E2 Intro to HC: Medication Safety and Error Prevention
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Where can medication error happen during the prescription medication use process (PDAM)
At any step!!!!
what diagram do we use to see where the error occurred?
5 why diagram
Assessing a drug event what do we look at?
preventability
Level of harm
Causality (probability)
When assessing ADE preventability there are 4 assessments, what are they?
definitely avoidable - poor drug treatment, inconsistent w/ present day knowledge
Possible avoidable - could’ve have been avoided (med was not erroneous)
Not avoidable - (unpredictable)
Unevaluable - no data or evidence was conflicting
True or false: NCC MERP index categorizes medication errors
TRUE:
NCCMERP - national coordinating council for medical error reporting and prevention!!!!!!!
it indexes medication errors by severity
A = no error
B,C,D = error, no harm
E,F,G,H = error, harm
I = error, death
What is the causality assessment of ADR?
evaluation of the likelihood that a suspected drug caused an adverse reaction
Relationship between drug and the reaction
Determining causality: temporal relationship
Timing between the start of drug therapy and the reaction
Determining causality: Dechallenge
Reduce dose, hold medication or discontinue therapy
Determining causality: Exclusion
Exclude some medications and other potential factors
Determining causality: Previous reports
Established vs. new classes
The WHO-UMC causality assessment was used to evaluate what?
Used to evaluate the likelihood that a specific drug, vaccine, other medical intervention has caused an adverse event
certain
Probable
Possible
Unlikely
Conditional/unclassified
Unassessable/unclassificable
Terminology: define side effect
expected well known reaction
Result in little or no change in patient management
Occurs with predictable frequency and whose intesity and occurrence are related to side of dose
Terminology: define Adverse drug event
unintended physical injury resulting from or contributed to by medical care
Required additional monitoring, treatment or hospitalization
Can result in death
Terminology: define Adverse drug reaction
response to a drug that is noxious and unintended
Occurs @ normal dose
ADR require normal dose, direct and A
Difference between ADR and ADE
ADR require normal dose, direct and ADE required use of a drug, proximity
Terminology: define medication errors
any preventable event that may cause or lead to inappropriate medication use or patient harm while the medication is then the control of the HCP, patient or consumer
Whats included in prescribing errors?
incorrect drug selection (dose, strength, route, etc)
Failure to comply with legal requirements for prescription writing
Whats included in dispensing errors?
error diuring the process from the receipt of a prescription in the pharmacy through to the supply of dispensed drug
1-24% error
Wrong product: look alike sound alike
Must be examined in the pharmacy and areas of stocking to prevent harm
Tall man lettering helps
What does tall man lettering help with?
Help with drugs with similar names
Whats included in administration error?
discrepancy between drug therapy revised by the patient and the drug therapy intended by prescriber
Highest risk areas in nursing
Error of omission where administration is omitted due to a variety of factors
Wrong administration technique, expired drugs, wrong prep administration
What are workarounds?
Something wrong with the system and people try to work around it
lead to medication error
What are approaches to reduce medication errors: person centered approach
looks at medication errors as occurring due to human frailty
Forgetfulness
Poor motivation
Carelessness
Negligence
What are approaches to reduce medication errors: System center approach
belief that errors expected to occur
View errors as the end result and not the cause
Beleif that there is potential for error and recurring errors in every system
Solutions are based on belief that conditions can be changed rather than changing humans
focusing on how and why system failed, not individual failure
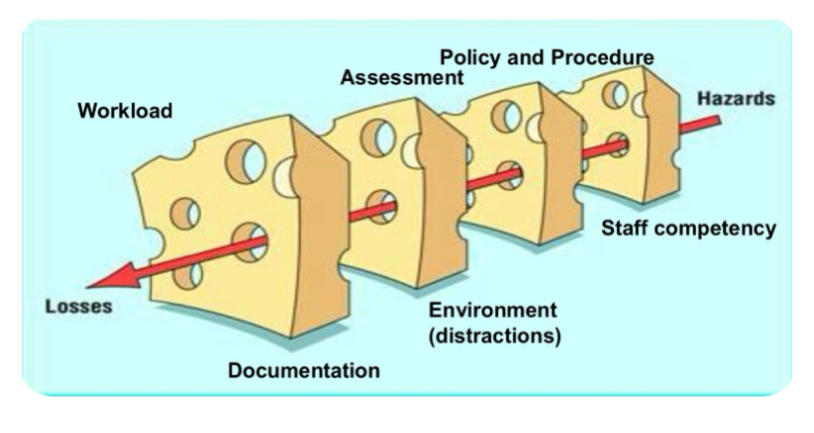
Whats the Swiss cheese model of system errors?
used to illustrate how adverse events or medication errors can occur based on multiple small system failures