Biology: Excretory System
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Excretion Overview
Removes metabolic waste from blood as urine
Main organ: Kidney
Functional unit of kidney: nephron loop
Smaller: Afferent → glomerulus → bowman's capsule
Kidney Functions
Filters blood and forms urine
Regulates:
Blood pressure
Blood pH
Red blood cell production (via erythropoietin)
Anatomy:
Cortex (outer)
Medulla (inner)
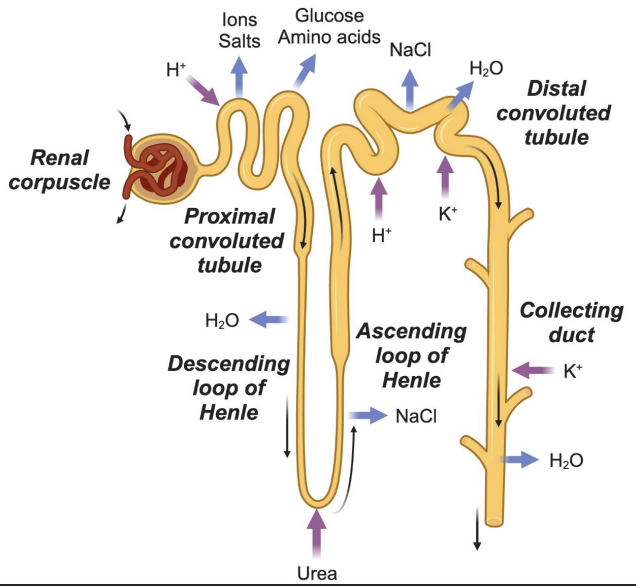
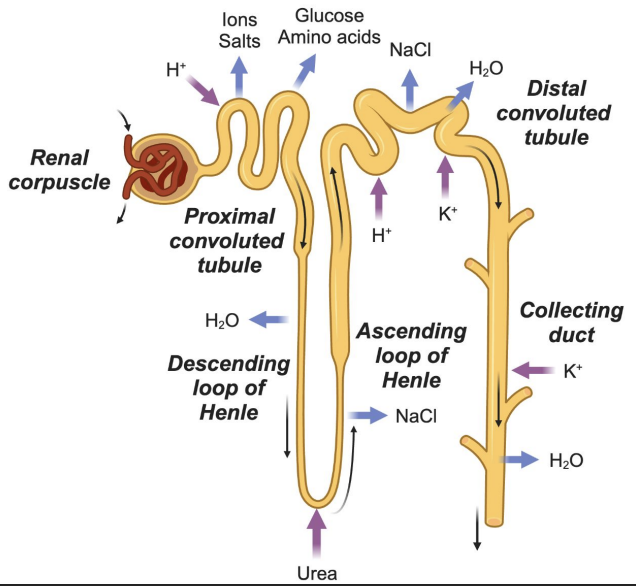
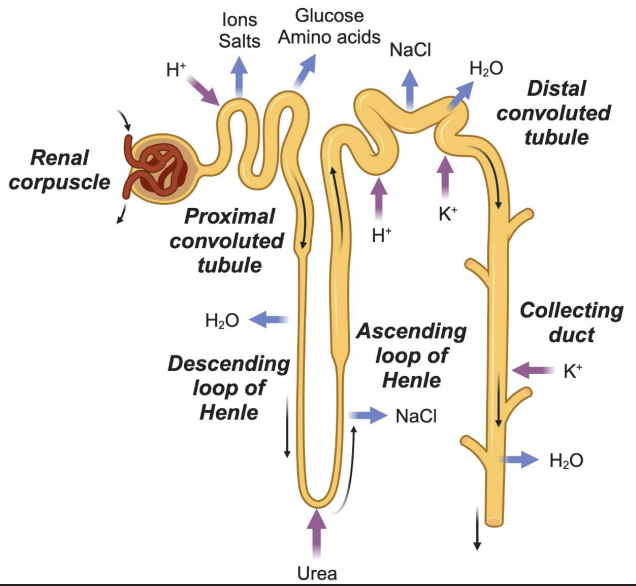
Nephron
Functional Unit of Kidney
Glomerulus: cortex
Located in renal corpuscle (Bowman’s capsule + glomerulus)
Site of blood filtration
Afferent arteriole
Efferent arteriole
Podocytes
Afferent arteriole
Brings blood in
Efferent arteriole
Carries filtered blood out
Forms peritubular capillaries (around PCT/DCT)
Forms vasa recta (around Loop of Henle)
Podocytes
Increase filtration selectivity
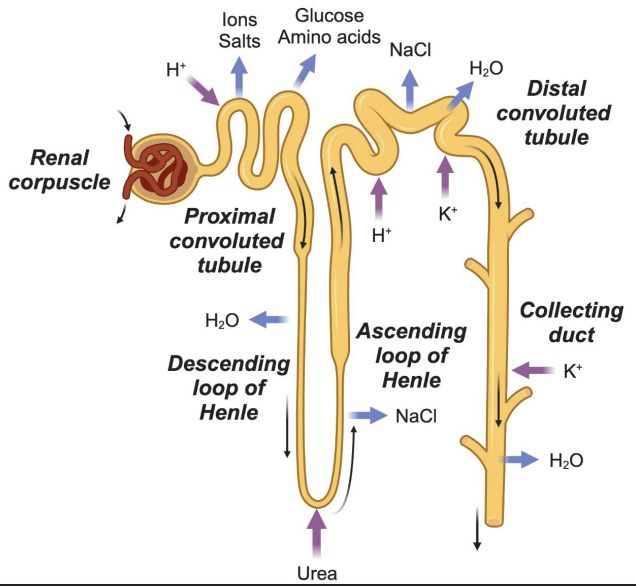
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Major site of reabsorption
Reabsorbs: Na⁺, Cl⁻, glucose, amino acids (100%)
Secretes: H⁺
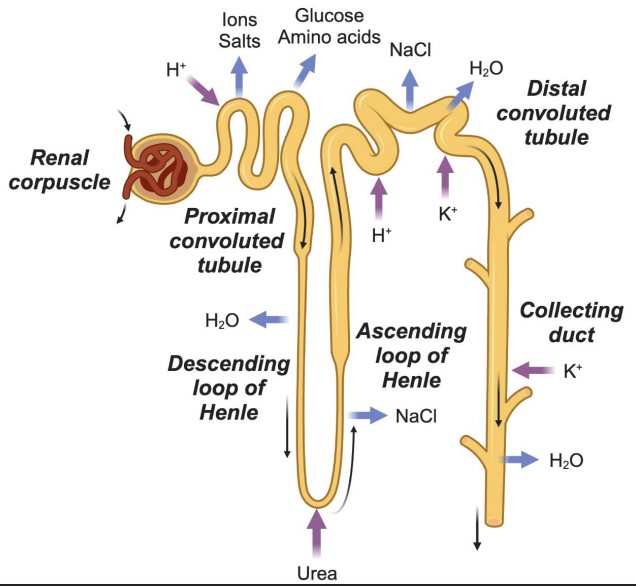
Loop of Henle: Descending limb
Permeable to water
Water exits → urine concentration increases
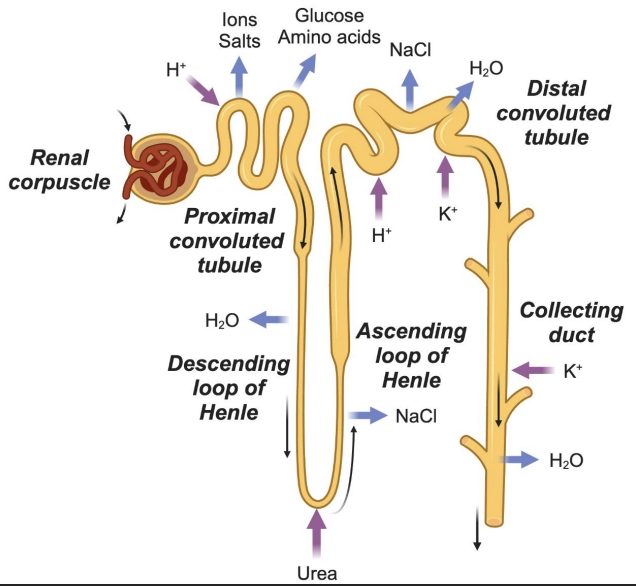
Loop of Henle: Ascending limb
Impermeable to water
Ions (Na⁺, Cl⁻) reabsorbed → urine concentration decreases
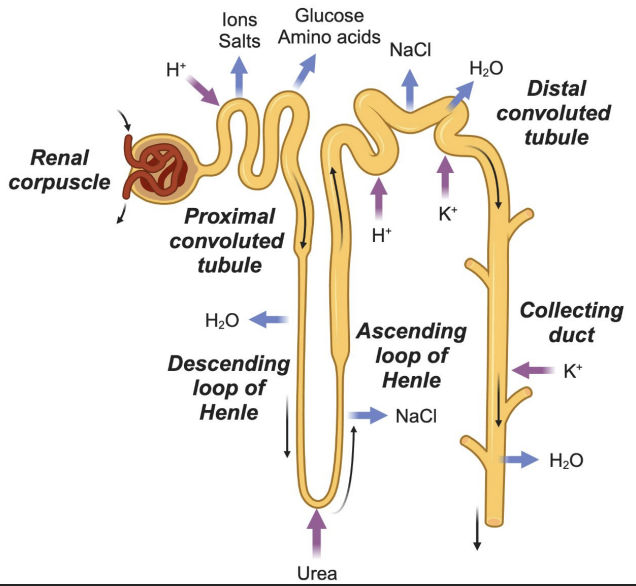
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Reabsorbs: Na⁺, Cl⁻
Secretes: K⁺, H⁺
Water follows salts by osmosis
Collecting Duct
Passive reabsorption of water
Secretes K⁺
Final concentration of urine
Urine Flow After Nephron
Collecting duct → Renal pelvis → Ureter → Bladder → Urethra
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS): increase blood pressure
Triggered by low blood pressure
Juxtaglomerular cells detect low BP → release renin
Renin converts angiotensinogen (liver) → angiotensin I
ACE (lungs) converts angiotensin I → angiotensin II
Angiotensin II effects
Stimulates aldosterone release
Increases Na⁺ reabsorption
Increases thirst
Vasoconstriction: shrink blood vessels increase BP
Aldosterone
Function: Keeps salt (Na⁺) and water in the body
Also makes you lose potassium (K⁺)
Goal: Raise blood pressure and blood volume
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone / Vasopressin)
Function: Keeps water in the body by adding aquaporins
Goal: Raise blood volume and concentrate urine
Blocked by alcohol → more pee
ANP (Atrial Natriuretic Peptide)
Function: Gets rid of salt and water
Increases urine production
Goal: Lower blood pressure and volume
Osmoregulation: Marine (Saltwater) Fish (HYPO)
Environment: hypertonic
Lose water passively
Adaptations:
Constant drinking
Rare urination
Salt secreted through gills
Osmoregulation: Freshwater Fish (HYPER)
Environment: hypotonic
Gain water passively
Adaptations:
Constant urination
Do not drink
Salt absorbed through gills
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Most reabsorption (Na⁺, Cl⁻, glucose, amino acids)
Loop of Henle
Descending = water out
Ascending = salt out
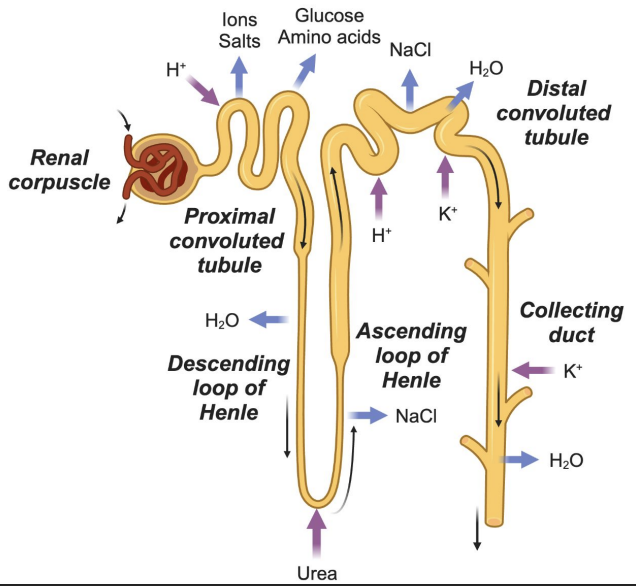
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Salt reabsorption, K⁺ and H⁺ secretion
Collecting Duct
Water reabsorption, K⁺ secretion
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
Raises blood pressure
ADH (Antidiuretic Hormone / Vasopressin)
Retains water (aquaporins)
ANP (Atrial Natriuretic Peptide)
Lowers blood pressure
Aldosterone
Increase Na+ and K+
If stopped working, more water than ions