BIO 121 - Ch 1: Intro to Biology
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
What is biology?
Biology is the scientific study of life
How do biologists recognize life?
…… through a series of properties shared by all living things
What does reproduction mean in living organisms?
It means the ability of all living organisms to produce offspring(s) of their own kind.
Why is reproduction considered a property of living things?
It is a property of living things because it allows organisms to continue their species over time.
What controls growth and development in all organisms?
They are controlled by information carried in genes.
How do genes affect an organism’s growth and development?
It provides instructions that control the pattern of growth and development in an organism.
How are reproduction and growth different as properties of living things?
Reproduction refers to producing offspring, while growth and development refer to changes in size, structure, and function controlled by genes.
What does energy use mean in living organisms?
It means that every organism takes in energy, converts it into useful forms, and expels energy.
Why is energy use considered a property of living things?
It is a property of living things because all organisms must obtain and transform energy to survive and carry out life processes.
What does order refer to in living things?
It refers to the complex but well-ordered structure that each living thing has. (living things tend to be organized)
List properties of living things.
Energy use and order
What do all living organisms consist of?
Cells
What does unicellular mean?
organisms are living things made up of just one cell.
In …… organisms, one cell performs all necessary life functions
What does multicellular mean?
organisms are living things made up of many cells.
they can have many cells, sometimes trillions of cells
What is a cell?
the fundamental unit of life
Why are cells considered the fundamental unit of life?
Because all living organisms are made of cells, and cells carry out all life processes.
How do unicellular and multicellular organisms differ?
Unicellular organisms have one cell, while multicellular organisms have many cells.
Are viruses considered living organisms?
No, viruses are not considered living (non-living).
Why are viruses not classified as living things?
Viruses are not considered living because they cannot reproduce, grow, or carry out life processes on their own and must rely on a host cell.
What does “response to the environment” mean in living organisms?
It means that all organisms can detect and respond to changes in their surroundings.
Give an example of how an organism responds to its environment.
A plant growing toward sunlight or a human sweating when it is hot.
What is the purpose of many environmental responses?
Many responses help keep an organism’s internal environment within narrow limits.
Which property of life is being described when an organism reacts to changes like heat or light?
Response to the environment
What is evolution in the context of living organisms?
Evolution is the process by which populations change over time as individuals with traits that help them survive and reproduce pass those traits on to their offspring.
What is the biosphere (planet)?
The biosphere consists of all life on Earth.
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem consists of both the living and non-living components such as air, sunlight, wind, and water.
studying the living things and how they interact with the non-living components
How is an ecosystem different from the biosphere?
The biosphere includes all life on Earth, while an ecosystem focuses on a specific area and the interactions between living and non-living components within that area.
What is a community?
A community consists of all the interacting populations in an ecosystem.
What does community specifically refer to?
Community refers to living things.
What is a population?
A population is a group of interacting individuals of one species.
What is the key characteristic that defines a population?
All individuals in a population belong to the same species and interact with one another.
What is an organism?
An organism is an individual living being.
What is an organ system?
An organ system is a group of organs that work together.
What is an organ?
An organ is a structure that consists of multiple tissues that cooperate to perform a specific task.
What is a tissue?
A tissue is an integrated group of similar cells that work together.
What is an organelle?
An organelle is a component of the cell that performs a specific function.
What is a molecule?
A molecule is a group of atoms bonded together.
What is an atom?
An atom is the fundamental unit of matter.
How are atoms and molecules related?
Atoms bond together to form molecules.
What does evolution explain about living organisms?
Evolution explains both the diversity and unity of life.
What is meant by the diversity of life?
The diversity of life refers to the large number of different species that exist.
yet there is tremendous unity among living things
What is evolution by natural selection?
Evolution by natural selection is the process by which populations of organisms change over generations as traits that improve survival and reproduction become more common.
What is the core theme of Biology?
Evolution
What does the phrase “descent with gradual modification” mean?
It means that modern species descend from ancestral species and change slowly over many generations, resulting in new traits and sometimes new species.
What does shared evolutionary history suggest about life on Earth?
Shared evolutionary history suggests that all life on Earth is connected.
Approximately how long does Earth’s evolutionary history span?
Earth’s evolutionary history spans over 3 billion years.
What does the phrase “Branches on the Tree of Life” represent?
It represents how all living species are connected through evolution, with each species being a branch that extends back to ancestral species.
At what level are all forms of life considered very similar?
All life is very similar at the cellular level.
evolution explains this
According to the Tree of Life concept, how is every living species related to others?
Every living species is related extending back through ancestral species, forming branches on the Tree of Life.
What does it mean when two species are considered similar?
Similar species share a recent ancestor.
Why is the Tree of Life described as having “branches”?
Because species evolve and diverge over time from common ancestors, forming separate evolutionary paths or branches.
Who proposed the Theory of Natural Selection?
Charles Darwin proposed the Theory of Natural Selection.
What is the Theory of Natural Selection?
The Theory of Natural Selection explains how species evolve over time through differences in survival and reproduction among individuals.
How did Darwin define natural selection?
Darwin defined natural selection as the nonrandom unequal reproductive success among individuals.
What is artificial selection?
Artificial selection is the process by which humans choose specific traits to be passed on by selectively breeding organisms.
example: selecting plants such as broccoli
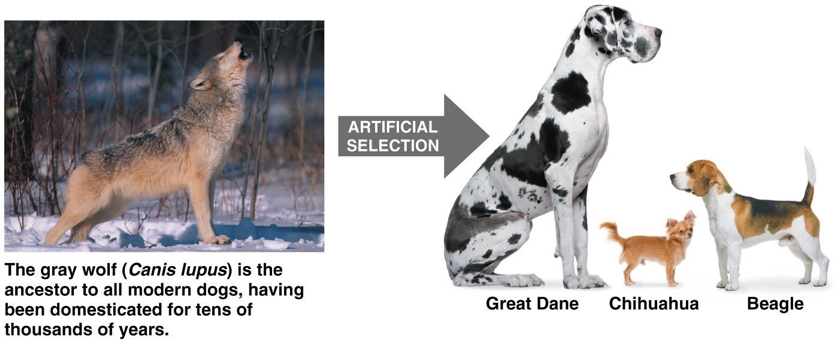
How is artificial selection different from natural processes of evolution?
Artificial selection is driven by human choice, while natural evolutionary processes occur due to environmental pressures.
Artificial selection demonstrates that selecting for specific traits can cause populations to change over time, supporting the idea of evolution.
What is meant by structure and function in biology?
Structure refers to the shape or physical form of something, while function refers to what it does or how it works.
they provide insight into each other
How is the structure of the lungs related to their function?
The structure of lungs are related to their function because the lungs have an increasingly smaller branching structure that ends in tiny sacs, which allows them to efficiently exchange gases into the blood
Why is branching an effective structure for the lungs?
Branching creates a large surface area, which increases the efficiency of gas exchange.
increased surface area improves gas exchange in the lungs by a larger surface area allowing more oxygen and carbon dioxide to be exchanged between the lungs and the blood at the same time.
What gases are exchanged in the lungs?
The lungs bring in oxygen (O₂) and remove carbon dioxide (CO₂).
What two main processes determine the dynamics of every ecosystem?
The dynamics of every ecosystem depend on energy flow and chemical recycling.
What is energy flow in an ecosystem?
Energy flow refers to the movement of energy through an ecosystem, typically beginning with sunlight and passing through organisms.
energy flow provides the power organisms need to live
What is chemical recycling?
Chemical recycling is the reuse of chemical nutrients within an ecosystem as they move between organisms and the environment.
chemical recycling ensures that essential nutrients are reused and remain available
Why are energy flow and chemical recycling essential for ecosystem stability?
Without energy flow, organisms could not survive, and without chemical recycling, essential nutrients would be depleted, causing the ecosystem to collapse.
What must happen for life to proceed?
Information must be received, transmitted, and used.
this information is encoded in genes
What is considered the molecule of life?
DNA is considered the molecule of life.
What do all cells contain?
All cells contain genes.
What are genes?
Genes are units of hereditary information.
What molecule are genes made from?
Genes are made from the molecule DNA.
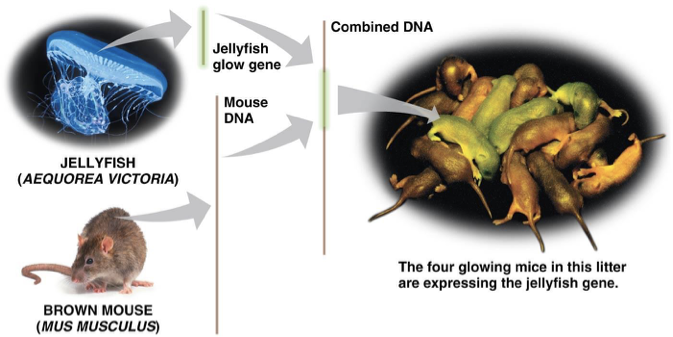
What does it mean that DNA can be “mixed and matched”?
It means that DNA segments can be cut, rearranged, or combined in new ways, allowing scientists to alter genetic information.
genes from one species may be cut and pasted into the DNA of a different species
What are Interconnections?
Interconnections refer to the relationships and interactions that exist within and between different levels of biological organization.
What are emergent properties?
Emergent properties are new level novel properties that emerge, due to the interaction of parts in an increasingly complex system.
How are interconnections related to emergent properties?
Interconnections allow parts of a system to interact, and these interactions produce emergent properties that define higher levels of biological organization.
Biologists organize species into groups, How many domains is life on Earth classified into?
Life on Earth is currently classified into three domains based on the type of cell.
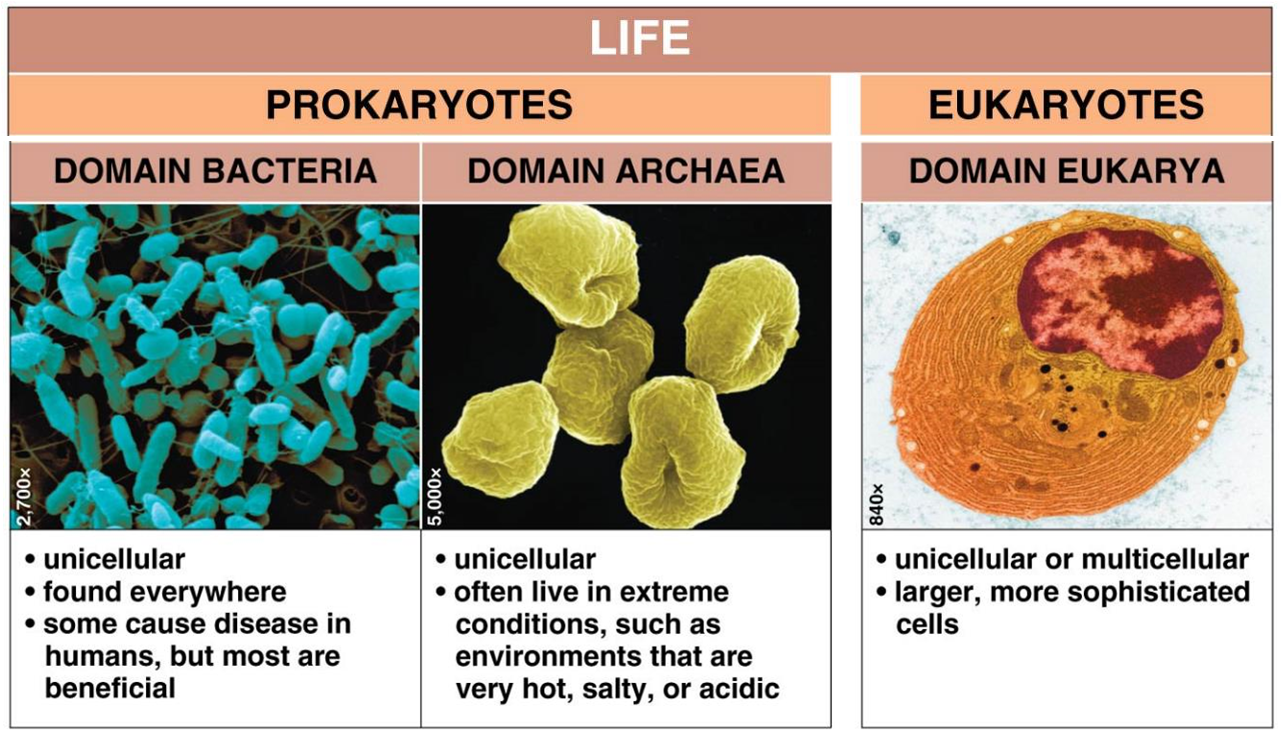
Life: Prokaryotes - Domain Bacteria
unicellular
found everywhere
some cause disease in humans, but most are beneficial
Life: Prokaryotes - Domain Archaea
unicellular
often live in extreme conditions, such as environments that are very hot, salty, or acidic
Life: Eukaryotes - Domain Eukarya
unicellular or multicellular
larger, more sophisticated cells
How is the domain Eukarya further organized?
The domain Eukarya is further subdivided into three kingdoms.
What is the domain that includes Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia?
The domain Eukarya.
What are the three kingdoms within Eukarya that are classified by how they obtain energy?
Plantae (plants)
Fungi
Animalia (animals)
What group are organisms placed in if they do not fit into Plantae, Fungi, or Animalia?
They are classified as protists.
Kingdoms of Domain Eukarya: Domain Eukarya - Kingdom Plantae
multicellular
use sunlight to produce sugars via photosynthesis

Kingdoms of Domain Eukarya: Domain Eukarya - Kingdom Fungi
single-celled or multicellular
decompose and digest dead organisms

Kingdoms of Domain Eukarya: Domain Eukarya - Kingdom Animalia
multicellular
eat and digest other organisms

Kingdoms of Domain Eukarya: Domain Eukarya - Protists
single-celled or multicellular
catch-all category for all remaining eukaryotes
includes many kingdoms
What is science?
Science is an approach to understanding the natural world through inquiry—a search for information, evidence, explanations, and answers to specific questions.
the process of science has a flow but is not always linear
What is the first step in science?
Observation is the first step in science.
Observation is important because it allows scientists to notice patterns, ask questions, and identify problems that can be investigated.
What is the purpose of the scientific method?
The scientific method serves as a guideline that helps scientists understand and explain observations.
the scientific method is a “recipe” that can provide insight about the natural world
What role do experiments play in the scientific method?
Experiments provide data that scientists use to test a hypothesis. This data can either support or refute the hypothesis.
What does the scientific method depend on?
The scientific method depends on hypotheses.
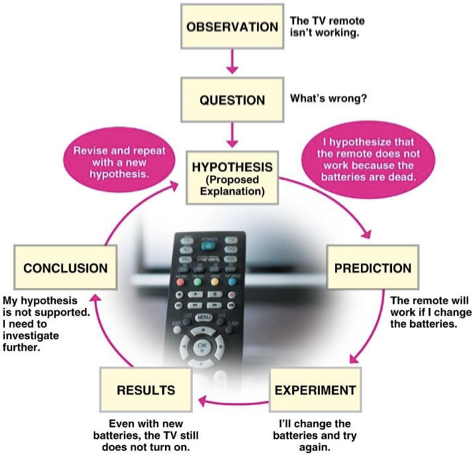
What is a hypothesis?
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation to a question that can be investigated.
What is at the heart of the process of science?
Forming and testing hypotheses are at the heart of the process of science.
What are recorded observations in science called?
Recorded observations are called data.
which are the evidence upon which scientific inquires are based
What does the process of science involve?
The process of science involves interacting phases.
What are the four interacting phases of the scientific process?
Exploration
Testing
Communication
Outcomes
What is the difference between a scientific hypothesis and a scientific theory?
A scientific hypothesis is a testable, tentative explanation for a specific observation, while a scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation that is supported by extensive evidence and explains a wide range of observations.
How is a scientific theory defined?
A scientific theory is a comprehensive, well-supported explanation that has been repeatedly tested and is able to explain many observations in the natural world.
Hypothesis* vs. Theory
*A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for an observation
no expectation of truth
narrow in scope
subject to immediate testing
falsifiable
example: warmer muscle contracts faster
Hypothesis vs. Theory*
*A theory explains a great many observations
well-substantiated
broad in scope
supported by a large body of evidence
falsifiable
example: cell theory
What is a fact?
A fact is something that is verifiable and considered to be objectively true based on current evidence.