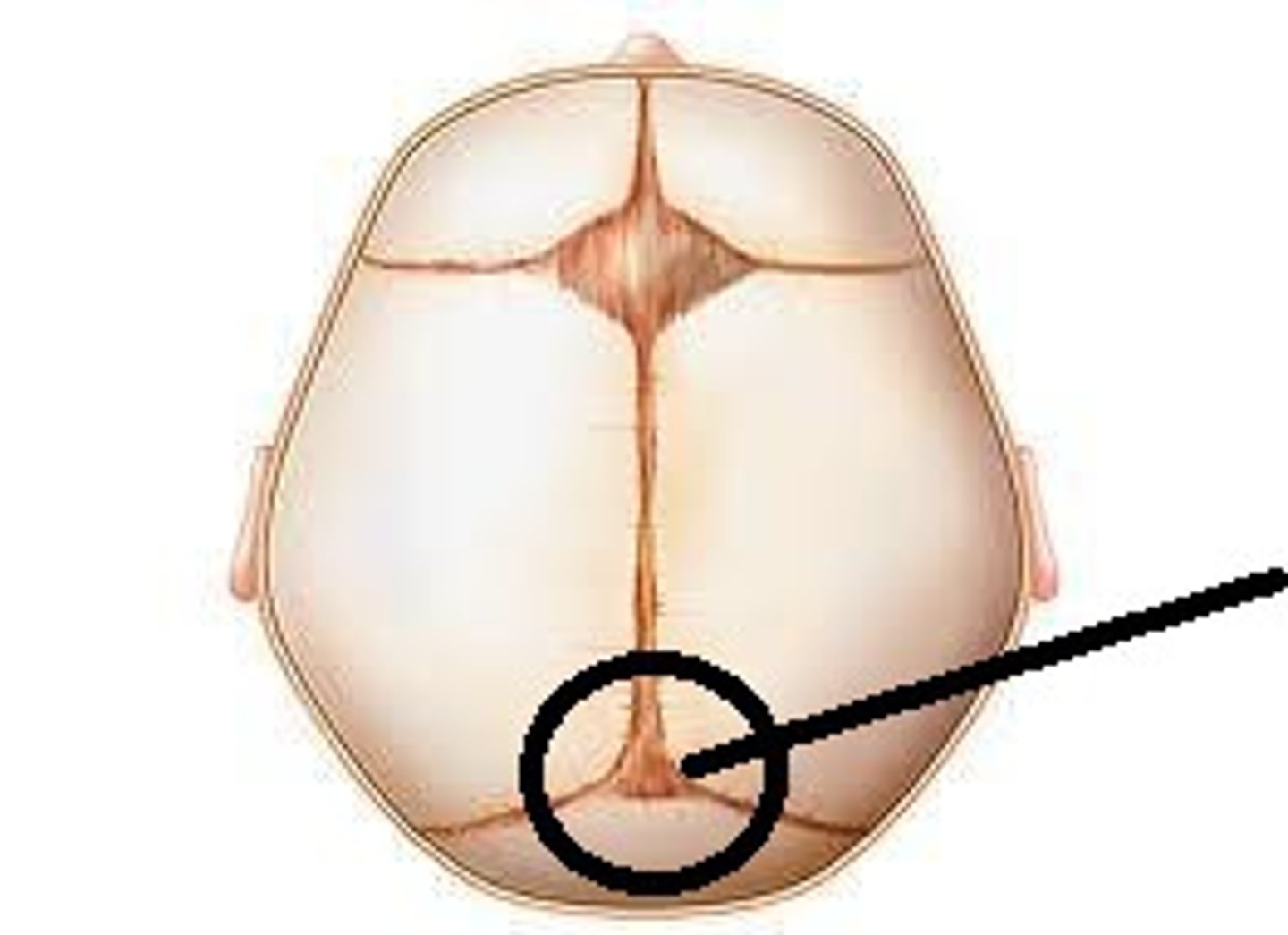
Fontanels
Gaps between a baby's skull that slowly close up during the first 18 months of life
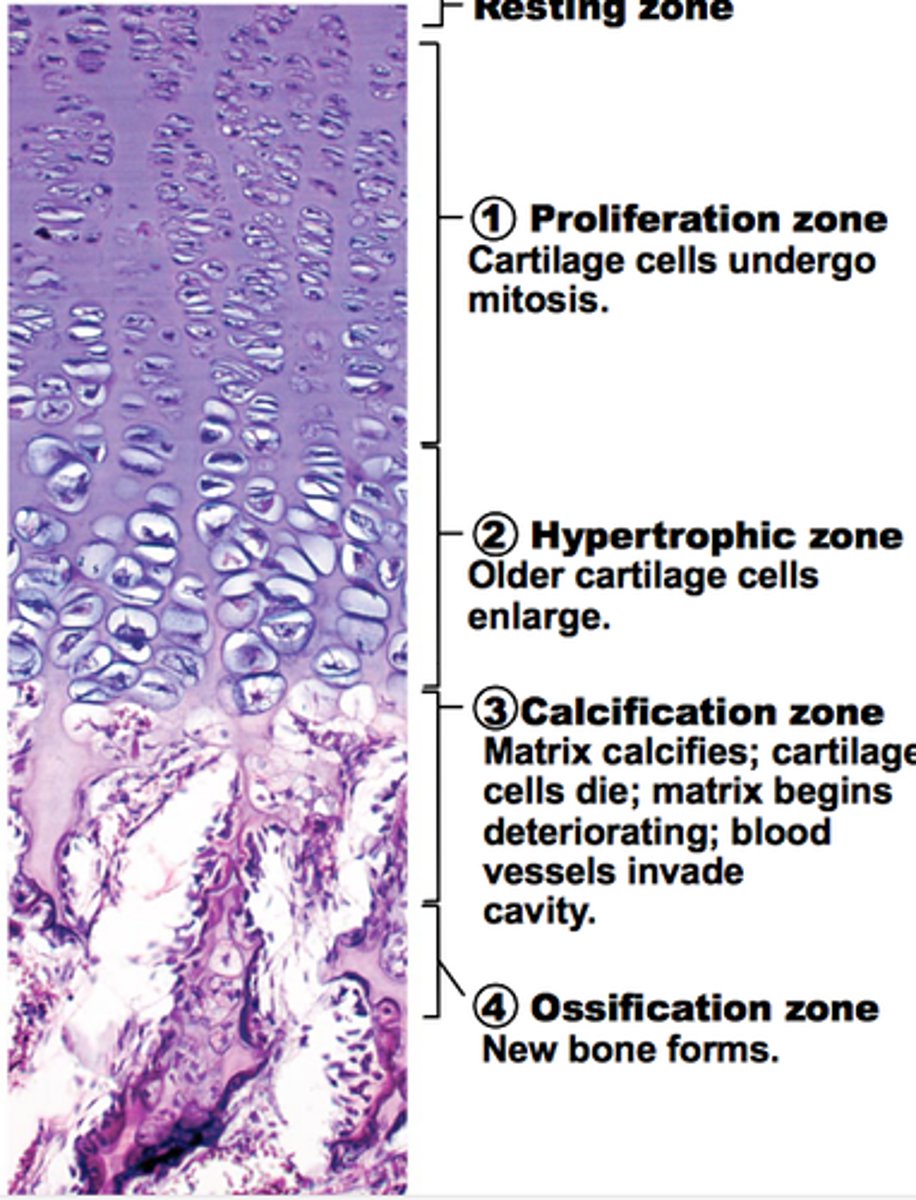
zone of proliferation
Within the epiphyseal plate, which zone houses actively dividing cartilage cells on the epiphyseal plate side
zone of ossification
ossification at diaphyseal side of plate
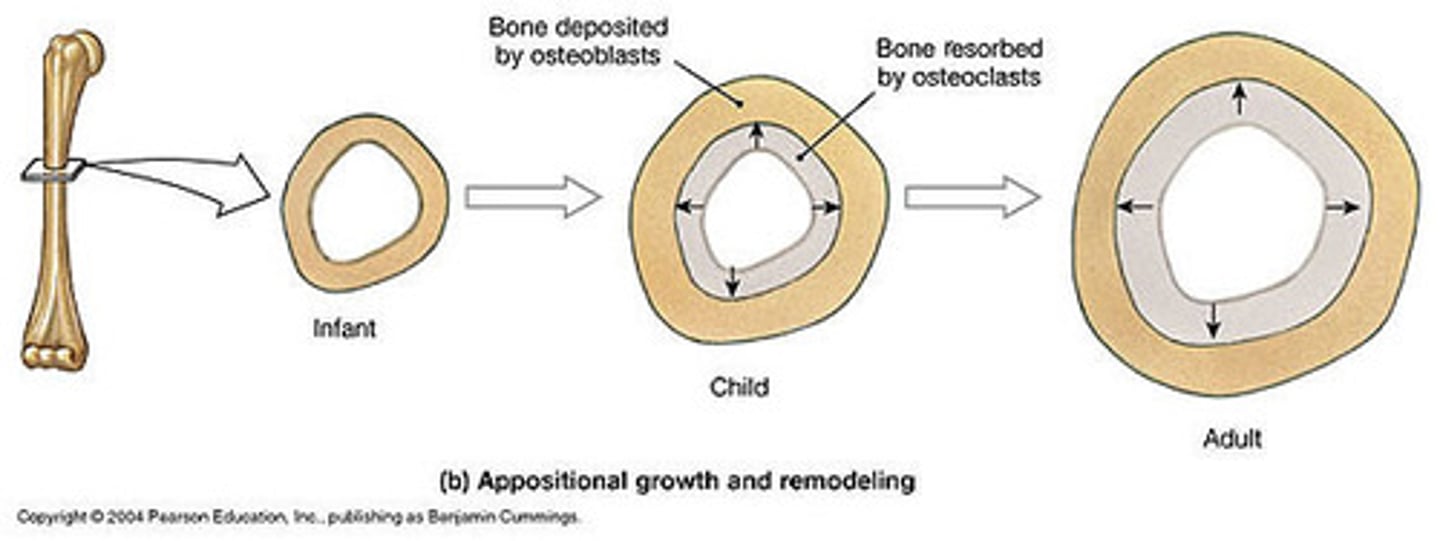
appositional growth
increase in bone thickness
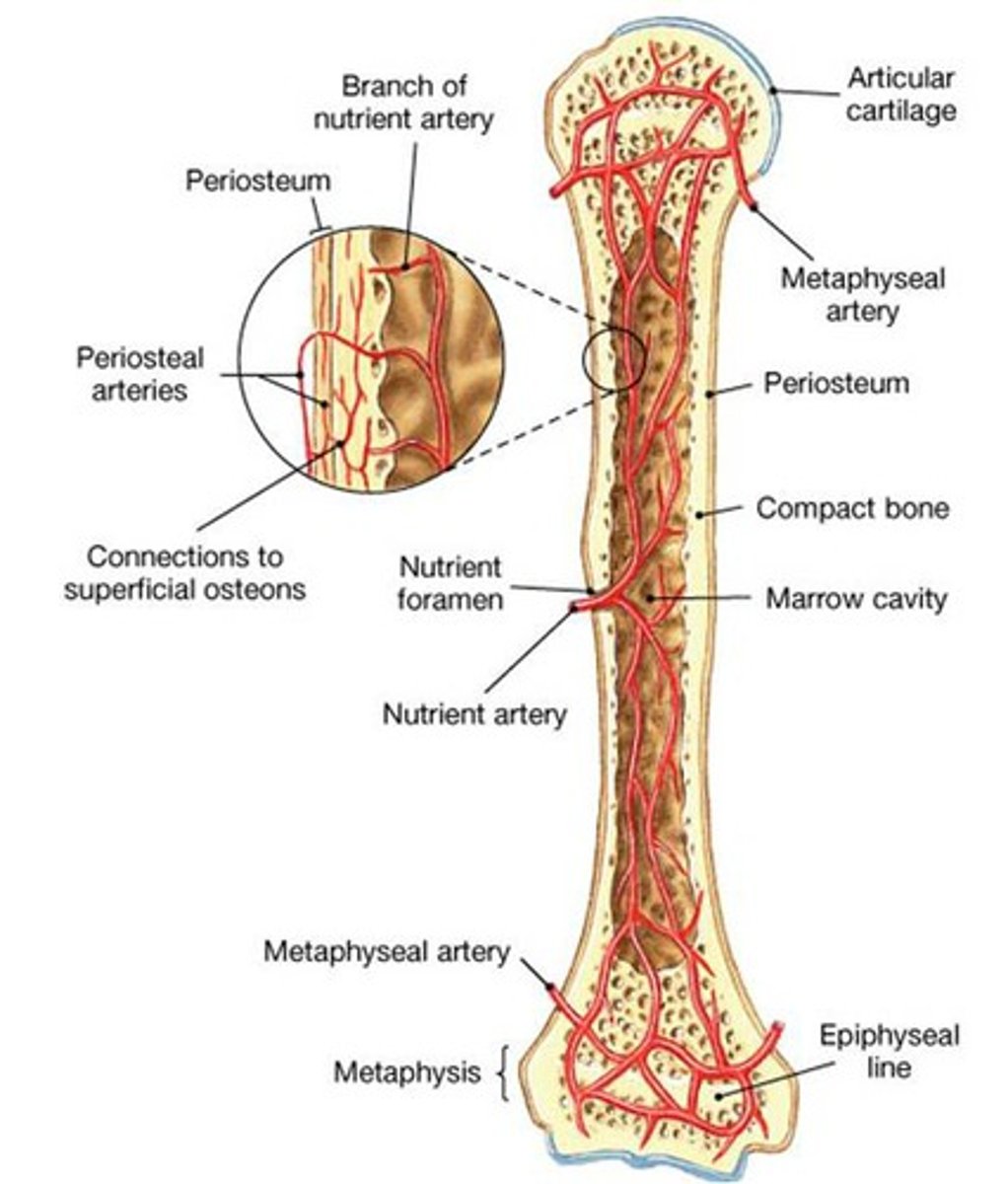
metaphyseal vessels
-supply the epiphyseal cartilage
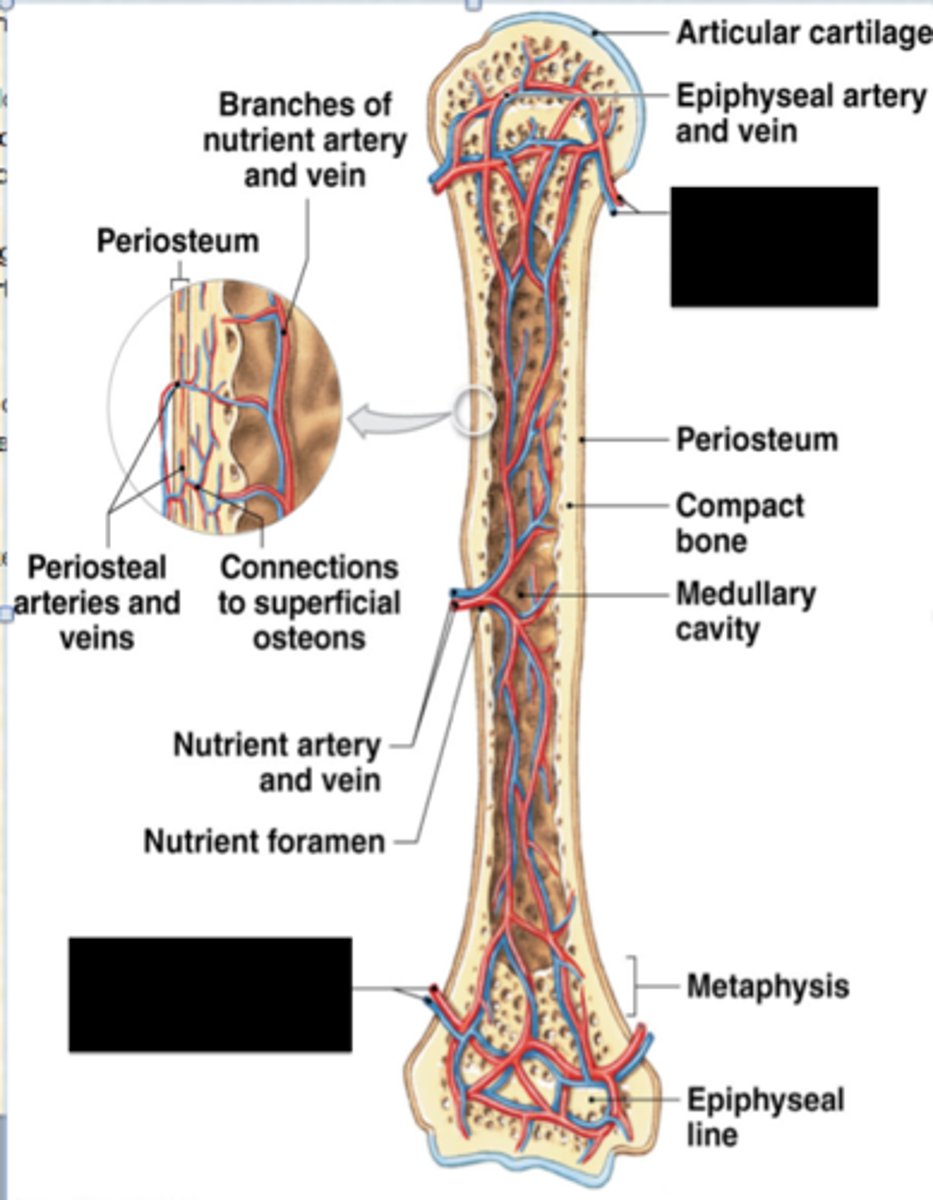
epiphyseal vessels
Supply nutrients to the cavities of the epiphysis
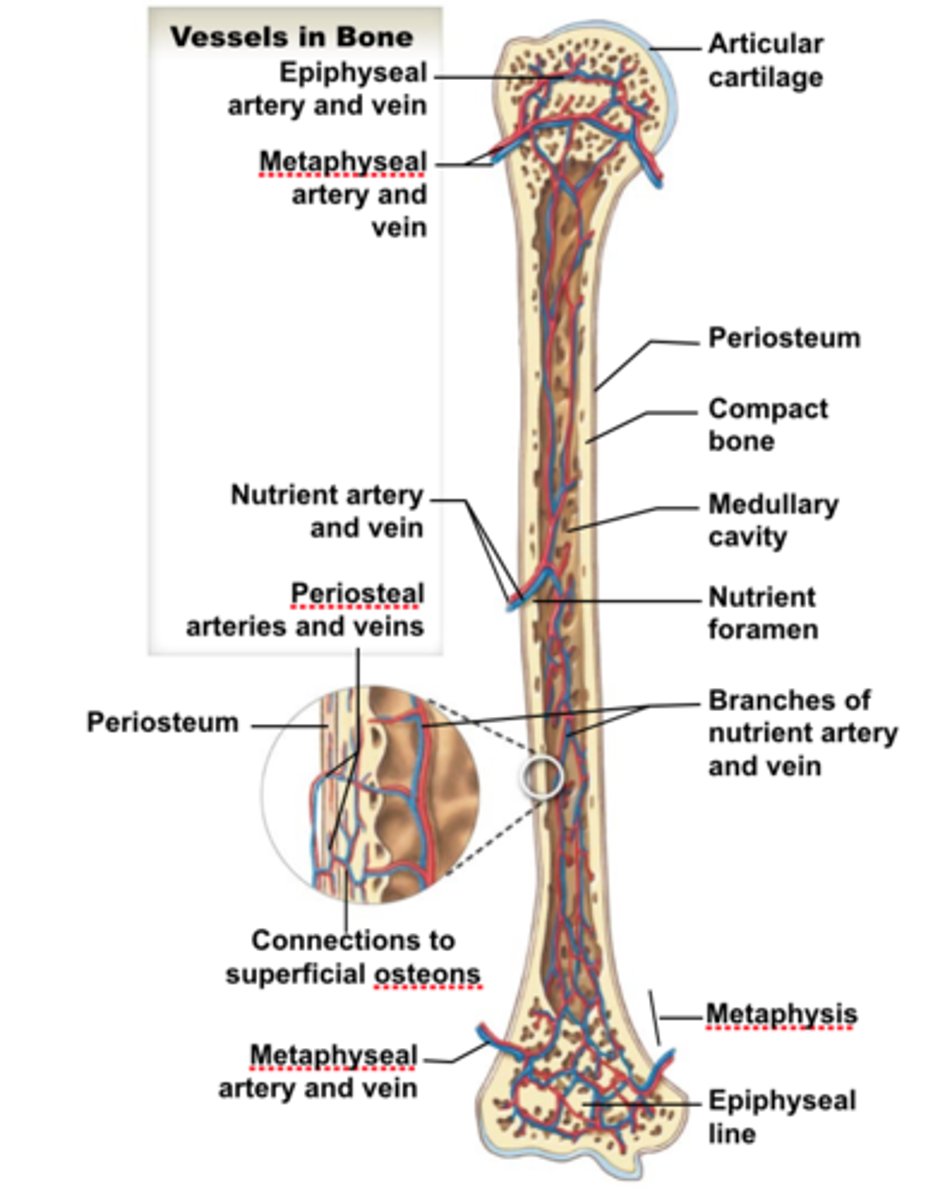
periosteal vessels
blood to superficial osteons
secondary ossification centers
parathyroid hormone
increases blood calcium levels by activating osteoclasts
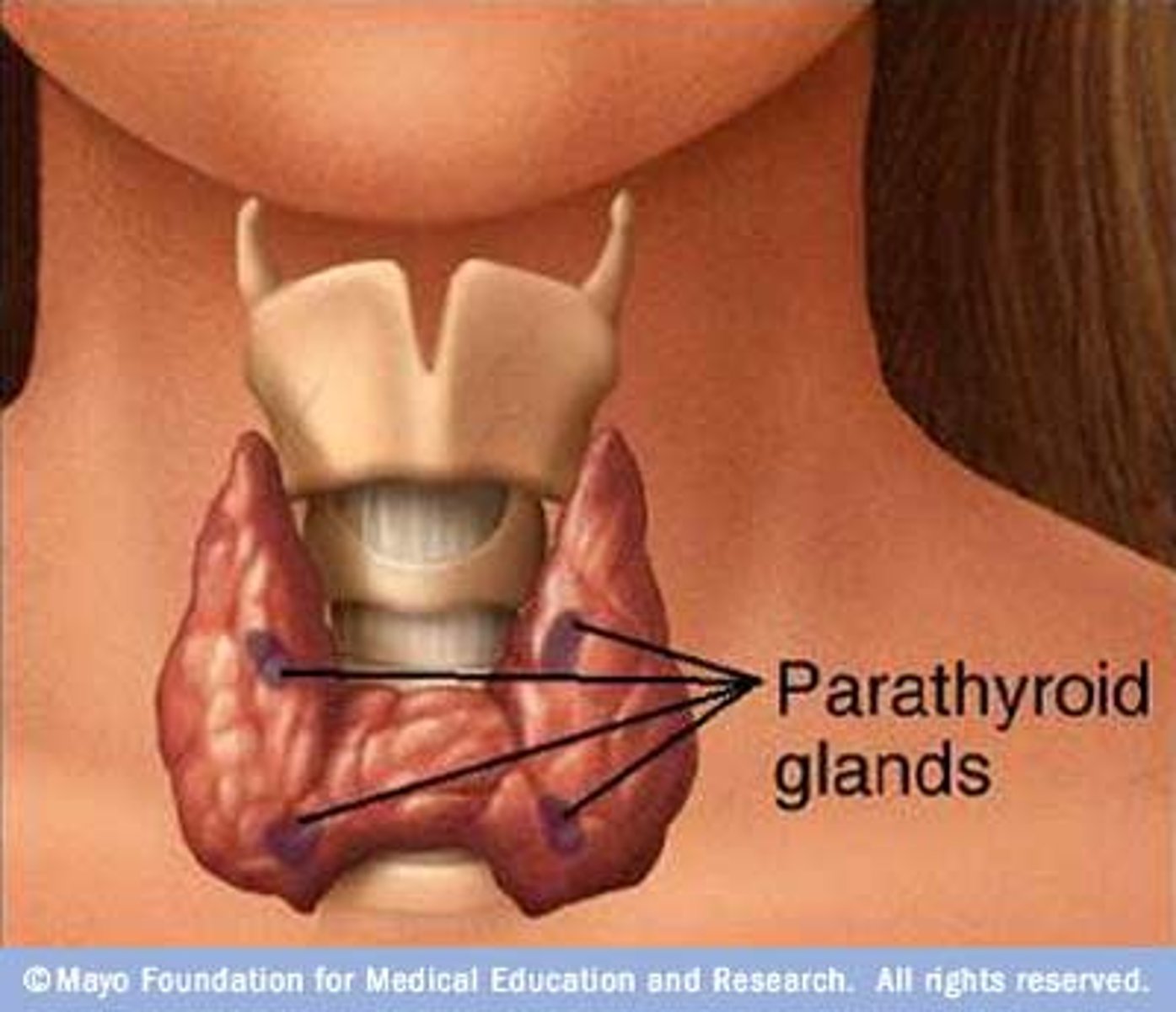
thyroid gland
secretes calcitonin to decrease calcium levels by activating osteoblasts
comminuted fracture
fracture in which the bone is splintered or crushed
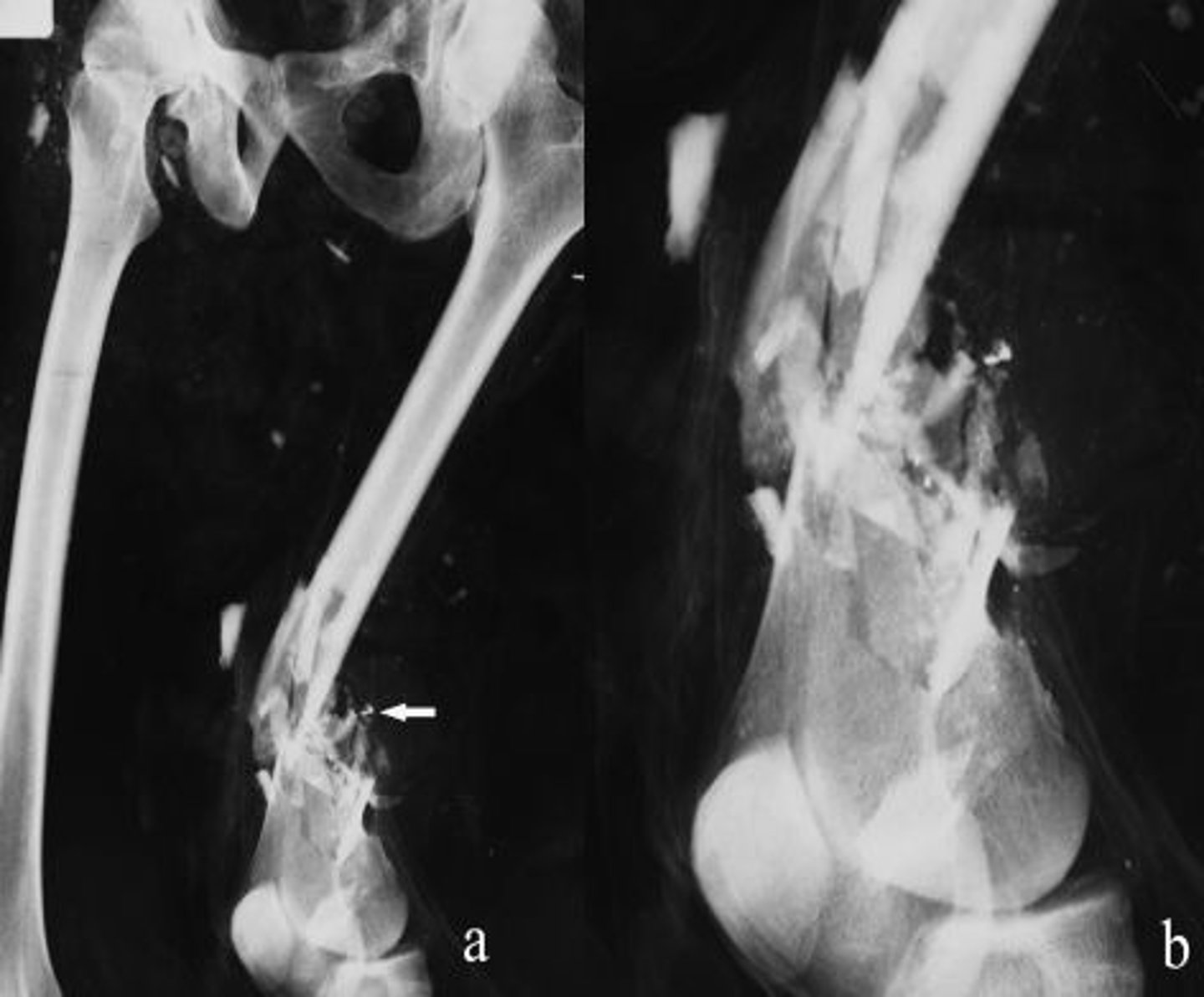
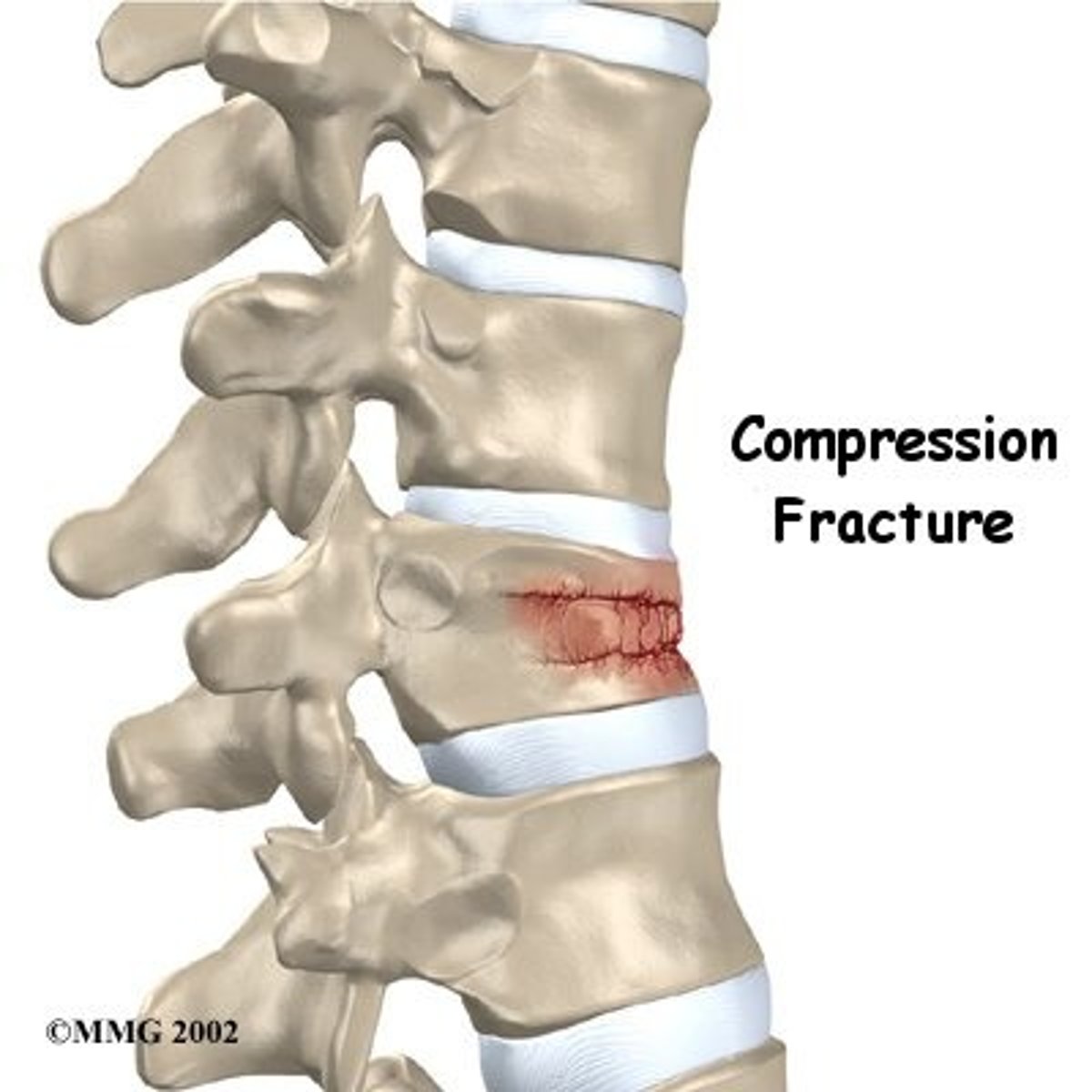
compression fracture
bone is crushed
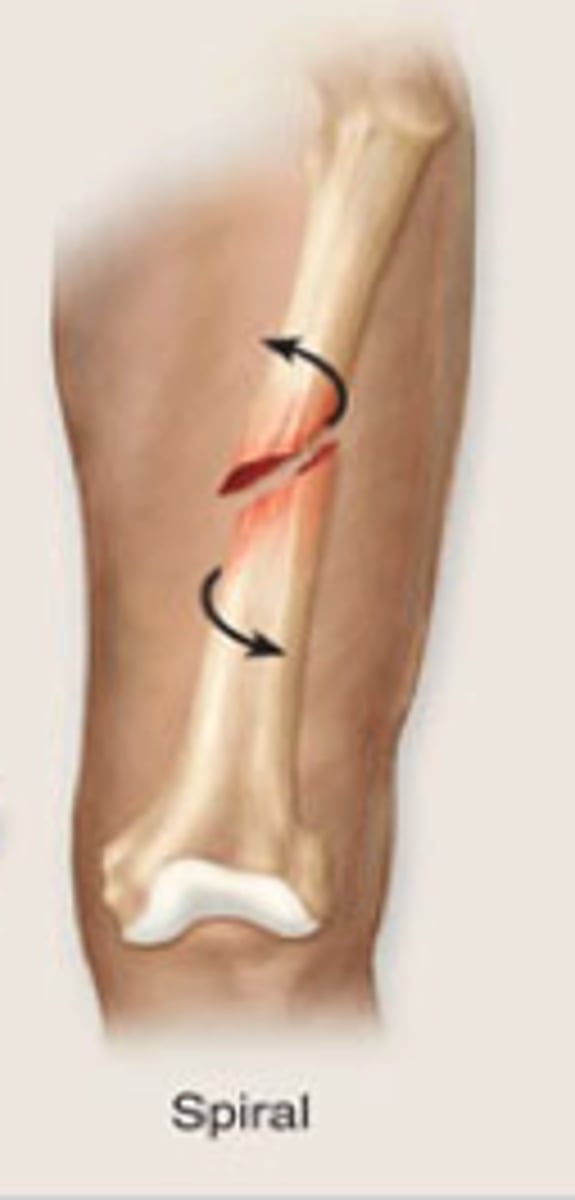
spiral fracture
a fracture in which the bone has been twisted apart
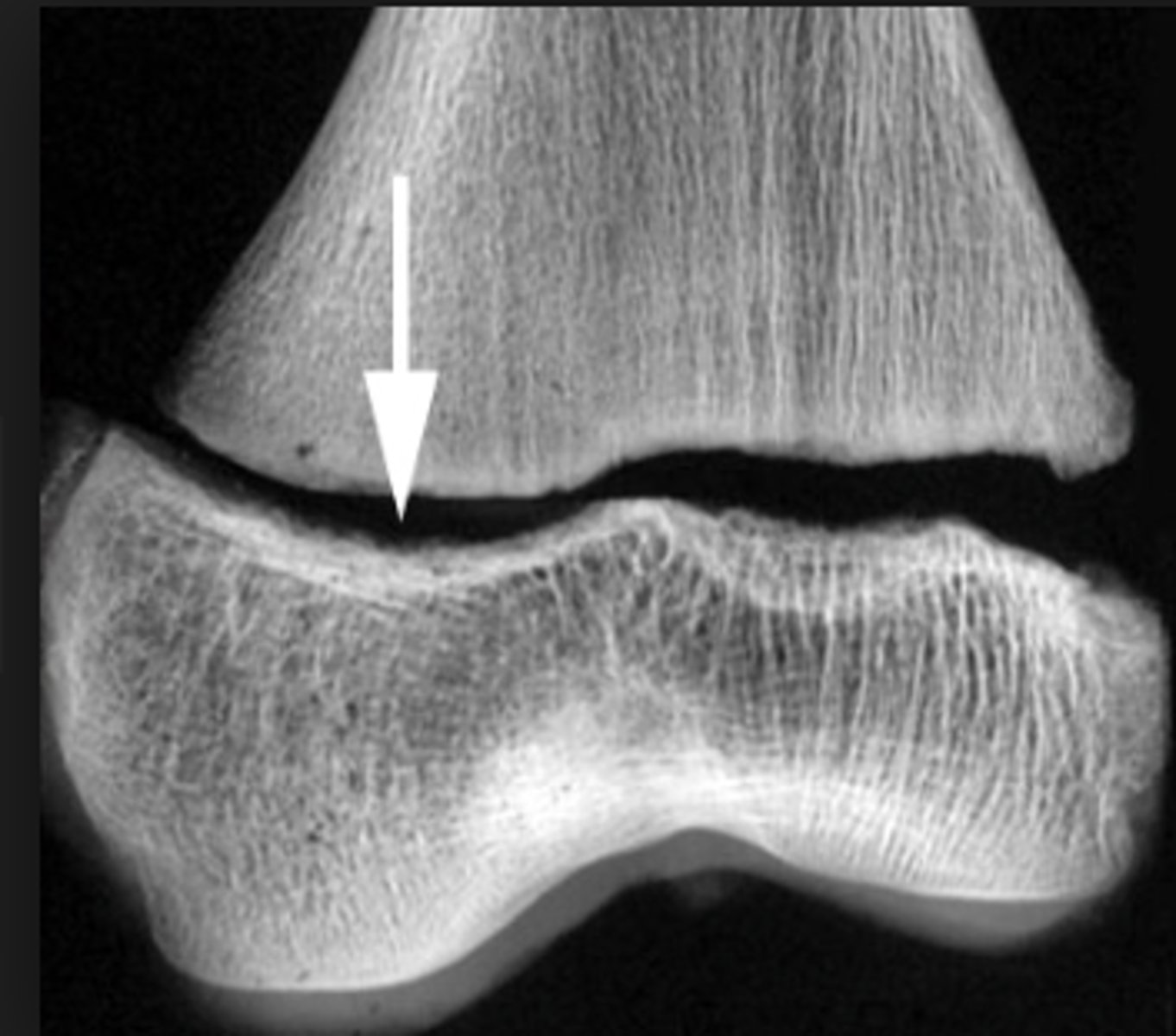
epiphyseal fracture
a break at the location of the growth plate, which can affect growth of the bone
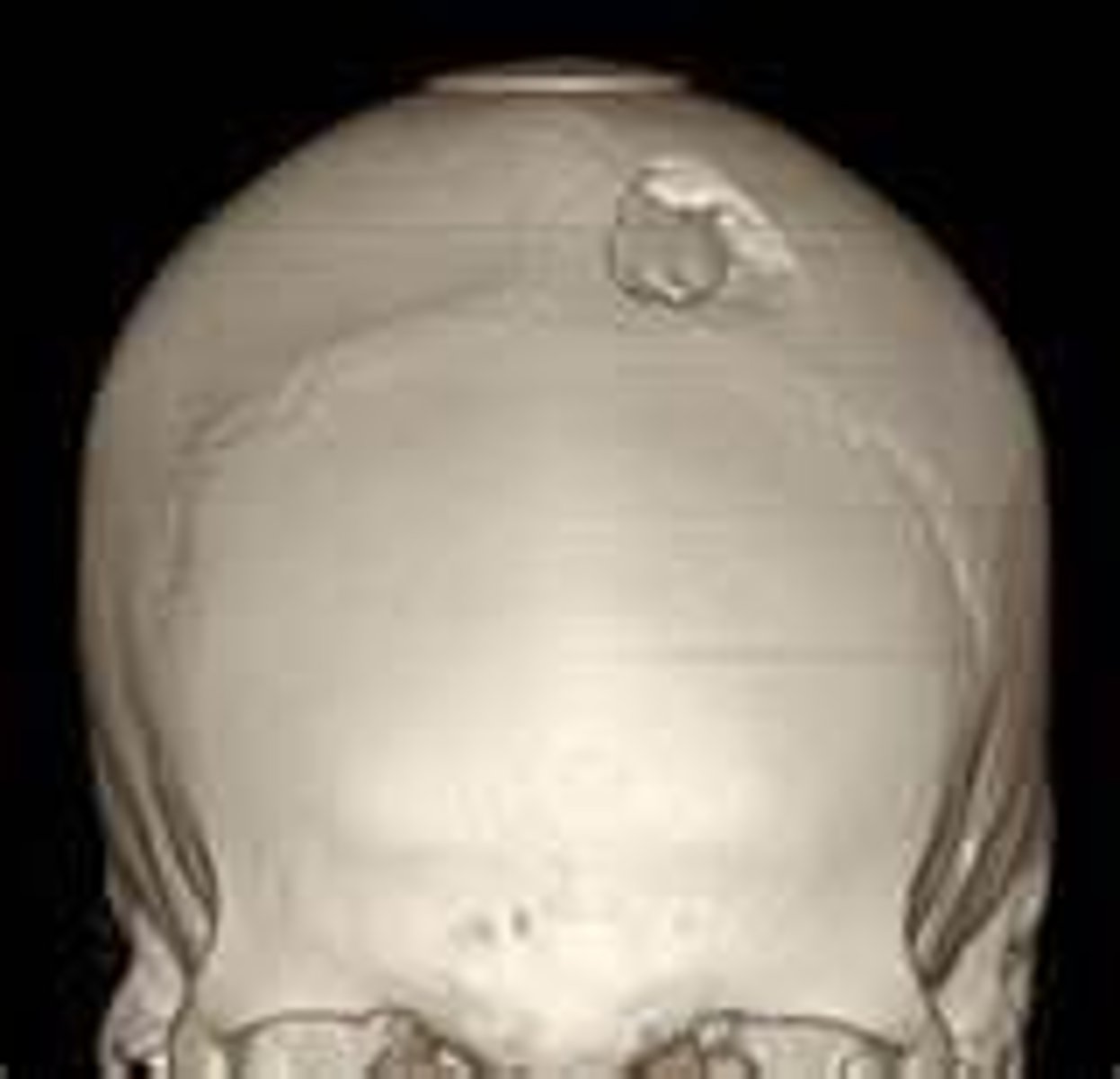
depressed fracture
broken bone portion is pressed inward
greenstick fracture
bending and incomplete break of a bone; most often seen in children
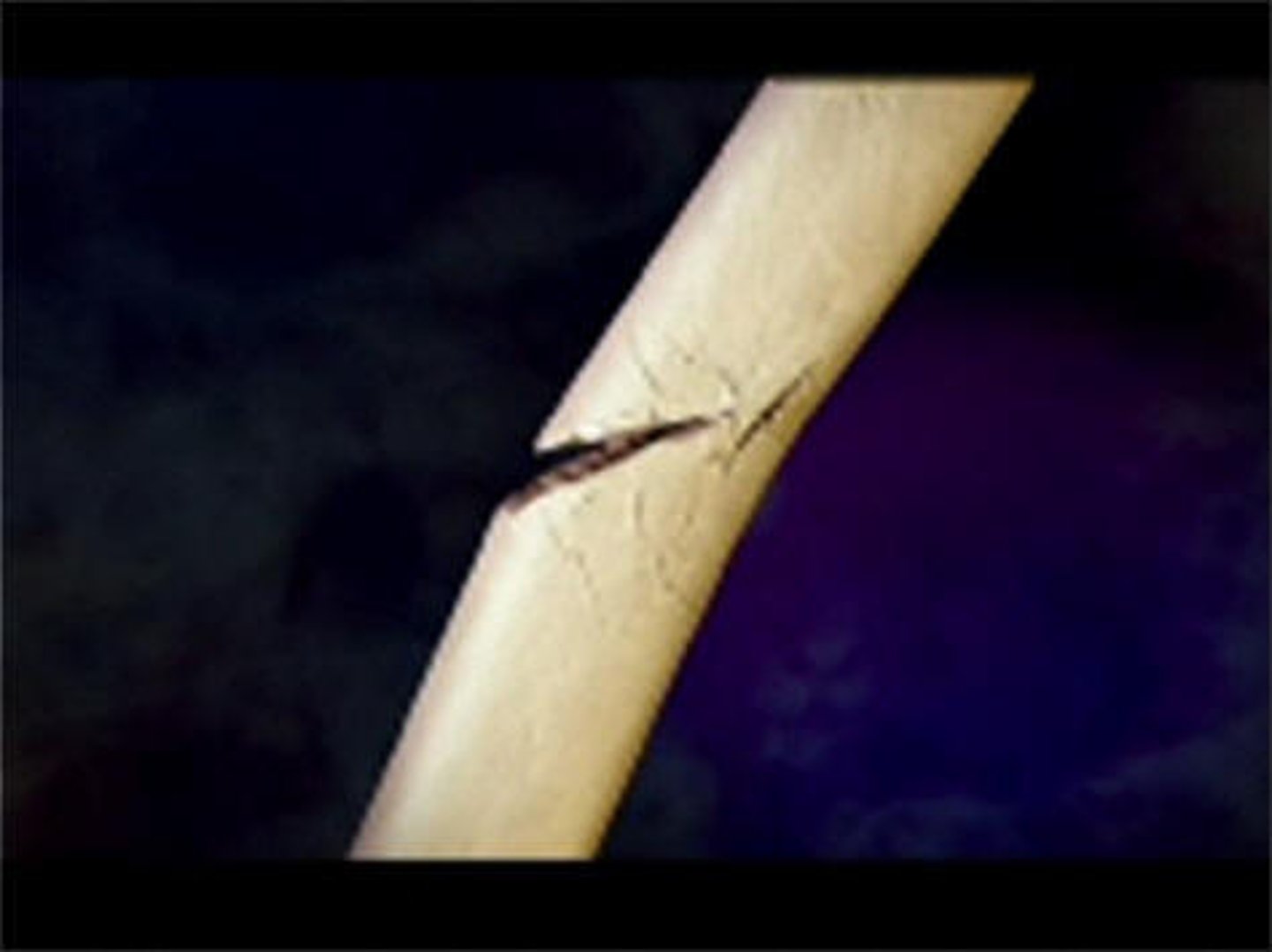

fracture hematoma
blood clot that forms at the site of a broken bone
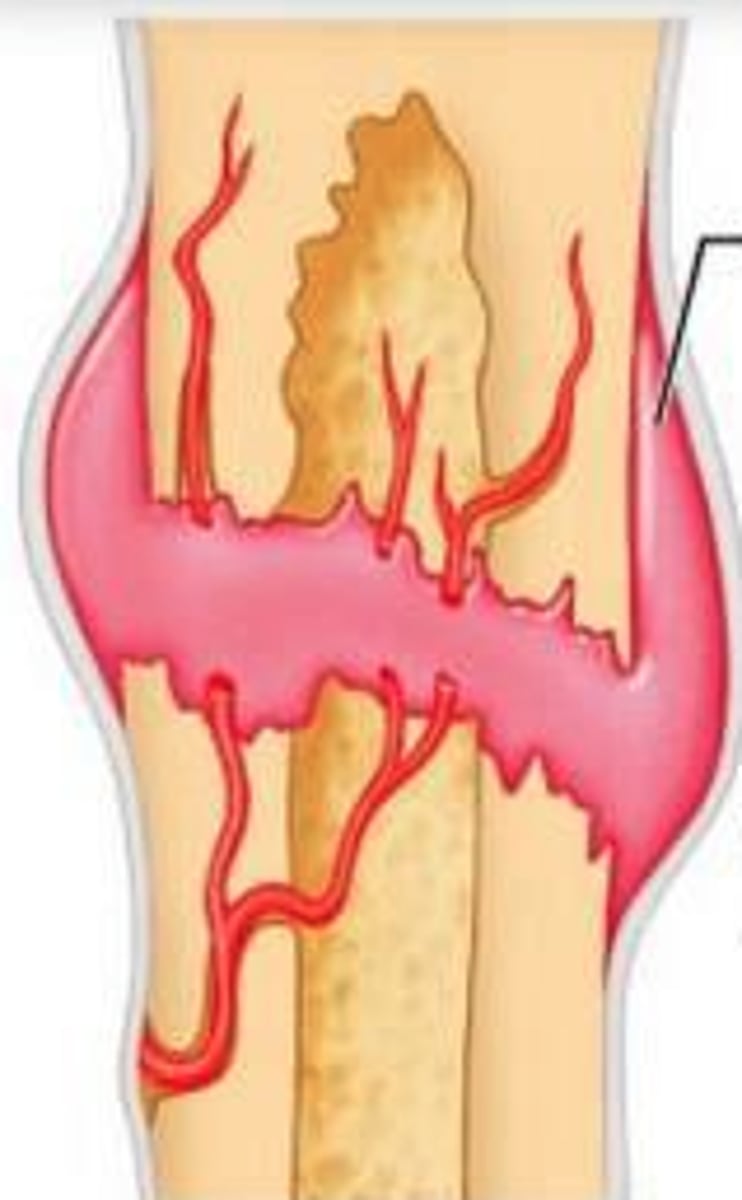
internal callus formation
blood vessels grow into clot in hematoma
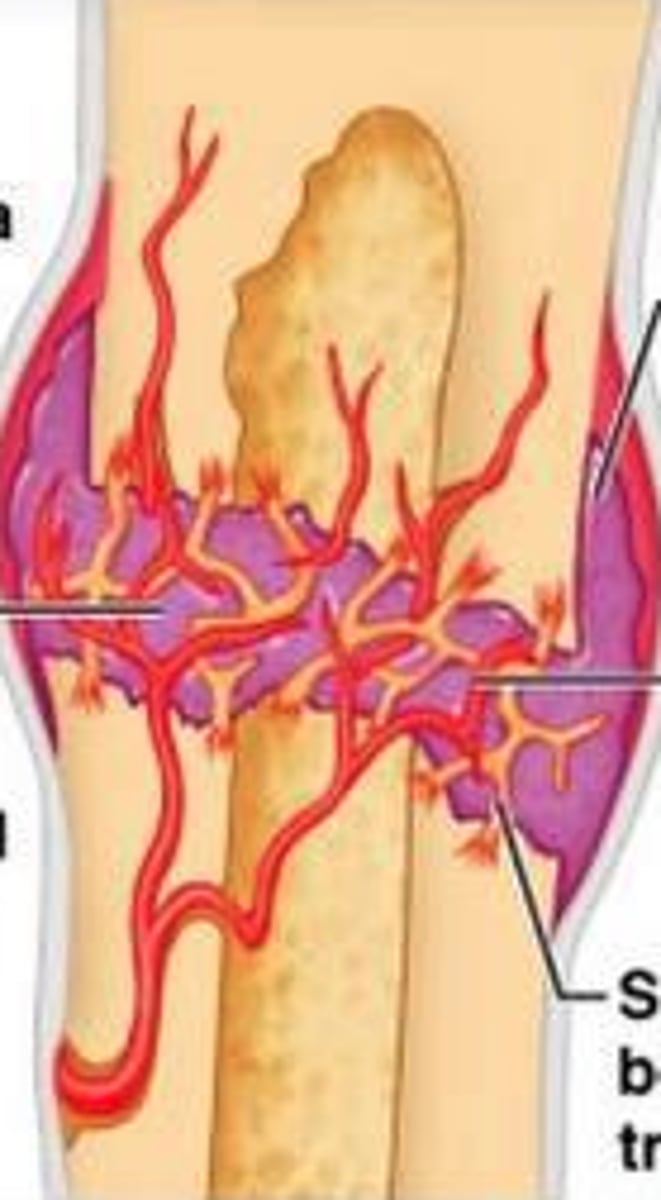
external callus
collar of hyaline cartilage and bone that forms around the outside of a fracture and will be eventually replaced by bone
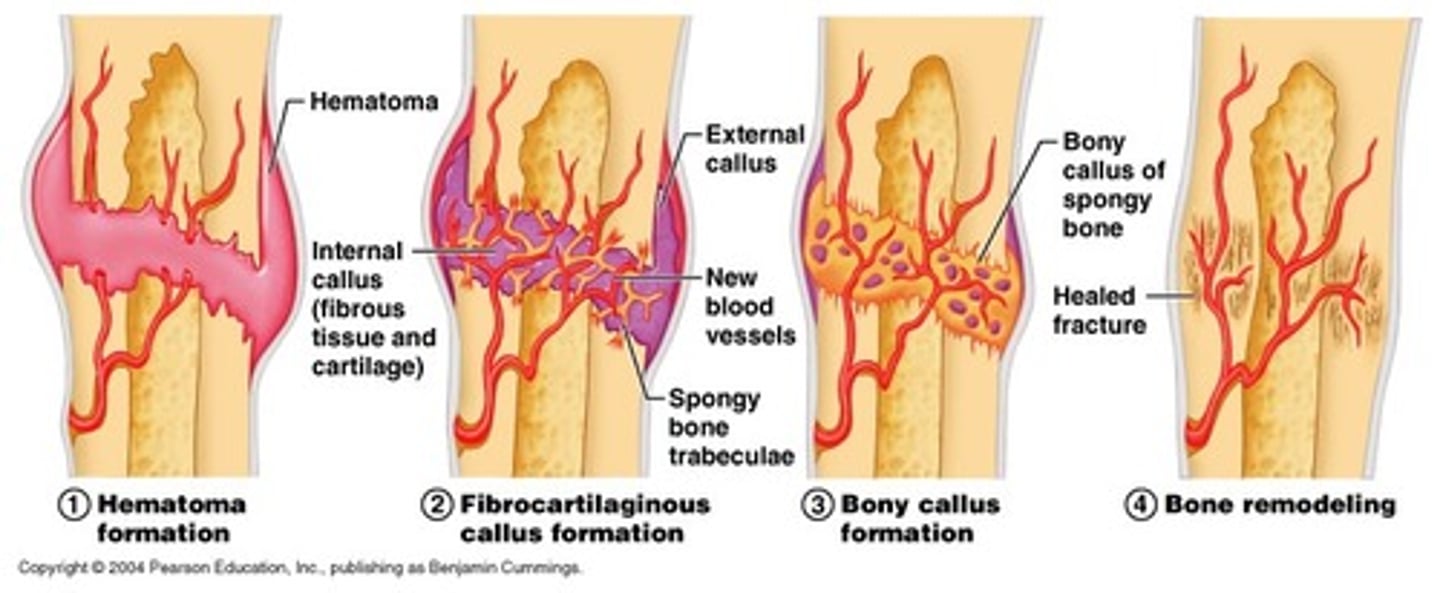
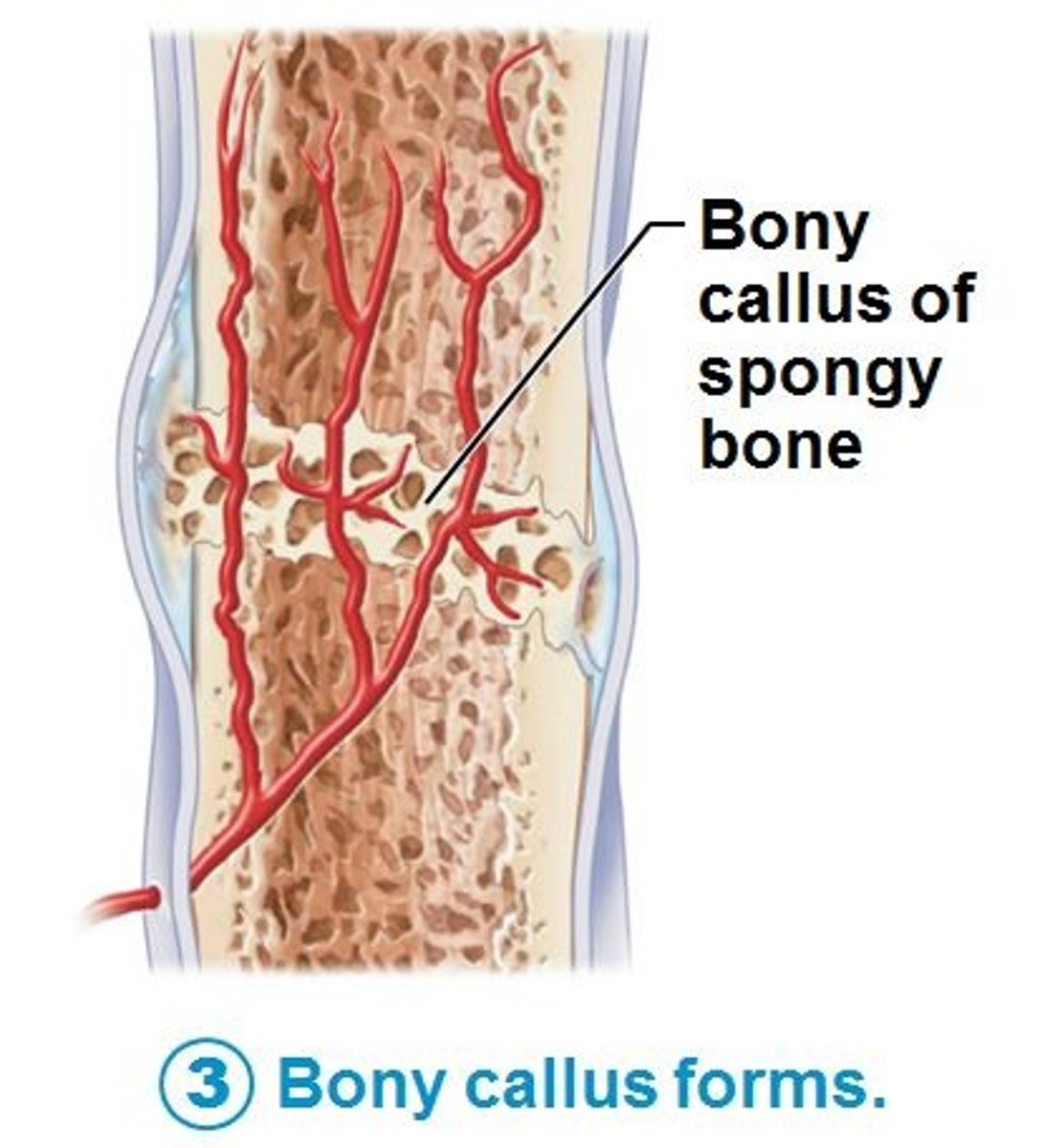
bony callus
this forms during fracture repair when the fibrocartilage is converted to spongy bone; lasts 3-4 months